Indigestion & Digestion
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 12: Tuesday, November 11th: Energy: Digestion & Dysregulation; Thursday, November 13th: Energy: Ingestion & Dysregulation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
eating is also known as _______
indigestion
breaking down food mechanically and chemically is known as _______
digestion
when we stop eating and signals distribute the molecules we ate into cells, this is known as _______
post digestion
energy expenditure is the process of using muslces to make _______
ATP
what does the brain/neurons use for energy?
glucose
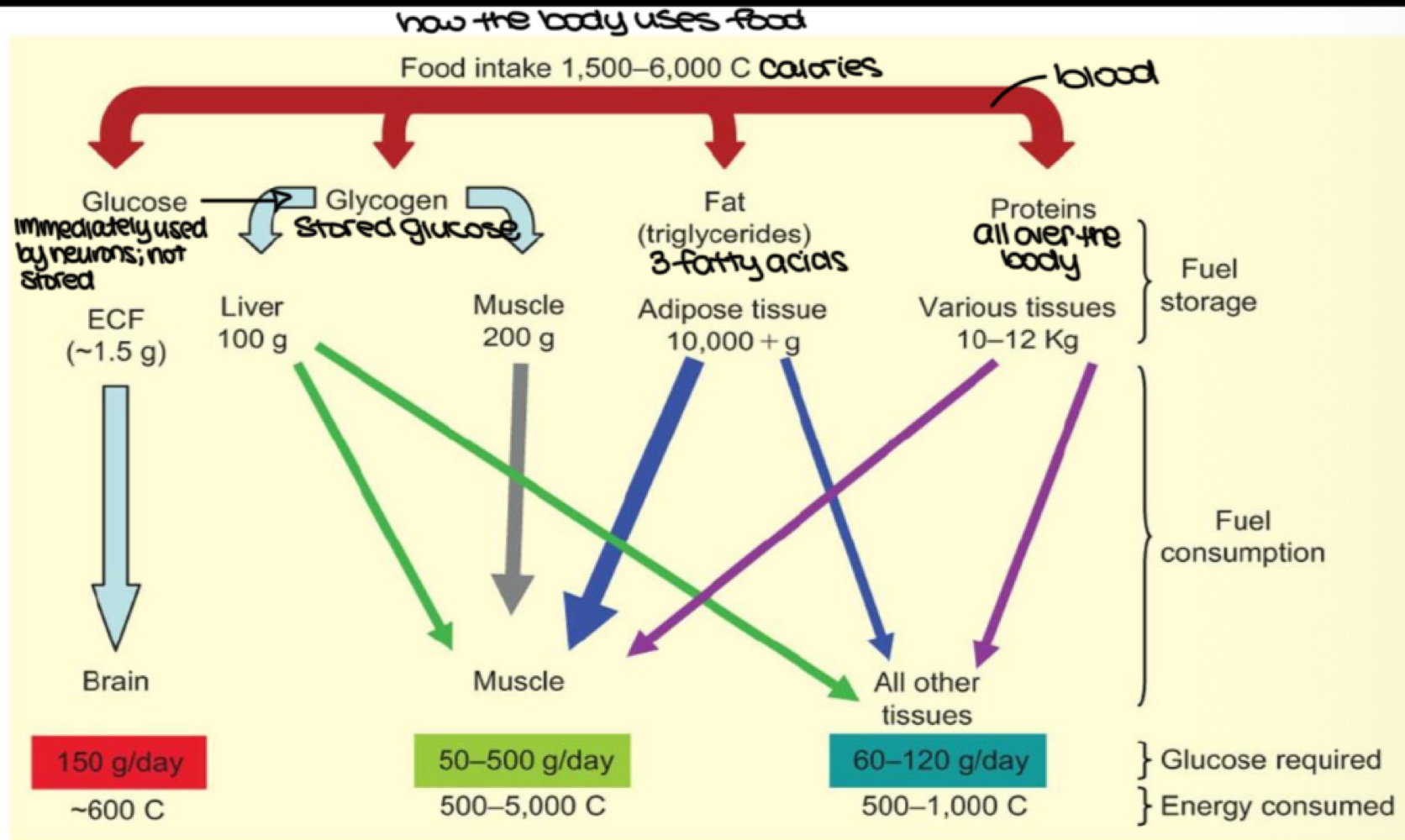
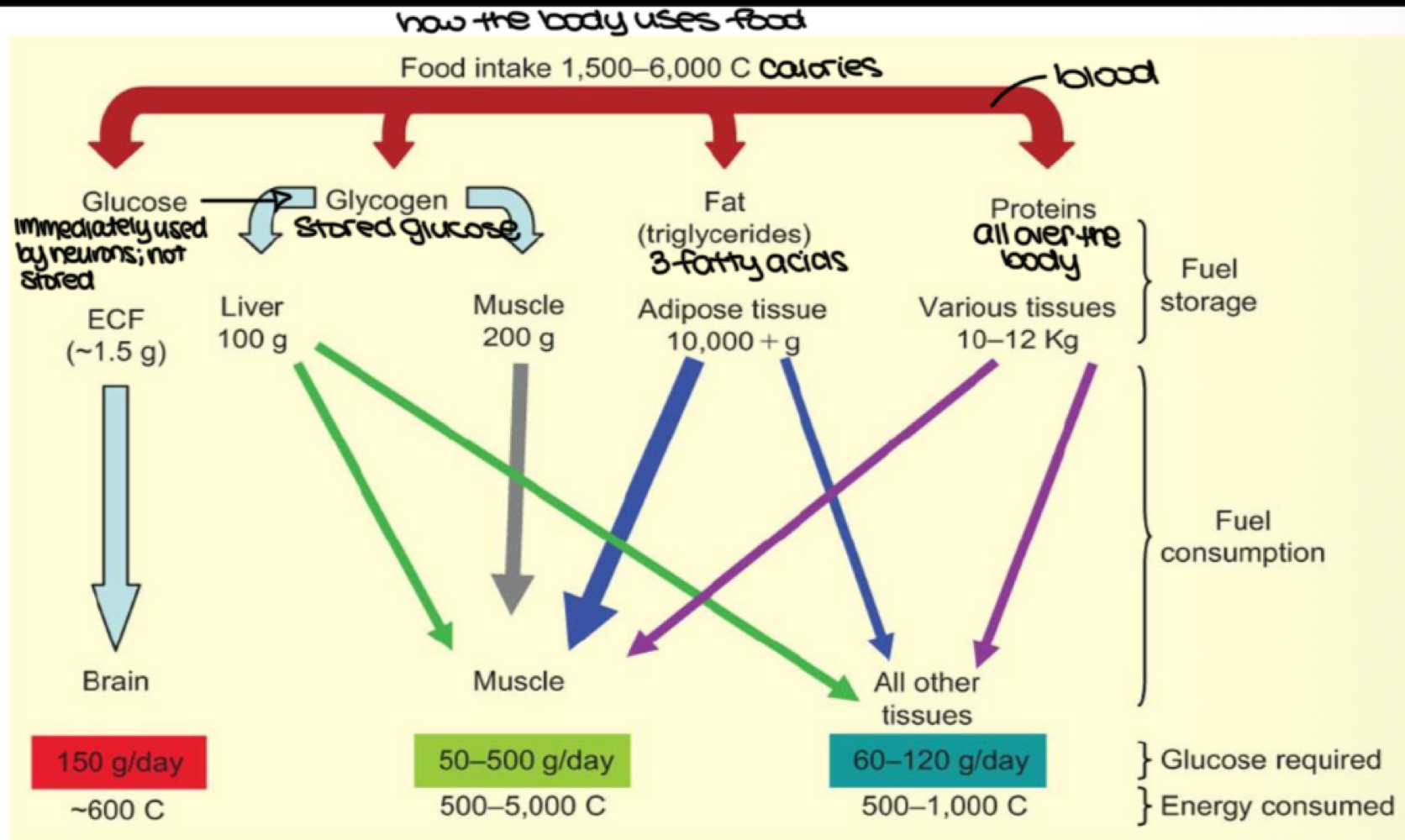
after we eat, blood glucose is stored as _______ in the liver, muscles, and other tissues
glycogen
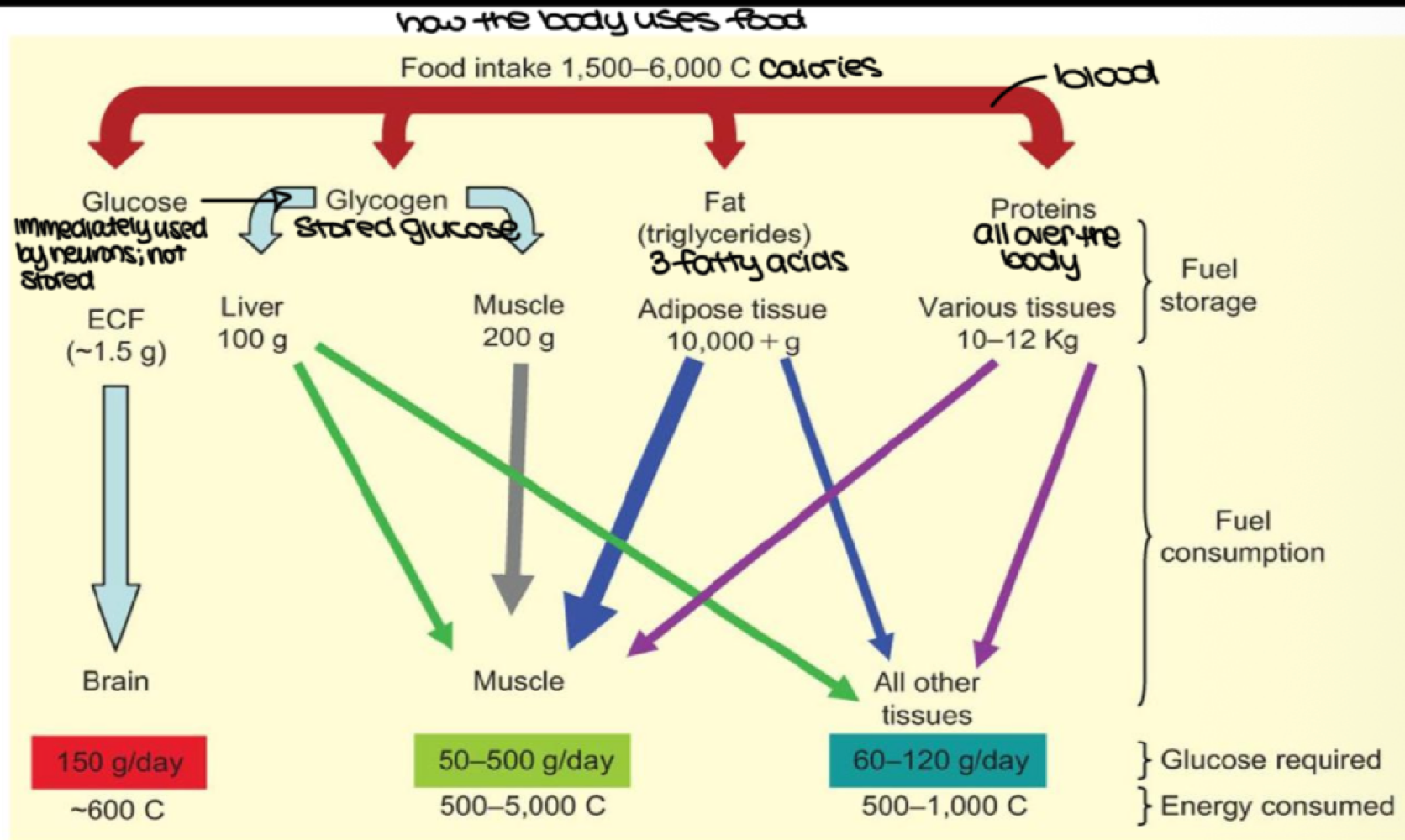
after we eat, fat in our blood is stored as _______ in adipose tissue
triglycerides
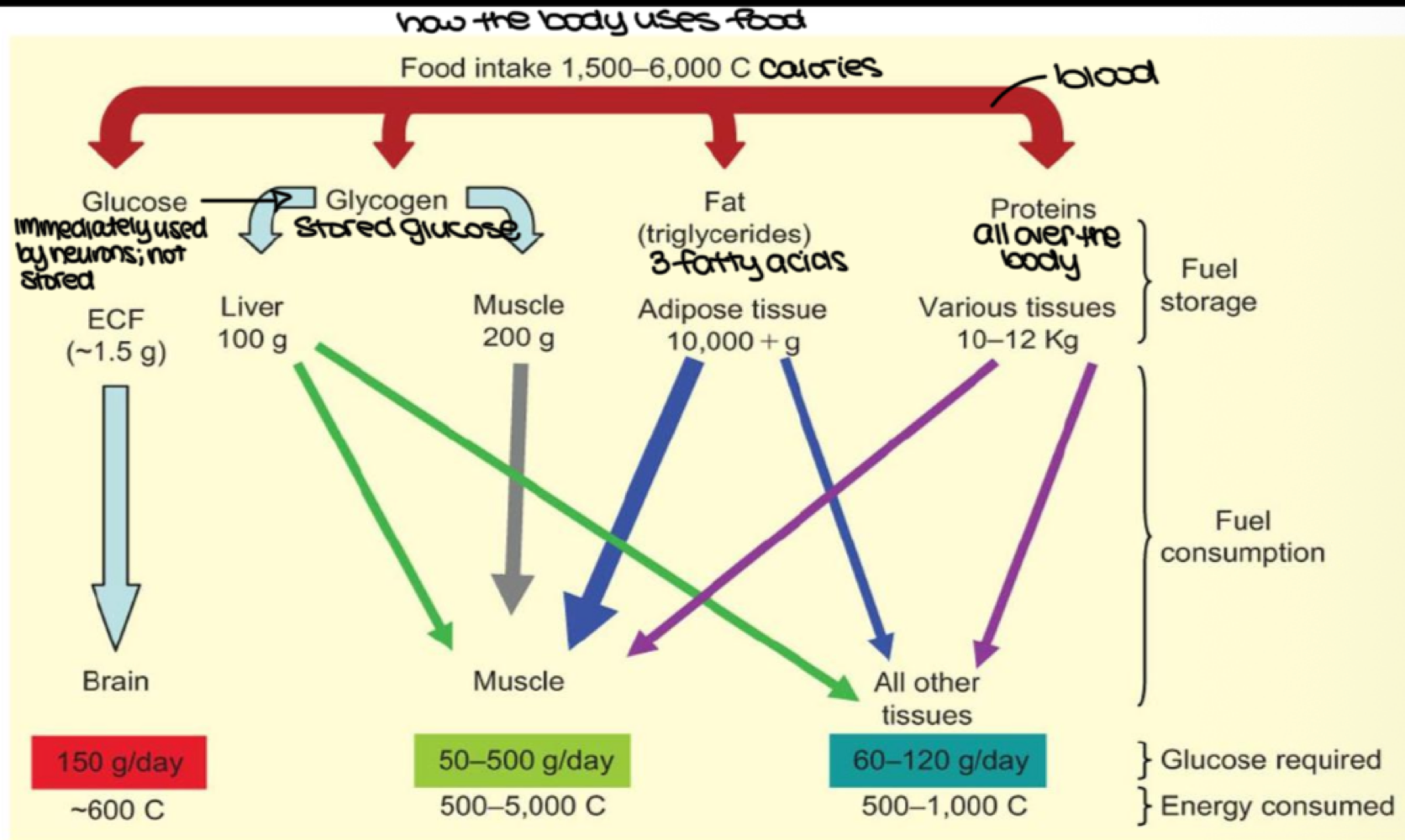
after we eat, proteins are stored where?
throughout the body
which part of the nervous system controls eating?
parasympathetic nervous system
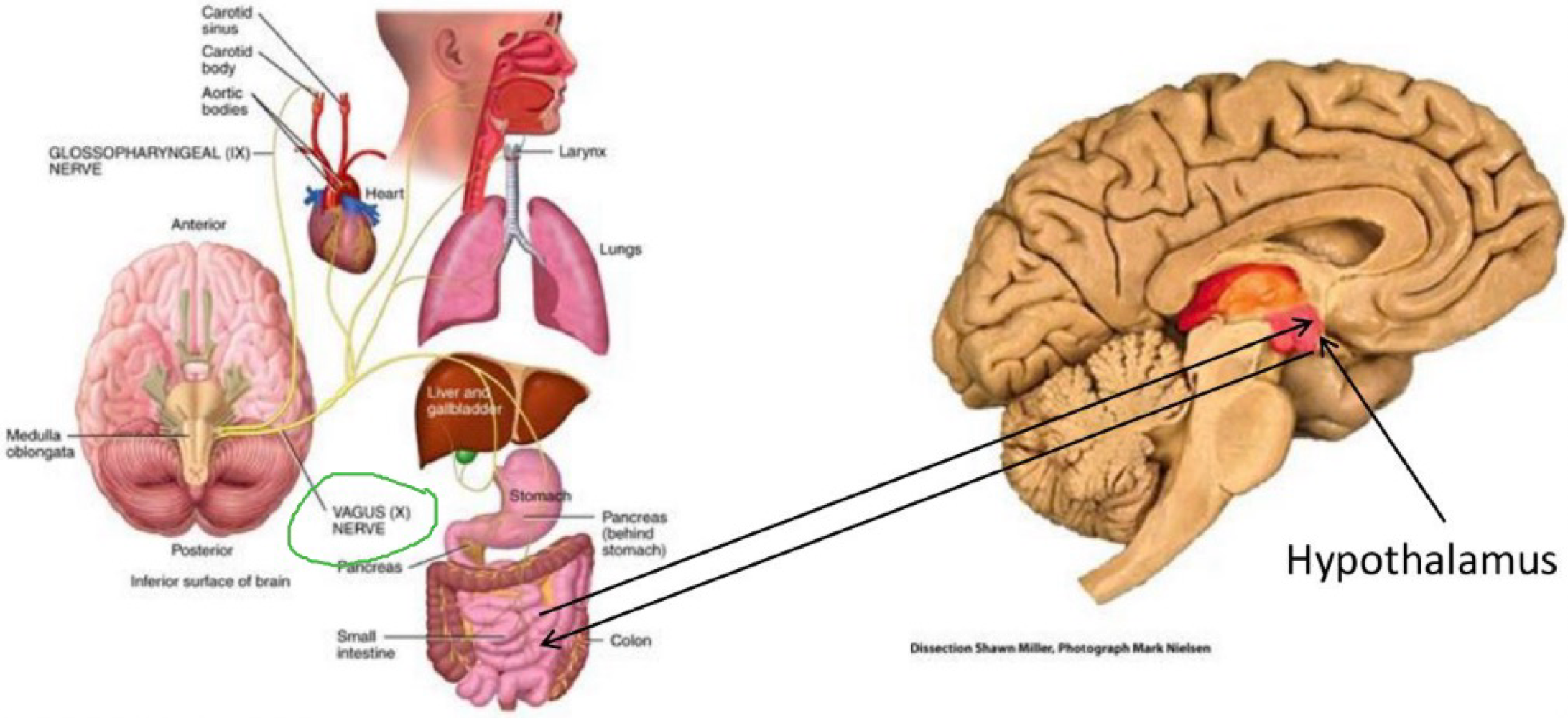
which nerve controls our digestion?
vagus nerve
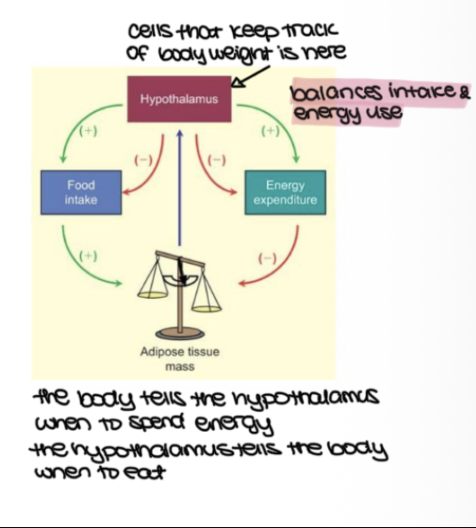
adjusting food intake and energy expenditure is control by the hypothalamus and adipose tissue mass to _______
maintain body weight
_______ being released from the GI tract to stimulate the hypothalamus is a body → brain hunger signal
ghrelin
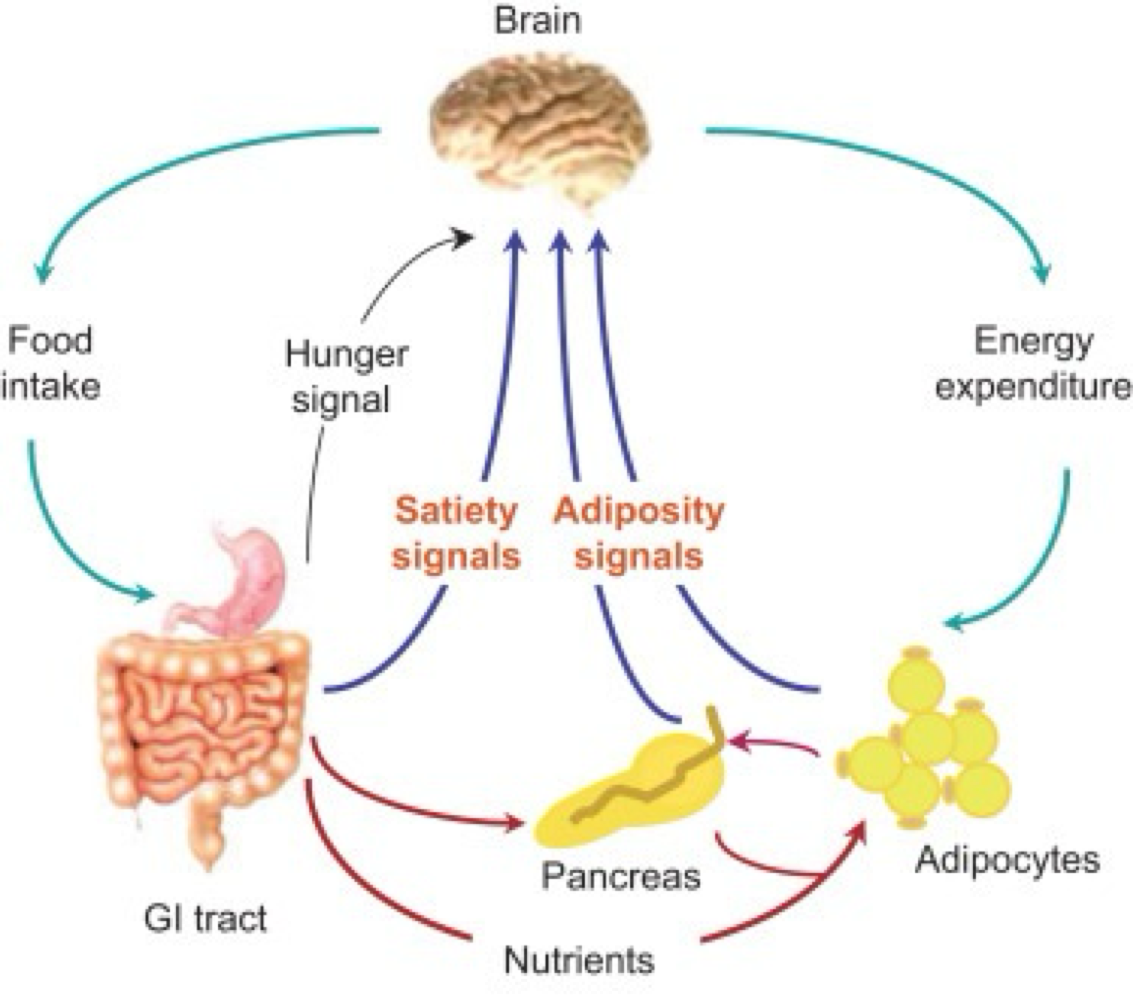
_______ being released from the hypothalamus to the body is a brain → body hunger signal
neuropeptide y
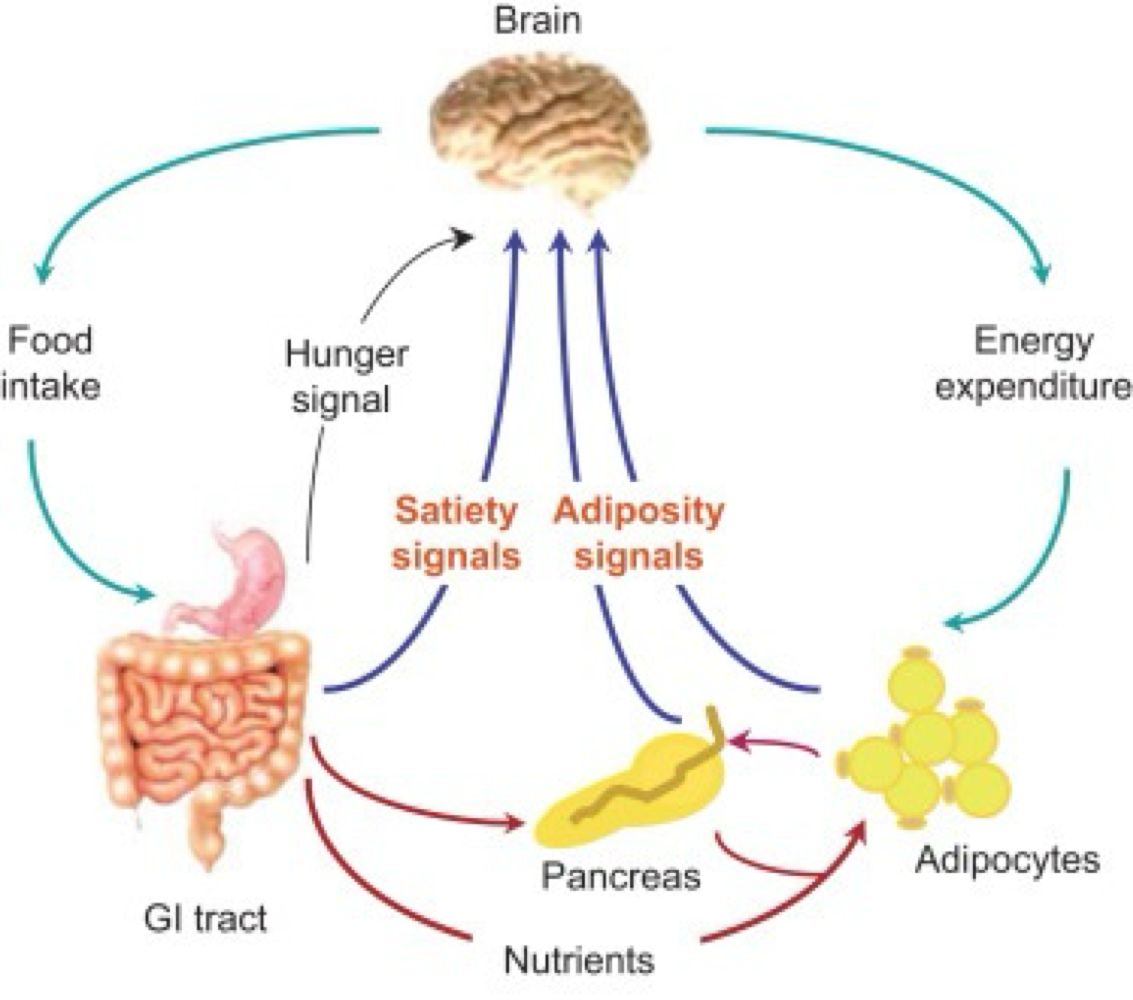
_______ being released from the GI tract to stimulate the hypothalamus is a body → brain satiety (fullness) signal
cholecystokinin (CCK)
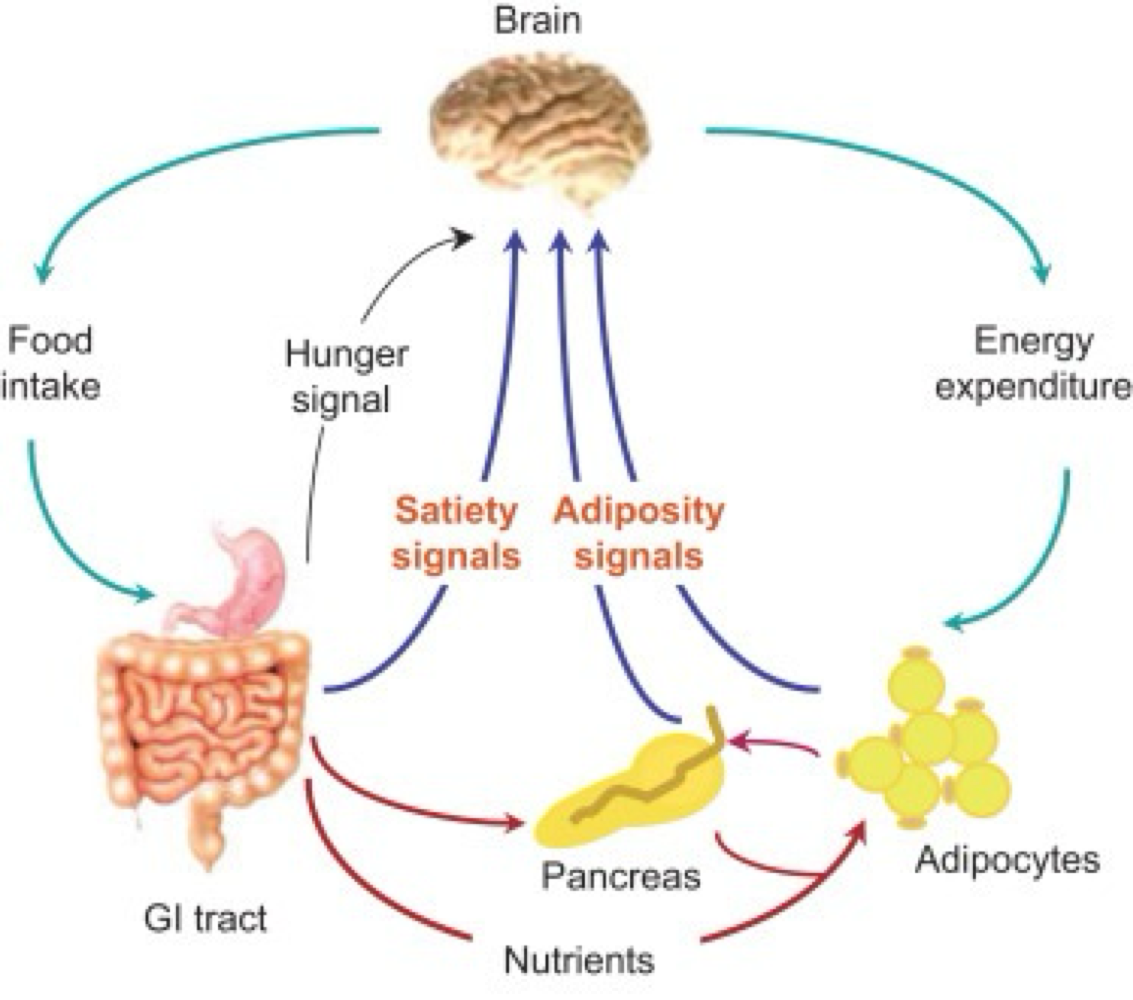
_______ being released from the hypothalamus to the body is a brain → body satiety (fullness) signal
alpha melanocyte stimulating horomone
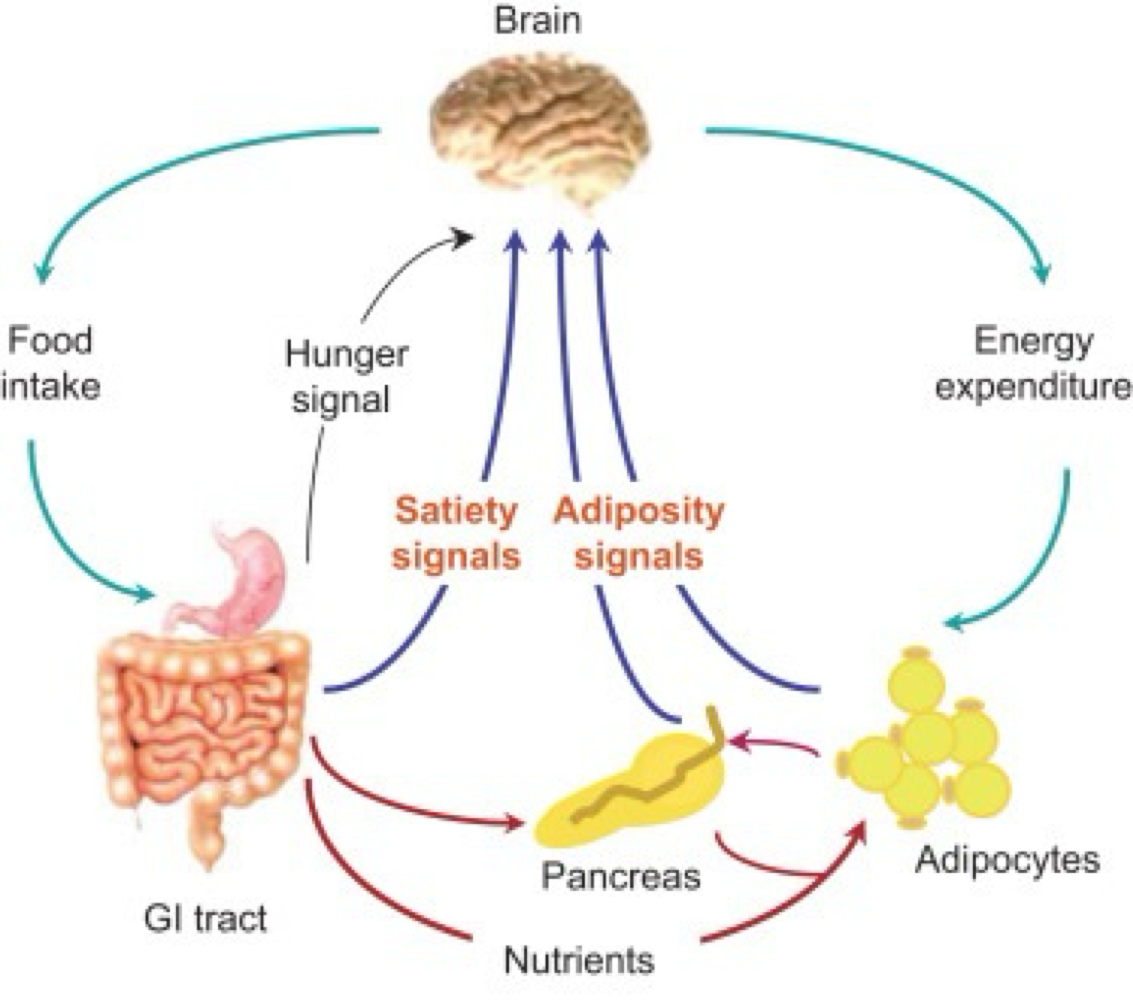
_______ released from the adipose tissue to stimulate the hypothalamus is a body → brain adiposity (fat satiety) signal
leptin
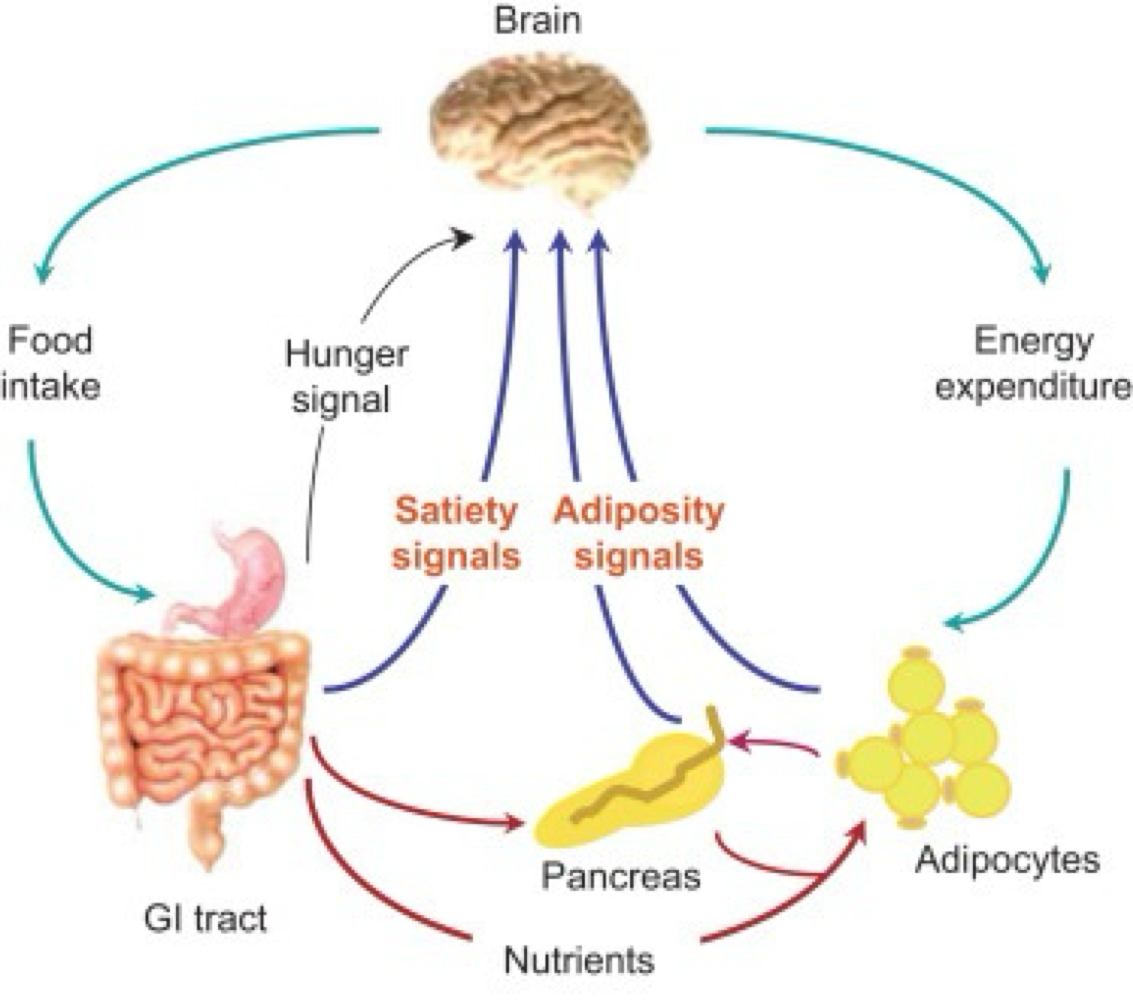
_______ released from the pancreas to stimulate the hypothalamus is a body → brain adiposity (fat satiety) signal
insulin
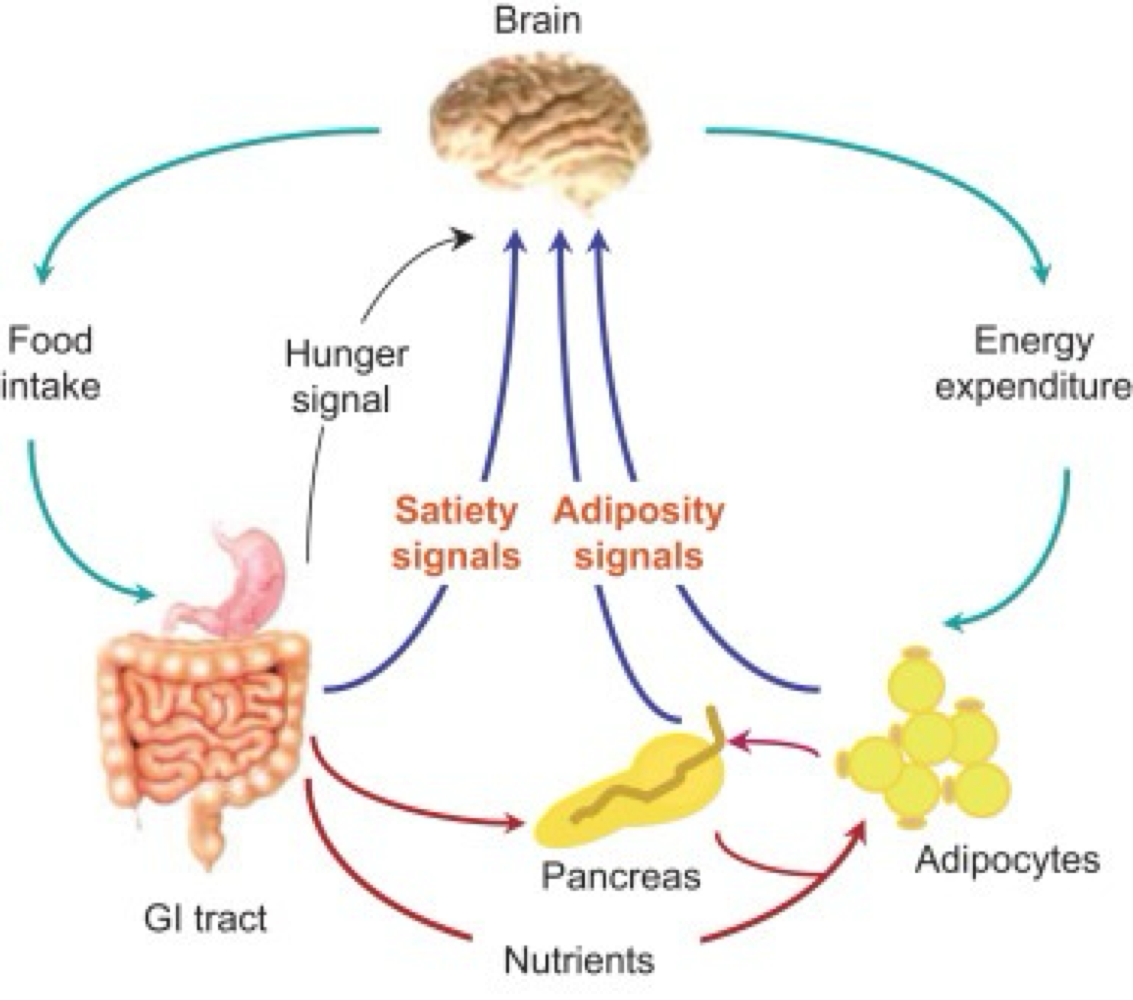
sensations, thoughts, imagination, and emotions are what types of stimuli that activate the vagus nerve from the brain to the gut?
neural stimuli
_______ are physical stimuli that respond to the GI tube stretching when food enters our stomach
mechanoreceptors
_______ are chemical stimuli that response to changes in pH or the presence of fatty acid or peptide chains
chemoreceptors
during digestion, our stomach breaks down proteins using _______
gastric acid
during digestion, our small intestine receives:
insulin from our _______ to break down glucose
bile from our _______ to break down fat
enzymes from our _______ to break down all molecules
liver, gallbladder, pancreas
_______ release digestive endocrine chemicals
entroendocrine cells
_______ are entroendocrine cells in the stomach that release gastrin
G cells
_______ are entroendocrine cells in the stomach and small intestine that release somatostatin
D cells
_______ are entroendocrine cells in the small intestine that release secretin
S cells
_______ are entroendocrine cells in the small intestine that release CCK
I cells
_______ are entroendocrine cells in the small intestine that release gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
K cells
during the digestion of proteins, peptides, and fats:
protein enters the stomach and signals G cells to release _______ (what chemical?)
gastrin stimulates _______ (what substance?) release from parietal cells
HLC denatures proteins, then activates _______ (what enzyme?) and signals S cells to release secretin
Peptides activate _______ (what cells?) to release CCK
CCK and secretin stimulate the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas to release _______ (what substance?)
CCK stimulates the _______ to release bile into the small intestines
gastrin
HLC (gastric acid)
pepsin
I cells
a basic solution
gallbladder
during digestion inhibition:
_______ inhibits gastric secretion and movement
D cells release _______ to regulate digestive actions via inhibtion
the Islets of Langerhans regulate digestion by releasing _______ and _______ to neutralize the stomach
GIP
somatostatin
water and HCO3- (bicarbonate ion)
during glocose metabolism:
glucsoe stimulates _______ (what cells?) to release GIP
GIP stimulates the Islets of Langerhans to release _______
insulin decreases blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia) by stimulating organs to intake _______ (what molecule?)
the Islets of Langerhans releases _______ (an insulin antagonist) and somatostatin
K cells
insulin
glucose
glucagon
the _______ of the pancreas regulaes energy storage adn metabolism
Islets of langerhans (endocrine)
_______ cells in the pancreas release glucagon, and _______ release insulin
alpha cells, beta cells
the absorptive phase of glucose regulation and inhibition is regulated by _______, which directs:
amino acids → _______ and _______
glucose → muscles, tissues, liver, and brain for _______
triglycerides → _______
insulin
muscles, liver
ATP
adipose tissue
during the absorptive phase of glucose regulation and inhibition, excess glucose is:
stored as glycogen in liver and muscles via _______ (what process?)
stored as fat in adipose tissue via _______ (what process?)
glycogenesis
lipogenesis
where is glucsoe transformed in to triglycerides before its storied in adipose tissue?
the liver
during the postabsorptive phase of glucose regulation and inhibition, what two processes occur for other molecules to be turned back into glucose?
glycogenosis and glycoenolysis
assited by stress and growth hormones, glucagon regulates nutrient mobilization to induce high blood sugar, which is also known as _______
hyperglycemia
insulin binds to _______ (what receptors?) on cells, then inserts _______ from the cytosol into cell membranes for glucose entry
tyrosine kinase receptors, glucsoe transporter molecules
specific glucose transporter molecules are found on specific cells:
GLUT 1 → _______
GLUT 2 → _______
GLUT 3 → _______
GLUT 4 → _______
all cells
liver and pancreas
neurons
fat tissue and muscles
broken or overstimulated beta cells causes no insulin release, which is also known as _______ (what disease?)
Type 1 diabetes
broken tyrosine koanse receptors causes unrecognition of insulin, which is also known as _______ (what disease?)
Type 2 diabetes