research final study guide
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
quantitative approaches
- experimental
- outcomes
- descrptive
experimental study design
- rigorous group comparison studies
- labs
outcomes study design
effectiveness of OT intervention techniques
descriptive study design
- non-experimental
- correlational
- normative
qualitative study design
- ethnography
- grounded theory
- critical theory
- phenomenology
ethnography
- what is the culure of this group of people
- values, roles, beliefs, and practices
- attemps to gain insider's view, focused on informants
grounded theory
- what theories emerge from systematic, comparitive analysis grounded in fieldwork observations
critical theory
- social theory thaat aims to critique and change society as a whole
- positive social and political transformation, reducing social injustices
phenomenology
- how do people make sense of their lived experiences
- only fully knowable by those who share the experience
overall data types
discrete
- values that cannot be broken down into smaller parts
- ex. number of subjects
continuous
- values that can be measured with great precision
- ex. age, weight, height
parametric data
quantitative data
interval
- difference between any two values is meaningful and consistent but no true zero point
- ex. temperature, blood pressure
ratio
- has all properties of interval data but has a meaningful true zero point
- ex. range of motion
nonparametric data
qualitative data
nominal
- value are categories or labels without order or ranking
- gender, eye color, blood type
ordinal
- values are categroies or labels with order and ranking
- likert scale, course grade
common parametric tests (and correlating nonparametric tests)
- chi square test
- t-test
- paired t-test
- ANOVA
- pearson correlation
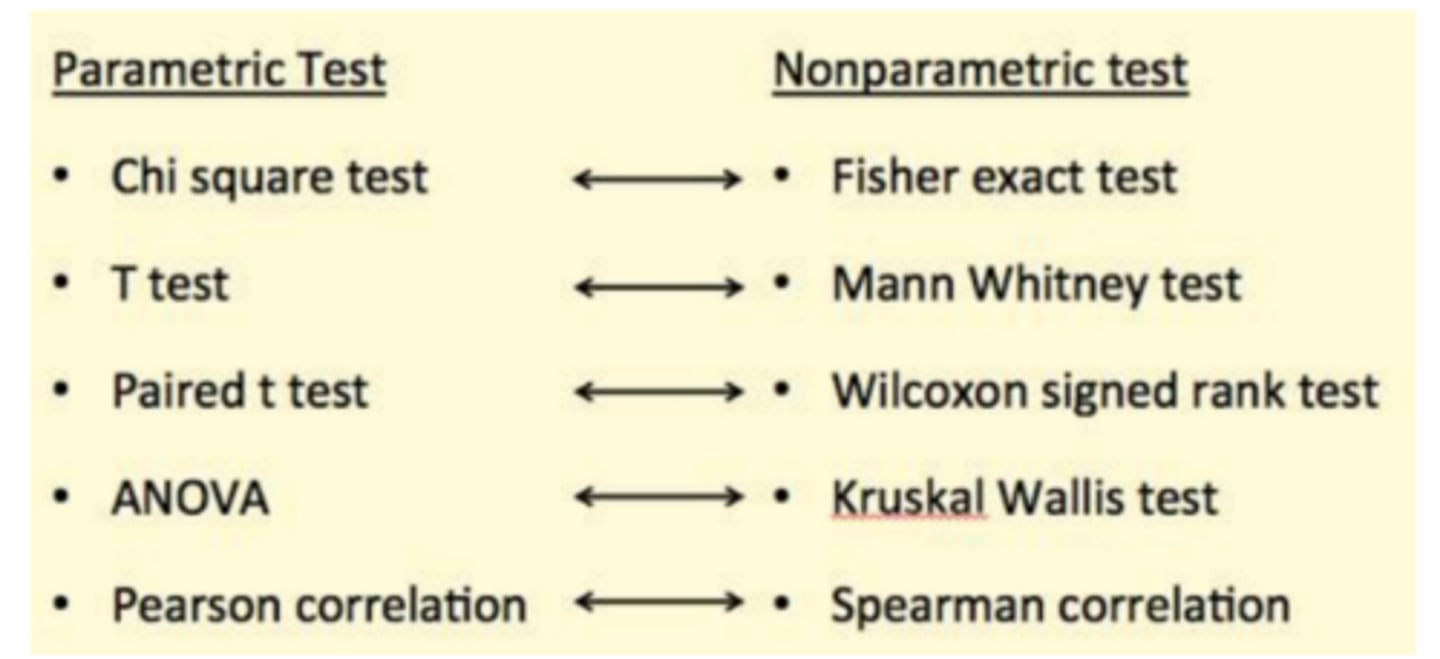
chi square test
to compare categorical variables

t-test
compare the mean of two given samples
paired t-test
test the difference between two variables for the same subject
- ex. before and after measurement
ANOVA
to compare 3 or more samples with a single test, or the manipulation of two or more independent variables
one-way ANOVA
one independent with one dependent
two-way ANOVA
two independent with one dependent
MANOVA
ANOVA with two or more multiple, dependent variables
one-way MANOVA
one independent with 2+ dependent
two-way MANOVA
two independent with 2+ dependent
ANCOVA
used to understand differences between groups but accounts for other variable that might influence the results (covariance)
pearson correlation
measure that shows the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables
- positive correlation
- negative correlation
- no correlation
rigor
reliability and validity
reliability
consistency
test-restest
how well a test produces similar scores over time when given to the same individual
inter-rater
extent to which different examiners obtain the same results for the same patient
internal
extent to which the score on the items of a scale correlate with each other
validity
accuracy
internal validity
how well the research study was conducted, whether the results can be attributed to the variables being tested
external validity
how well the results of a study can be generalized to other settings, people, or times beyond the study itself
categories of trustworthiness
- credibility
- dependability
- transferability
- confirmability
ways to increase trustworthiness
- management of bias
- interviewer training
- traingulation
- prolonged engagement in the field
- project based methods
- member checks
- reflexivity
- audit trails
mean
average
mode
most frequently occuring value in the set of a score
median
middle score for a set of data that has been arranged in order of magnitude
standard deviation
measure of variance (spread of score) within a set of data
- ex. mean = 30, stdev = 3. 33 would be within 1 stdev
inferential statistics
drawing conclusions about a population based on the data from a sample
- generalization of the data
- hypothesis testing
- makes predictions about populations using sample data that represents study population
descriptive statistics
organizes and summarizes data
- mesaures frequency
- central tendency
- dispersion or variation
- position
measures of central tendency
mean, median, mode
measures of dispersion or variation
range, variance, standard deviation
measures of position
percentile and quartile ranks
how does p value influence what we decide to do with the null hypothesis
p-value: the probability of finding an observed value or a data point relative to all other possible results for the same variable
p < 0.001 or 0.05 = significant difference, reject null
p > 0.001 or 0.05 = no significant difference, accept null
type I error
false positive
- getting a sig result when there is no effect present
- rejecting a null hypothesis even though it is true
ex. convict someone of a crime when they are actually inncocent
type II error
false negative
- failing to get a sig result when some effect is present
- not rejecting a null hypothesis even though it is false
ex. free a quily individual when they are guilty of a crime
what type of error is false negative
type II
what type of error is rejecting the null hypothesis when it's actually true
type I
what type of error is not rejecting the null hypothesis when it's actually false
type II
what type of error is failing to conclude there was an effect when there actually was one
type II
what is dissemination
- key characteristics
means for investigators to describe the research process so that peer scholars are able to evaluate its rigor and ability to be replicated
- shares knowledge with stakeholders so it can be used for practical ends
peer reviewed dissemination
important to research for providing quality control
- typically undertaken by an expert panel / committee
reviewers make on of the following recommendation
- rejection
- invitation to make major revision and submit for rereview
- acceptance pending minor or no revision
- reviewers generally provide detailed feedback, which provides the rationale for the recommendation
non-peer reviewed dissemination
- invited presentations
- continuing education courses
- books
- professional publications and newletters
- nonprint materials containing info about research findings and their implications
where does research work get disseminated to
professionals and scientists
- form of presentations and posters at conferences and journal publications; either peer-reviewed or non-peer-reviewed
stakeholders
- sharing info with research participants, public presentations to consumer and community groups, collaborating organizations
- reports to gov and private agencies, legistlative bodies, and public officials
- public websites
- targeted brochures
- released to popular press and media
in research, what is a stakeholder
anyone outside the scientific and professional community who may be informed or influenced by the research findings either in their personal lives or in the exercise of their responsiblities
- research participants
- recipients of related services
- agencies making health care decisions
- funding sources
- people who are impacted by the new knowledge