β-hemolytic Streptococcus pyogenes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Where is S. pyogenes found?
Throat, nasopharynx, occasionally skin
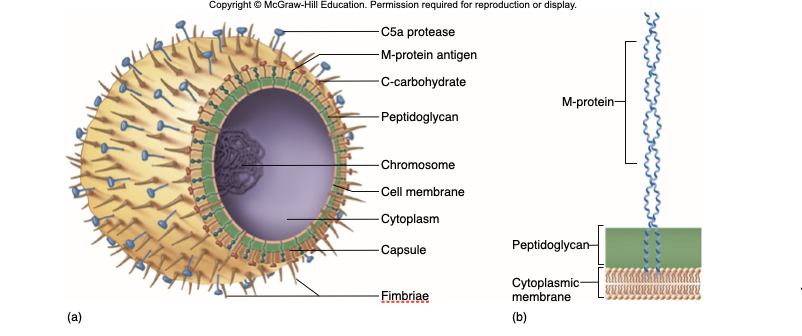
C-carbohydrates
Virulence factor of S. pyogenes
protect against lysozyme
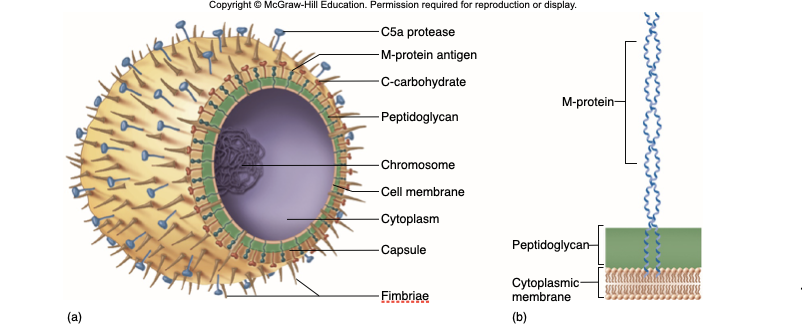
Fimbrirae
Virulence factor of S. pyogenes
Adherence
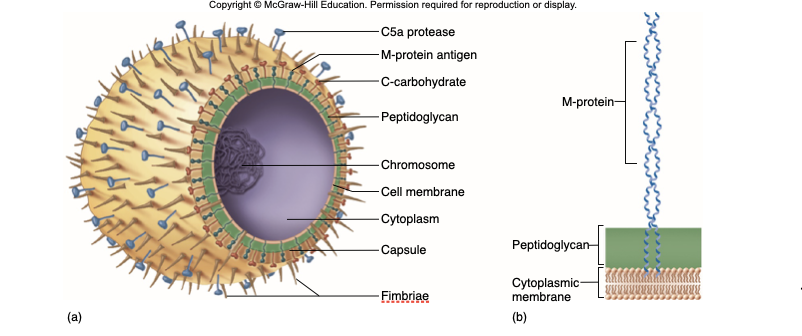
M-protein
Virulence factor of S. pyogenes
Contributes to resistance to phagocytosis
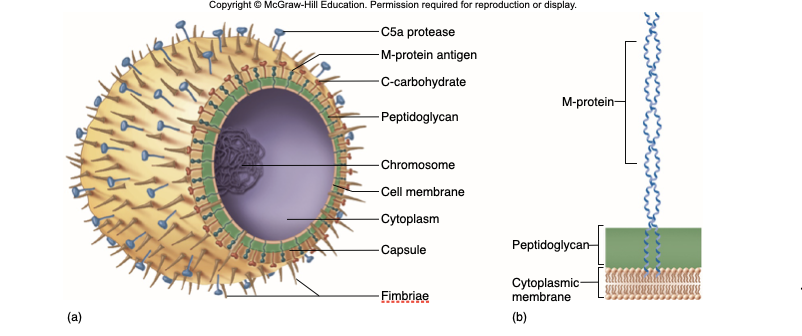
Hyaluronic Acid Capsule
Virulence factor of S. pyogenes
Provokes no immune response
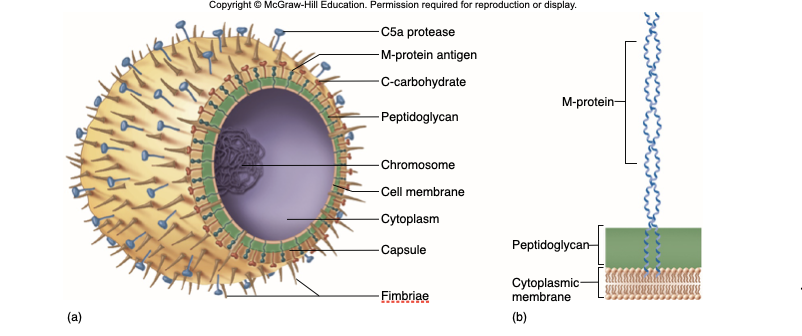
C5a Protease
Virulence factor of S. pyogenes
hinders complement & neutrophil response
Streptolysins
Virulence factor of S. pyogenes
Extracellular toxin
hymolysins; streptolysin O (SLO) and streptolysin S (SLS)- both cause cell & tissue injury
Erythrogenic toxin (pyrogenic)
Virulence factor of S. pyogenes
Extracellular toxin
induces fever & typical red rash
Superantigens
Virulence factor of S. pyogenes
Extracellular toxin
Strong monocyte/lymphocyte stimulants; cause the release of tissue necrotic factor
S. pyogenes Epidemiology & Pathogenesis
Humans only reservoir
Inapparent carriers
Transmission – contact, droplets, food, fomites
Portal of entry generally skin or pharynx
Children predominant group affected for cutaneous and throat infections
Systemic infections and progressive sequelae possible if untreated
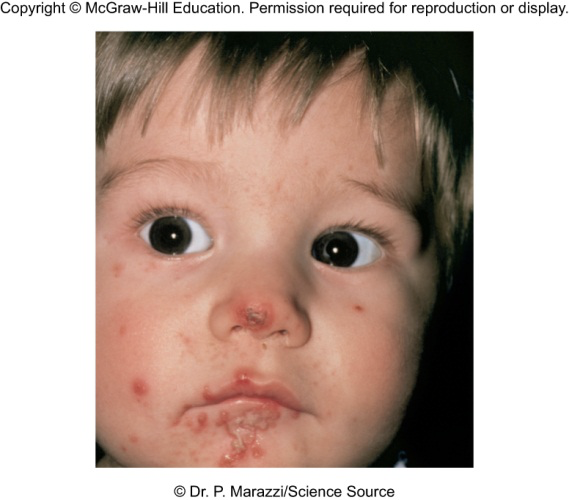
Impetigo (pyoderma)
Skin infection of S. pyogenes
superficial lesions that break and form highly contagious crust; often occurs in epidemics in school children; also associated with insect bites, poor hygiene, and crowded living conditions
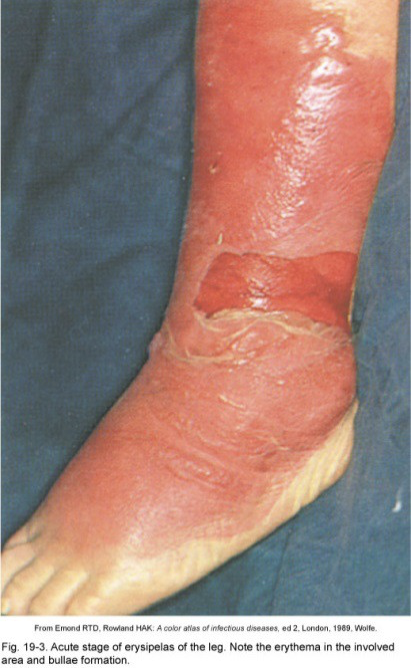
Erysipelas
Skin infection of S. pyogenes
pathogen enters through a break in the skin and eventually spreads to the dermis and subcutaneous tissues; can remain superficial or become systemic; more invasive
Cellulitis
Skin infection of S. pyogenes
Deeper, boarders less well defined
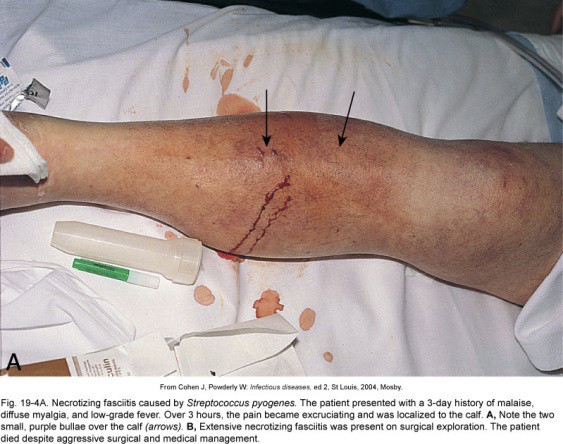
Necrotizing fasciitis
aka “Flesh-eating bacteria”
most common S. pyogenes
Rare strains make special enzymes and toxins (e.g. superantigens)
Not usually antibiotic resistant
Early diagnosis & treatment important
20% mortality
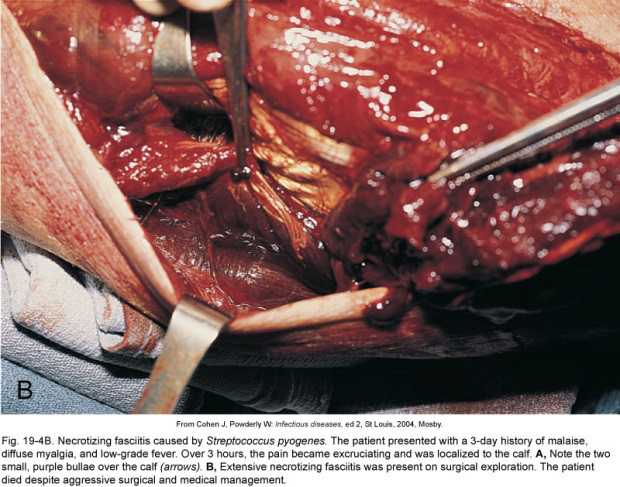
Streptococcal pharyngitis
Throat infection
strep throat
Scarlet fever
Systemic infection
strain of S. pyogenes carrying a prophage that codes for erythrogenic toxin; can lead to sequelae
Septicemia
Systemic infection
Pneumonia
Systemic infection
Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome
Systemic infection
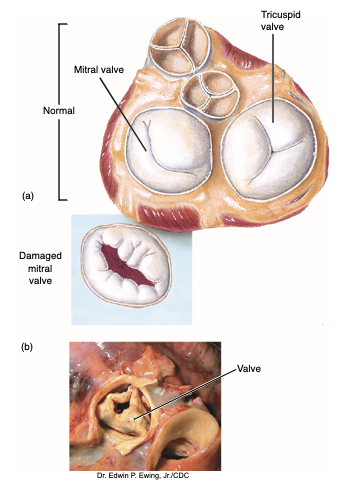
Rheumatic Fever
Long-term complication of Group A infection
follows overt or subclinical pharyngitis in children; Breakdown of tolerance, carditis with extensive valve damage possible, arthritis, chorea, fever
Acute glomerulonephritis
Long-term complication of Group A infection
nephritis, due to immune complexes, increased blood pressure, occasionally heart failure; can become chronic leading to kidney failure