Clinical Chemistry: Non-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds
1/272
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
273 Terms
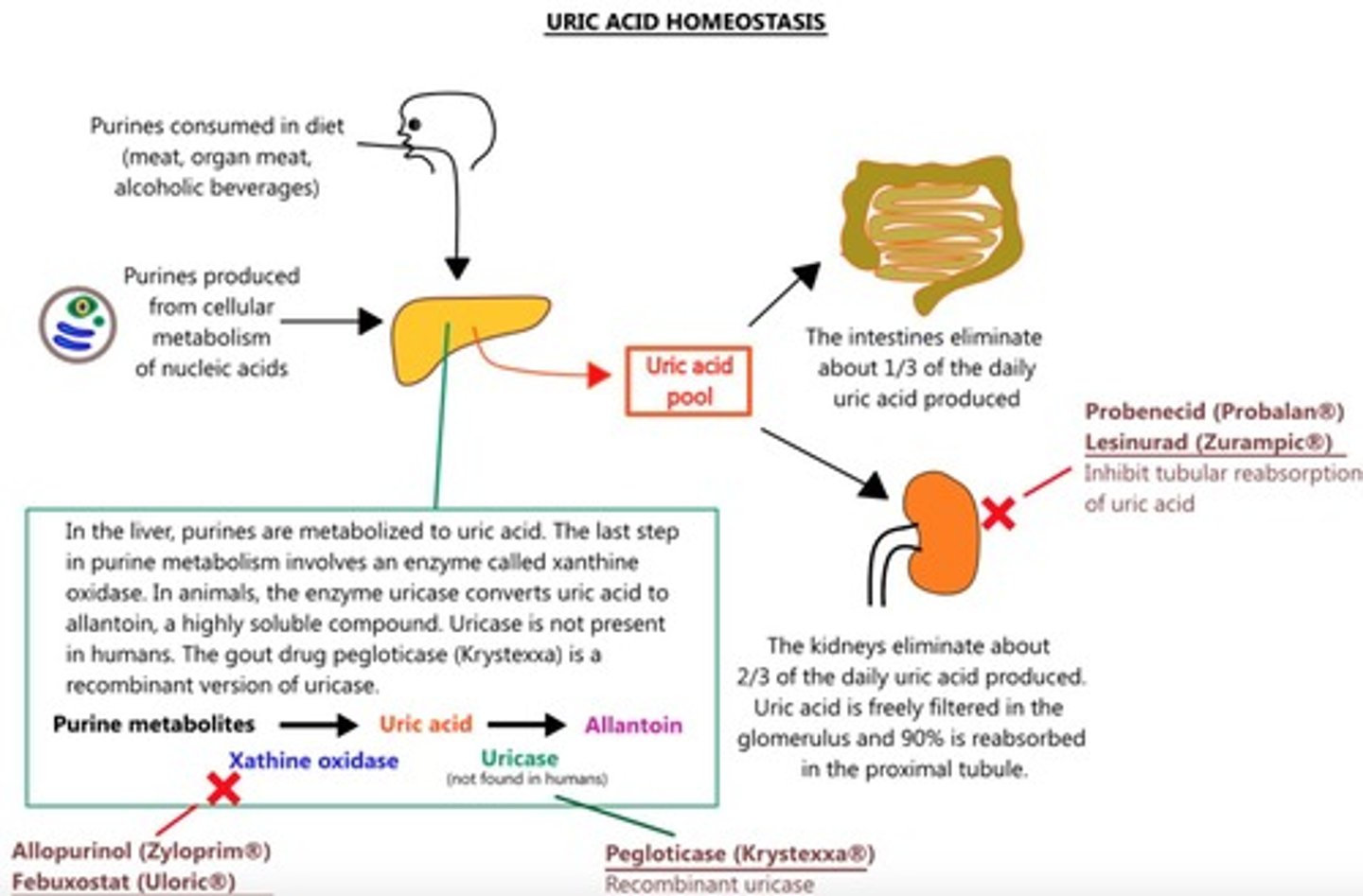
Uric Acid
Product of catabolism of the purine nucleic acids (i.e. Adenine and Guanine)
Clinical Utility of Uric Acid
Confirm diagnosis and monitoring treatment of gout
Clinical Utility of Uric Acid
Prevent uric acid nephropathy during chemotherapeutic treatment
Clinical Utility of Uric Acid
Assess inherited disorders of purine metabolism
Clinical Utility of Uric Acid
Detect kidney dysfunction
Clinical Utility of Uric Acid
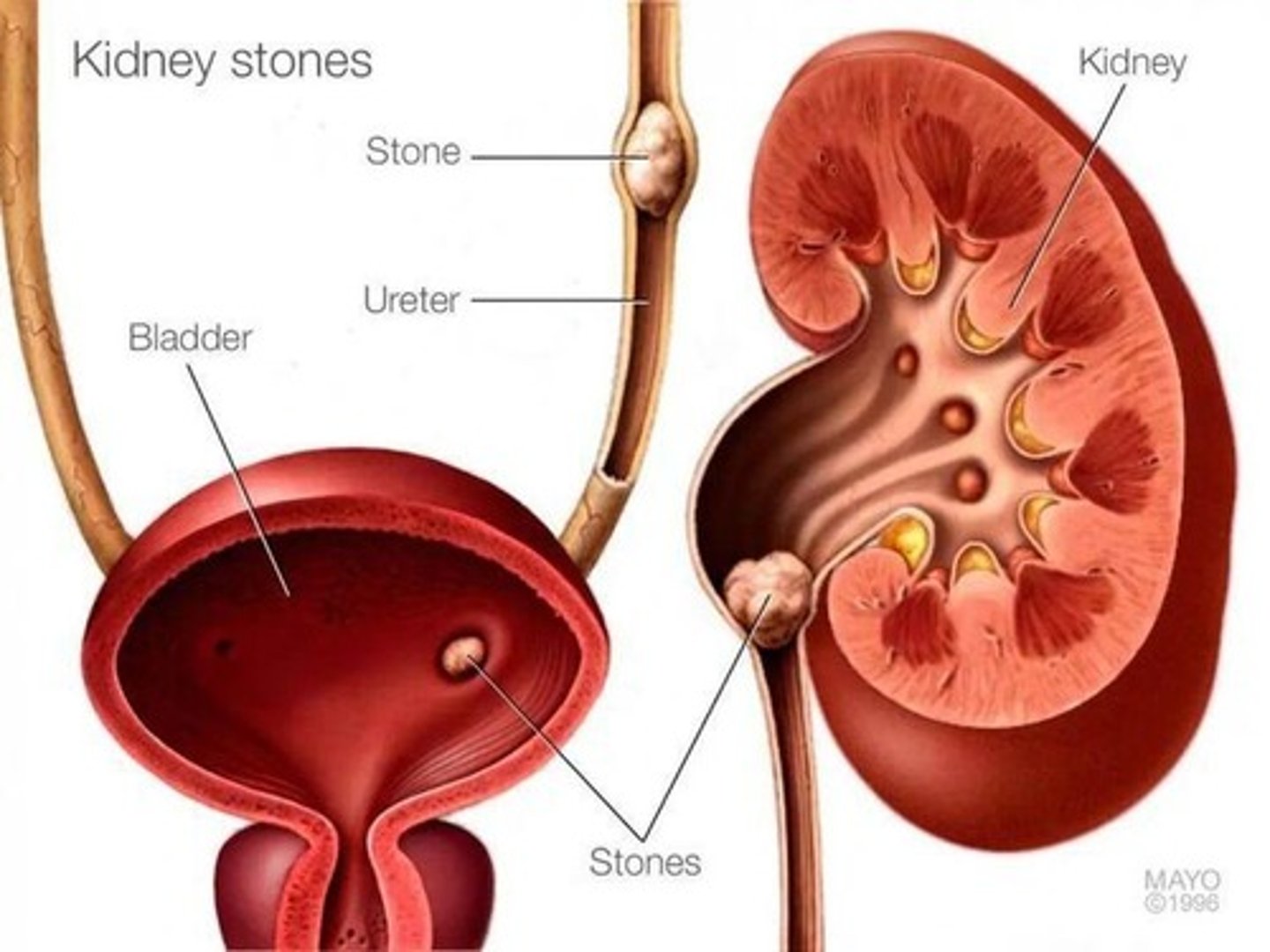
Assist in the diagnosis of renal calculi/stones
Phosphotungstic Acid Method
Performed in an alkaline solution; Principle: oxidation of uric acid to allantoin via uricase
Enzymatic Methods
Similar first step: catalyzed by uricase; More commonly used
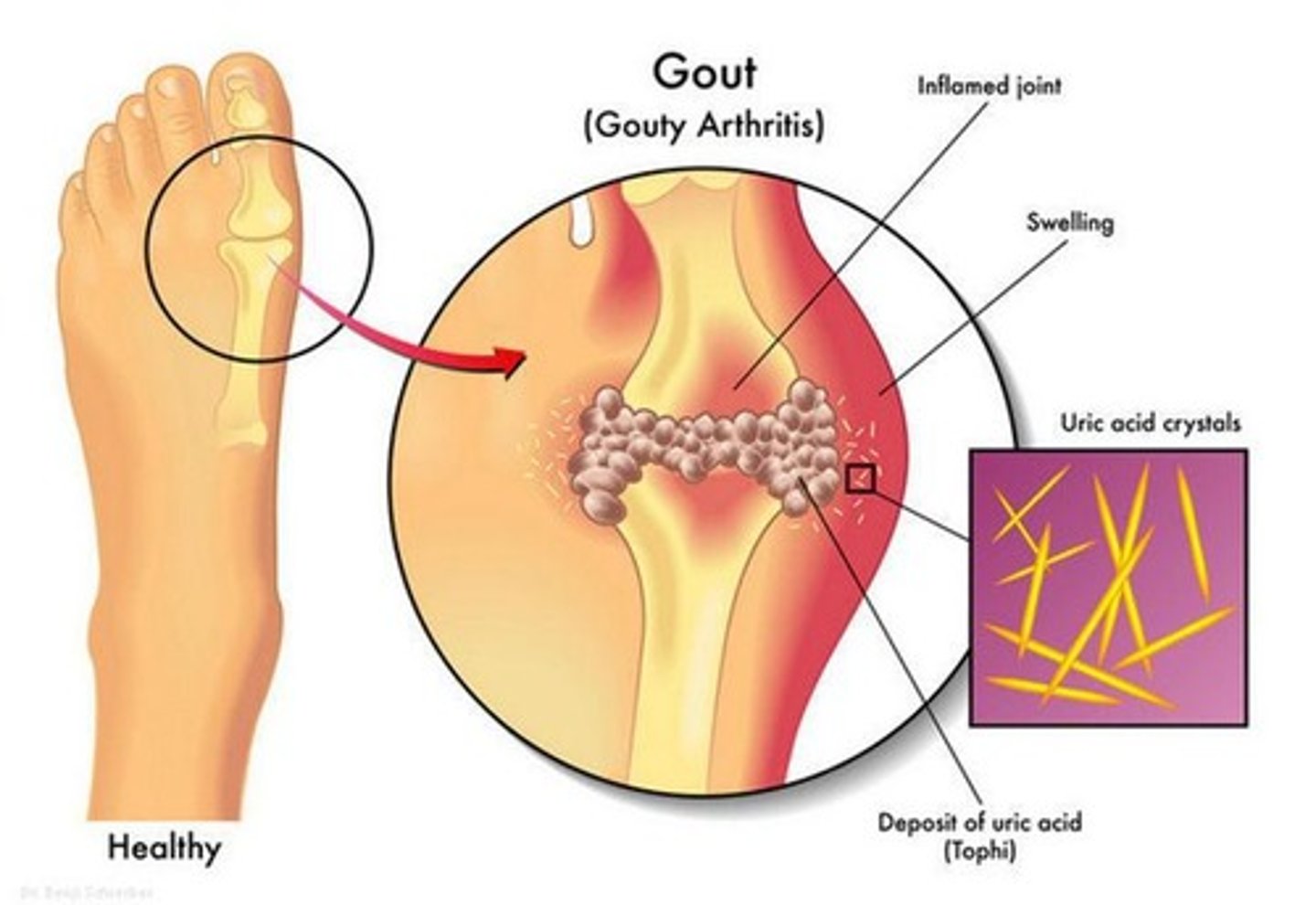
Monosodium Urate
Nearly all of uric acid in plasma is present in this form; Relatively insoluble in plasma (pH of ~7)
Uric Acid Saturation
When uric acid concentration > 6.8 mg/dL: Plasma becomes saturated; Urate crystals may form and precipitate in the tissues
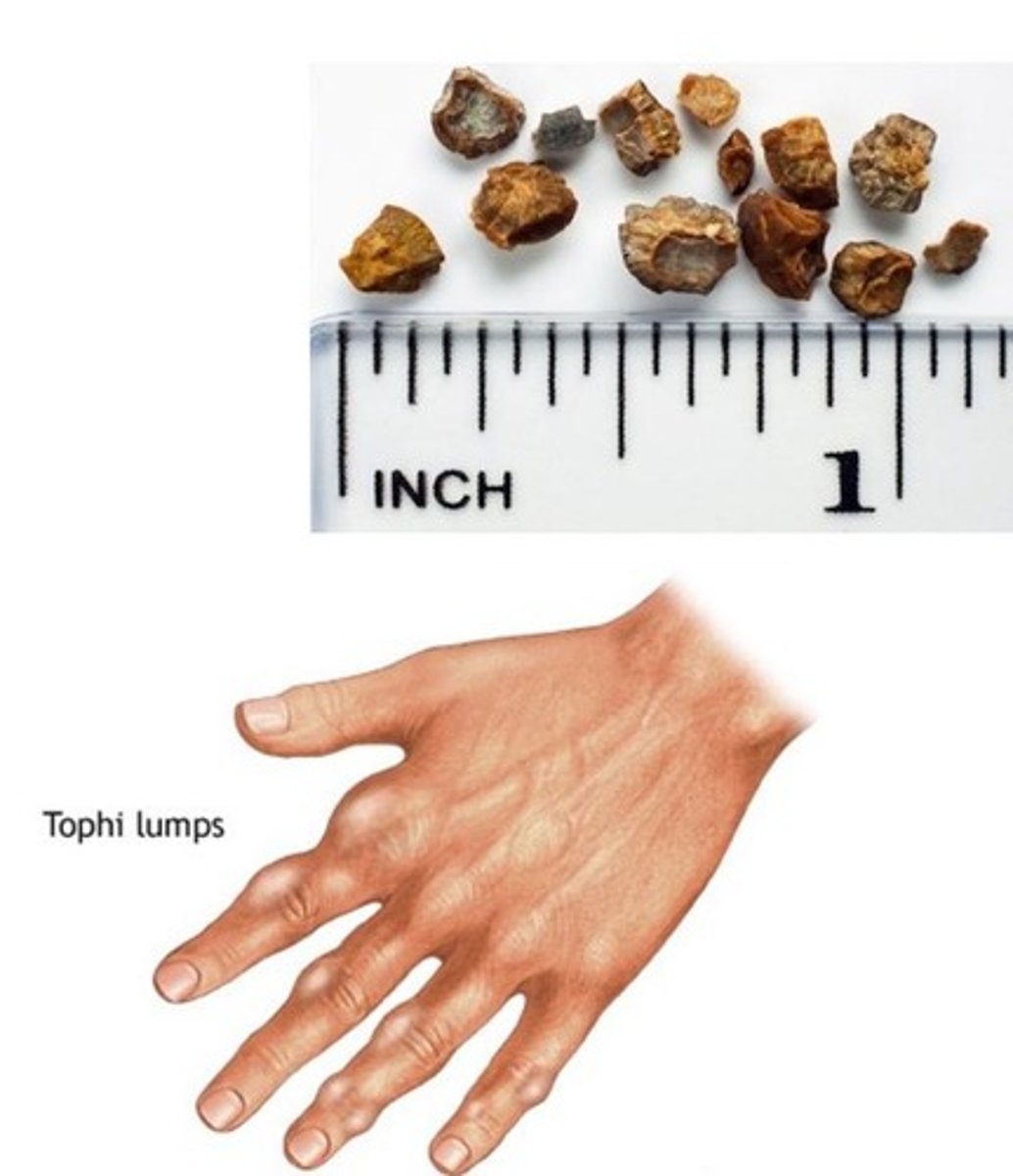
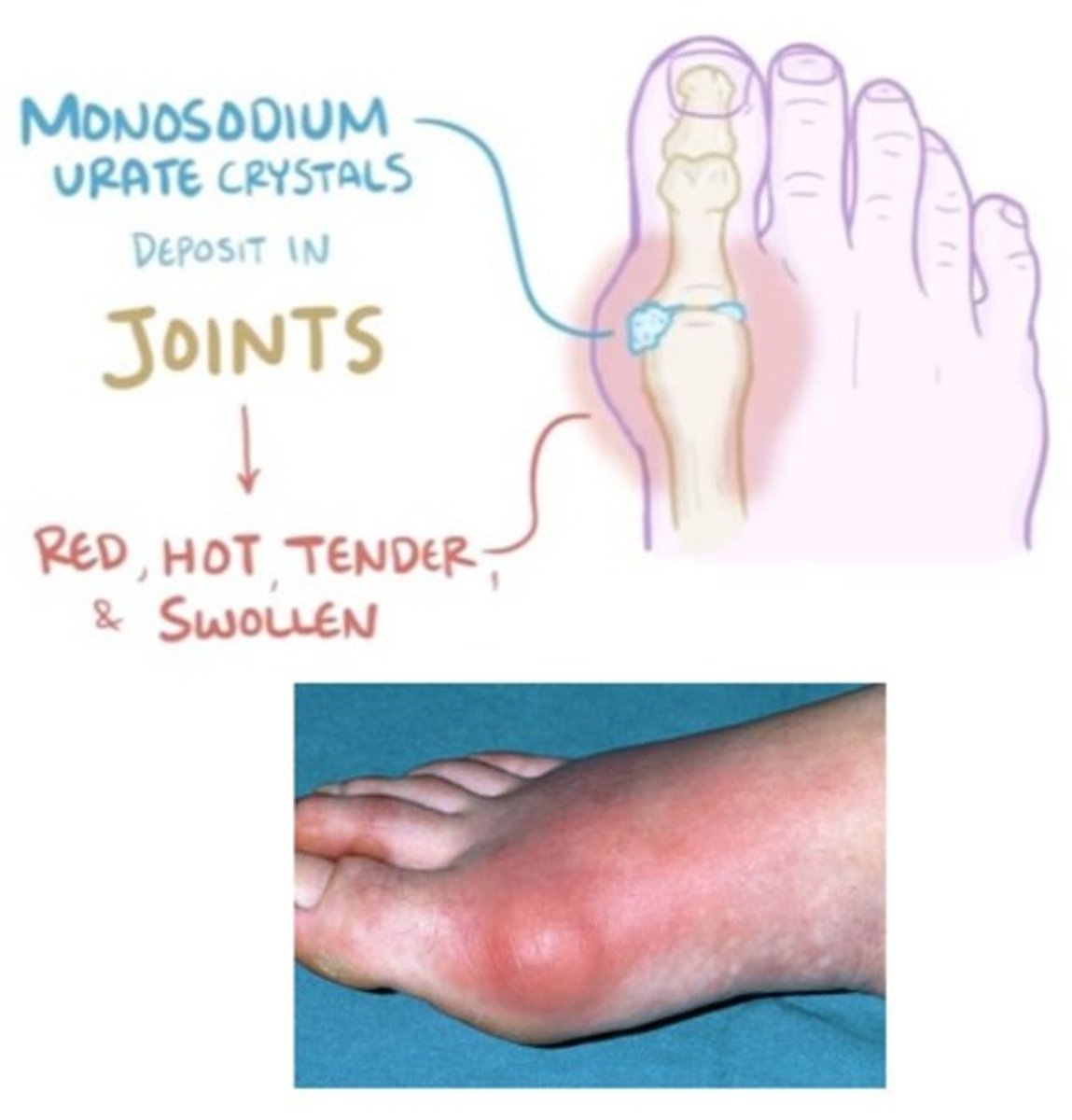
Tophi
Deposit of uric acid; Joints are swelling/inflamed due to uric acid crystals between the bones
Gout
May cause gout (gouty arthritis)
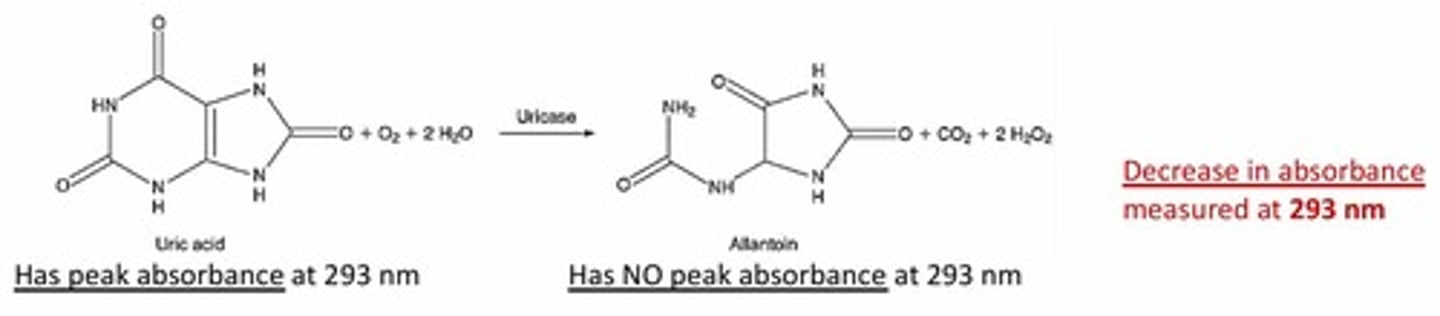
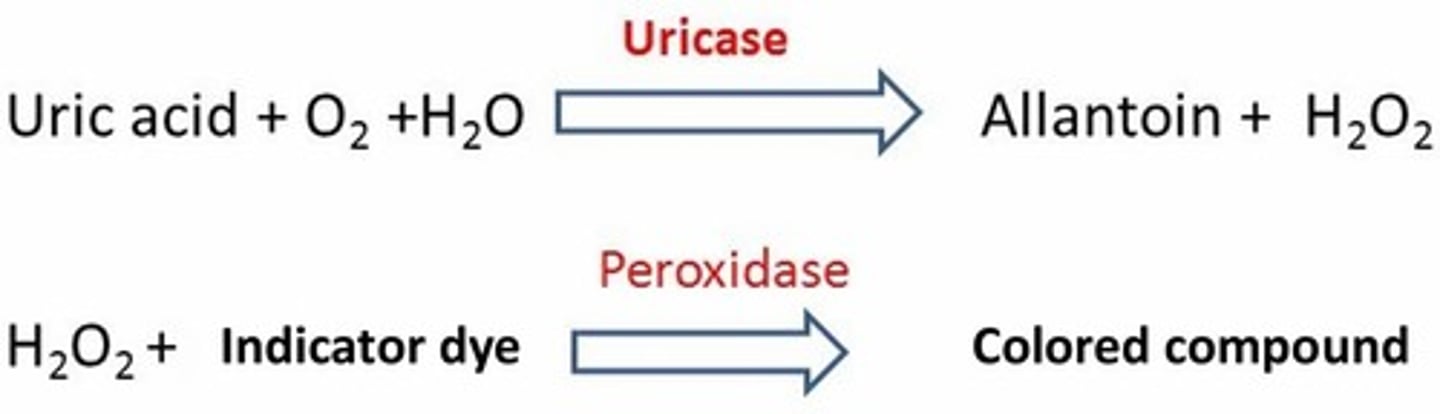
Spectrophotometric: Uricase Method
Result: Decrease in absorbance measured at 293 nm
Peroxidase Coupled Enzymatic Method
Color produced is proportional to the quantity of uric acid
Hypouricemia
Secondary to liver disease; Inability to produce uric acid in the liver
Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (IDMS)
Detection of characteristic fragments following ionization; Quantification using isotopically labeled compound
Uric Acid Crystals
Presence of uric acid crystals in the tissue
Bilirubin and Ascorbic Acid
Can destroy peroxidase in commercial preparations
Potassium Ferricyanide
Added to minimize interference in peroxidase coupled enzymatic method
Uric Acid Concentration in Plasma
10% in plasma concentration
Uric Acid Concentration in Urine
1.7% in urine concentration
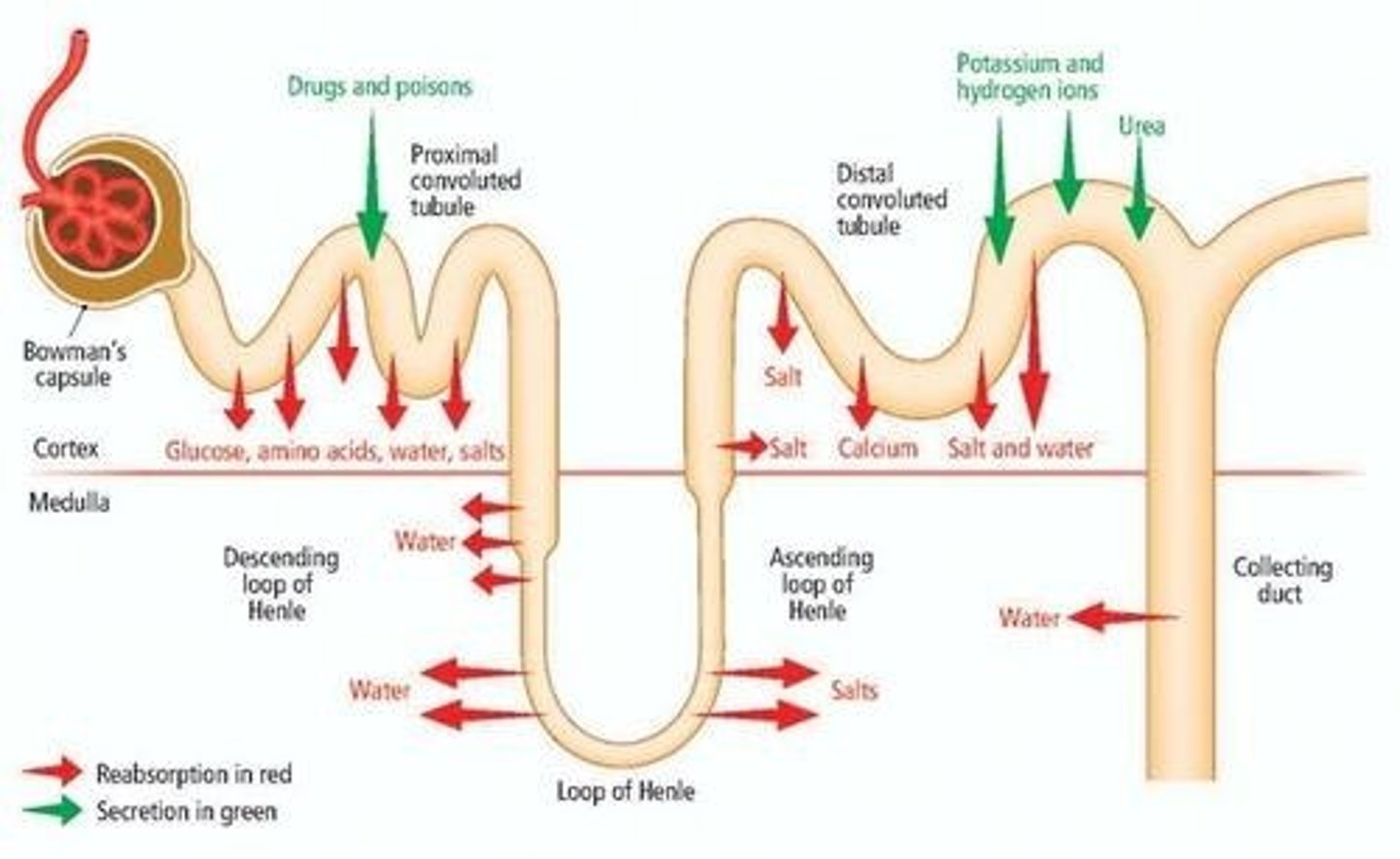
Uric Acid Reabsorption
Most uric acid is reabsorbed in the proximal tubules and reused
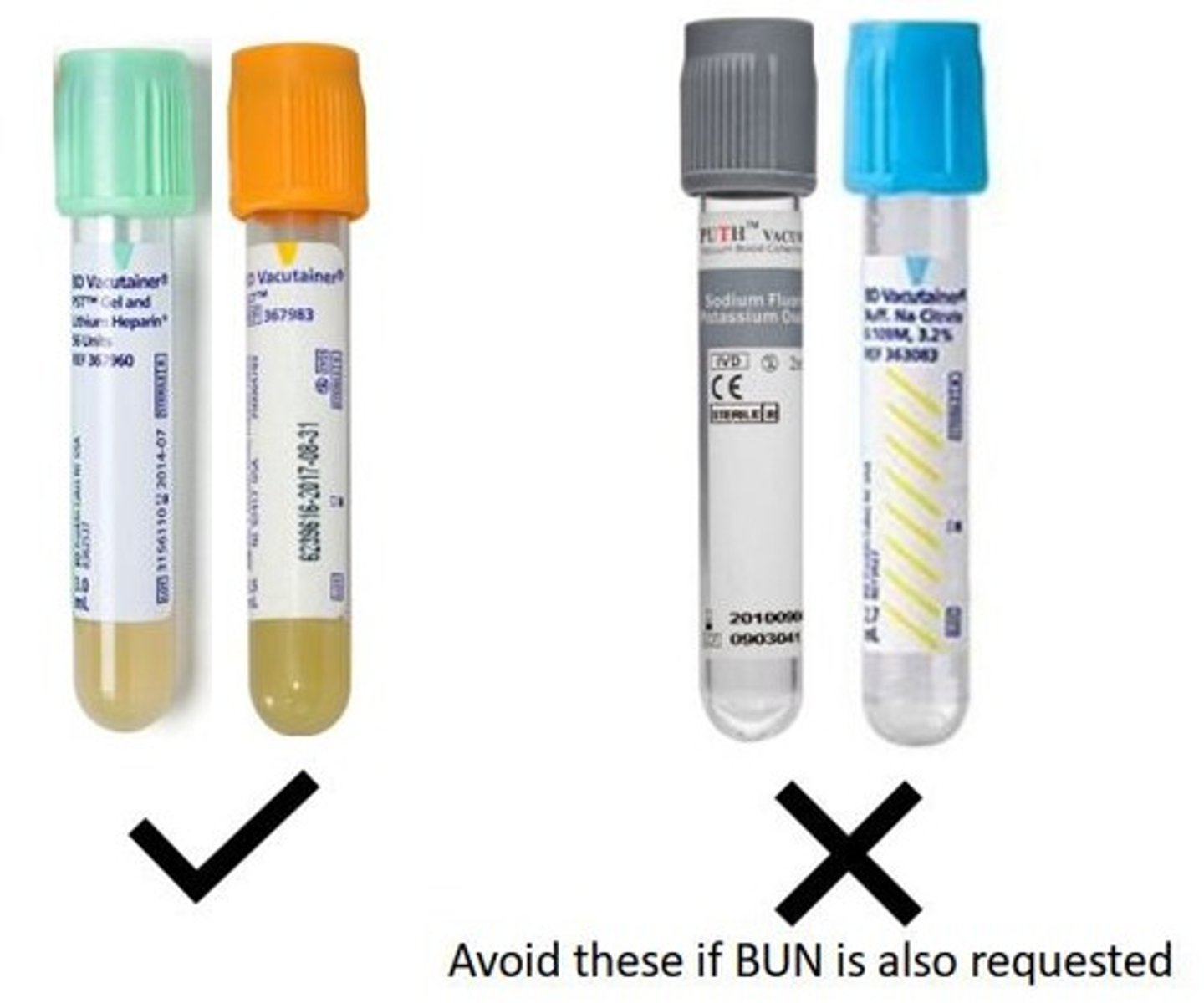
Specimen Requirements
Serum, heparinized plasma or urine; fasting is not required; avoid gross lipemia; uric acid is stable in plasma or serum after RBCs have been removed; serum may be refrigerated for 3 to 5 days; EDTA (lavender) and fluoride (gray) additives should not be used for uricase methods; collected urine must be alkaline (pH 8).
Reference Values
Conversion factor (conventional to SI) → 0.0595 [mmol/L].
Plasma or Serum Male Adult Reference Range
3.5 - 7.2 mg/dL or 0.21 - 0.43 mmol/L.
Plasma or Serum Female Adult Reference Range
2.6 - 6.0 mg/dL or 0.16 - 0.36 mmol/L.
Plasma or Serum Child Reference Range
2.0 - 5.5 mg/dL or 0.12 - 0.33 mmol/L.
Urine, 24 h Adult Reference Range
250 - 750 mg/d or 1.5 - 4.4 mmol/d.
Hyperuricemia
Overproduction of uric acid in 25-30% of patients; exacerbated by purine-rich diet, drugs and alcohol.
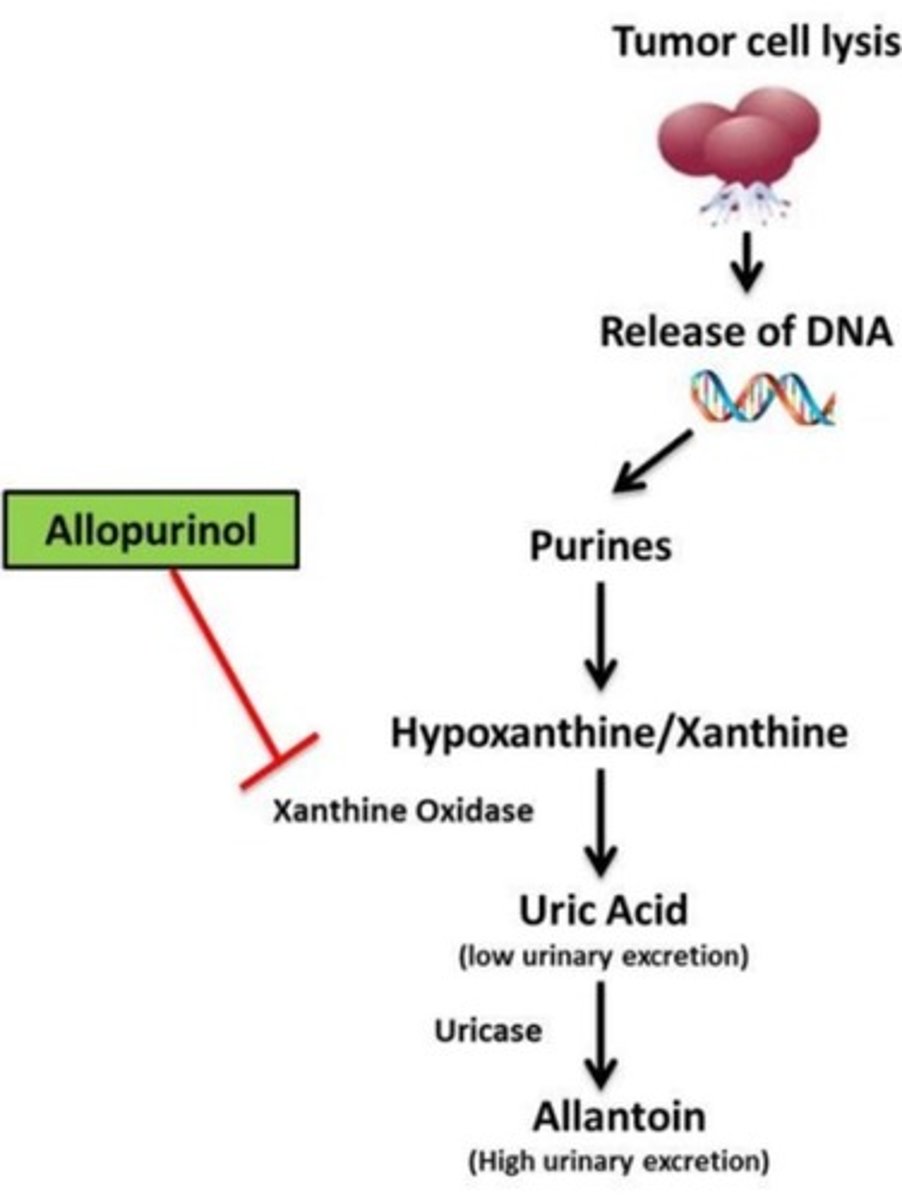
Plasma Uric Acid Concentration
> 6.0 mg/dL.
Tophi
Occurs in severe cases; uric acid crystal deposits form in tissue, causing deformities.
Gout Symptoms
Pain and inflammation of joints; monosodium urate crystals will be deposited between joints causing it to become red, hot, tender and swollen.
Causes of Hyperuricemia
High uric acid in the blood; gout; chemotherapeutic treatment; increased catabolism of nucleic acids; renal disease.
Chemotherapeutic Treatment
Administered to patients undergoing chemotherapy for proliferative diseases such as leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and polycythemia.
Allopurinol
Drug that inhibits xanthine oxidase; used for treatment to reduce uric acid production.
Uric Acid Nephrolithiasis
Formation of renal calculi; acidic urine forms insoluble uric acid precipitates.
Treatment for Renal Stones
Stones may be dissolved by alkalinization of urine, increased fluid intake, or intake of xanthine oxidase inhibitors.
Purine Metabolism Disorder
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome; causes increased metabolism of cell nuclei resulting in overproduction of uric acid.
Increased Uric Acid Causes
Hemolytic or megaloblastic anemia; increased tissue catabolism due to starvation; decreased uric acid excretion.
Purine-Rich Diet
Includes liver, kidney, sweetbreads, and shellfish; patients with increased uric acid must avoid purine-rich food.
Tophi Lumps
Physical manifestation of deposits; bulging lumps will form at the joints.
Postmenopausal Women
Have increased urate concentration.
Age Group Diagnosis
Gout is usually diagnosed between 30-50 years old; found primarily in men.
Anchovies
A type of small fish often used in cooking.
Liver
An organ that processes nutrients and detoxifies substances.
Asparagus
A green vegetable known for its long, slender stalks.
Codfish
A popular fish used in various cuisines.
Sweetbreads
A culinary term for the thymus or pancreas of an animal.
Fava Beans
A type of broad bean used in cooking.
Haddock
A type of fish commonly used in fish and chips.
Brains
The organ responsible for processing information in the body.
Garbanzo Beans
Also known as chickpeas, used in various dishes.
Herring
A small, oily fish often eaten pickled.
Bacon
Cured meat from the belly of a pig.
Edamame (Soy)
Young soybeans often served as a snack or appetizer.
Mackerel
A type of fish known for its rich flavor.
Turkey
A large bird often eaten during Thanksgiving.
Mushroom
A type of fungus used in cooking.
Mussels
A type of shellfish commonly used in seafood dishes.
Veal
Meat from young cattle.
Peas
Small, round green seeds often used in cooking.
Sardines
Small, oily fish often canned.
Venison
Meat from deer.
Lentils
Small legumes often used in soups and salads.
Scallops
A type of shellfish known for its sweet flavor.
Beef
Meat from cattle.
Spinach
A leafy green vegetable rich in iron.
Trout
A type of freshwater fish.
Chicken
Meat from domesticated birds.
Cauliflower
A white vegetable in the cabbage family.
Crab
A type of shellfish with a hard shell.
Duck
A waterfowl often raised for its meat.
Lobster
A large marine crustacean known for its claws.
Ham
Cured meat from the hind leg of a pig.
Rare, X-linked genetic disorder
Affects males more and is associated with a complete deficiency of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT).
HGPRT deficiency
When this enzyme is lacking, purine bases are not reutilized, causing high concentration of uric acid in blood and urine.
Compulsive self-mutilation
Behavior observed in patients with HGPRT deficiency, particularly affecting the head and hands.
Mental retardation
A condition often associated with HGPRT deficiency.
Involuntary muscular movements
A symptom presented in patients with HGPRT deficiency.
Gout
A form of arthritis characterized by severe pain and swelling, often due to high uric acid levels.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
The rate at which ultrafiltrate is formed by the glomerulus, approximately 100-120 mL per minute.
Plasma creatinine concentration
A function of relative muscle mass, rate of creatine turnover, and renal function.
Creatinine
A waste product in the blood that is excreted in urine, used to assess kidney function.
Creatine
A compound that is 5% in plasma concentration and is involved in energy production.
Creatine
Synthesized primarily in the liver from arginine, glycine, and methionine, then transported to other tissues, such as muscle, where it is converted to creatine phosphate.
Creatine Phosphate
Loses phosphoric acid and creatine loses water to form the cyclic compound, creatinine.
GFR
Glomerular filtration rate, calculated using the formula GFR = V/t.
Volume of Filtered Plasma (V)
The volume of plasma that is filtered through the glomeruli per unit time.
Time (t)
The duration over which the volume of filtered plasma is measured.
Creatinine
Formed from creatine and creatine phosphate in muscle when creatine loses water and creatine phosphate loses phosphoric acid; excreted into plasma at a constant rate related to muscle mass.
Creatinine Clearance (CrCl)
A measure of the amount of creatinine eliminated from the blood by the kidneys, providing a reasonable approximation of the GFR, involving a 24-hour urine collection to measure creatinine excretion.
Creatinine Clearance Formula
CrCl = (UCr VU) / (PCr t), where UCr = urine creatinine concentration (mg/dL), PCr = plasma creatinine concentration (mg/dL), VU = urine volume (mL), and t = time (minutes).
Enzymatic Method
A method involving coupled enzymatic reactions to measure the concentration of substances.
Jaffe Reaction
A chemical method for measuring creatinine that lacks sensitivity.
Creatininase Method
A series of reactions catalyzed by enzymes including creatininase, creatine kinase, pyruvate kinase, and lactate dehydrogenase, producing NAD+ measured as a decrease in absorbance.
Creatininase: Hydrogen Peroxidase Method
Uses enzymes like creatininase, creatinase, sarcosine oxidase, and peroxidase, adapted for dry slide analyzers, and is more specific than the Jaffe method.
Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (IDMS)
A highly specific detection method using isotopically labeled compounds and accepted as a reference method.
Specimen Requirements
Includes serum, plasma, or urine; fasting not required, and specific sample handling instructions for different methods.
Urine Volume (VU)
The total volume of urine collected for measurement.
Urine Concentration of Substance (US)
The concentration of a specific substance in the urine.