Biology Mod 5
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Sexual Reproduction
Fusion of male and female gametes - sperm + egg
Making copies of likeness e.g. producing offspring that resembles parents.
To survive genetic material must be passed on.
Sexual
Involves 2 parents
Mixing of genes
Offsprings are unique
Asexual
Involves only one parent
Offspring genetically identical (clones)
Haploid
Half the number of chromosomes
Gametes
Sex cell
Diploid
Contains full set of chromosomes
Zygote
The first diploid cell formed when a sperm and egg fuse during fertilisation, containing a full set of chromosomes from both parents.
Internal Fertilisation
Union of gametes and development of offspring inside the female reproductive tract
External Fertilisation
Union of gametes and development outside of the body
Advantages of Sexual Reproduction
Genetic variation → enables a species to survive and reproduce in varied environment
Facilitates the selection of beneficial traits and elimination of unfavourable traits
Increasing beneficial genetic variation
Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction
Energy must be used to produce gametes
Rely on environmental conditions and sometimes other species to ensure population
Finding a mate
Competing for males can be fatal
Parental investment is high shortening lifespan of parent
Internal Fertilisation Advantages
Less risk of genetic dehydration
Higher offspring survival
External Fertilisation Advantages
Typically in bodies of water
Mass releases of sperm + egg = high variation
Anther
Pollen grains are formed
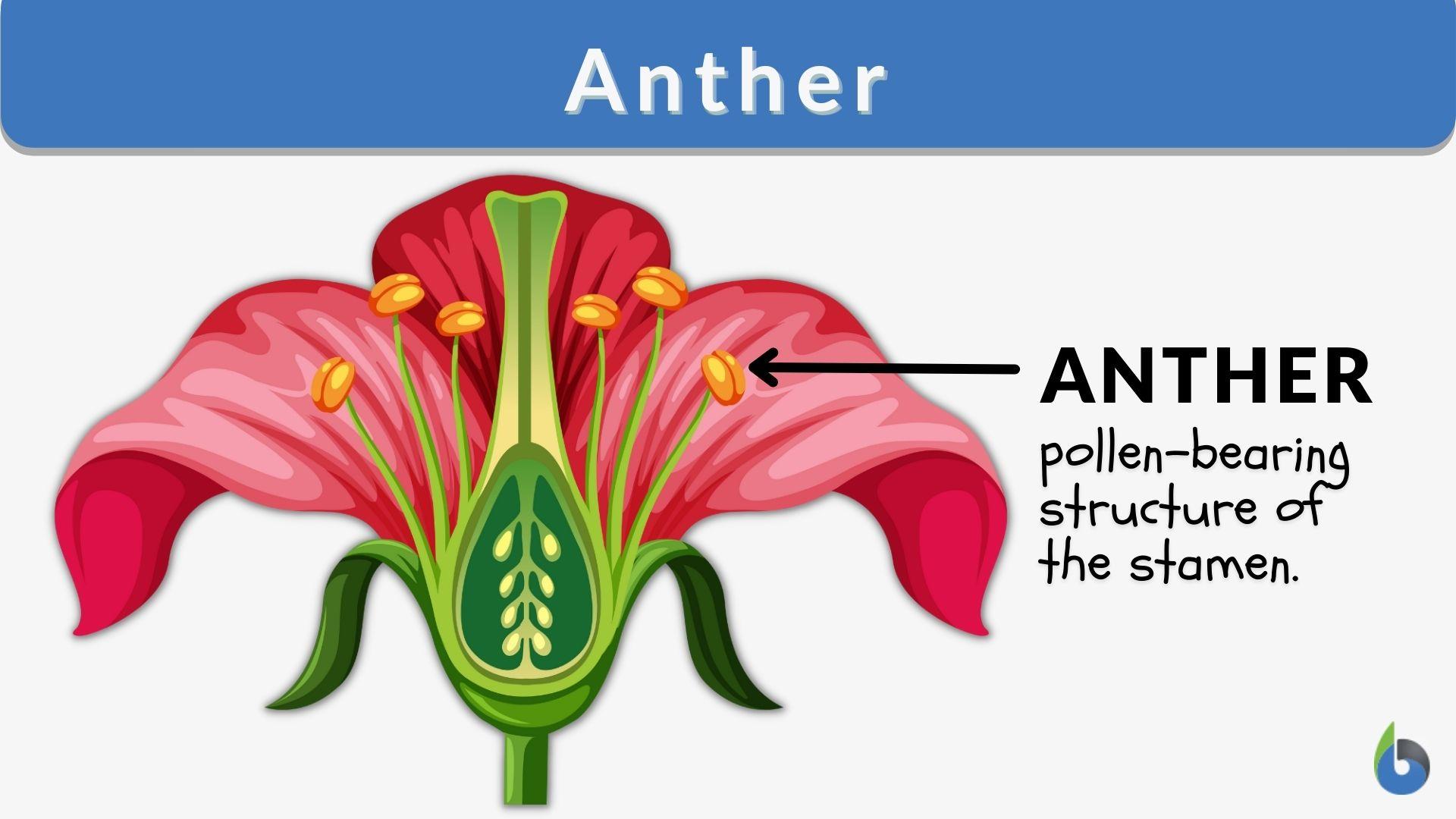
Stamen
Male parts of the flower

Fillament
Stalk that carries the Anther

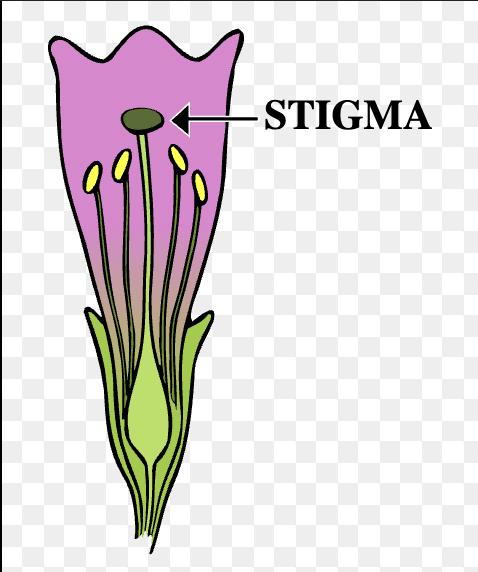
Stigma
Sticky / where pollen adheres

Style
Joins the Stigma to Ovaries
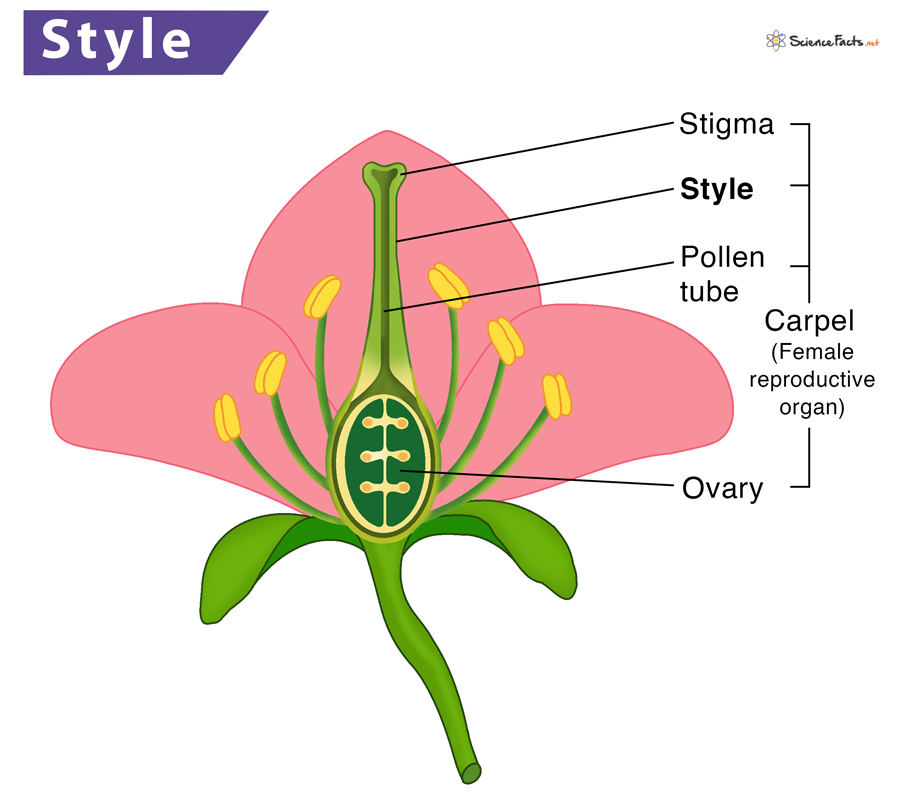
Ovary
When ovaries are formed

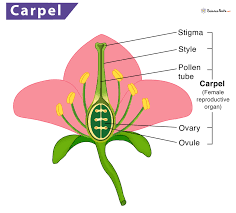
Carpels
Females part of the flower
Ferns
Reproduce sexually by producing spores which germinate and produces sex cells
Seed Dispersal
Dispersal relies on the type of fruit in which the seeds occur, by animals, by wind and self dispersal
Pollenation
Pollen transferred from the anther (male) to stigma (female)
Fertilisation
Pollen (male gamete) is transferred to the Ovum (female gamete), Occurs inside the ovaries
Asexual Reproduction
Production identical offspring from one parent
Produces new individuals (offspring) by mitosis in which a daughter cell receives a copy of every chromosome of the parent cell
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Efficient and simple
Mitosis is less demanding
Works well when environment is relatively static
Less time + energy needed (no need to find a mate)
Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
All genetically the same
Rapid growth leads to overcrowding and increased competition for resources
Lack of genetic variation could cause death of entire population if conditions change.
Fission
Splitting of one cell into two (binary fission) or many (multiple fission) of equal size
Budding
Outgrowths from a parent call each smaller than the parent
Bacteria
Unicellular, microscopic prokaryotic that reproduce asexually
Quicker than eukaryotic cells (very quick)
Protist
Aquatic of most environments
Uni of multicellular
Autotrophic or heterotrophic (both asexually and sexually)
Membrane bound organelle
Fungi
Spores released e.g. from fruiting (mould, mushrooms and puffballs)
Budding e.g. Yeast
Chain of independent cells
Spores by meiosis (meiospores) are haploid reproductive cells
Structure sporangium
Asexual Plants
Lack of genetic variation
Rapid increase in number of plants growing in area
Advantages Sexual
High genetic variability
Facilitates adaptation
‘Speeds’ up evolution
Disdvantages Sexual
Energy cost
Courtship its time/resource consuming
Usually sacrifices the fitness of one sex to the other
Advantages Sexual
Saves energy
Courtship is an issue
Greatest increase in fitness for each individual
Disadvantages Sexual
How genetic variability
Adaptation to environment is difficult
“Retards” evolution
Divide (Cleavage stage)
1 zygote splits into 16
3 days mulgula → hollow sphere (blastocyst)
Implantation
Takes 5 days finished after 12 days
HGC doing work (hormones)
Placenta formed (umbilical chord)
Labour
Dilation - Child head is pushed (labour)
Expulsion stage - Baby pops out
Placental stage - Placenta is released
Menstrual Cycle
Balance of 4 different hormones - Lueinizing hormone (LH), Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), Oestrogen, Progesterone
Avg cycle = 28 days
Menstruation (1 - 4 days)
Uterine bleeding, accompanied by shedding of the endometrium
Pre - Ovulation (5 - 12 days)
Endometrial repair beings, development of ovarian follicle, uterine lining gradually thickens
Ovulation (13 -15 days)
Rupture of mature follicle, maturing egg
Secretion (16 - 20 days)
Secretion of watery mucus by glands of endometrium, cervix and uterine tubes, movement and breakdown of unfertilised egg, development of corpus lutuem.
Pre - Menstruation (21 - 28 days)
Degeneration of corpus lutuem, deuterium of endometrium
Fertilisation
Fusion of two haploid gametes to form a single diploid zygote cell
Conception
Occurs when haploid nucleus of the egg fuses with that of the sperm forming, a diploid fertilised cell called a zygote
Following fertilisation the egg divides as it travels along the oviduct and begins developing into and embryo