Logistic Growth Model
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is the logistic growth model used to describe?
The growth of a population under limited resources, producing an S-shaped (sigmoid) curve that levels off near the carrying capacity K.
Why don't exponential growth patterns continue forever in natural populations?
Because resources like food, space, and water are finite, causing growth to slow and stabilize as population size approaches carrying capacity.
Name the three phases of logistic growth.
Lag phase, Log phase (logarithmic phase), stationary phase
Describe the Lag phase
population size is small, thus resources are abundant.
growth is slow due to few individuals reproducing.
Describe the Log phase
Population grows rapidly; resources are sufficient; and growth rate is near maximum (biotic potential).
Describe the Stationary phase
Rsources become limiting; growth slows to zero as N→K, which means as population size (N) approaches carrying capacity (K); and thus births balance deaths.
Write the logistic growth differential equation.
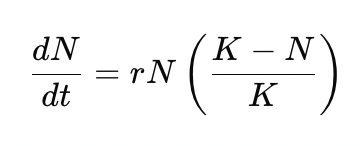
What does each symbol represent in the logistic model?
dN/dt = instantaneous growth rate
N = current population size
r = growth rate per capita
K = carrying capacity
How does the term K-N/K affect growth as N increases?
It reduces growth rate as N approaches K;
when N = K, —> K-N/K = 0
and dN/dt = 0
Why might real populations deviate from the ideal logistic curve?
Because resource availability often varies due to competition, environmental changes, and other abiotic/biotic factors.
Give a real-world example of logistic growth.
A long-term sigmoid trend in a wildlife population (e.g., fur seals) showing initial rapid growth that slows as resources limit expansion.
What is carrying capacity?
The maximum population size that the environment can sustain indefinitely given the available resources.
How does the logistic model relate to r and K?
Growth rate is driven by rN but scaled by K-N/K ; r sets per-capita growth potential while K imposes the environmental limit.