Preliminary Biology NSW
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Complete Preliminary Biology NSW Syllabus
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
1
New cards
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
2
New cards
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
3
New cards
Cell wall
Surrounds plant, fungi and protist cells for protection
4
New cards
Cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
5
New cards
Cytoplasm
All fluids and organelles contained by the membrane
6
New cards
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
7
New cards
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
8
New cards
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
9
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesises and transports materials. Rough ER synthesises protein and has ribosomes on the surface, smooth ER is free of ribosomes and produces lipids and steroids
10
New cards
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
11
New cards
Lysosomes
Cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
12
New cards
Vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area
13
New cards
Ribosomes
Not membrane bound, synthesises proteins
14
New cards
Mitochondria
Stores and synthesises ATP. Powerhouse of the cell.
15
New cards
Chloroplasts
Contains chlorophyll, which traps energy from sunlight for photosynthesis and gives plants their green colour
16
New cards
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibres that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
17
New cards
Peroxisomes
Break down fatty acids and produce hydrogen peroxide
18
New cards
Plastids
A group of membrane‐bound organelles commonly found in photosynthetic organisms and mainly responsible for the synthesis and storage of food.
19
New cards
Cell theory
1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
3. Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
20
New cards
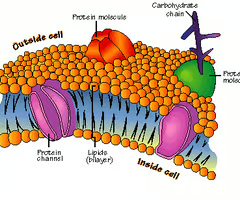
Fluid mosaic model
Describes the structure and function of ALL cell membranes --\> composed of a phospholipid bilayer
21
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
Diffusion of substances through the cell membrane via channel and carrier proteins. Does not require energy and goes along the concentration gradient
22
New cards
Simple diffusion
the movement of any molecule from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached
23
New cards
Osmosis
The movement of water from a high concentration of water to a low concentration of water across a semi-permeable membrane
24
New cards
Cell membrane permeability
Permeable to small neutral molecules. Hydrophobic molecules will diffuse across the membrane easier.
25
New cards
Protein pump active transport
Specific carrier proteins embedded in the membrane bind with and are able to transport small charged molecules. Requires ATP.
26
New cards
Endocytosis
transport of matter into the cell using vesicles that engulf particles
27
New cards
Pinocytosis
Endocytosis of liquids. Engulfing liquids into the cell
28
New cards
Phagocytosis
Endocytosis of a solid. Engulfing solids into the cell
29
New cards
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
protein receptors trigger endocytosis of specific molecules
30
New cards
Exocytosis
Transport of matter out of the cell using vesicles.
31
New cards
Remember EX because you want to get far away from your ex lol.
32
New cards
Surface area to volume ratio
The greater the SA:V ratio, the faster diffusion will occur.
33
New cards
inorganic compounds
A compound that does not contain the element carbon or contains carbon bound to elements other than hydrogen. E.g. water, oxygen, mineral ions and carbon dioxide
34
New cards
organic compounds
Compounds that contain carbon. E.g. carbohydrates, nucleic acids, vitamins, lipids and proteins.
35
New cards
Ions
Charged molecules
36
New cards
Photosynthesis general equation
carbon dioxide + water --\> glucose + oxygen
37
New cards
Respiration general equation
glucose + oxygen --\> carbon dioxide + water + ATP
38
New cards
Light dependent stage of photosynthesis
In the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, it is the splitting of water and release of oxygen, production of ATP and storage of electrons
39
New cards
Light independent stage of photosynthesis
In the stroma of chloroplasts, using ATP produced in the first stage, and glucose is formed.
40
New cards
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions. Proteins. They are substrate specific.
41
New cards
Catabolic reactions (enzymes)
Breaking down of a substance using enzymes
42
New cards
Anabolic reactions (enzymes)
combining of substances using enzymes
43
New cards
Factors affecting enzyme activity
Temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, substrate concentration
44
New cards
Enzyme inhibitors
substances that block some or all of the action of enzymes
45
New cards
Unicellular organisms
One cell, can survive on its own, obtains nutrients and gases through simple diffusion across surface
46
New cards
Hierarchical structure of organisms
Organelles make up cells which make up tissues which make up organs which make up systems which make up organisms
47
New cards
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food (usually via photosynthesis)
48
New cards
Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food and must consume it.
49
New cards
Stomates
Openings in leaves to exchange photosynthetic gases: water vapor, carbon dioxide, and oxygen
50
New cards
roots
Absorbs water and minerals from the soil. Anchors plants in the ground.
51
New cards
Xylem
Transports water and minerals from the roots up the plant
52
New cards
Phloem
Transports food up and down the plant.
53
New cards
gas exchange structures in fish
Oxygen diffuses into gills when water washes over them. At the same time, carbon dioxide diffuses out.
54
New cards
Gas exchange structures in amphibians
Uses the lungs, the lining of the mouth and the skin's surface for gas exchange
55
New cards
gas exchange structures in humans
Occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. Oxygen diffuses into the capillaries and binds to the haemoglobin of red blood cells. Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the capillary.
56
New cards
Physical digestion
Physically breaking down food into smaller pieces, occurs by chewing in the mouth and peristalsis of the stomach
57
New cards
Chemical digestion
Digestive enzymes break down food into absorbable molecules. Most chemical digestion occurs in the stomach and small intestine but the process starts in the mouth with the enzyme amylase from saliva which begins breaking down carbohydrates
58
New cards
Absorption
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of the digestive system into the blood to be transported around the body.
59
New cards
Components of blood
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, plasma
60
New cards
Open transport system
No heart or system of closed tubes. Haemolymph is used as the medium for transport.
61
New cards
closed transport system
No openings, consists of heart, arteries, capillaries and veins
62
New cards
Arteries
carry blood away from heart; oxygenated except for pulmonary circulation
63
New cards
Veins
Carry blood deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Oxygenated for pulmonary circulation.
64
New cards
Fossils
The preserved remains or traces of organisms that once lived on Earth.
65
New cards
Theory of natural selection
1. Survival of the fittest
2. Individuals will pass on genetic material to offspring
3. Individuals vary in terms of structure, behaviour and physiology
66
New cards
Adaptations
Features that allow organisms to survive and reproduce. they can be structural, behavioural and physiological.
67
New cards
Selection pressures
Any environmental change that affects individuals in a population. Individuals with variations that enable them to survive under changing conditions have a selective advantage.
68
New cards
Convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
69
New cards
Divergent evolution
When two or more species sharing a common ancestor become more different over time
70
New cards
Evidence for evolution
Fossils, biogeography, comparative anatomy/embryology, biochemistry
71
New cards
Pangaea
The name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today's continents.
72
New cards
Biodiversity
Variety of life
73
New cards
Keystone species
A species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem
74
New cards
Niche
The role an organism plays within an ecosystem
75
New cards
Abundance
the number of individuals in a population
76
New cards
Distribution
The areas where the organism is found
77
New cards
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed
78
New cards
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
79
New cards
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
80
New cards
Allelopathy
The production of chemicals by plants that inhibit the growth of neighbouring plants
81
New cards
Decomposer
Break down chemical energy of dead organic matter into simpler forms so it can be used as nutrients for other organisms. E.g. fungi and bacteria
82
New cards
Human impacts
Introduced species (cane toads), pollution, deforestation, land clearing, management of waterways, roadkill, overharvesting, global warming
83
New cards
Food web
A community of organisms where there are several interrelated food chains
84
New cards
Abiotic factors
Non-living components of environment. E.g. light, water pressure, humidity, oxygen availability, salinity
85
New cards
Biotic factors
living parts of an ecosystem e.g. plants, animals
86
New cards
Sclerophyll plants
Vegetation adapted to long periods of dryness and heat. They have adapted with hard leaves, leaves parallel to sunlight and short internodes
87
New cards
Prickly pear adaptations
Shallow roots, sharp spines, flattened leaves, thin stem
88
New cards
interspecific competition
competition between different species
89
New cards
intraspecific competition
competition between individuals of the same species
90
New cards
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
91
New cards
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
92
New cards
Hypertonic solution
High concentration of solute compared to cell. Causes cell to shrivel
93
New cards
Hypotonic solution
Low concentration of solute compared to cell. Causes cell to burst.
94
New cards
Isotonic
Same concentration of solute in solution and cell
95
New cards
spongy mesophyll
loosely packed, irregularly shaped cells with spaces around them located below the palisade mesophyll. Wide gaps to facilitate gas exchange
96
New cards
palisade mesophyll
under the upper epidermis; high concentration of densely packed chloroplasts; where most photosynthesis takes place
97
New cards
Heart
A hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
98
New cards
induced fit model
Change in the shape of an enzyme's active site that enhances the fit between the active site and its substrate(s)
99
New cards
lock and key model
The model of the enzyme that shows the substrate fitting perfectly into the active site. Less correct.
100
New cards
Transpiration cohesion tension theory
Explains how water flows up the xylem of plants. Involves, transpiration drawing water through the leaf from the stomata and cohesion & adhesion which help draw water up the xylem