unit 4: division and inheritance quiz review
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
True or False: Cell division is a form of sexual reproduction
false
Define cell division
a reproduction of cells to create exact replicas of one another
*know the terms
What are the purposes of cell division
for the growth of an organism
to repair damaged cells
replacing dead or dying cells
About how long does the cell cycle take
about 24 hours
What are the three parts of the eukaryotic cell cycle
interphase
mitosis
cytokinesis
Where does the cell spend most of its time
interphase
What happens during interphase
cell growth
chromosomes + DNA replication
Define haploid
half the number of total chromosomes
What are the 3 phases of interphase
G1, S, G2 (G0 is not a part of the main process but its still there)
Define diploid
the full number of chromosomes
What happens in G1
cell growth
stimulates cell signals (cyclin)
cell organelles are being replicated
What is the purpose of checkpoints within the cell cycle
to make sure that the processes at each phase of the cell cycle have been correctly preformed before moving into the next phase
What is at the G1 checkpoint
checks for DNA damage
checks if the signal (cyclin) is ok (by using the CDK enzyme)
What happens during S phase
DNA is duplicated
What does the ‘S’ stand for in S Phase
synthesis
What form of reproduction is cell division
asexual
What happens during the S phase checkpoint
it is confirmed that the DNA duplicated correctly
What happens during G2
higher amounts of signals (cyclin)
cell growth continues
specific organelles prepare for next phase
What is the purpose of G0
some cells need a ‘pit stop’ and rest here and stay until they are signaled to move on
Why do some cells stay in G0 permanently
if the cell is unable to reproduce/divide
Why does the cell spend most of its time in interphase
interphase is where the actual cells are created and its where the chromosomes are duplicated so the cell needs to make sure it was done correctly.
Define mitosis
the nucleus getting divided
What are the phases of mitosis (PMAT)
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telephase
What happens during prophase
chromosomes are visable
microtubes are forming spindle fibers
What happens during metaphase
chromosomes are at the middle of the cell and spindle fibers hold them there
What is the purpose of the checkpoint during mitosis
to check if the spindle fibers grabbed the chromosome
What is the formation of the cells in telephase
1 cell, 2 nucleus
Define cytokinesis
cytoplasm is divided between the cells, this process ends with a diploid number
What is a diploid number
the total number of chromosomes
Is the DNA identical in each diploid number cell
yes
How does an organism have so many cells
the process of differentiation
What does differentiation begin with
embryonic stem cells
What does pluropotent mean
cells that are able to become any kind of cell
How many chromosomes must a sperm and egg have to form 1 zygote
23 each
What happens, in relation to division, to a zygote
the cell will keep dividing until it is 8 cells in blastula
What occurs in the stage blastula
differentiation actually occurs by sending an epigenetics signal to the DNA to ‘turn’ on and off to create spesific cells. after that, the potency is lowered and the cell becomes multipontent. at the blastula, folds occur
Define multipotent
the cell is given a spesific job
What are the folds in the blastula called
ecotderm
mesoderm
endoderm
What falls into the ectoderm category
cells connected to the outside
ex. skin, eyes, neurons
What falls into the mesoderm category
blood cells, teeth, bones, tissues
What falls into the endoderm category
cells for internal organs
Define telomeres
caps for our chromosomes to protect the chromosome during DNA duplication (happens during interphase at S phase)
Do telomeres contain genes
no
What happens to telomeres as chromosmes continue to duplicate
the telomreres become shorter and shorter until it reaches cell differentiation
Which cells are immortal (2 answers)
embryotic stem cells (able to become any cell)
cancer cells (bc of an enzyme that goes to the chromosome to repair and replace telomeres)
What does the protein telomerase do
allows the cell to continuously replicate
What causes cancer
DNA becomes mutated, this then allows for out of control cell growth
Name the causes of cancerous cells
radiation
uv radiation
smoking
genetics
Which of the 4 main causes of cancer are environmental (radiation, uv radiation, smoking, genetics)
genetics
What does the term carcinogens mean
cancer causing
Why does uncontrolled/quick cell growth occur
the cell skips checkpoints
In relation to the growth limitations of cells, how do normal cells behave
divide into the space they are given and utilize the nutrients available
In relation to the growth limitations of cells, how do cancer cells behave
divide continuously and clump up on top of each other. takes all the nutrients from the environment, effectively draining healthy cells from nutrients which results in cell death
What is the difference between a proto-oncogene and a oncogene
proto-oncogenes stimulate the cell cycle and oncogenes keep the cell cycle going uncontrollably
What does a proto-oncogene do
stimulates the cell cycle
controls the cell cycle
What happens if a proto-oncogene is mutated
if a mutation occurs, the cell cycle goes at a quick rate, thus creating cells replicating out of control and checkpoints becoming ignored. out of control cells replicating are called oncogenes
What is angiogenesis
cancer cells send a signal to the environment to create/form new blood vessels
What do blood vessels do for a cancer cell
provide nutrients
provides a pathway for the cancer cells to move to a new location
What is it called when a cancer cell moves to a different location
metastasis
If a parent cell has 18 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will its daughter cells have and why
the daughter cells would both have 18 chromosomes because in cell division, the parent cell creates 2 exact copies of its self
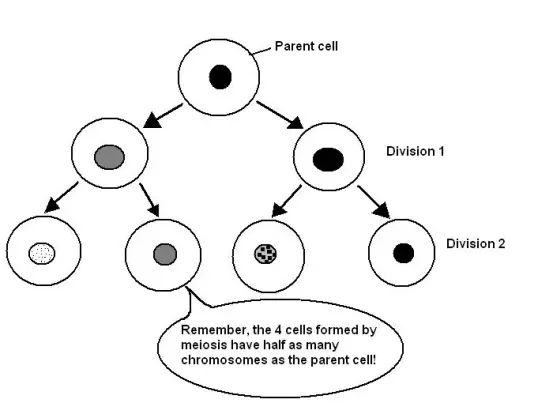
Is meiosis cyclic (occurring in a cycle)
no
Where does meiosis occur
in gametes (sperm, egg)
What are the purposes of meiosis (2)
to create a haploid cell
to increase genetic diversity
Why would one of the goals of meiosis be to create a haploid cell
bc when 2 haploid cells come together, they create a zygote
How many chromosomes are in an egg
23
How many chromosomes are in a sperm
23
If a sperm has 23 chromosomes, and an egg also has 23 chromosomes, how many chromosomes does 1 cell have
46
What are the 2 subtopics of interphase
meiosis 1
meiosis 2
What happens during interphase
DNA replicates in S phase
cell growth
checkpoints needed
organelles replicated
Define metastasis
cancer spreads to a new location
What is a centromere
‘band’ that holds the chromosomes together
What is one side of a chromosome called
a chromatid
Define homologous chromosomes
chromosomes are paired up with similar genes (alleles). these genes are not identical bc they carry different forms of a certain gene
What happens during prophase 1
homologous chromosomes are paired up with one another, they can become tangled with each other and they swap DNA
What happens during metaphase 1
homologous chromosomes move to the middle of the cell with spindle attachment. the homologous chromosomes arrange themselves at that location.
What is it called when when homologous chromosomes randomly arrange themselves at a certain location
independent assortment
What happens during anaphase 1
homologous chromosomes are moved to the ends of the cell
What happens during telophase 1/cytokinesis 1
2 haploid cells are present
What happens in meiosis 2
a process like mitosis occurs, working with 2 cells and ending with 4 haploid cells that are genetically different
Why is there not interphase between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
the DNA would duplicate
Define spermatogenesis
the process of creating sperm
How many cells are viable in spermatogenesis
4 out of 4 cells
Define oogenesis
the process of creating eggs
How many cells are viable in oogenesis
1 out of 4 cells
When are eggs produced in a woman
when in utero
what kind of cells undergo cellular division
somatic cells
what happens when mitosis goes wrong
the overproduction of cells occurs
what happens when meiosis goes wrong
imbalances of the amount of chromosomes in each daughter cell