G3 : Bioreactor operations and scale up
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what are challenges with scale-up challenges
changes in volume to surface ratio
what are some scale up rules?
keep following parameters constant
power input (Pg/V)
constant oxygen transfer rate
speeds at impeller tip
constant maximum shear
Explain the complexity of systems of variables
T, DO and pH control
setpoints, sensors, controllers
interaction between these and many other variables making it complex to analyze
What is the proecess from target to market
Discovery
Process Development
Clinical Supply Production
Process Development and scale up
Final Manufacturing Facility, Validation and Licensing
What is the Process Development Group responsible for?
process suitable for manufacturing equipment
accurately defined in process documents
operate properly at plant start up
What is the Manufacturing Group responsible for?
equipment work as designed
logistics
timely startup
facilities
staff
equipment
raw materials
Implement process as described in process documents
What are frequent problems in process transfers
cells do not grow at expected rate
product yields lower than expected
product less stable than expected
What are the key purposes of agitation?
Gas-Liquid Mass Transfer
smaller bubbles→ larger surface area
dispersing bubbles through the tank
maintaining concentration Gradient
Liquid-Liquid Mixing
mixing of acid/base to maintain pH
mixing feed solutions for fed-batch
Suspension of Solids
insoluble nutrients
cell aggregates
microcarriers
agitation prevents settling
cell aggregate size control
break up large clumps
prevents shear damage by controlling speed
balance between fragmentation and stability
Why do smaller bioreactors require external heating?
They lose heat to environment and need jacketed vessels to maintain temperature
What is the primary challenge with scaling up bioreactors
Removing excess heat from mechanical and metabolism processes
What is the purpose of jacketed vessels in bioreactors
Supply heat to the reactor by circulating hot fluids around it
Why is heat removal more critical in larger scale reactors
produce more heat that can accumulate and harm the system
Heat Generation by microbial metabolism and enthalpy
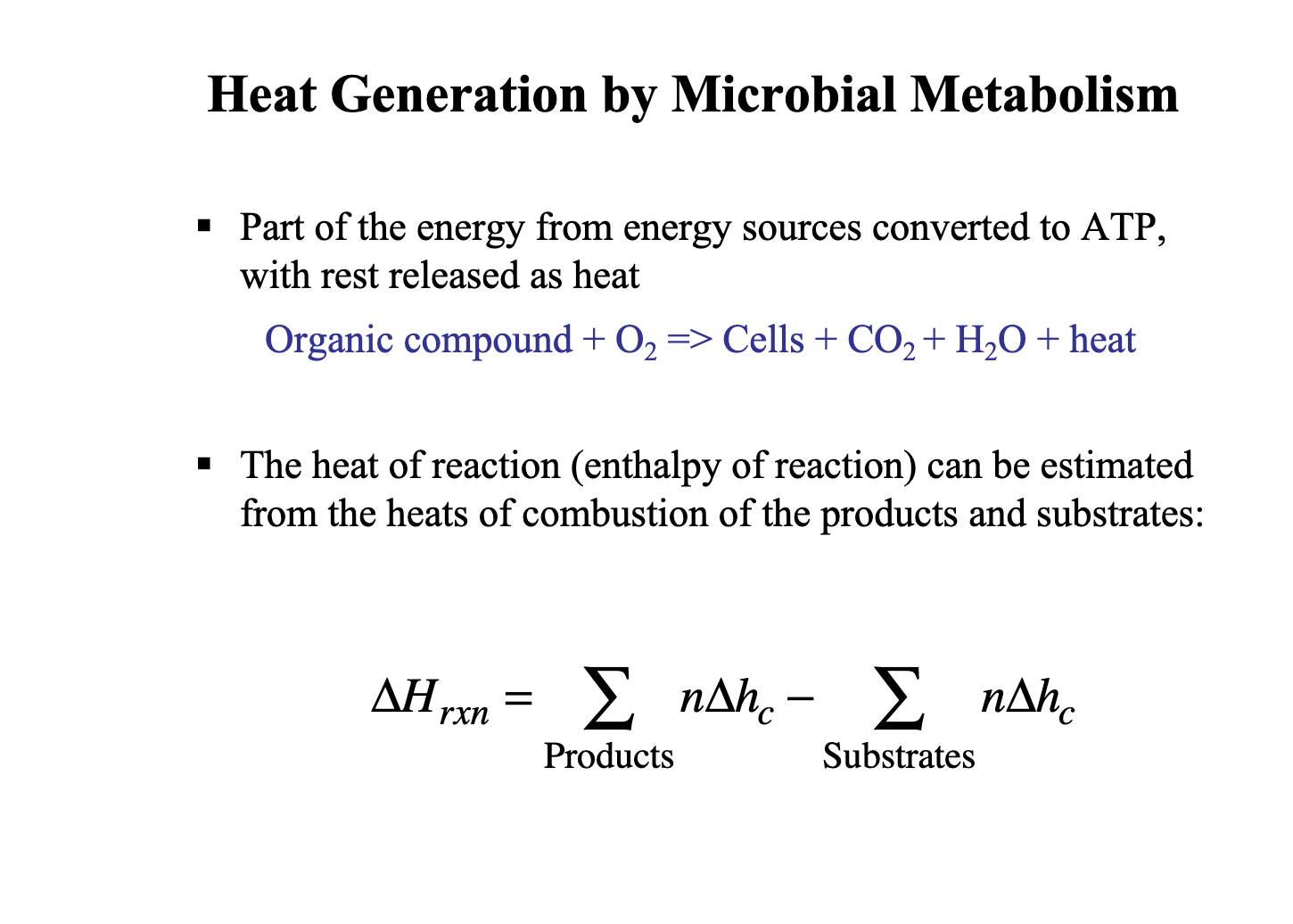
What physical parameter is aerobic metabolic heat most closely correlated with?
Oxygen uptake rate (OUR).
Why is oxygen uptake rate used to estimate metabolic heat in aerobic fermentations?
Because it's easier to measure than heat directly and correlates well with metabolic activity.
How can oxygen uptake rate guide bioreactor heat exchanger design?
By estimating heat evolution from the OUR to size the heat exchanger accordingly.
Write the empirical relationship between volumetric heat evolution and oxygen uptake rate?
units:
f - kcal/Lh, o2 - mmol/Lh
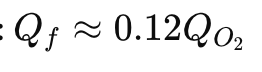
Why is it important to reduce pCO₂ in mammalian cell cultures?
Because high CO₂ levels can harm cells and affect product quality.
Why is NaHCO₃ removed from the medium?
Because it contributes to CO₂ buildup.
What two buffering agents replaced NaHCO₃ in this strategy?
MOPS and histidine buffer
What is the benefit of using Na₂CO₃ instead of NaHCO₃ as a base?
Na₂CO₃ neutralizes more H⁺ per mole and produces less CO₂.
Why is NaOH not used in mammalian cell cultures?
It causes transient pH spikes that lead to cell aggregation.
What is the main difference between radial and axial flow impellers?
Radial impellers pump fluid outward; axial impellers pump fluid along the shaft axis.
Why is the Rushton impeller less suitable for large-scale reactors?
slows top-down mixing
leads to poor base mixing
What is one advantage of the axial flow hydrofoil impeller over the Rushton type?
It requires less energy for the same oxygen transfer.
What power number is typical for Rushton and hydrofoil impellers, respectively?
Rushton: ~5; Hydrofoil: ≤ 1
What is the formula for power number dependence on impeller type
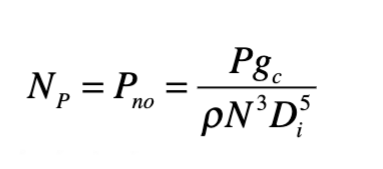
list different impeller power numbers
Why does scale-up present challenges in bioprocessing?
surface-to-volume ratio decreases, making it hard to replicate physical conditions like heat and mass transfer.
Why is Pg/V often kept constant during scale-up?
To maintain a constant oxygen transfer rate (OTR).
What does keeping impeller tip speed constant help maintain?
Constant maximum shear stress.
What variable is often kept constant to preserve kLa during scale-up?
N3D2
What are primary Variables?
pH
DO
What secondary variables are affected by efforts to control primary variables?
CO2 Accumulation
Osmolality ( salt concentration)
bubble-burst shear
mixing time
hydrodynamic shear
who is responsible for process transfer accountability?
process development group
manufacturing group
What is the process development group responsible for?
process must be suitable for larger-scale equipments
clear and complete process documentation
Process works properly at plant start up
What is the manufacturing group responsible for?
process equipment will work as designed
logistics in place for timely startup
facilities, staff, equipment, raw materials
implement process as described in process documents
What is the investigation and resolution game plan for startup problems?
collect all data and samples relating to the problem
make a list of hypothesis as to what could have happened
perform experiments and analyses to isolate the potential sources of the problem