Understanding Chemical Bonding and Its Properties
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outer shell of an atom.
Molecular Structure
Arrangement of atoms within a molecule.
Bond Properties
Characteristics affecting molecular properties.
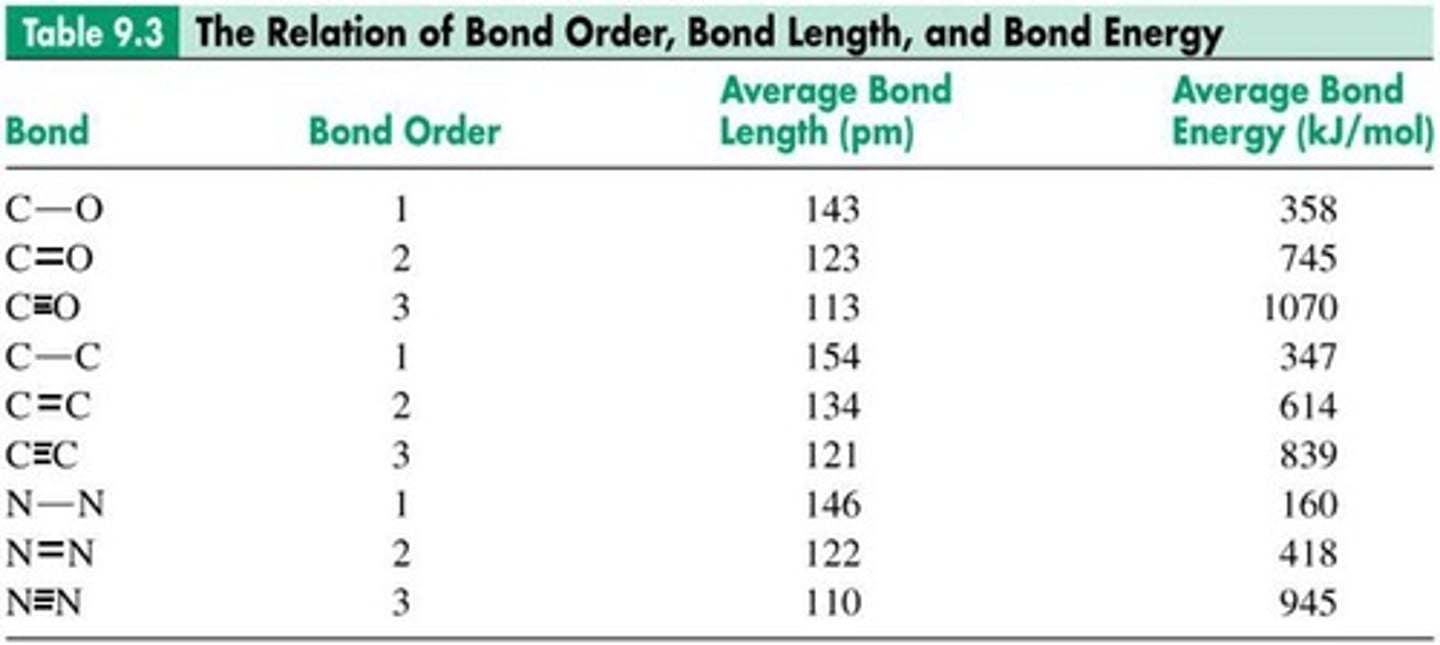
Bond Order
Number of bonding electron pairs between atoms.
Single Bond
One pair of shared electrons between atoms.
Double Bond
Two pairs of shared electrons between atoms.
Triple Bond
Three pairs of shared electrons between atoms.
Lewis Structure
Diagram showing bonds and lone pairs in molecules.
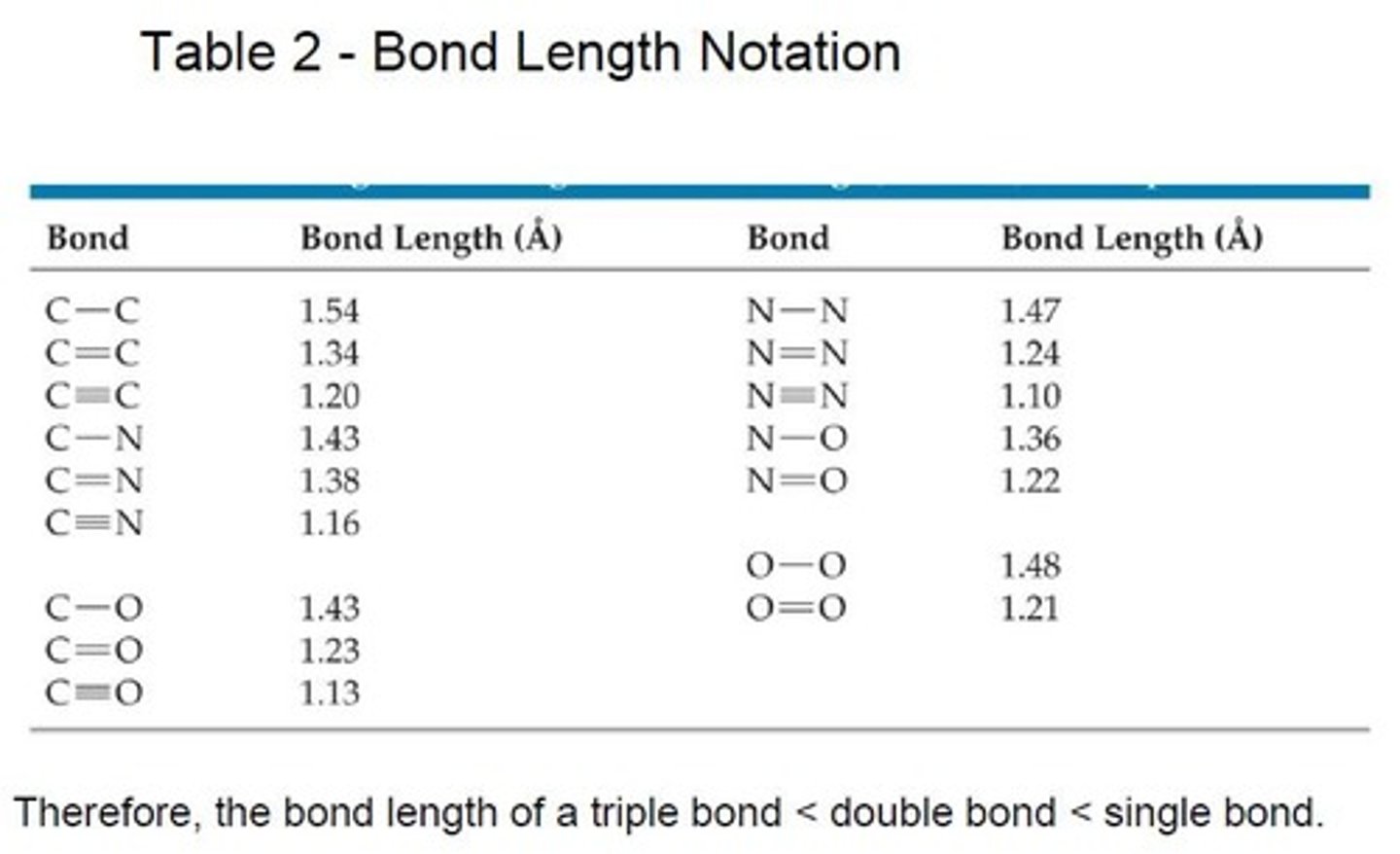
Bond Length
Distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms.
Covalent Radii
Half the distance between two bonded atoms' nuclei.
Bond Energy
Energy required to break a chemical bond.

Bond Dissociation Energy
Energy needed to break a specific bond.

Energy Input
Energy required to break chemical bonds.
Energy Release
Energy released when forming chemical bonds.
Net Energy Change
Difference between energy required and released.
Bond Length Measurement
Typically reported in picometers or nanometers.
Bond Length Calculation
Sum of covalent radii of bonded atoms.
Bond Stability
Higher bond order indicates greater bond stability.
Inversely Related
Shorter bonds require higher energy to break.
Bond Order Calculation
Total bonds divided by bond groups.
C-Cl Bond Length
Measured as 174 picometers in CCl4.
Chemical Reaction Steps
Bonds broken, then new bonds formed.
Bond Energy Correlation
Higher bond order correlates with shorter bond length.