4.1, 4.2, 4.3 – Monopolies and Regulation & Price Discrimination
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is a characteristic of monopolies regarding price?
Monopolies are price makers.
What is the source of monopoly power?
Barriers to entry.
What is market share?
The percentage of total sales attributed to a single firm.
What happens to marginal revenue for a monopoly when it lowers its price to sell more?
Marginal revenue decreases.
Why is marginal revenue less than demand in a non-price discriminating monopoly?
Because to sell more, the firm must lower the price for all units sold.
What does a downward sloping demand curve indicate for imperfectly competitive firms?
Firms must lower prices to sell additional units of output.
What is the profit-maximizing rule for monopolies?
A monopoly produces where marginal revenue equals marginal cost (MR=MC).
What is allocative efficiency/socially-optimal/revenue-maximizing price?
When the price equals marginal cost (P=MC). Monopolies are not allocatively efficient.
What is price discrimination?
The practice of selling the same product at different prices to different consumers.
What conditions must be met for price discrimination to occur?
Must have monopoly power, be able to segregate the market, and consumers must not be able to resell the product.
What is a natural monopoly?
A market structure where a single firm can supply the entire market demand at a lower cost than multiple firms, often due to high fixed costs and low marginal costs. It makes economic sense to only have one provider.
How can the government regulate monopolies?
By implementing price controls (price ceilings) and ensuring efficiency.
What happens to consumer prices when a monopoly produces at the allocatively efficient level?
Consumer prices may decrease.
What is deadweight loss in monopoly terms?
The loss in total welfare that occurs when a monopoly reduces output to raise prices.
What is a fair-return price?
Price equals average total cost (P=ATC) ensuring normal profit.
What happens to total surplus when a monopoly exists?
Total surplus decreases due to deadweight loss.
What is the primary reason monopolies are considered inefficient?
They charge a higher price and produce less than in competitive markets.
If the marginal cost curve shifts up for a monopoly, the monopolist’s price will ____?
increase
Why could a monopoly be considered beneficial in some cases?
Due to economies of scale, it can keep prices low in industries like utilities.
How do monopolies affect consumer surplus compared to perfect competition?
Monopolies reduce consumer surplus compared to perfect competition.
What is the difference between elastic and inelastic demand for monopolies’ production?
Monopolies only produce in the elastic range of the demand curve.
What’s the relationship between price and marginal cost in a ANY imperfectly competitive market?
Price is greater than marginal cost.
Describe the effect of price discrimination on consumer surplus.
It typically eliminates consumer surplus as consumers are charged their maximum willingness to pay.
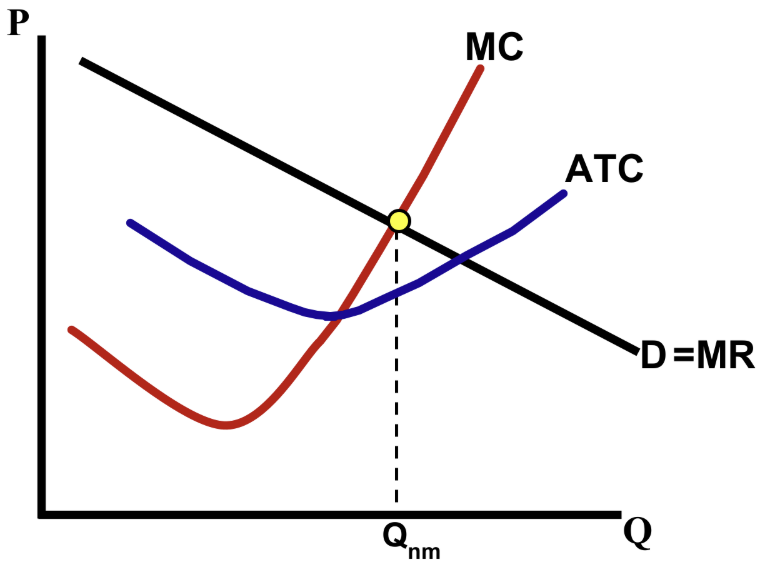
What is the relationship between marginal revenue and price in price-discriminating monopolies?
For a perfectly price-discriminating monopoly, marginal revenue equals price.
How do economies of scale relate to monopolies?
They enable a single firm to produce at a lower cost, justifying the monopoly's existence.
What occurs if a monopolist produces too much output?
Economic inefficiency could result, with wasted resources.
What leads to deadweight loss in monopolistic markets?
The reduction in output caused by a monopolistic firm's pricing strategy.
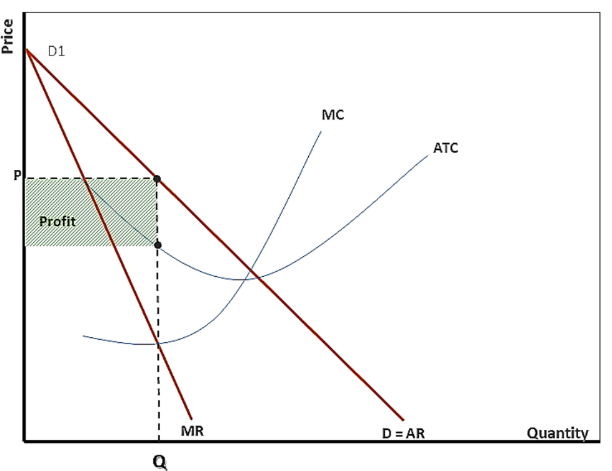
How do you calculate profit in a monopolistic market?
Profit in a monopolistic market is calculated by subtracting total costs from total revenue, where total revenue is determined by the price charged for the product multiplied by the quantity sold.
(Price charged * quantity sold) - total costs
(In simple terms: look where MR and MC intersect, and then go up until you hit the demand line. It’s from the demand line to the ATC line, in that rectangle.)
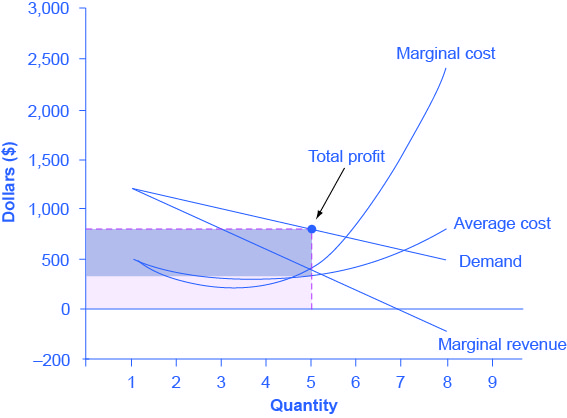
In an imperfectly competitive market, what’s the relationship between MR, AR, and P?
MR < AR = P
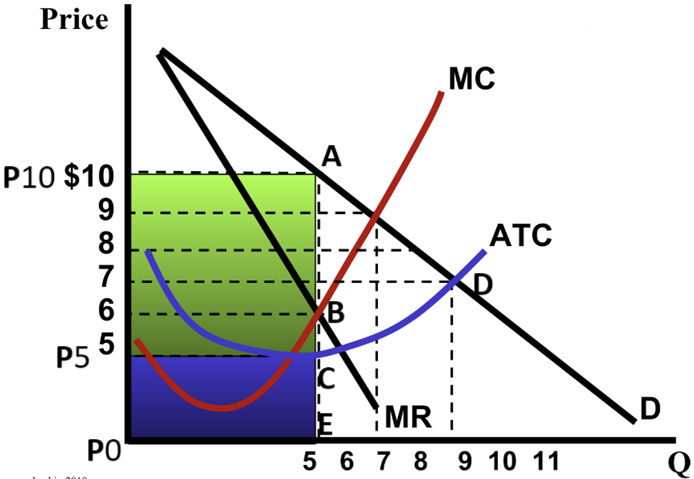
Identify total revenue, total cost, profit/loss, and profit/loss per unit.
Identify both the area labels (e.g. ABP5P10) and the $ amount (e.g. $50).
Total revenue: AEP0P10; $50
Total cost: CEP0P5; $25
Profit/loss: ACP5P10; profit of $25
Profit/loss per unit: $5 per unit
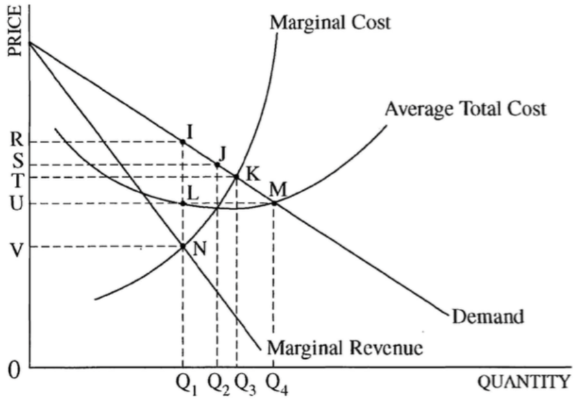
Identify total revenue, total cost, and profit/loss.
Total revenue: RIQ10
Total cost: ULQ10
Economic profit: RULI
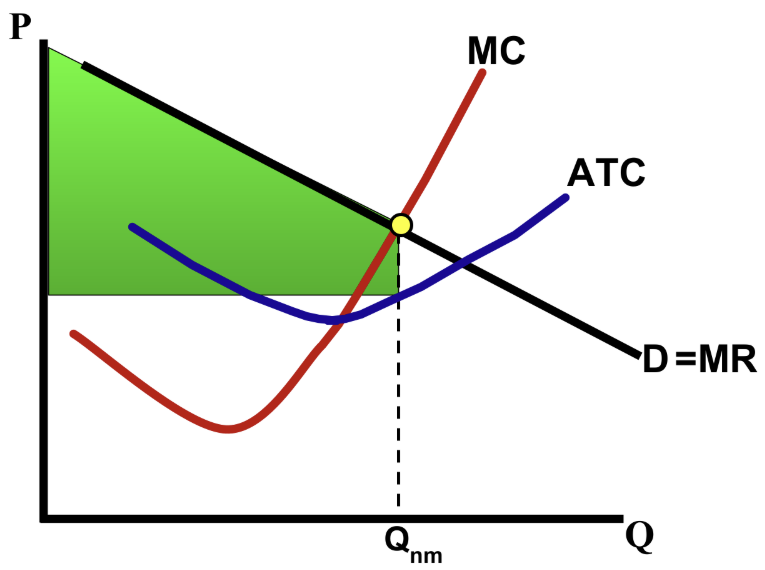
Identify profit in a price-discriminating monopoly.
Look where MC intersects the D = MR curve, then go down to ATC and color the polygon.
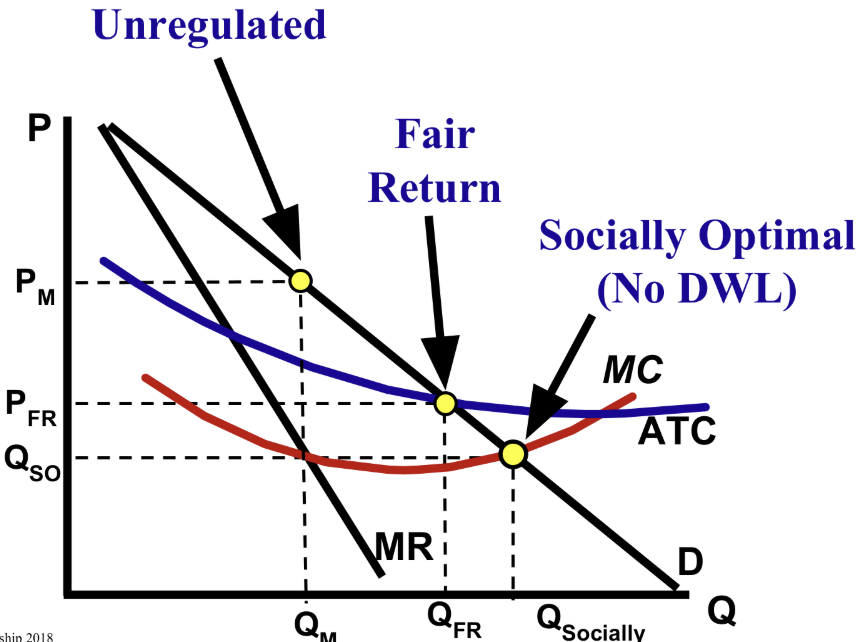
In a natural monopoly, where is the unregulated price, fair-return price, and socially optimal price?
Unregulated price: Intersection between MR and MC, then go up to demand.
Fair-return: Intersection between demand and ATC.
Socially optimal: Intersection between demand and MC.
Identify deadweight loss at the socially optimal price for monopolies.
There is no deadweight loss at the socially optimal price.
A monopolistically competitive firm’s demand curve is (more/less) elastic than a monopoly’s demand curve due to the availability of ____.
more, substitutes