concept 49.2: the vertebrate brain is regionally specialized
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
what are the three major regions of the vertebrate brain
forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain
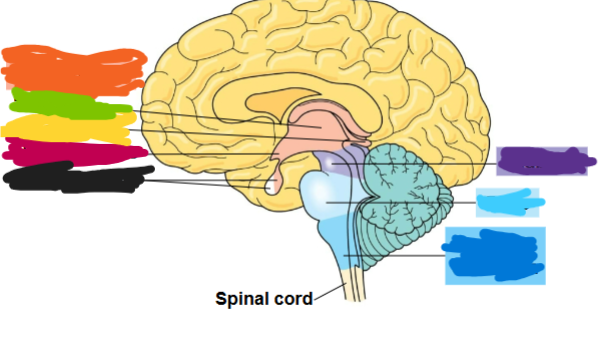
what is the dark blue region
medulla oblongata
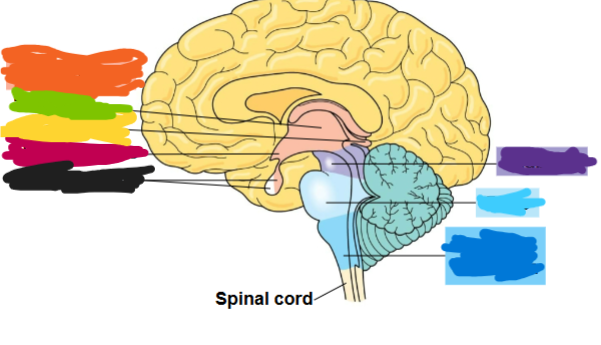
what is the light blue area called
pons
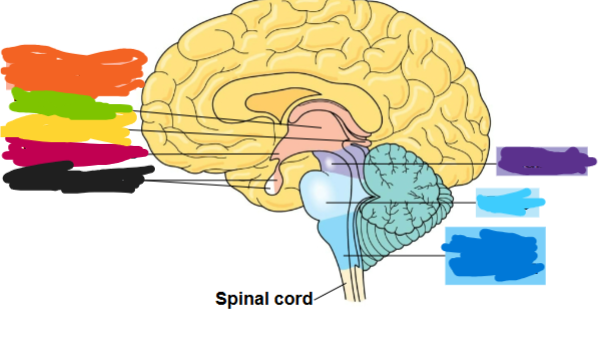
what is the purple part called
midbrain
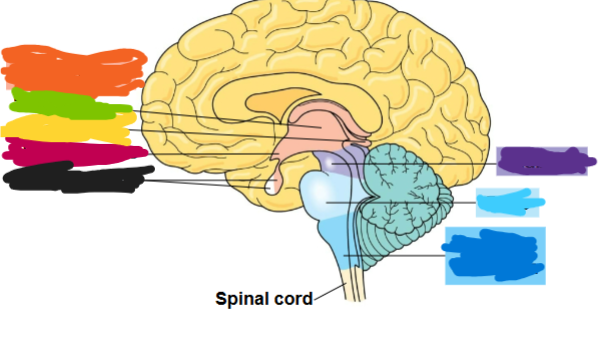
what is the orange part called
diencephalon
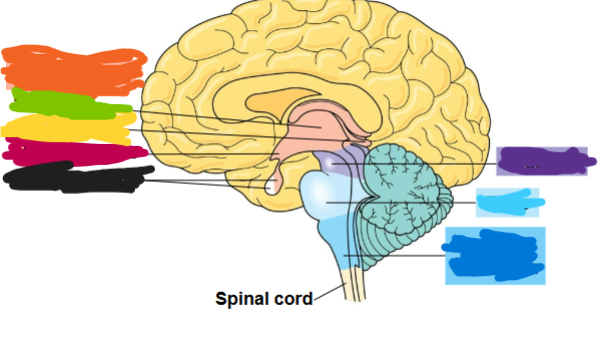
what is the green part called
thalamus
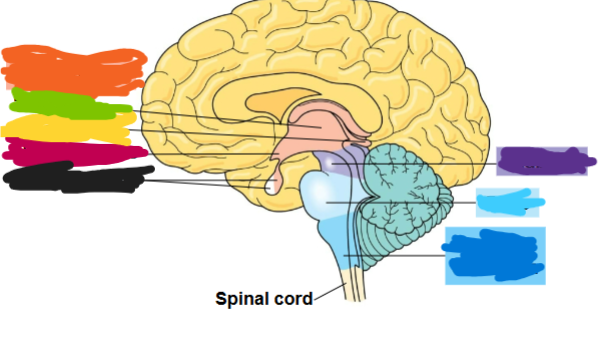
what is the yellow part called
pineal gland
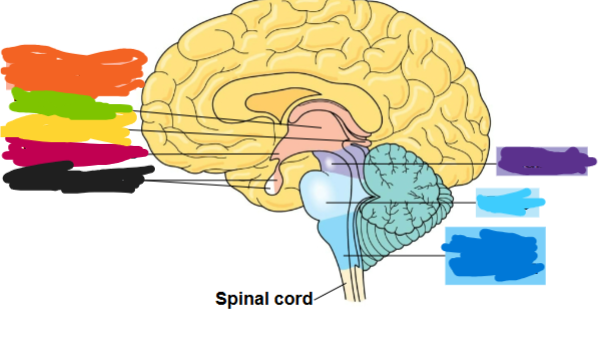
what is the red part called
hypothalamus
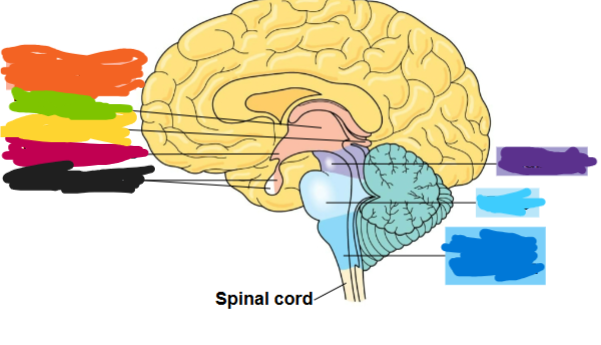
what is the black part called
pituitary gland
what makes up the forebrain
the cerebrum and hypothalamus
function of the cerebrum
essential for awareness, language, cognition, memory and consciousness
what makes up the midbrain
consists of the superior part of the brain stem
purpose of the midbrain
receives and integrates sensory info
what makes up the hindbrain
cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata
purpose of the cerebellum
coordinates muscle movements
purpose of the pons and medulla oblongata
controls internal body functions, breathing and heart rate
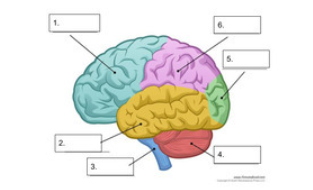
what is number 1
frontal lobe
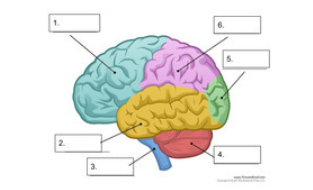
what is number 2
temporal lobe
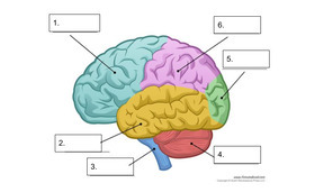
what is number 3
spinal cord
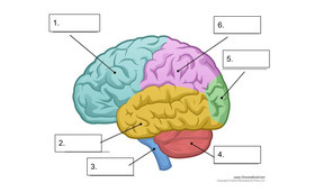
what is number 4
cerebellum
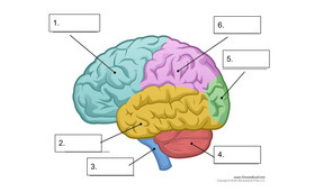
what is number 5
occipital lobe
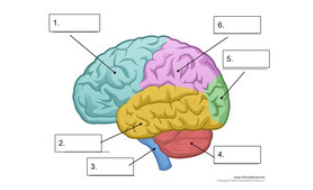
what is number 6
parietal lobe
what is the left hemisphere of the brain good at
language, math, logic, processing of serial sequences- basically school
what is the right hemisphere best at
pattern recognition, nonverbal thinking, and emotional processing- basically creativity and art
lateralization
linked to handedness, the differences in the hemisphere function
how do the left and right hemisphere work together
through the fibers of the corpus callosum or the axons that connect the two hemisphere
frontal lobe function
have substantial effect on executive functions
what would happen if your frontal lobe was damaged
it could impair decision making and emotional response, but your intellect and memory would be fine