ALLIED HEALTH UNIT 4
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HEALTHY BODY SYSTEMS TEST 1: Cells, tissues and organs ; digestive system ; musculoskeletal systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
levels of the organisation in human body
atoms > molecules > organelles > cells > tissues > organs > body system > organisms
function of an animal cell
provides structure and support
absorbs nutrients and converting them into energy
containing genetic material
allowing for movement
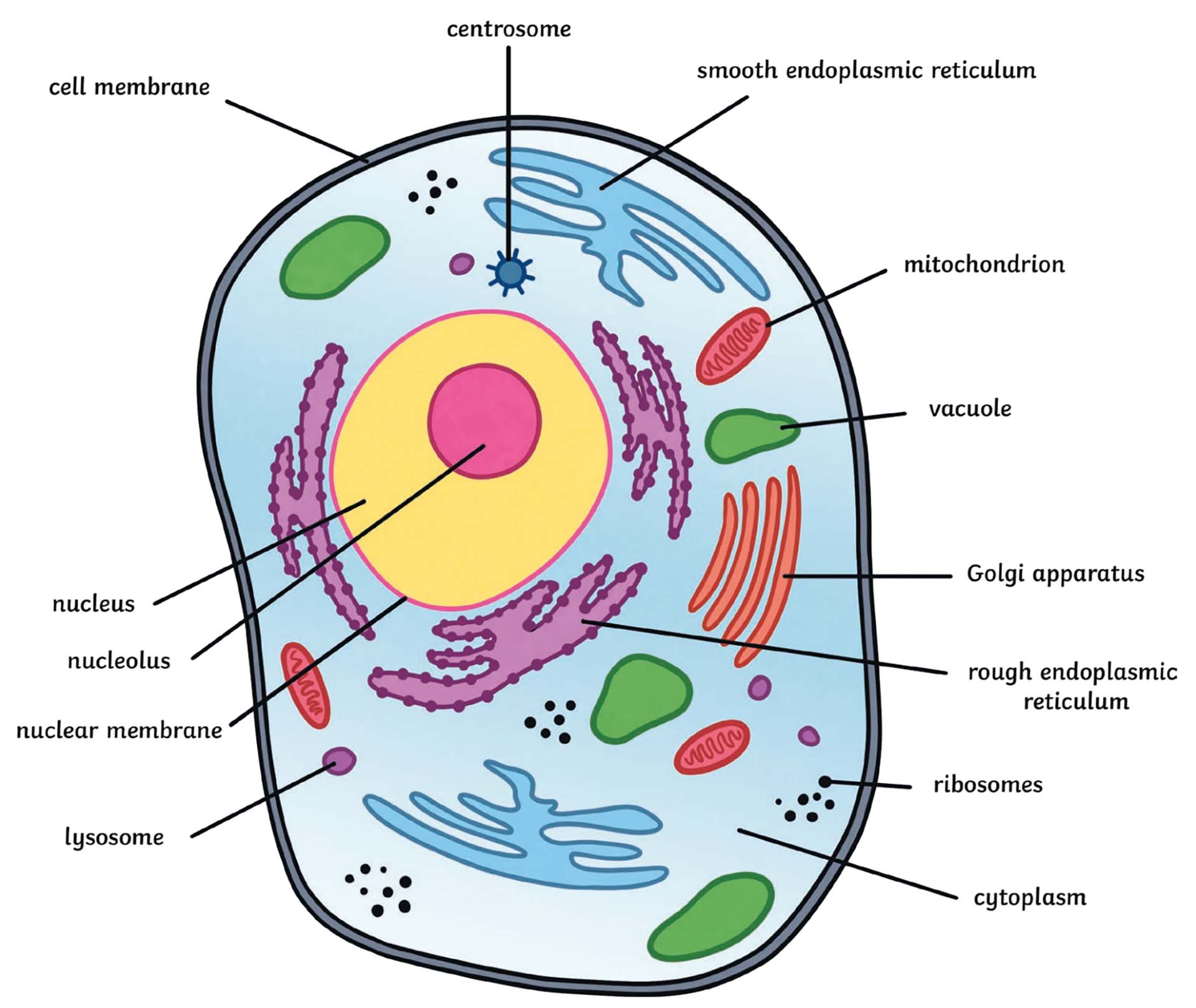
label the animal of cell
mitchondria
nucleus
ribosomes
SER
RER
centrioles
ribosomes
golgi appartus
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
nucleolus
4 types of tissues (definition + example)
connective: transports, insulates, protects, structural support to the body; blood, ligaments, cartilage, tendons
epithelial: protects, secretion, absorption of body; simple, squamous, cuboidal, columnar, stratified
muscle: ability to control and relax movements, helps to control movement of O2, blood, nutrients, remove waste; smooth, cardiac, skeletal
nervous: coordinates and controls body activities, simulates muscle contractions, plays a role in memory and emotions; neurons, glial cells
function of mitchondria
supplies cellular energy (ATP)
function of the nucleus
contains genetic info
function of cytoplasm
holds cytosol, sytoskeleton, organelles (except nucleus)
function of nucleolus
makes ribosomal RNA
function of plasma m embrane
fluid semi-permeable boundary that controls what enters and leaves the cell
function of centrioles
cellular division (mitosis)
function of ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
function of lysosomes
contains lysozyomes
function of rough endoplasmic reticulum
protein synthesis, folding, and sorting
function of the golgi apparatus
stores, packages, transports and modifyes proteins
function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
synthesises lipids
3 types of muscular tissue + its function and example
smooth: involuntary; stomach and intestines
cardiac: involuntary; heart
skeletal: voluntary; biceps, hamstrings
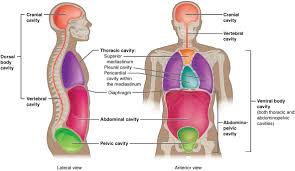
function of the body cavities
protect internal organs and allow for flexibility in organ movement and growth
label the different cavities
cranial
spinal
thoracic
abdominal
pelvic
functions of the body membranes
protection
lubrication
removing wastes
allows movement
exchange of nutrients
describe the 4 types of membranes
epithelial membrane - internal structures
mucous membrane - gastrointestinal, genitourinary, respiratory tracts (muscus)
serous membrane - watery fluid contained with a double layered loose connective tissue (lungs, abdominal cavity, heart)
synovial membrane - cavities of the joints
name the membranes that line the cavities surrounding the heart, lung and guts
pleura (lungs)
pericardium (heart)
peritoneum (guts)
label the organs of the digestive system
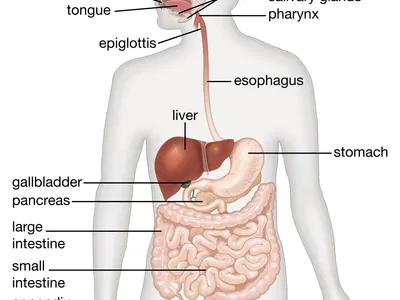
function of mouth cavity
provides mechanical and chemical digestion to breakdown foods
teeth tears, grinds, cuts and breaks food into smaller piece
saliva is excreted (contains amylase) that begins to break down starches into simple sugars
function of the liver
produces bile
stores nutrients (glycogen, vitamine D)
detoxifies harmful substances ( alcohol)
function of the oesphagus
transport food and liquids to the stomach
moves food along digestive tract using peristalsis ( involuntary wave action)
function of stomach
mechanical digestion: stomach churns food into a thick liquid called chyme
chemical digestion: uses gastric juices to faciliate digestion of food (HCI, Pepsin, Mucous)
function of the gall bladder
stores and concentrates bile
releases bile into duodenum when fatty food enter small intestines
function of the small intestines + different areas
absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream
main nutrients: carbohydrates, protein, lipids
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum
function of the large intestines + different areas
water and electrolyte absorption
formation and storage of faeces
cecum, ascending, transverse, decending, rectum, anus
function of the pancreas
releases enzymes into the duodenum
releases bicarbonate to neutralise stomach acid in chyme
function of appendix
maintains gut health
function of anus
to expel waste from the body
function of rectum
to store stool before eliminating it from the body
mechanical digestion + examples
involves physically breaking down food into smaller pieces
increases the surface area of food to make chemical digestion more effective
( teeth chewing food, peristalsis helps churn the food in the stomach)
chemical digestion + examples
involves enzymes and digestive chemicals breaking down large molecules into smaller ones
(enzymes in saliva, enzymes from stomach)
eg. amino acids, simple sugars, fatty acids and glycerol
list the main enzymes
amylase
protease
lipase
function of amylase
breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars (glycogen > glucose)
function of lipase
to break down fats into smaller components for easier absorption
function of protease
break down proteins into smaller units called amino acids
how are nutrients absorb in the small intestines
through structures called villi
function of villi
to absorb nutrients from digested foods
function of microvilli
increases the surface area of cells lining the small intestine, to enhance nutrient absorption
function of the musculoskeletal system
Muscular
allows movement
stabilises our joints
generates heat
maintains posture
Skeletal
provides a supportive structure (framework)
allows movement
attachments for tendons and muscles
storage for calcium
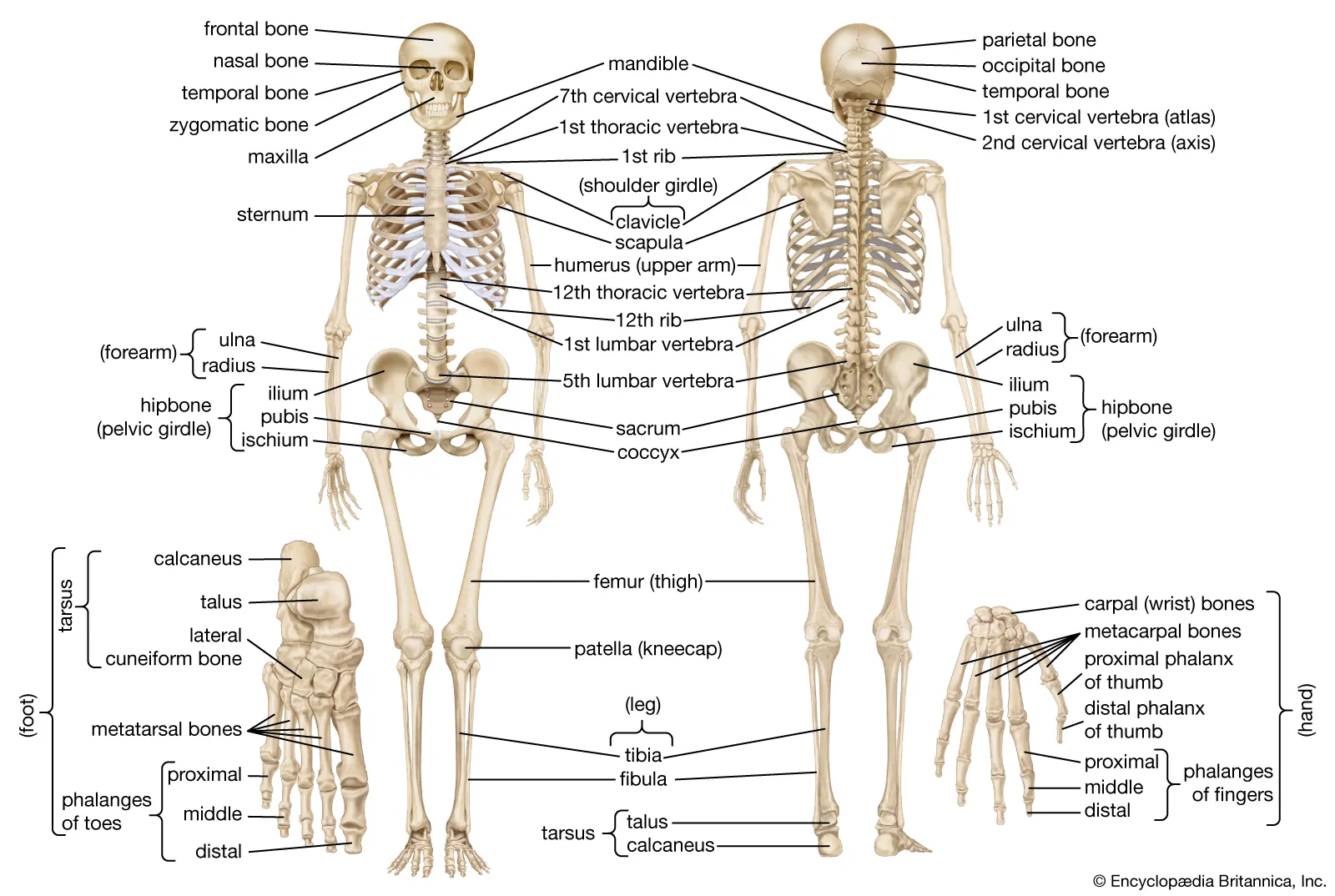
types of bones + example
long bones (femur, humerus)
short bones (carpals, tarsals)
irregular bones (vertebrae)
flat bones (sternum, skull bones)
sesamoid (patella)
label the bones
what is the purpose of a joint and its structure
provides stability and enables movement
structures where two or more bones connect
types of joints + examples
fibrous: tough connective tissue and often permit no movement (suture lines between skull)
cartilaginous (fibrocartilage)
synovial: a space with a capsule between 2 articulating bone (hinge, ball and socket)
different types of synovial joints
ball and socket
hinge
saddle
condyloid
gliding/plane
pivot
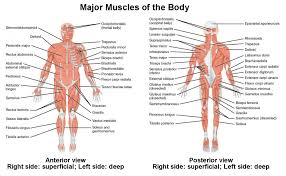
label the muscles
function of ligaments
connect bone to bone
plays role in muscolskeletal biomechanics
soft collagenous
function of tendons
connect muscle to bone
capable of resisting hugh tensile forces while transmitting forces from muscle to bone
different types of movement produced by musculoskeletal system
flexion/extension
internal/external rotation
abduction/adduction
rotation
circumduction