CR Lecture 5 - Developmental Robotics
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Developmental Robotics Principles
Development as a Dynamical System
Phylogenetic and Ontogenetic Interaction
Embodied and Situated Development
Intrinsic Motivation and Social Learning
Nonlinear, Stage-Like Development
Online Open-Ended Cumulative Learning
Bifurcation points
A value of the parameter that causes a change in the nature of the equilibrium
Dynamical Systems
Systems whose state evolves over time characterised by:
Decentralised system
Self-organising and emergence
Multi-causality
Nested timescales
Dynamical Systems: Decentralised System
Behaviour determined by many factors, not one central factor. Central factor would be brain
Many behaviours determined by local interactions (environment, internal state)
Dynamical Systems: Self-organising and emergence
Many mechanisms that organise themselves in such a way that creates the stable state of the child
Emergence: emerges from three elements
Environment, body shape, brain
Dynamical Systems: Multi-causality
Many causes that explain the behaviour
In the walking: water, environment, maturation, movement etc
Dynamical Systems: Nested timescales
Fast timescale for producing behaviour (100s of ms) time taken for neuron to move a muscle
Maturation
Changes in physical structure of the body and the brain
Critical period
A critical period is a time during early postnatal life when the development and maturation of functional properties of the brain, its “plasticity,” is strongly dependent on experience or environmental influences.
Example: Language development can’t be native speaker after critical period
Duckling responding to person like it’s their mother
Phylogenesis and Ontogenesis
Phylogenesis: Evolution
Ontogenesis: development in lifetime
Maturation
Critical period
Learning
Embodied and Situated
Embodiment: Body-brain-environment interaction
Situatedness: learning in context
Enaction: own model of the world
Morphological computation
Grounding
Intrinsic Motivation and Social Learning
Reasons for wanting to learn
Intrinsic motivation:
Curiosity
Instinct to learn about anything that is new
Surprise
Novelty-seeking
Values
Drives
Social learning and imitation
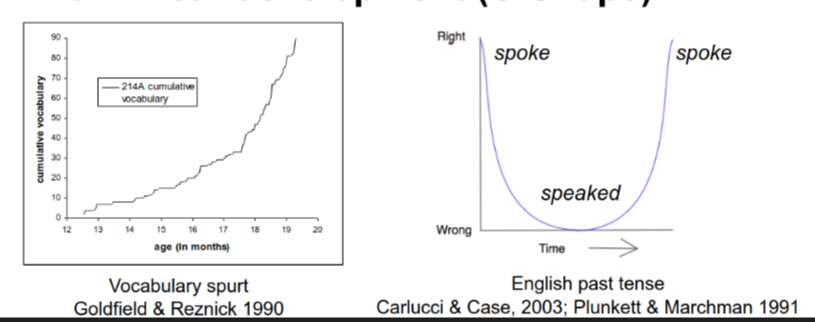
Nonlinear, Stage-like development
Developmental milestones
Qualitative stages (Piaget)
Non-linear development (U-shape)
Fast mapping
Say “kiwi” once, I learn kiwi
Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development
Sensorimotor stage (Birth to 2 yrs)
Think about doing things, don’t reason logically or internally
Preoperational stage (2 to 7)
Practical logic
Concrete operational stage (7-11)
Bit more formal
Formal Operational Stage
Equations… formal logic
Online, Open Ended, Cumulative
Idea you never stop learning
Online learning
Learn when you do things
Cumulative (add through linear or non-linear stages)
Cognitive bootstrapping
Can speed up performance by re-arranging my strategy
Cross-modality