Topic 15- Forces and Matter
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Springs, Pressure and Pressure in fluids, Upthrust
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
objects can change their shape by…
stretching
bending
compressing
in order for stationary objects to change their shape, it requires…
more than one force:
stretching- multiple forces away from an object in opposite directions (sometimes causing a tenson force)
compressing- multiple forces towards the object in opposite directions
bending- multiple forced at different points on the object in opposing directions
difference between elastic and inelastic distortion
elastic distortion = objects return to their original shape when the stretching force is removed
inelastic distortion = objects remain stretched and do not return completely to their original shape even when the stretching force is removed
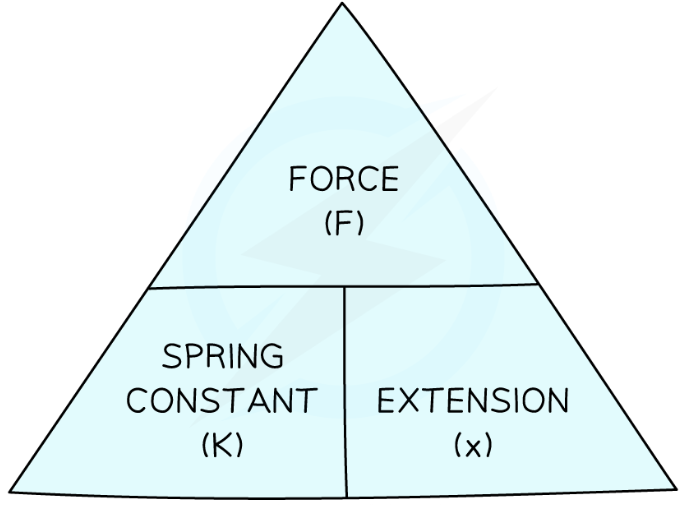
Hooke’s Law (linear elastic distortion) eqn
Force exerted on a spring (N) = spring constant (N/m) x extension (m)
F = k x 𝑥
work done in a stretching spring eqn
energy transferred [work done] (J) = 0.5 x spring constant (N/m) x extension2 (m)
E = ½ x k x 𝑥
difference between linear and non-linear relationships between force and extension
linear = the graph formed is a straight line- they are proportional up to the limit of proportionality, in elastic materials
non-linear = the graph is not a straight line, in inelastic materials that don’t obey Hooke’s law
when a spring is stretched or compressed, what work is done on it?
energy is transferred to the elastic potential energy store of the spring
energy transfer = work
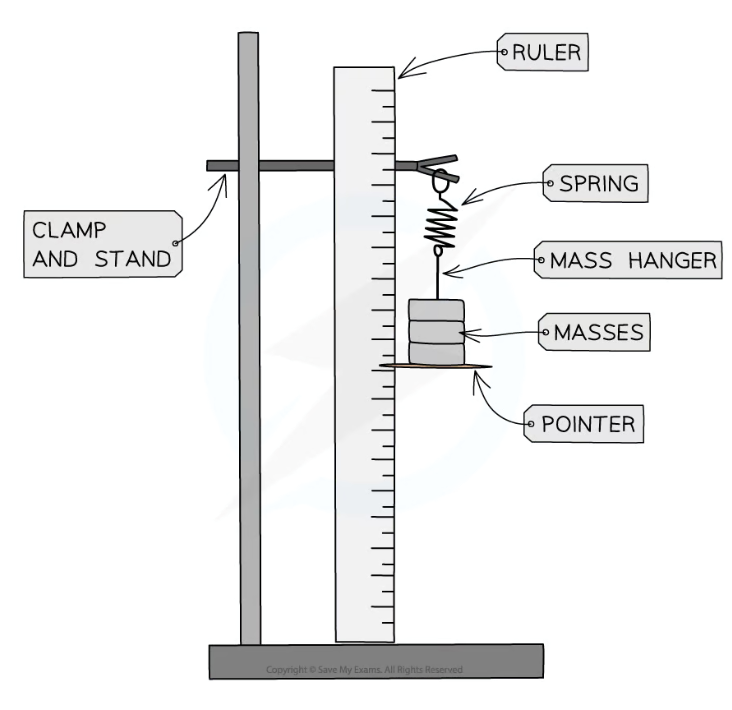
CORE PRAC 7: Investigating the extension and work done when applying forces to a spring
investigates the relationship between force and extension for a spring
changing force, measuring extension, controlling spring constant
set up apparatus as shown
align marker with value on ruler, record this initial length of spring
add 100g mass onto spring, record extension (new length - original), repeat
repeat entire process three times for more accurate results
force added to spring = weight (mxg)
plot results on a graph and draw line of best fit
why does atmospheric pressure vary with height about the Earth’s surface?
atmospheric pressure is the total weight of the air above a unit area at a certain altitude
with higher altitude, there are fewer molecules above the unit area, so less weight
therefore less pressure
pressure in fluids is due to…
the fluid pressure and the atmospheric pressure
pressure + forces in fluids
pressure in fluids causes a force normal to any surface on an object submerged in it, from all directions
pressure definition
the force per unit area (concentration of a force)
real life examples of how objects’ area and force effects the pressure
TRACTORS have large tyres, spreading the weight over a large area
→ reduces the pressure exerted which prevents tractor from sinking into mud
NAILS have sharp pointed ends with a very small area, concentrating the force over a small area
→ increases pressure, so nail can be hammered into wall
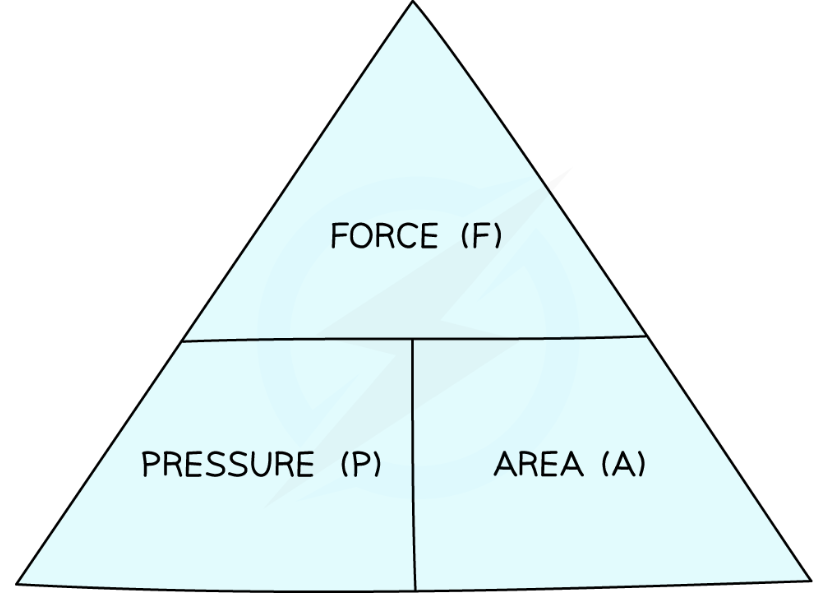
pressure equation- HAVE TO LEARN!!
Pressure = force normal to surface / area of surface
P (Pa) = F (N) /A (m2)
pressure in fluids ____ with depth and density
increases (deeper = higher pressure, denser = higher pressure)
why does pressure vary with density and depth?
Pressure in a liquid is caused by the weight of liquid pushing against objects immersed in it.
As an object gets deeper, there is a greater volume (and therefore weight) of liquid above it, meaning pressure increases
the more dense a liquid the greater its weight per unit volume, therefore a more dense liquid will exert a higher pressure
pressure in liquids equation
Pressure due to a column of liquid = density of liquid x gravitational field strength x height of column
P = ρgh
P = Pascals (Pa)
ρ = kg/m3
g = N/kg
what is/causes upthrust?
when an object is submerged (partially or completely) in a fluid,
the pressure of the fluid exerts a force on it from every direction.
Pressure increases with depth, so the force on the bottom is greater than the force on the top of the object- difference in pressure
this creates a resultant force upwards, AKA upthrust
upthrust is equal to the…
weight of the fluid displaced
how to calculate upthrust
Find weight of fluid displaced:
upthrust = density of liquid x volume displaced x gravitational field strength
AKA:
upthrust = mass of liquid displaced x gravitational field strength
What makes an object sink?
object is more dense than fluid (doesn’t have a large enough volume to displace enough fluid to equal its weight- so object’s weight is always larger than the upthrust)
Weight of object > upthrust/weight of fluid displaced
pressure difference between top + bottom of object causes a resultant force less than object’s weight
what makes an object float?
object is less dense than fluid (displaces a volume of liquid that can equal its weight- so the objects weight is equal to upthrust)
weight of object = upthrust/weight of fluid displaced
pressure difference between top + bottom of object causes a resultant force equal to object’s weight