DHS AP Psych Unit 5 Clinical Psychology-Disorders Only
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
psychological disorder
a syndrome marked by a clinically significant disturbance in an individual's cognition, emotion, regulation, or behavior
3-D's of Clinical Psychology
To be considered a disorder it must be considered: Deviant- out of the norm, Distressing - causes behavior causes significant psychological, emotional, physical, or social harm, Dysfunctional- interferes with normal day-to-day functioning
Philippe Pineal
French reformer; madness is a sickness of the mind caused by severe stresses and inhumane conditions
medical model
the concept that diseases, in this case psychological disorders, have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and, in most cases, cured, often through treatment in a hospital.
psychopathology
scientific study of psychological disorders
DSM-V
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition; a widely used system for classifying and identifying psychological disorders.
Does not offer therapy options.
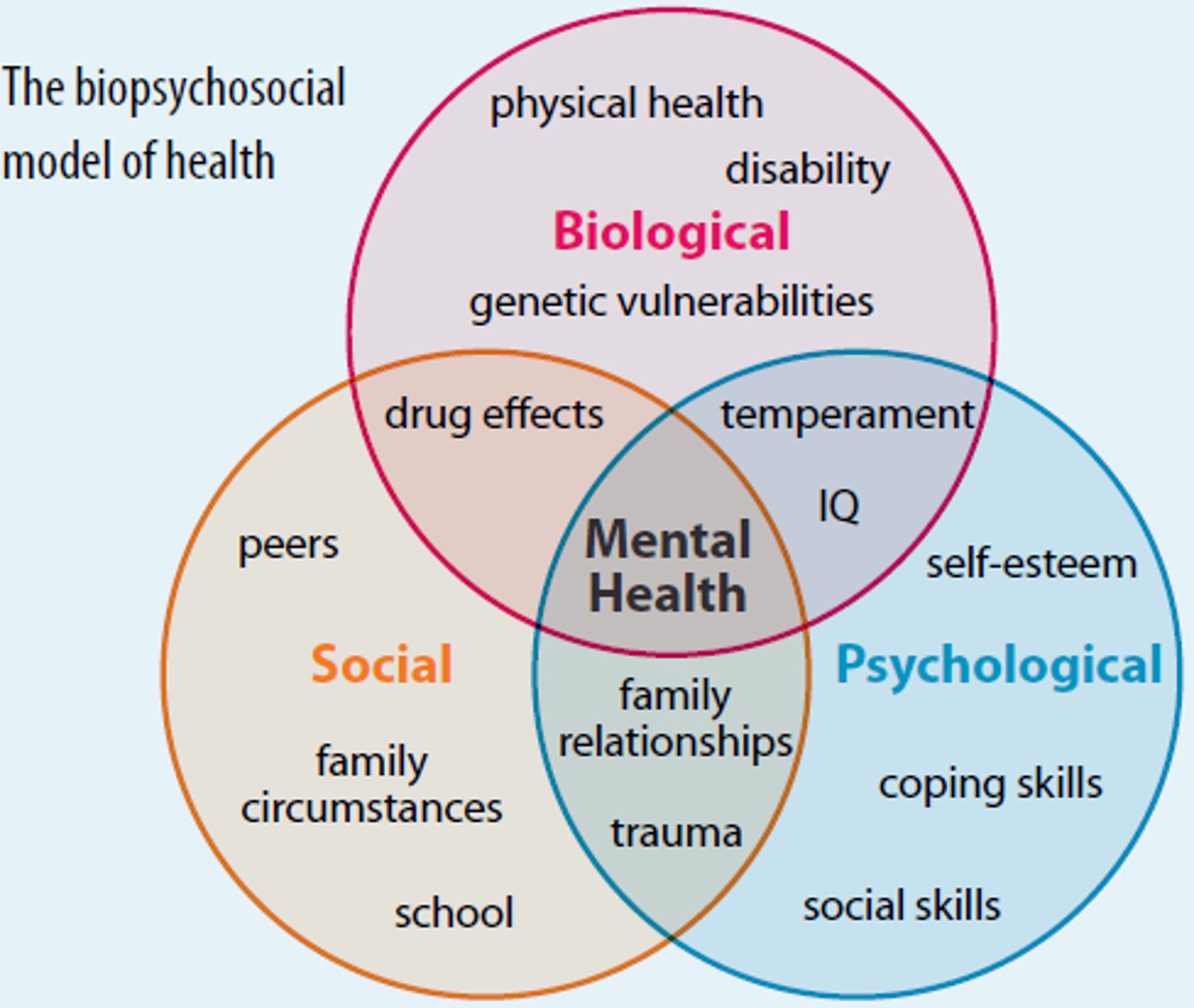
biopsychosocial model
a model of health that integrates the effects of biological, behavioral, and social factors on health and illness
culture-bound syndromes
disorders found only in particular cultures

susto
conditioned marked by severe anxiety, restlessness, and a fear of black magic

amok
sudden outburst of violent behavior

Tianjin-Kyofusho
social anxiety about one's appearance combined with a readiness to blush and a fear of eye contact
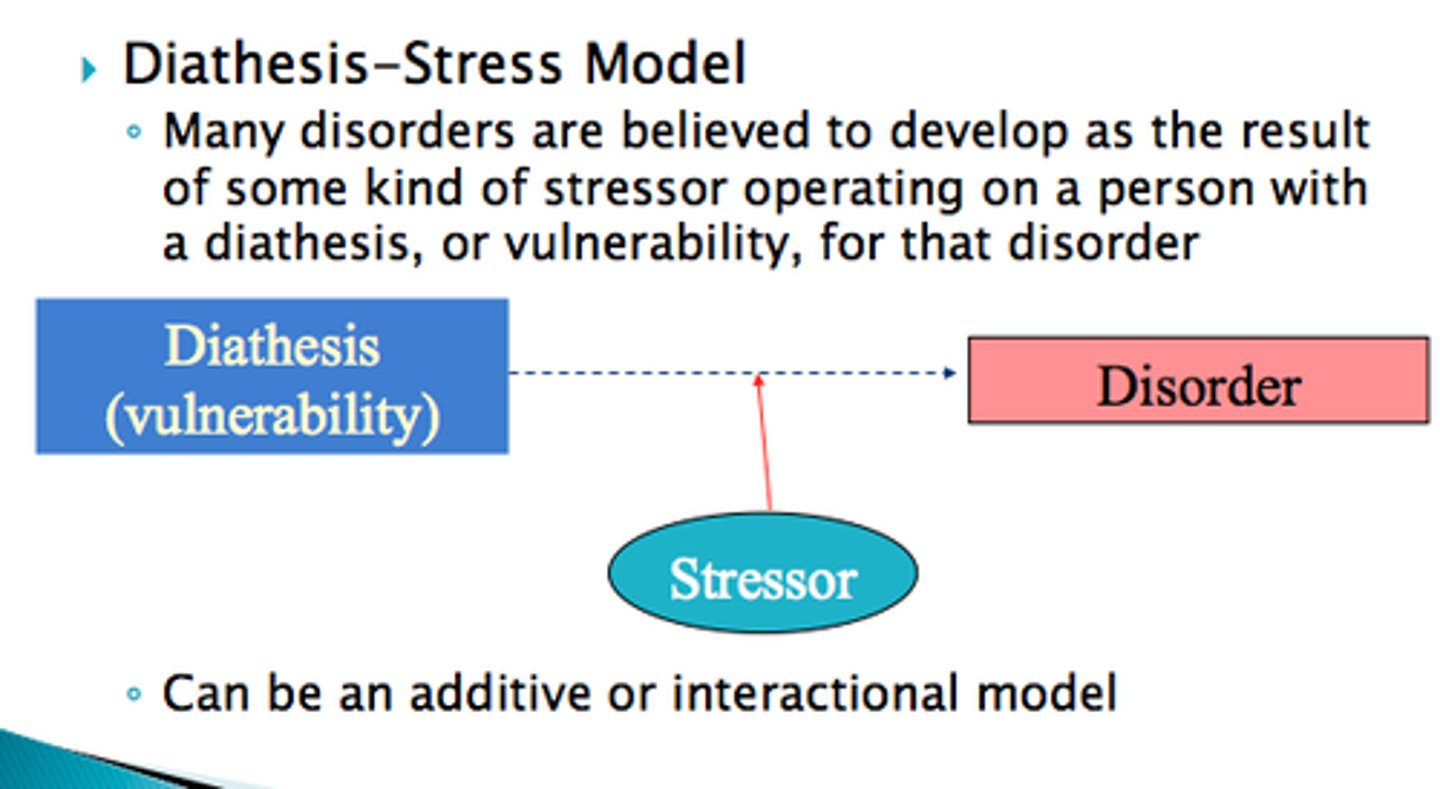
diathesis-stress model
a theory holding that a vulnerability plus stress creates problems in behavior - can be a trigger for the onset of mental disorders
epigenetics
changes in gene expression that take place without a change in the DNA sequence - example - schizophrenia has a genetic component, but the gene can lay dormant unless switched on by environmental factors
psychodynamic perspective
disorders causes from unconscious drives and conflicts
humanistic perspective
disorders caused by the failure to strive to one's potential or being out of touch with one's feelings.
behavioral perspective
disorders caused by how you were reinforcement and the environment.
cognitive perspective
disorders caused by irrational, dysfunctional thoughts or distorted ways of thinking.
social-cultural perspective
disorders are caused by dysfunctional expectations of a culture
biological perspective
disorders are caused by physical/organic problems, biochemical imbalances, genetic predispositions.
evolutionary perspective
disorders are caused because believes that some traits that were once beneficial have become maladaptive in modern society
attention-decifit/hyperactivity disorder ADHD
A psychological disorder marked by the appearance by age 7 of one or more of three key symptoms: extreme inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
psychological disorders
any pattern of behavior that causes people significant distress, causes them to harm others, or harms their ability to function in daily life
anxiety disorders
Psychological disorders characterized by distressing, persistent anxiety or maladaptive behaviors that reduce anxiety.
social anxiety disorder
intense fear of negative evaluation in social situations
generalized anxiety disorder
An anxiety disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal.
panic disorder
An anxiety disorder marked by unpredictable minutes-long episodes of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations.
specific phobia
An anxiety disorder marked by a persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of a specific object or situation.
agoraphobia
fear or avoidance of situations, such as crowds or wide open places, where one has felt loss of control and panic
obsessive-compulsive disorder
Anxiety disorder characterized by persistent and uncontrollable thoughts and irrational beliefs that cause the performance of compulsive rituals that interfere with daily life.
post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
an anxiety disorder characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, and/or insomnia that lingers for four weeks or more after a traumatic experience
post traumatic growth
positive psychological changes as a result of struggling with extremely challenging circumstances and life crises
mood disorders
psychological disorders characterized by emotional extremes. See major depressive disorder, mania, and bipolar disorder.
major depressive disorder
A mood disorder in which a person experiences, in the a medical condition, two or more weeks of significantly depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or pleasure in most activities.
persistent depressive disorder - aka dystemic depression
prolonged times of depression - milder than major depression - lasts 2 or more years
postpartum depression
a new mother's feelings of inadequacy and sadness in the days and weeks after giving birth
bipolar disorder
A mood disorder in which the person alternates between the hopelessness and lethargy of depression and the overexcited state of mania.
mania
A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state.
bipolar 1
periods of severe mood episodes from mania to depression
bipolar 2
milder episodes of hypomania that alternate with periods of severe depression - often undiagnosed
rumination
compulsive fretting; overthinking about our problems and their causes
psychotic disorders
a group of disorders marked by irrational ideas, distorted perceptions, and a loss of contact with reality
schizophrenia
A psychotic disorder characterized by gross distortions of reality and disturbances in the content and form of thought, perception, and behavior.
psychosis
a psychological disorder in which a person loses contact with reality, experiencing irrational ideas and distorted perceptions
positive symptoms of schizophrenia
presence of inappropriate behaviors: hallucinations, word salad, inappropriate laughter, tears, or rage

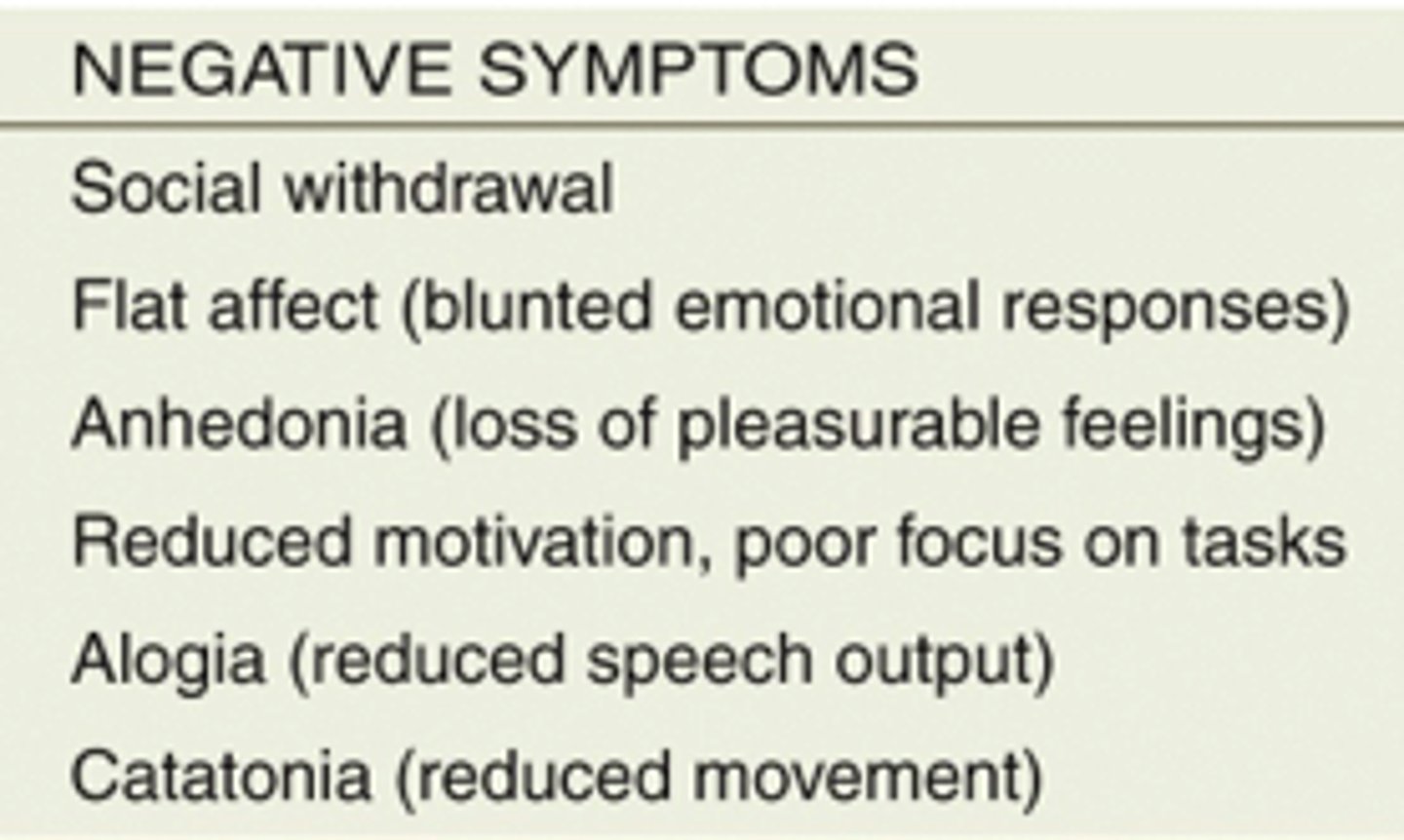
negative symptoms of schizophrenia
absence of appropriate behaviors: toneless voice, expressionless faces
paranoia
prone to delusions of persecution
delusions
False beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur, that may accompany psychotic disorders
hallucination
a false sensory perception that seems to be real but for which there is not an actual external stimulus
world salad/clang associations
jumbled words and ideas-often occurs with Disorganized Schizophrenia
seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
depression comes and goes with seasons and light; too little serotonin and too much melatonin
flattened affect
an emotionless state when there should be emotions

catatonia stupor
stop responding to their environment, remaining motionless and silent for long stretches of time
catatonia excitement
move excitedly, sometimes wildly waving their arms and legs
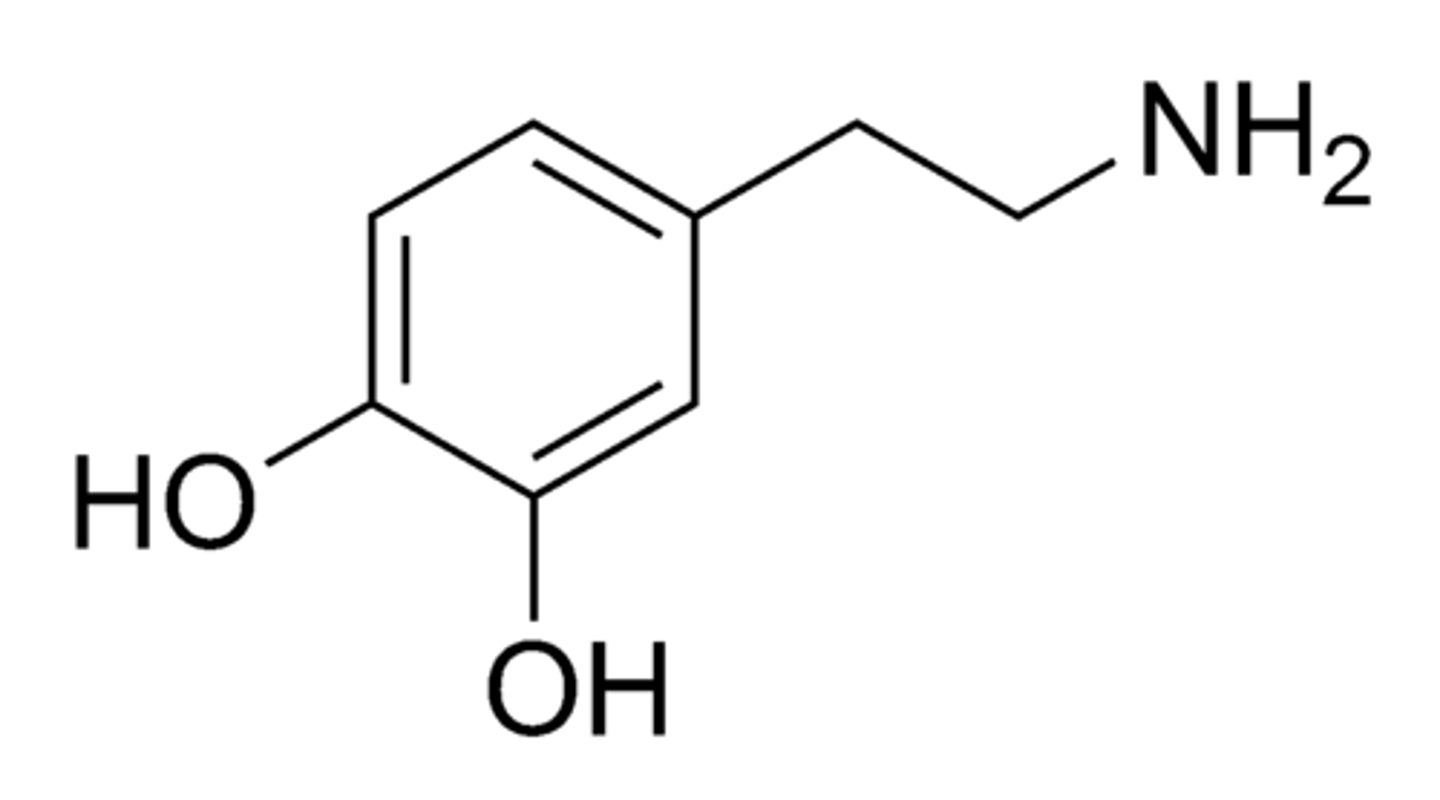
dopamine theory of schizophrenia
the theory that schizophrenia is caused by too much dopamine and, conversely, that anti-schizophrenic drugs exert their effects by decreasing dopamine levels
thalamus
very active during hallucinations
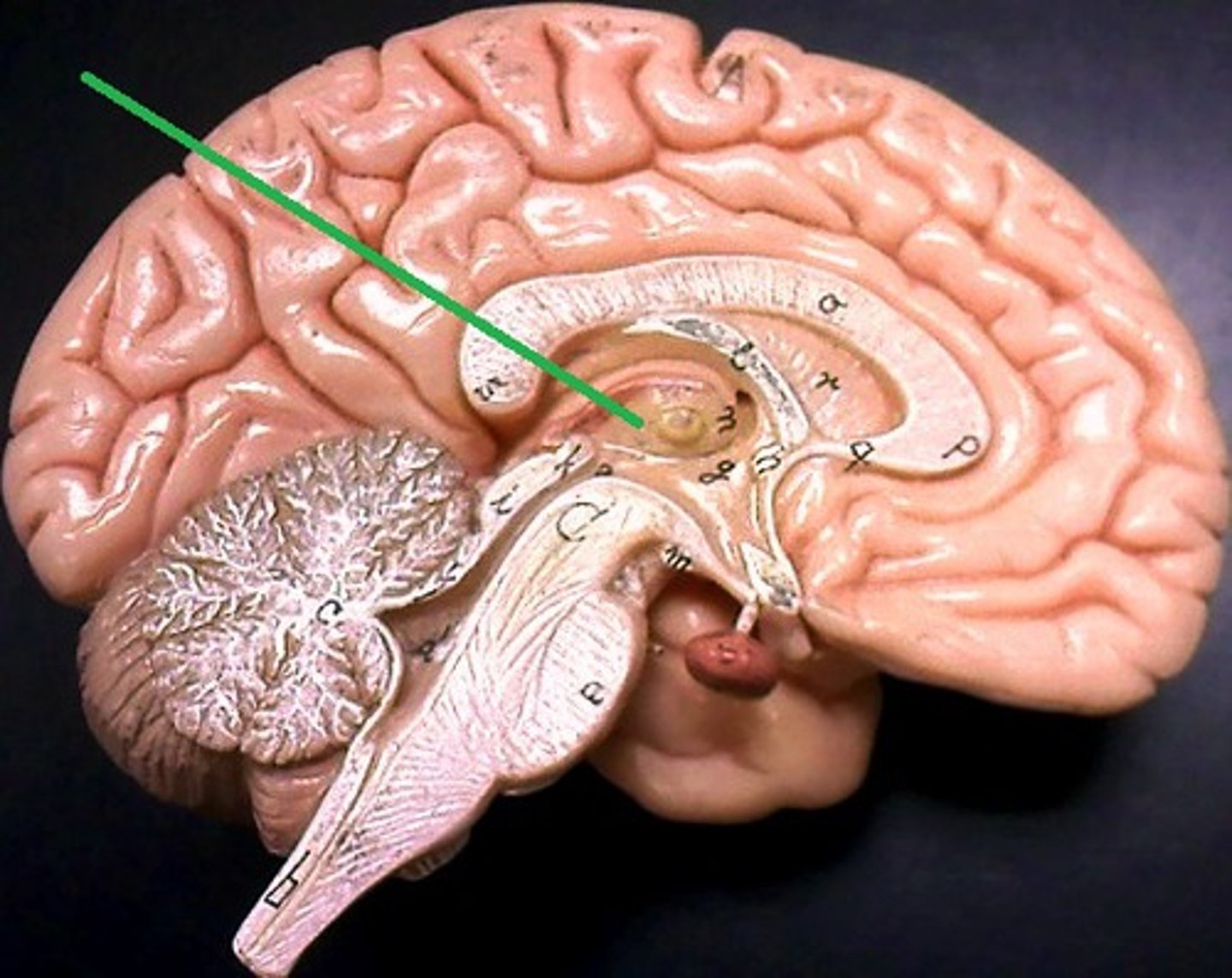
ventricle tissues
enlarged, fluid filled areas and a corresponding shrinkage and thinning of cerebral tissues - larger in schizophrenic's brains
frontal lobe activity
low activity in patients with schizophrenia
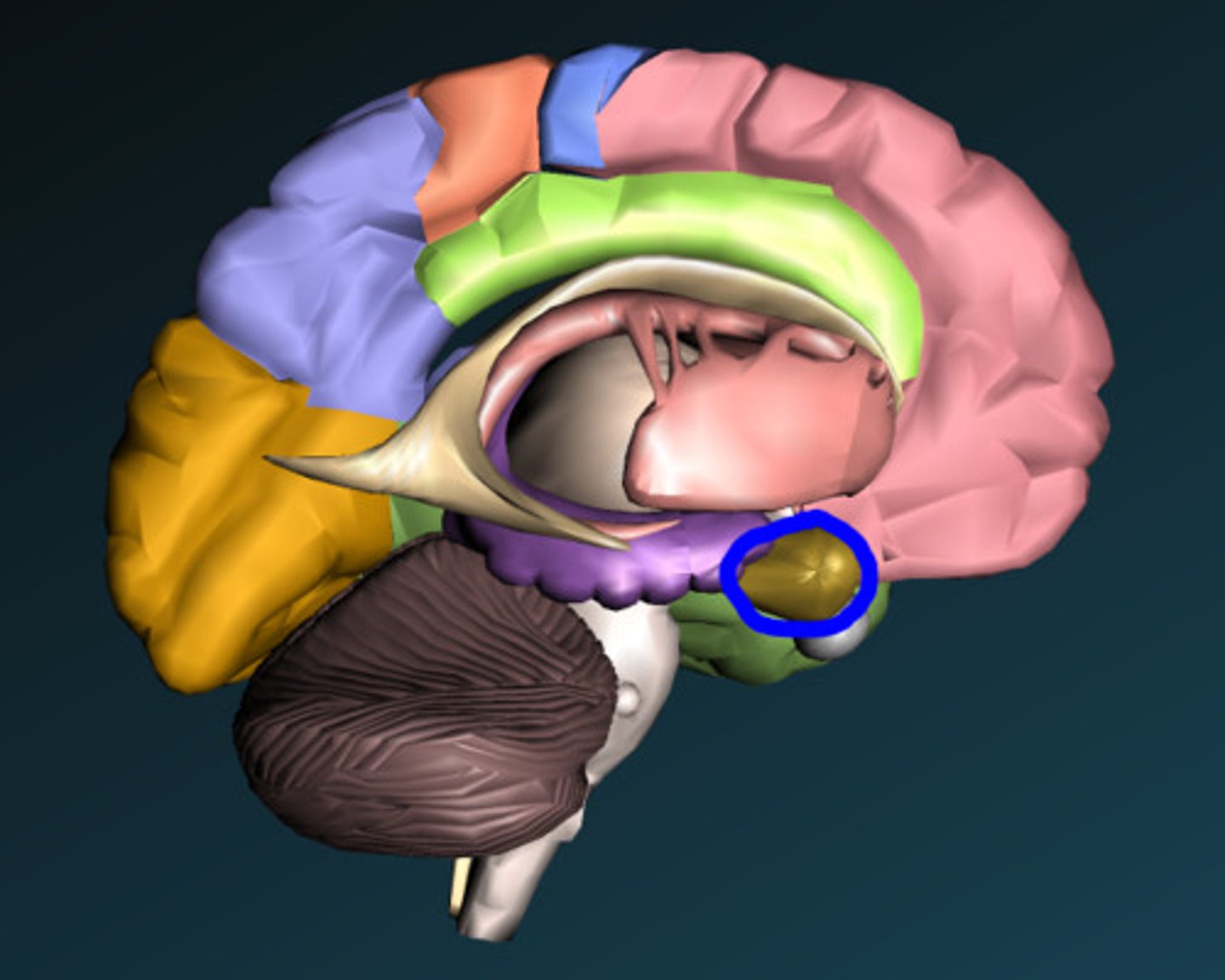
amygdala
increased activity in people with paranoia
Tardive dyskinesia (TD)
Potentially disabling motor disorder that may occur following regular use of antipsychotic drugs - used in treating schizophrenia. Drugs cause a reductions in dopamine- symptoms mimic Parkinson's.
dissociative disorders
Disorders in which conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings.
dissociative identity disorder (DID)
A rare dissociative disorder in which a person exhibits two or more distinct and alternating personalities. Also called multiple personality disorder.
Feeding Disorders
inappropriate and unhealthy behaviors related to the types of substances eaten and attitude toward food.
anorexia nervosa
An eating disorder characterized by an obstinate and willful refusal to eat, a distorted body image, and an intense fear of being fat
bulimia nervosa
An eating disorder characterized by episodes of overeating, usually of high-calorie foods, followed by vomiting, laxative use, fasting, or excessive exercise.
binge-eating disorder
significant binge-eating episodes, followed by distress, disgust, or guilt, but without the compensatory purging, fasting, or excessive exercise that marks bulimia nervosa
personality disorders
Psychological disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning.
3 W's of personality disorders
A: "Weird" Odd, Eccentric Behavior
B:"Wild" Erratic, Impulsive, Unpredictable Behavior
C: "Worried" Anxious, Fearful Behaviors
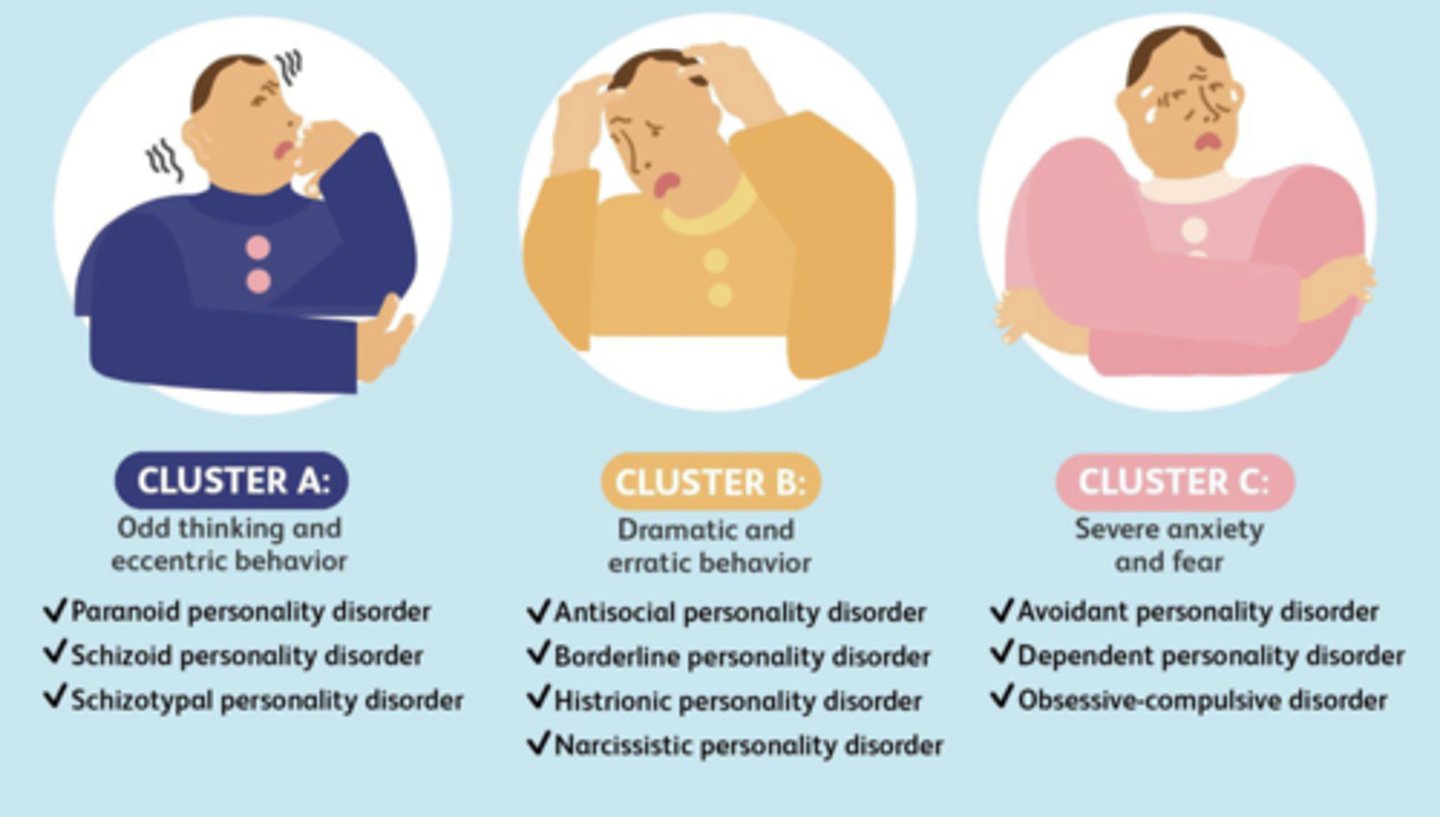
maladaptive
interfere with normal day to day life
avoidant personality disorder
feelings of extreme social inhibition, inadequacy, and sensitivity to negative criticism and rejection

schizoid personality disorder
lack of interest in social relationships

histrionic personality disorder
a pattern of excessive attention-seeking emotions

narcissistic personality disorder
Having an unwarranted sense of self-importance
Lacks empathy, overly self involved

borderline personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by lack of stability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and emotion; impulsivity; angry outbursts; intense fear of abandonment; recurring self-harming gestures

antisocial personality disorder
A personality disorder in which the person (usually a man) exhibits a lack of conscience for wrongdoing, even toward friends and family members. May be aggressive and ruthless or a clever con artist.

paranoid personality disorder
type of personality disorder characterized by extreme suspiciousness or mistrust of others

schizotypal personality disorder
a psychological disorder characterized by several traits that cause problems interpersonally, including constricted or inappropriate affect; magical thinking; and odd beliefs, speech, behavior, appearance, and perceptions

dependent personality disorder
A personality disorder characterized by a pattern of clinging and obedience, fear of separation, and an ongoing need to be taken care of.

obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by preoccupation with orderliness, perfection, and control
