Biology 30 - Complete
1/239
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
240 Terms
Genetic drift
-Random change in allele frequencies that occurs in small populations
-A change in the gene pool of a small population, brought about by chance.
Gene pool
-All the genes, including all the different alleles for each gene, that are present in a population at any one time.
-All of the genes that occur within a specific population.
Gradualism
-The theory that evolution occurs slowly but steadily.
-A model in evolutionary biology that sees evolution proceeding more or less steadily thoughout time.
Punctuated equilibrium
-The theory that species evolve during short periods of rapid change.
-A model that views evolution as being concentrated in short periods of time followed by long
Variation
-Any difference between individuals of the same species.
-Differences in genetic makeup of organisms.
Adaptation
-A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce.
-An inherited trait or set of traits that improve the chances of survival and reproduction of organisms.
Speciation
-Formation of new species.
Pangaea
-The name of the single landmass that broke apart 225 million years ago and gave rise to today's continents.
-A large supercontinent that existed appoximately 225 mya.
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
Polyploidy
A condition in which an organism possesses more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes (ex) 3n or 4n
Geographic Isolation
-Form of reproductive isolation in which one population is separated into two populations because they are separated physically by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains, or stretches of water.
Reproductive Isolation
-Separation of species or populations so that they cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
-The loss of the ability to interbreed by two isolated groups/populations.
Migration
The movement of organisms between two distict geographic areas.
Adaptive radiation
-An evolutionary pattern in which many species evolve from a single ancestral species.
-The process by which a species evolves into a number of different species, each occupying a new environment.
Co-evolution
-Process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other.
-When two or more species evolve in response to each other through cooperative or competitive adaptations.
convergent evolution
-Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments.
-The development of similar forms from unrelated species due to adaptation to similar environments.
industrial melanism
-Darkening of populations of organisms over time in response to industrial pollution.
-The development of dark coloured organisms in a population exposed to pollution.
vestigial structures
-A structure that is present in an organism but no longer serves its original purpose.
-No longer serving a purpose in modern day organisms.
homologous structures
-Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry.
-Having similar origins but different uses in different species. The front flipper of a dolphin and the forelimb of a dog.
analagous structures
-Similar function but different structure - does not show common ancestry - Ex: butterfly wing and bat wing)
-Similar in function and appearnace but not in origin. The wing of an insect and the wing of a bat.
Plasma (cell) membrane
- A selectively permeable surface that encloses the cell contents and through which all materials entering or leaving a cell must pass.
- The gatekeeper of the cell.
- Phospholipid bilayer, fluid mosaic model.
- Controls what enters and leaves the cell - selectively permeable.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
-The region of the endoplasmic reticulum that has few or no ribosomes on its cytoplasmic surface and synthesizes carbohydrates, lipids, and steroid hormones; detoxifies chemicals like pesticides, preservatives, medications, and environmental pollutants, and stores calcium ions.
-Free of ribosomes; the area where fats and lipids are synthesized.
Lysosomes
-An organelle containing digestive enzymes.
Chromoplast
-A colored plastid, typically containing a yellow or orange pigment.
-Gives color to fruit and flowers.
Mitochondria
- An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
- The powerhouse of the cell.
- The site of cellular respiration.
-Enclosed by a double membrane.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
-The region of the endoplasmic reticulum that is studded with ribosomes and engages in protein synthesis.
-Ribosomes attached to the surface; site of protein production.
Ribosomes
-Site of protein synthesis
-rRNA; Involved in the process of putting amino acids together to form proteins; can be found attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum or floating free in the cytoplasm.
Leucoplasts (Amyloplasts)
Type of plastid, stores starch
Cytoplasm
-The watery gel inside a cell that holds various parts.
-Contains the organelles and has a grainy appearance.
Golgi apparatus
- A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell.
- Made up of a series of membranes, involved in secretion and packages materials for storage and delivery.
Centriole pairs
-Barrel-shaped organelles composed of tubulin; anchors the spindles, functions cell division.
-Made up of microtubules and take part in cell division.
Vacuole
-Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates.
-Serve as reservoirs for a variety of substances.
-Large central vacoules are found in plant cells; small vacuoles that may appear and disappear depending on conditions are found in animal cells.
Chloroplast
-Organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy.
-Type of plastid that is responsible for photosynthesis. Captures energy of the sun.
-Enclosed by a double membrane.
Nucleus
-Control center of the cell.
-Found in eukaryotic cells. The control center of the cell involved in cell reproduction and growth.
Cell wall
-A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
-In plants made of cellulose
-In fungi made of chitin
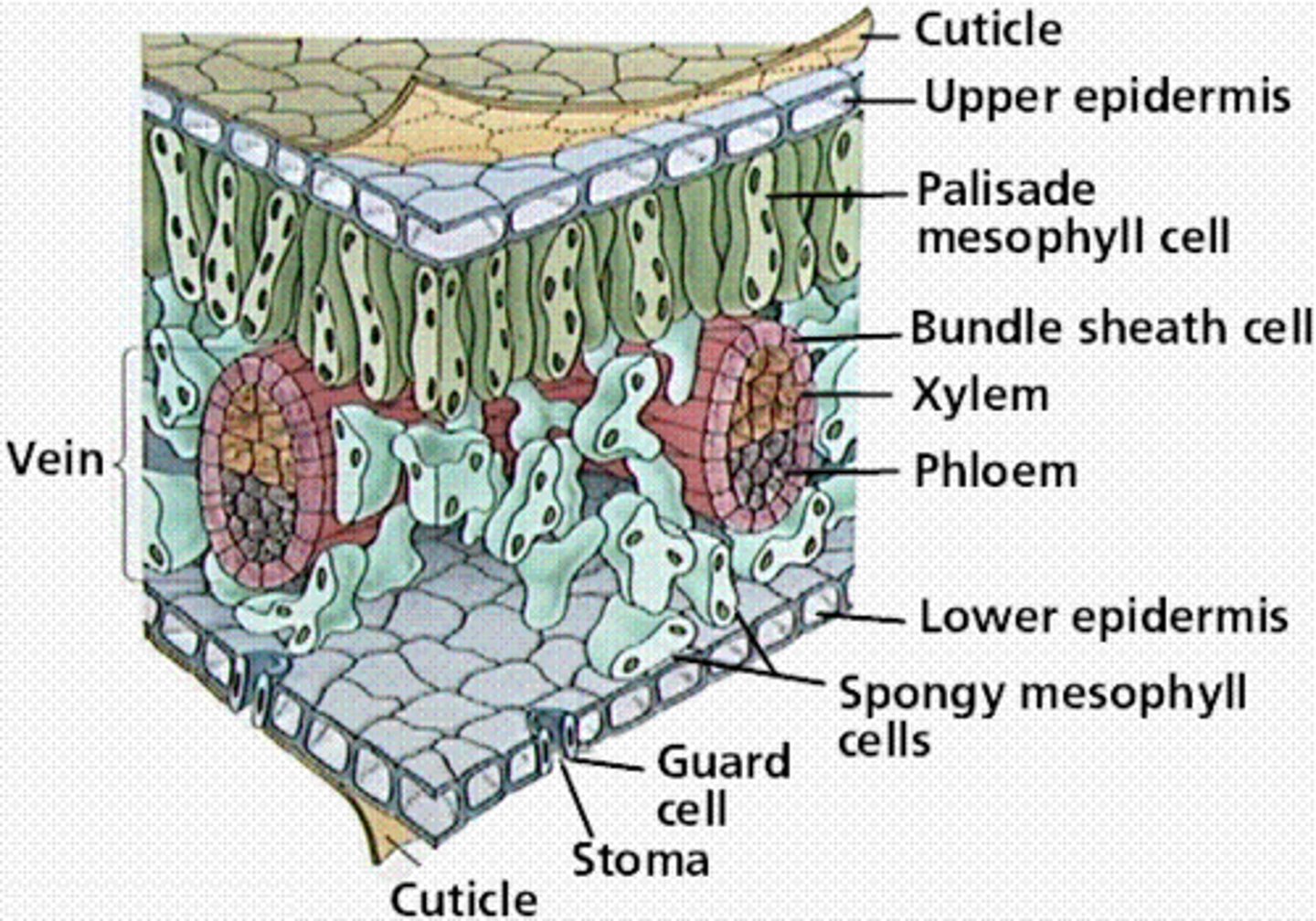
Leaf cross section diagram
Be prepared to label all of these parts.
Lamark's theory of evolution
-Principle of acquired characteristics - If an organism changes during life in order to adapt to its environment, those changes are passed on to its offspring.
- Principle of use and disuse
Principle of Acquired Characteristics
Concept, popularized by Lamarck, that traits gained during a lifetime can then be passed on to the next generation by genetic means; considered invalid today.
Principle of Use and Disuse
Concept popularized by Lamarck that proposes that parts of the body that are used are often strengthened and improved, whereas parts of the body that are not used become weak and ultimately may disappear. Considered invalid today.
Charles Darwin Theory of Evolution
1. The Origin of species- Darwin was a British biologist. His book On The Origin of Species, challenged the idea of special creation by proposing the revolutionary theory of biological evolution
2. Key points- Informed by Thomas Malthus's Essay on Population, Darwin concluded that every living plant and animal takes part in a constant "struggle for existence." Only the "fittest" Species survive this struggle. The fittest are determined by a process of natural selection in which new species emerge after gradually accumulating new modifications.
Survival of the Fittest (Natural Selection)
Charles Darwin - process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully.
Struggle for existence
Charles Darwin - competition among members of a species for food, living space, and the other necessities of life
Natural Selection
Charles Darwin - A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Overproduction
Charles Darwin - organisms produce more offspring than can survive. This leads to competition for resources.
Competition
Charles Darwin - the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources. There is competition for water, nutrients, space, etc.
Mitosis
- asexual cell division
- 2 diploid daughter cells are produced that are identical to the parent cell.
-Occurs in body (somatic cells)
-No genetic variation produced
-Only 1 division
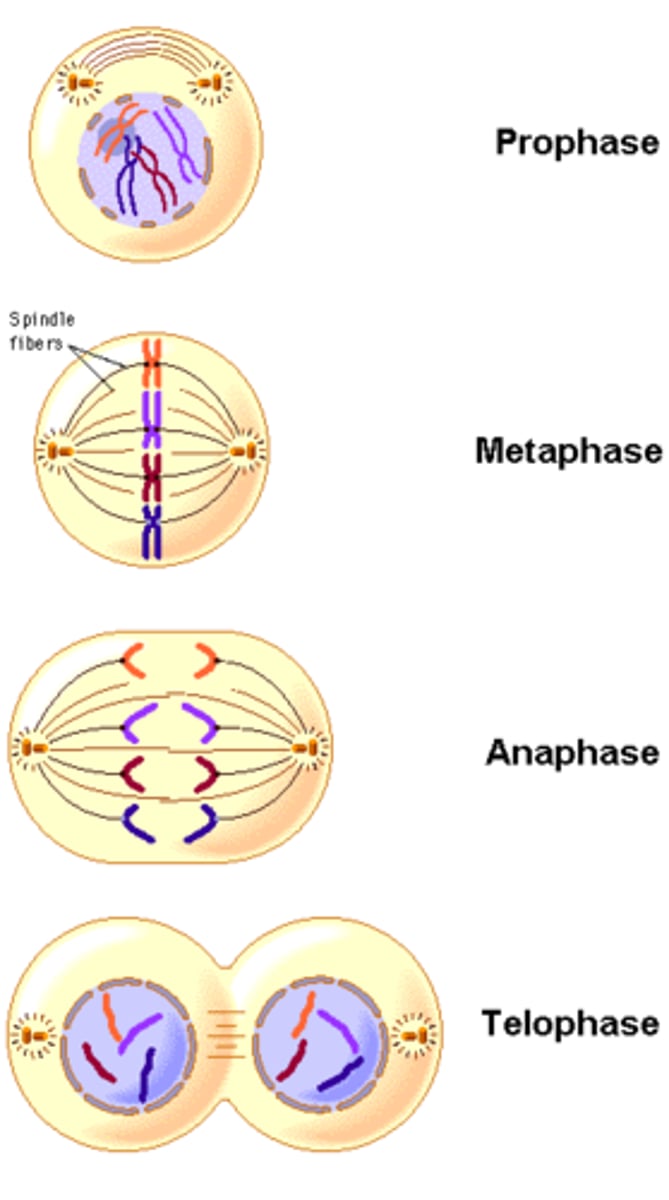
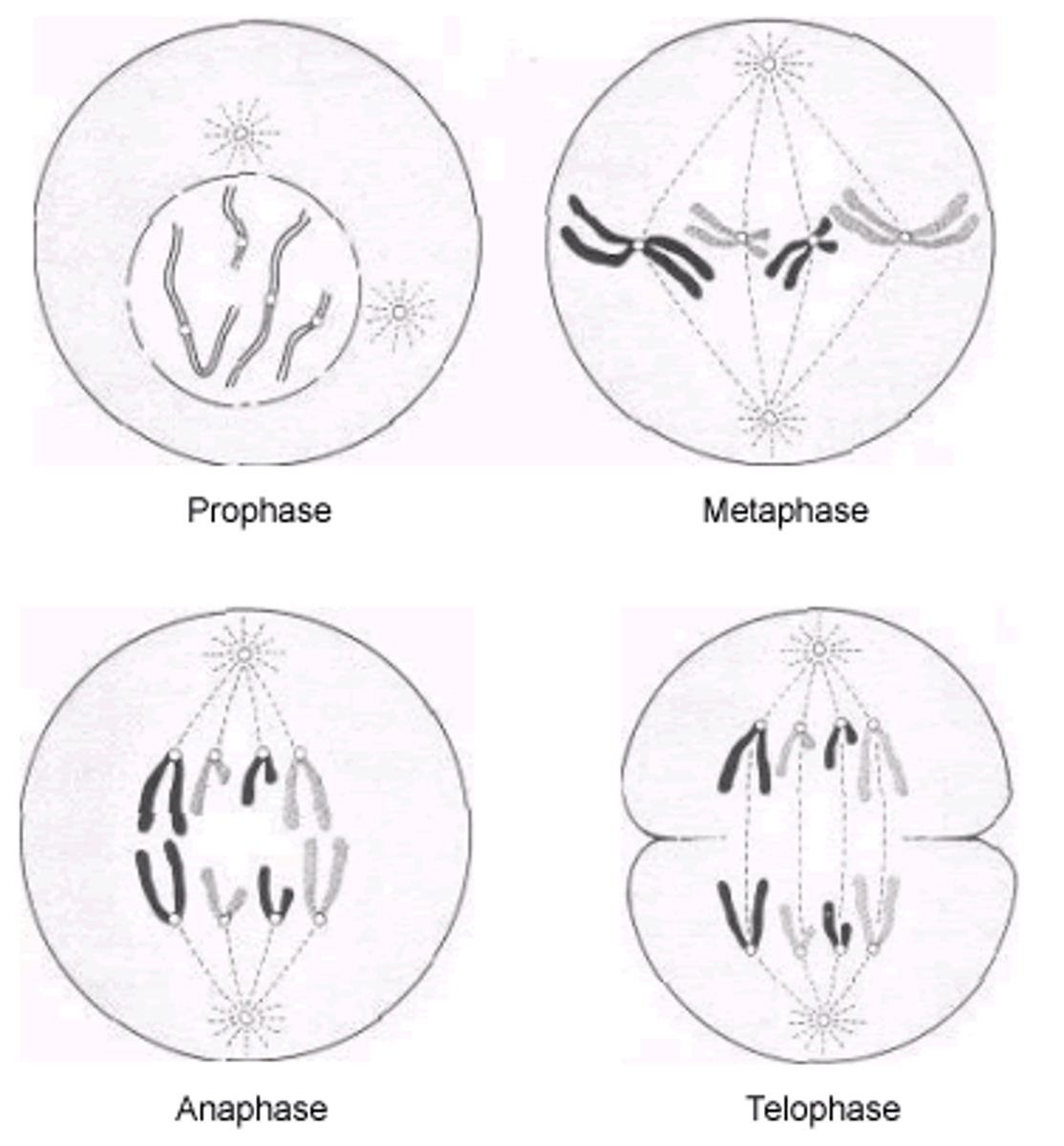
Stages of mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Meiosis
Sexual cell division
Produces gametes (sex cells)
2 division - Meiosis I and Meiosis II
Produces 4 haploid cells that are genetically uniquie.
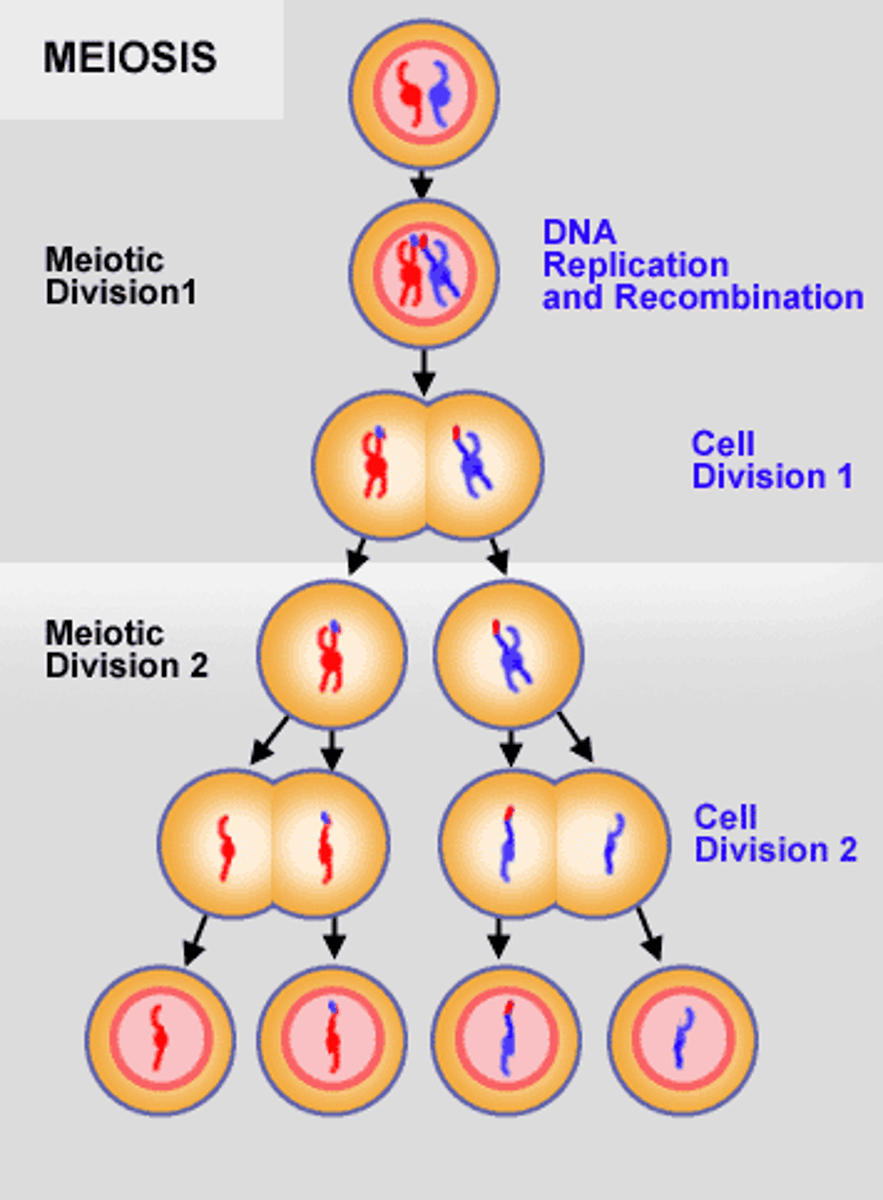
Mitosis versus Meiosis
Mitosis 2 identical cells, no mixing of chromosomes, diploid cells
Meiosis 4 different cells, mixing of chromosomes, haploid cells
ABO blood typing system alleles
IA = IB
i
Fungi
Kingdom of organisms, eukaryotic organisms that have no means of movement, reproduce by using spores, and get food by breaking down substances in their surroundings and absorbing the nutrients, multicellular, ingestive heterotrophs

Animalia
kingdom of multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs whose cells do not have cell walls; movement at some time in their life cycle

Plantae
Kingdom of multicellular photosynthetic autotrophs that have cell walls containing cellulose; eukaryotic multicellular autotrophs

Bacteria lack....
membrane bound organelles; they are prokaryotic cells
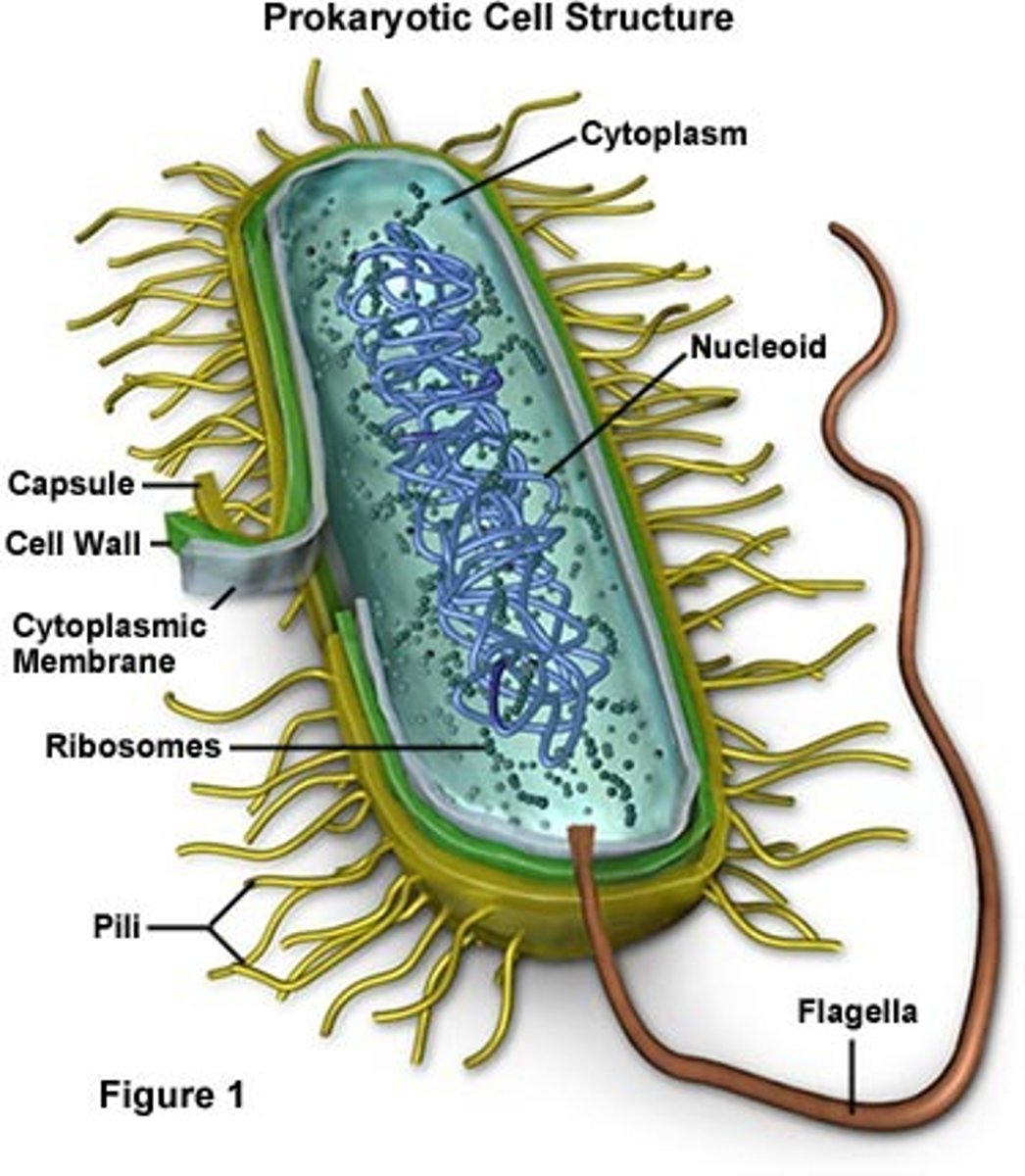
What organisms have cell walls?
plants, fungi, some bacteria, some protists
What organisms are autotrophs?
plants, some bacteria, some protists
Veins in plants are called vascular tissue and contain...
xylem and phloem
Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant
Xylem
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant
Biology
The study of life and living organisms.
Charles Darwin sailed on what ship?
HMS Beagle
What islands did Darwin study?
Galapagos Islands
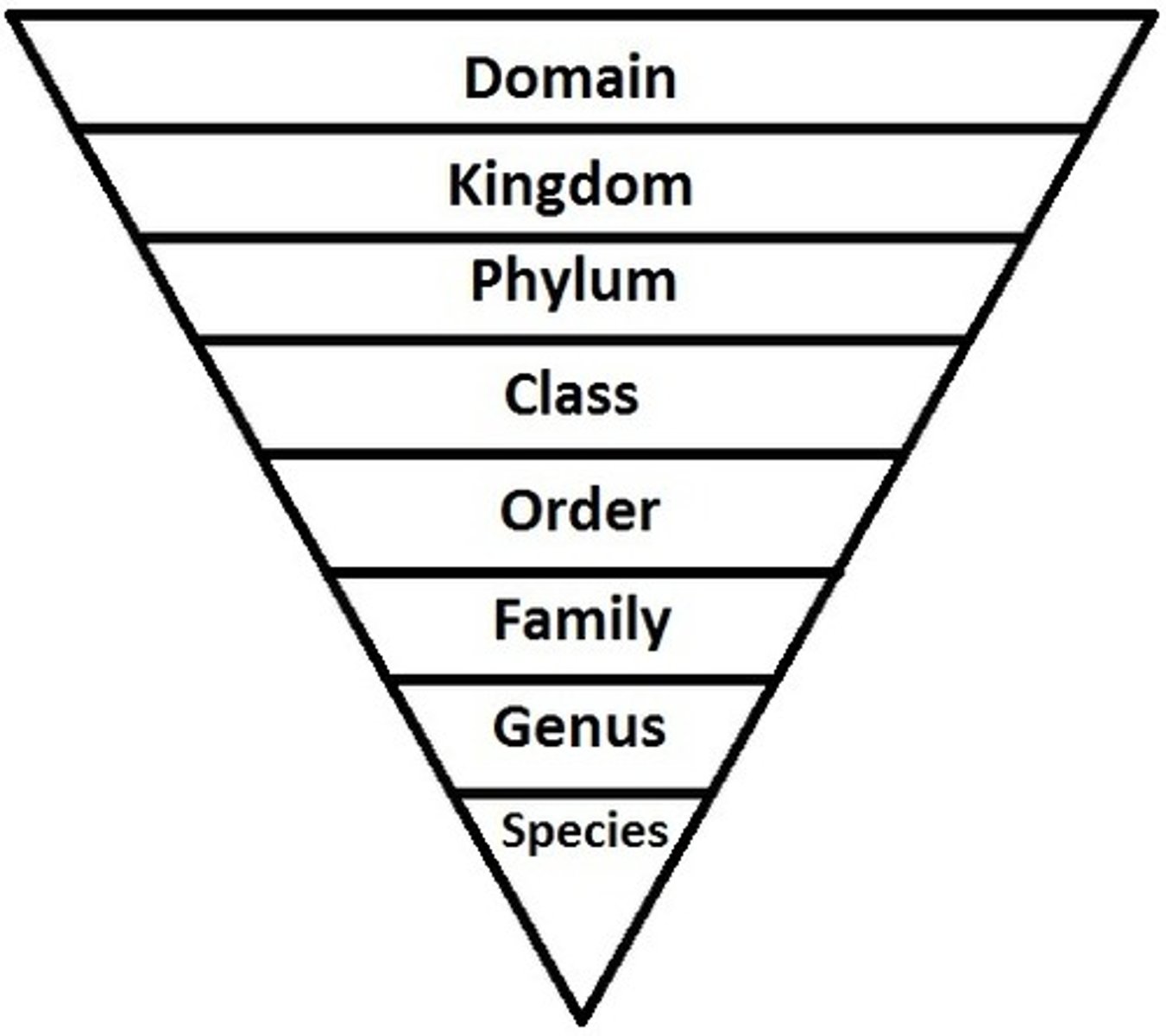
Taxonomic Levels of Organization
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Lichen
symbiotic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic algae
Homeostasis
Process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment; balance
Extremophile
Archaeabacteria that live in extreme environments.
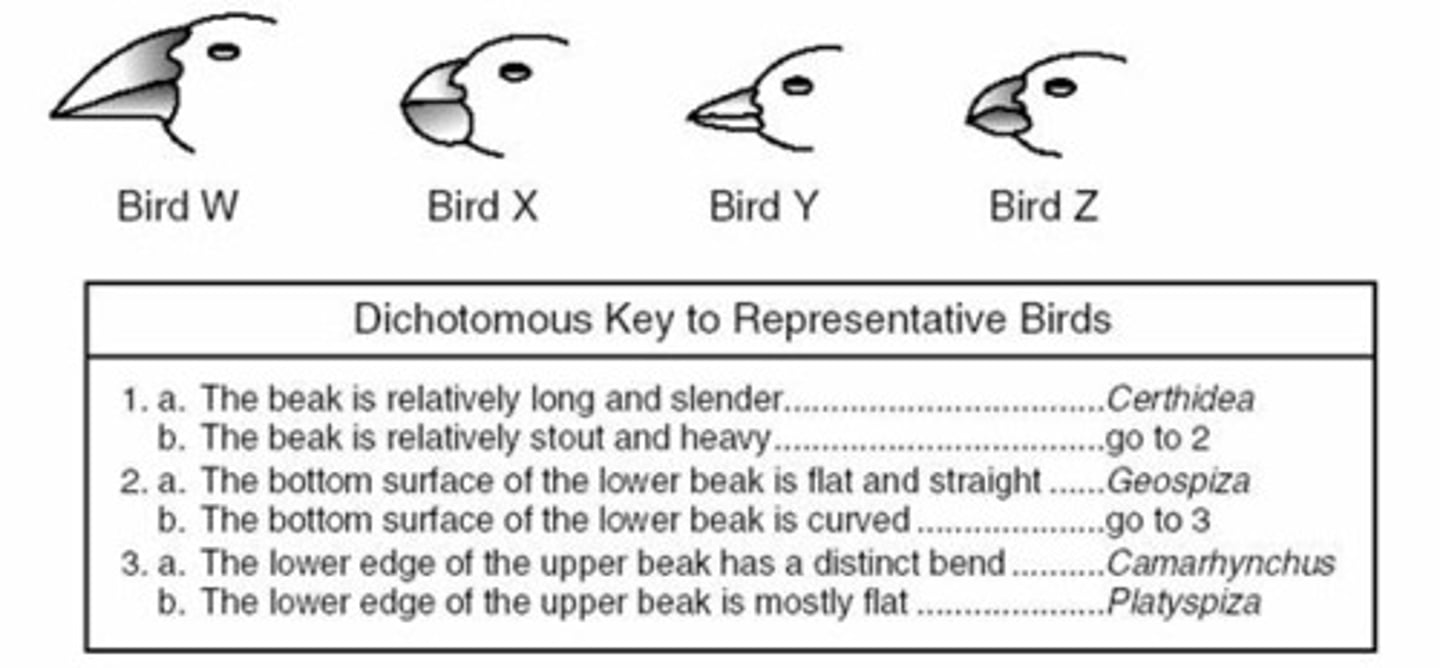
Dichotomous key
A key for the identification of organisms based on a series of choices between alternative characters
What 2 kingdoms of life have multicellular organisms exclusilvely?
Plantae and Animalia
Name the 6 kingdoms of life
Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
binomial nomenclature
Classification system in which each species is assigned a two-part scientific name
Rules for binomial nomenclature
1st: Genus name; capitalized
2nd; species name; lower case
Underline or type in italics
Latin
What kingdoms are prokaryotic?
Eubacteria and Archaebacteria
What kingdoms are eukaryotic?
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
Who came up with binomial nomenclature?
Carolus Linnaeus
Taxonomy
Branch of biology that groups and names organisms based on their characteristics
Science of classification
Alternation of generations
The alternation between the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte in a plant's life cycle
Haploid
n
Diploid
2n
What kingdon does E. Coli belong to?
Escherichia coli; Kingdom Eubacteria
Name the 3 domains of life
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Name the kingdon in Domain Bacteria
Kingdom Eubacteria
Name the kingdom in Doman Archaea
Kingdom Archaebacteria
Name the 4 kingdoms of Domain Eukarya
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
What Kingdom does an amoeba belong to?
Domain Eukarya, Kingdom Protista
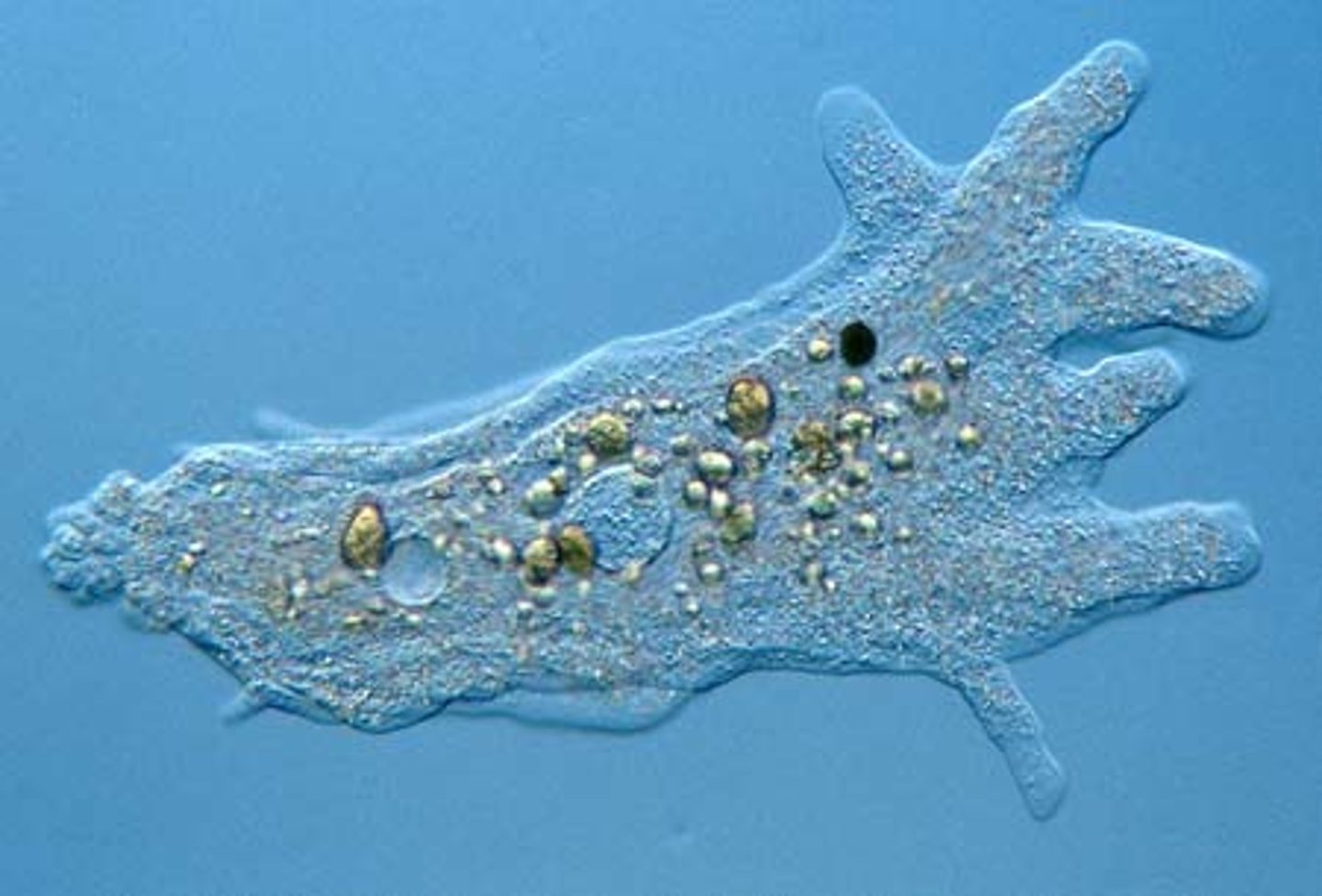
Characteristics of Kingdom Protista
- All eukaryotes
-Generally unicellular, some multicellular
-All live in moist or aquatic environments
-Classified by their mode of nutrition
-Kingdoms Plantae, Fungi and Animalia each evolved from a type of protist
-The catch all kingdom
Name the 9 animal phyla we discussed in class
Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida, Mollusca, Arthropoda, Echinodermata, Chordata
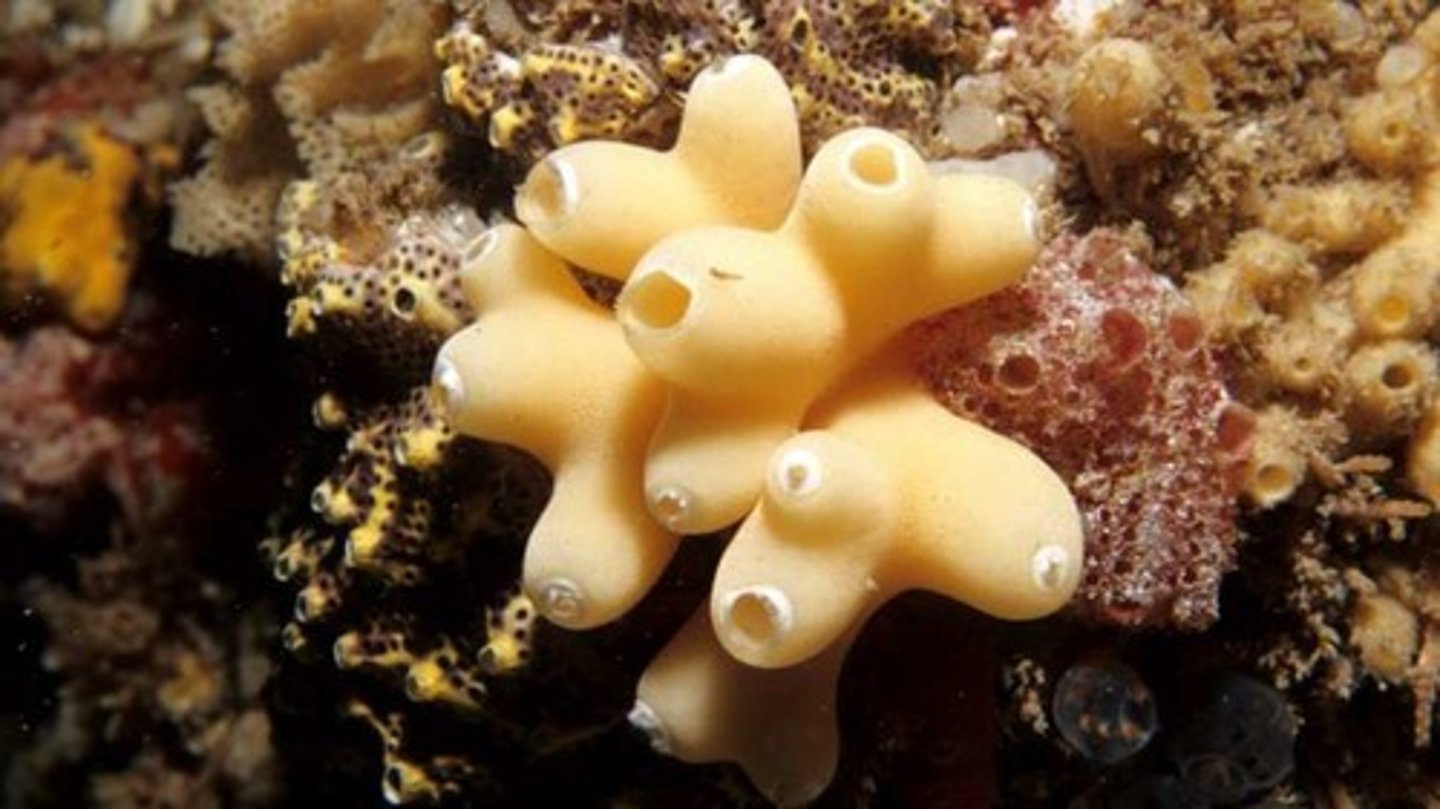
Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Porifera
sponges
sessile
filter feeders
no true tissues
osculum

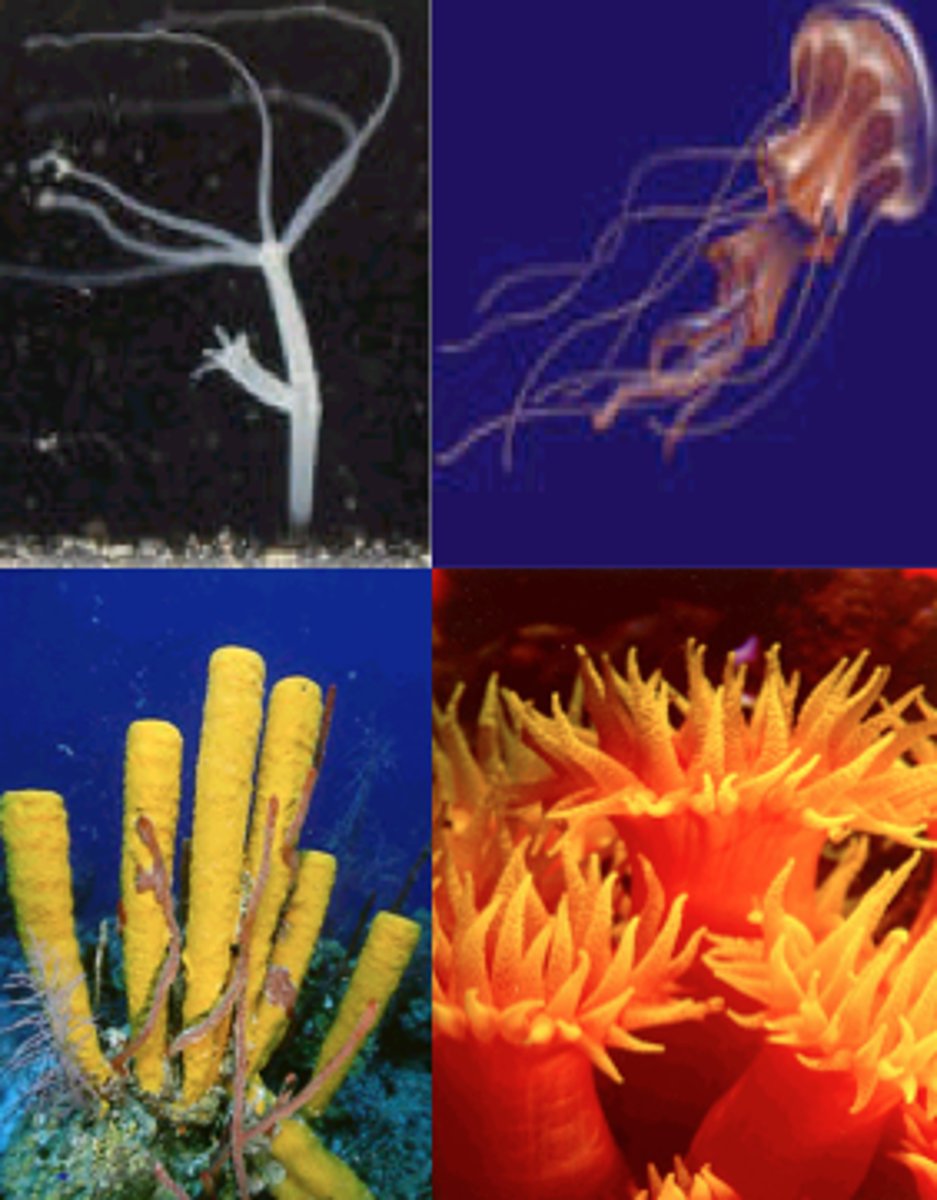
Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Cnidaria
jellyfish, sea anemones, corals
2 body forms - medusa and polyp
marine

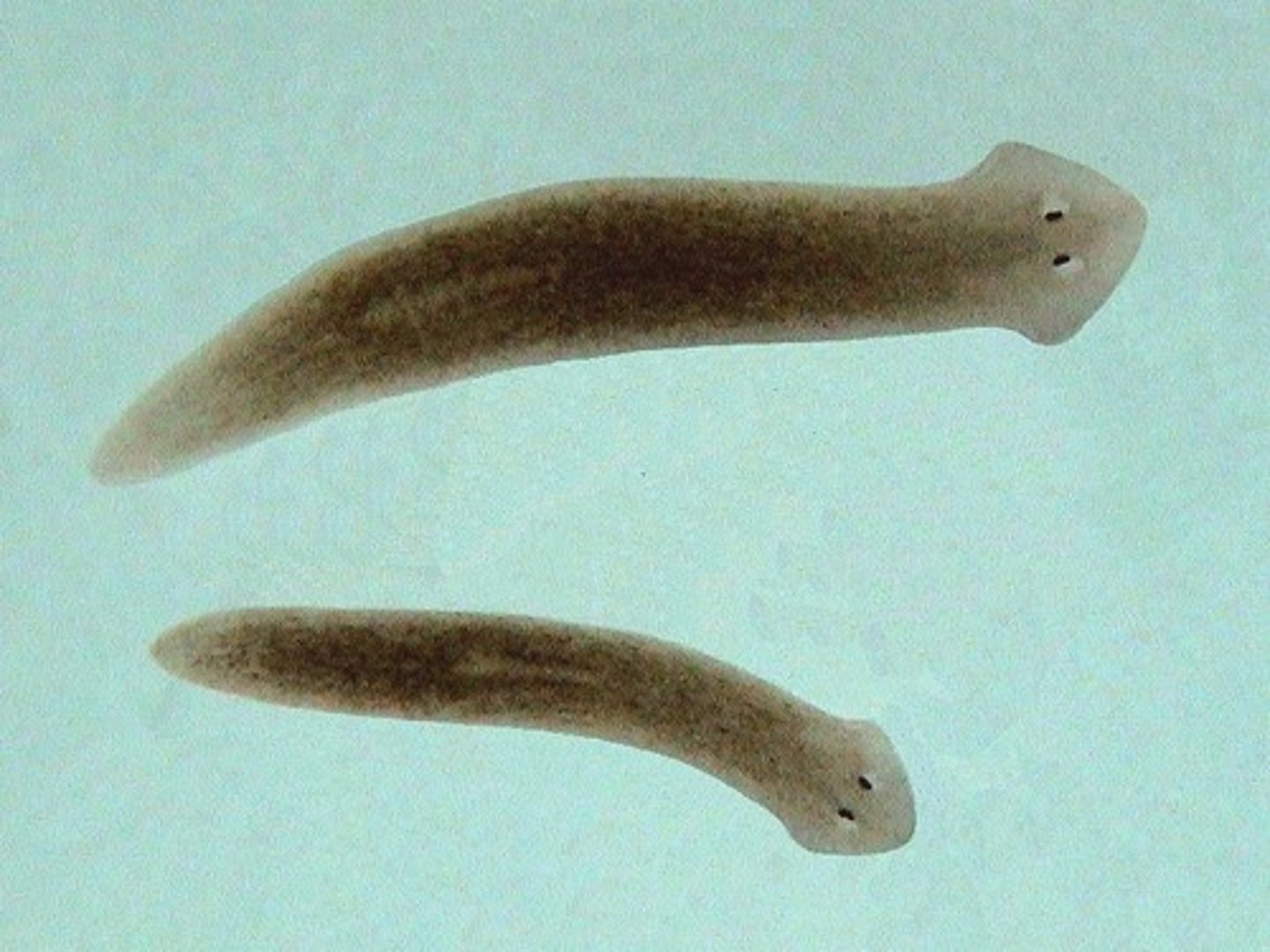
Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Platyhelminthes
-flatworms, flukes, tapeworms, planaria
-The majority of them are white, colorless and some derive color from ingested food while free-living forms are grey, brown-black or brilliantly colored.
-Their anterior end of the body is differentiated into the head = cephalization

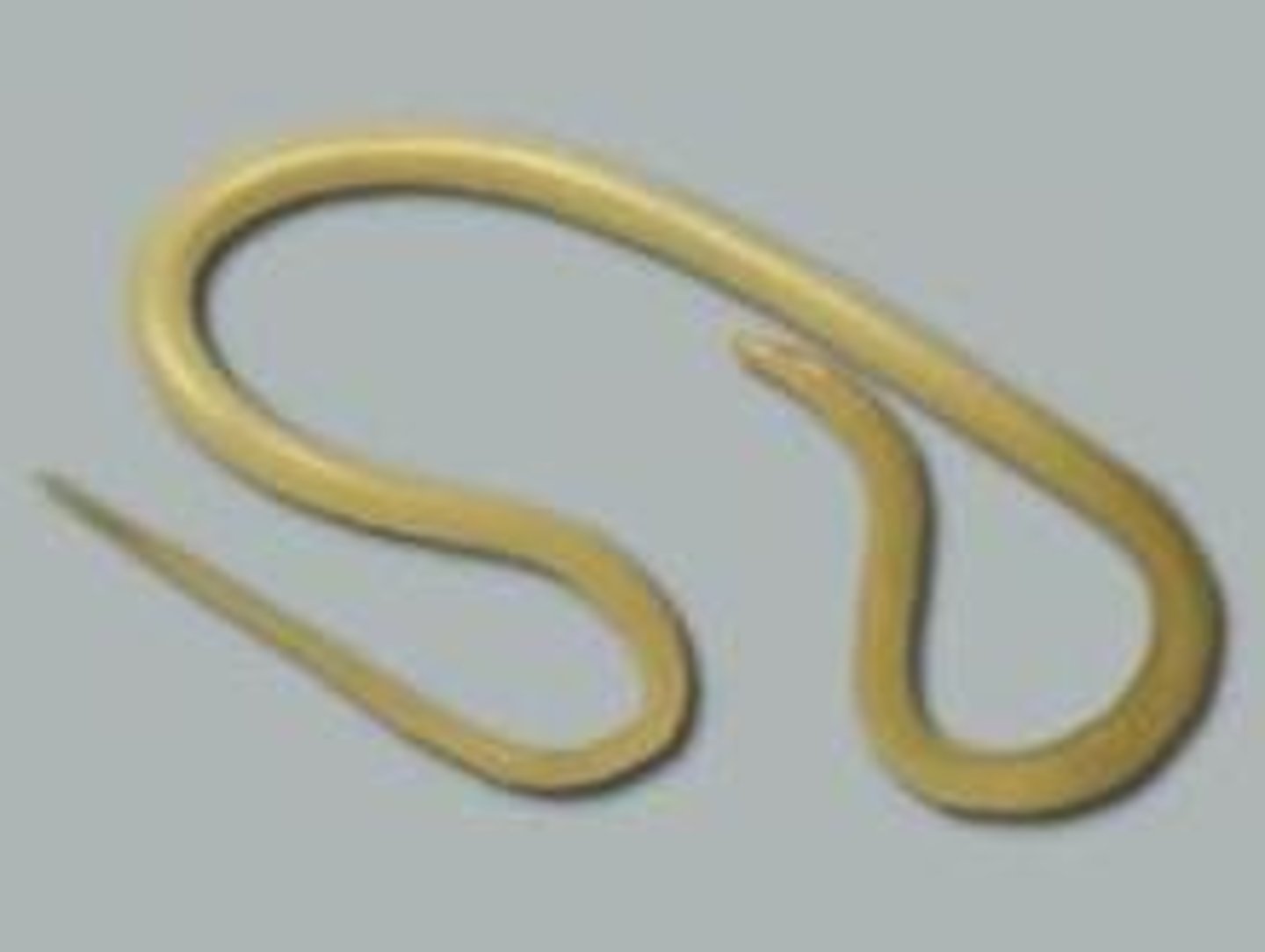
KIngdom Animalia, Phylum Nematoda
-Roundworms, pinworm, asccaris
-They are widely distributed, aquatic or terrestrial, parasitic or free-living.
-Their body is elongated, cylindrical, unsegmented, worm-like, bilaterally symmetrical and tapering at both ends.
-The digestive system is complete with a distinct mouth and anus.

Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Annelida
earthworms, leech, segmented worms.
-have closed circulatory system
-reproduce sexually and asexually
-have bodies made up of many linked sections called segments
-have complete digestive system (mouth and anus)

Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Mollusca
- 3 Classes:
~ Class Bivalvia (clams, oysters)
~ ClassGastropoda (snails, slugs)
~ Class Cephalopoda (octopus, squid)
- Have a foot, visceral mass, mantle
- Soft body, hard shell

Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Arthropoda
spiders, insects, crabs, lobster, centipedes, millipedes
-bilateral symmetry
-sexual reproduction
-have exoskeleton made of chitin
-can molt
-segemented body - head, thorax, abdomen
-jointed appendages

Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Echinodermata
-radial symmetry
-marine
-tube feet with suchess
-jaw like ring
-regeneration
-advanced embryos
ex) sea urchins, starfish, sea cucumbers

Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Chordata
fish, dogs, reptiles, amphibians, birds, mammals
-vertebrates and invertebrates
-bilateral symmetry
-closed circulatory system
-have segmented bodies
Passive transport
-Requires NO energy (ATP)
-Movement of molecules from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached
-Moves with the concentration gradient or down the concentration gradient
-Types of passive transport include diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
Active Transport
-Energy-requiring process
-moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient (low - high)
-types of active transport include exocytosis, endocytosis, and movement with a protein carrier molecule.
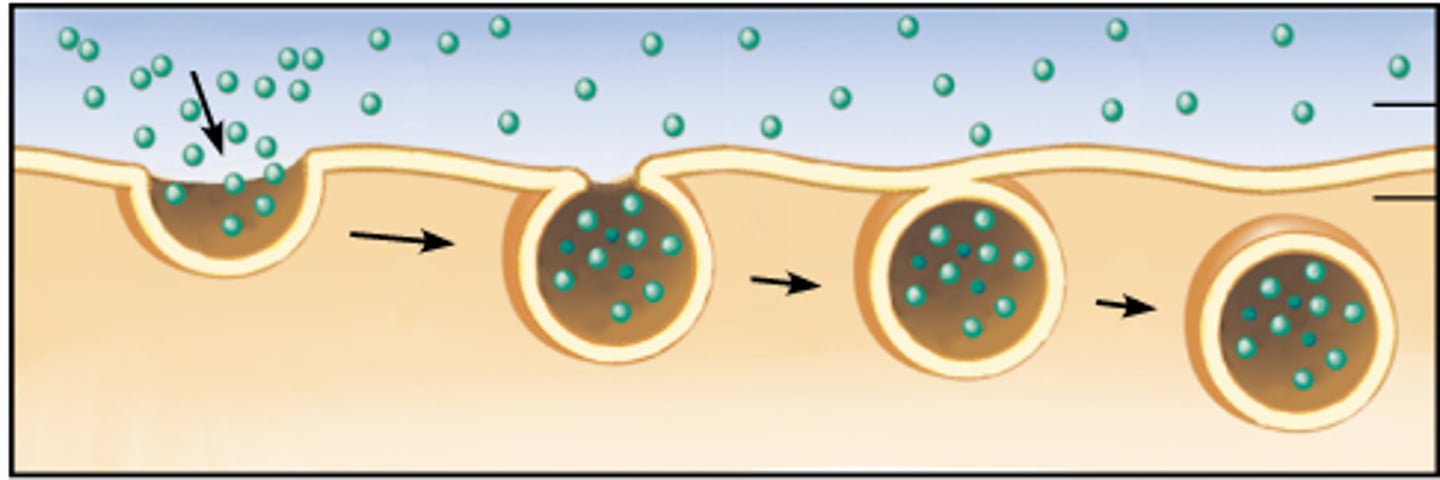
endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane. Requires energy. Two types - pinocytosis and phagocytosis
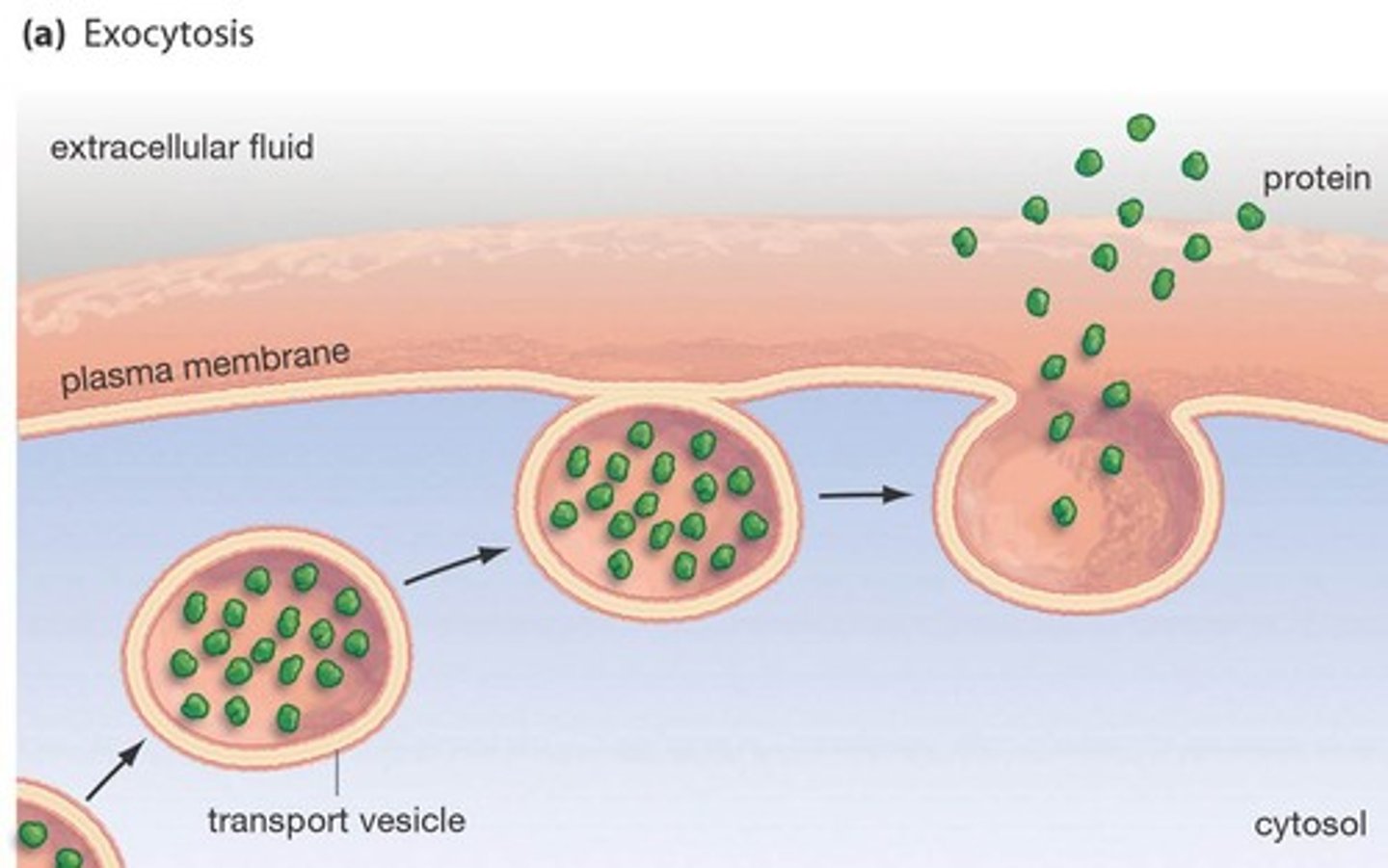
exocytosis
Release of substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane. Requires energy.