Lecture 17 - Exoplanets (results from searches for exoplanets)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
how many exoplaets (march 2025) have been confirmed
5862
how many exoplanets have been unconfirmed (march 25)
7767
how does looking at position find exoplanets
observe the star (for years) and mesaure the relative position with respect to distant stars along the line of sight. the amplitude and period can be used to determine the mass and distance of planet
how to find a planet on velocity
measure the velocity of the star and look for periodic mostion. the period and velocity range of this motion can be used to determine the amss and distance of pertubing planets
how to measure using the doppler technique
We measure P (the period of the oscillation)
and K (the amplitude). P gives directly the orbital period
how does orientation effect finding planets
observed amplitude (K) is the modulated orbital (maximum) velocity of the star (v*) and depends on the inclination angle (I) of the system: K = v* sin(i)
how to get the mass of the planet
need to use Kepler’s 3rd law which relates the orbital period to the radius of the orbit
we can deduce the velocity component of the orbiting planet deduced from K
we get the mass of the planet using (mplanet = M*K/vp sin (i))
what is Upsilon Andromedae
Binary star (~44 ly away) in constellation Andromeda, consisting of an F-type main-sequence star (slightly younger than our Sun) and a red dwarf in a wide orbit around the primary star
what is importnat about Upsilon Andromedae
As of 2010, four confirmed exoplanets are know to orbit the primary star (likely comparable in size to Jupiter).
Upsilon Andromedae was both the first multiple-planet system discovered around a MS star and the first multiple-planet system known in a multiple-star system.
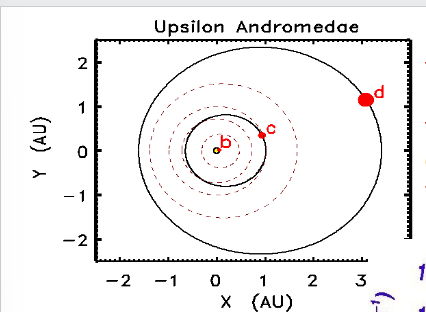
waht does this show
The red dots mark the orbits of
planets b,c and d.
The dashed circles show the orbits
of Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars
to give the scale of the orbits.
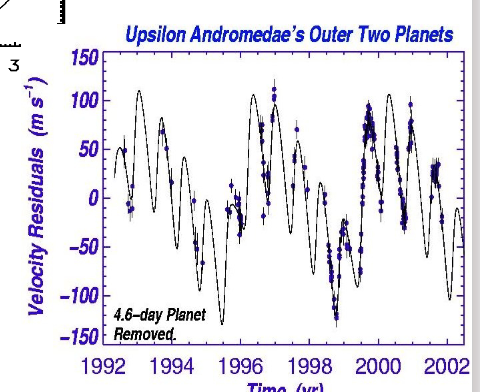
what does this show
Measured velocities for Upsilon Andreomdae are fit with a model containing 2 Jupiter-mass companions.
The inner (4.6 day) planet is subtracted to see better the wobble caused by the outer two planets
what is important to consider when finding planetary system
Finding a planetary system where the orbits of two planets are not in the same plane makes future studies more complicated.
Astronomers can no longer assume all planets orbit their host star in a single plane
what is the range of exoplanet
30 to 0.001 m jupiters
what are hot jupiters
Many of the massive exoplanets are in close orbit to their
host star (sometimes even within Mercury's orbit) causing
high surface temperatures.
what are the conditions of hot jupiters
too close to be in the habitable zone
still some interesitng atmospheric chemistry and physics
hot jupiters transits
they have a much greater chance of transiting their
host star as seen from a further outlying point than planets of
the same mass in larger orbits
hot jupiter inward migrations
all are thought to have migrated to their
present close-in orbits, because there would not haven been
enough material so close to the star for a massive planet to
have formed in situ
hot jupiters tidal locking
they have probably synchronized their rotation
and orbital periods, so they always show the same face to
their host star.
tidal locking earth and moon
Earth’s gravity pulls on the surface of the moon creating a slight bulge.
However, it takes some time for the bulge to form, and during that time the Moon has moved and rotated.
This results in forces that are not aligned with the line between the centre of mass (CoM). Force B is greater than Force A, because B is closer to the centre of the Earth than A is.
This will produce a small torque, slowing down the rotation
of moon, and this will continue until the rotational rate
matches the orbital period.Hence, the bulge is always aligned with the CoM.
what are super earths
Terrestrial (“rocky”) exoplanets defined exclusively by their
mass. The term does NOT imply temperatures, compositions,
orbital properties, habitability, or environments similar to
Earth!!
what are the conditions of super earths
More massive than Earth, less massive than Jupiter (in literature used range is 1 - 10 Earth masses)
Not necessarily “habitable”, as the name might suggest
when were the first super earths discovered
1992
what happened in 2005 with super earths
first super-earth discovered around a main-sequence (MS) star (Gliese 876), with an estimated mass ~7x Earth, and a very short orbital period of just about 2 days
fact file of Gliese 876
Parent star:
Red dwarf (M), and T=3480 K & L=0.0124 Lsun
Outermost Gas Giant (discovered by Doppler method)
Named Gliese 876b with M=2.4MJ & a=0.208 AU
Gas Giant (further analyses of radial velocity (RV) measurements)
Named Gliese 876c with M=0.7 MJ & within orbit of Gliese 876 b
Super Earth (~7x Earth mass) discovered in 2005 via RV method.
Inside orbits of both Gliese 876 b and c (P=1.9days)
Fourth planet discovered in 2010 (~16MEarth)
factfile of gliese 581
Parent star: red dwarf (M), T=3500 K, L=0.012 Lsun
Gas Giant (Neptune-sized) M=20.5 ME, a = 0.04 AU
Rocky Planet M=6.8 ME within habitable zone (temp could be -3 oC
or 500 oC due to runaway greenhouse).Super Earth (?)
M=7 ME
within habitable zone
existence has been put
put into doubt by some
authors (due to stellar
activity).
Super Earth
M=2.5 ME at 0.03 AU
P=3.15day
what are circular orbits
e=0 have a constant orbital velocity
what is elliptical orbits
0<e<1 they are going slower/faster depending on the position in their orbit (faster closer to their host star and slower when further away
what is the pattern for exxentricities
The closer the planet to their host star, the
more circular the orbit.Probably due to tidal forces circularizing
close-in orbits.It is estimated that any planet inside a 4-
day orbit will get circular within 1 billion
years
what is a pattern for planetary orbit eccentricities
Planets orbiting at small distances from the star (<0.1 AU) have almost circular orbits. At larger distances, the orbits may be either circular or highly eccentric
This pattern is not found in binary star systems, so it must be related to planetary formation.
High eccentric orbits may result from tidal interaction between exoplanets, planetesimals & protoplanetary disk
what is the planetary orbit sizes
easier to find big planets close to their host stars
what is a prefered orbit size for planets
<0.2 AU
Do host stars of planetary systems have a specific location
in the HR diagram
stars younger than F7 have only a few useful features in centre of the visible band
what is the trend for metallicity of host stars
There is a strong preference for metal-rich stars to
host planets (see L12 & L13).Metal-poor stars reveal few planets even though
they make up ~70% of all stars searched
what is the law of ellipses
path of planets is elliptical in shape, with the sun located at one focus
what is the law of equal areas
an imaginary line drawn from the centre of the sun to the centre of the planet will sweep out equal areas in equal intervals of time
what is the law of harmonies
ratio of the squares of the periods of any two
planets is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their average
distances from the sun [P2/a3 = constant = 4π2/GM, with G,
gravitational constant & M the mass of the planet + star]
what is kepler’s law
Kepler's efforts to explain the underlying reasons for such motions are no longer accepted; nonetheless, the
actual laws themselves are still considered an accurate description of the motion of any planet and any satellite.