AP Human Geography Chapter 1
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Geographers
Identify locations of important places and explain why human activities are located beside one another.
Historians
Identify dates of important events and explain why human activities follow one another chronologically.
5 Themes of Geography
Place, region, scale, space, and connection
Place
A specific point on Earth, distinguished by a particular characteristic. Every place occupies a unique location, or position, on Earth’s surface.
Region
An area of the Earth defined by one or more distinctive characteristics. Examples include South America, Middle East, etc.
Scale
The relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole. Can be local, global, or a variety of scales in between.
Space
The physical gap or interval between two objects.
Connection
The relationships among people and objects across the barrier of space, including cultural, political, and economic ties.
Map
A 2-D flat-scale model of Earth’s surface. Serves as a reference tool and/or communications tool.
Cartography
Art and science of mapmaking
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system that determines precise geolocation by using satellites, tracking stations, and a receiver in the device.
Geotagging
Identification and storage of a piece of information by its precise latitude and longitude coordinates.
Geographic Information Science (GIScience)
Analysis of data about Earth acquired through satellite and other electronic information technologies.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
Captures, stores, queries, and displays the geographic data gained through GIScience.
Remote Sensing
Use of satellites or other long distance data collection methods to scan and map Earth’s surface. Satellites scan small areas (pixels). Pixels are combined into grids to create maps.
Volunteered Geographic Information (VGI)
Individuals create and share geographic information for the purpose of mapping.
Citizen Science
Research by amateur scientists.
Participatory GIS (PGIS)
Community-based mapping
Mashup
Overlays data from one source on top of a map provided by a mapping service such as Google maps.
Application Programming Interface (API)
Allows individuals to create their own mashups.
What do cartographers have to decide when making a map?
The map’s scale and projection.
Projection
Transferring locations on Earth’s surface to a flat map.
4 Types of distortion
Shape, distance, relative size, and direction.

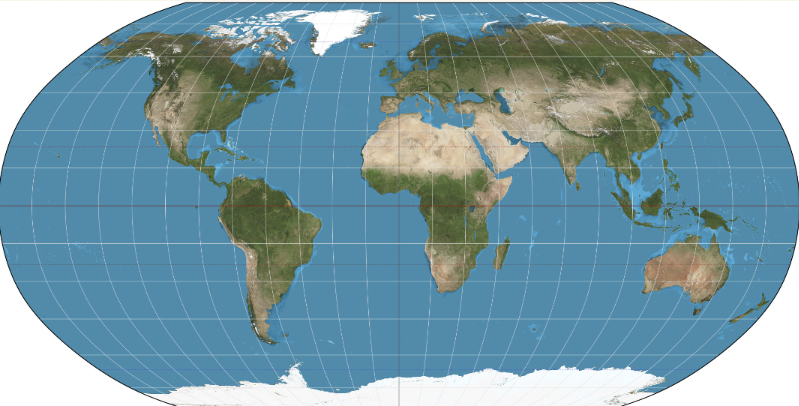
What projection is this?
Equal-Area Projection
Characteristics of Equal-Area Projections (4)
Minimizes distortions.
Does distort areas near the poles.
Eastern and Western Hemispheres are separated.
Meridians and parallels don’t form right angles.
What projection is this?
Robinson Projection
Characteristics of Robinson Projections (2)
Better for displaying information across oceans
Distorts the size of land masses
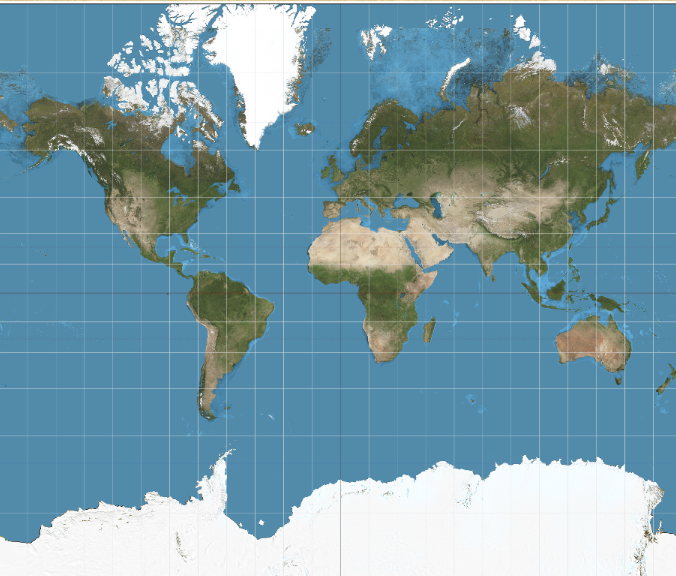
What projection is this?
Mercator Projection
Characteristics of Mercator Projections (2)
Little distortion of shape or direction.
Distorts areas around the poles greatly.
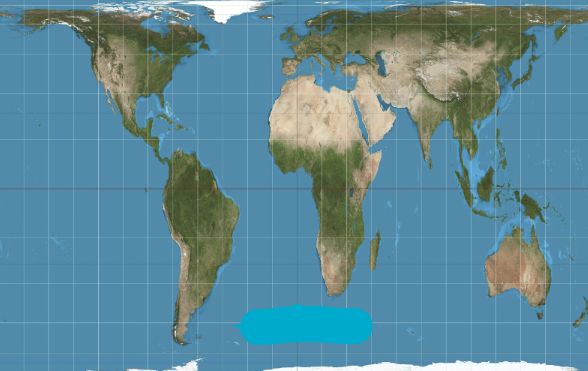
What projection is this?
Gall-Peters Projection
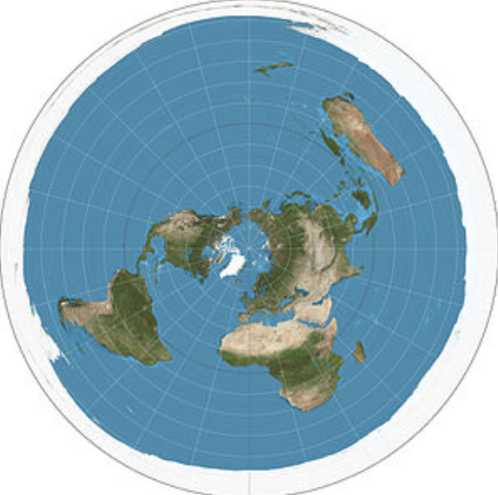
What projection is this?
Polar Projection
Thematic Maps
Depict data or information about a place.
Kinds of Thematic Maps (5)
Choropleth
Dot Map
Graduated Symbol Map
Isoline Map
Cartogram
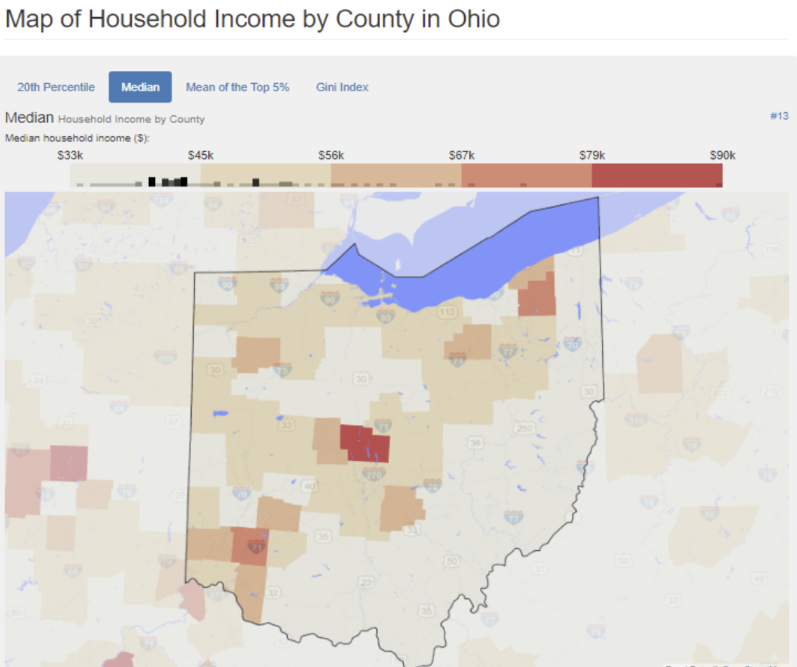
What kind of thematic map is this?
Choropleth
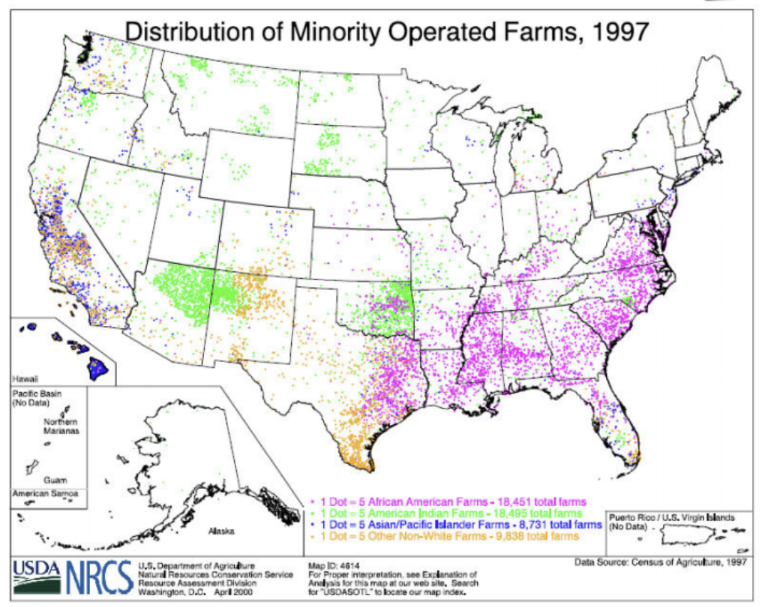
What kind of thematic map is this?
Dot Map
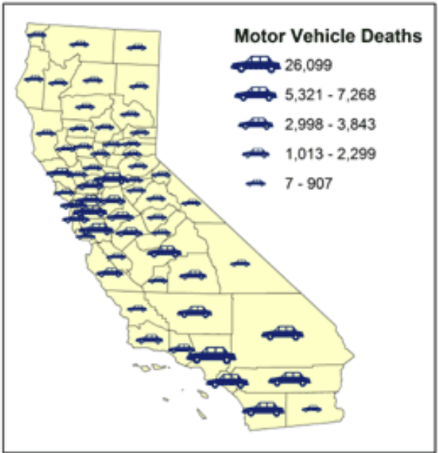
What kind of thematic map is this?
Graduated Symbol Map
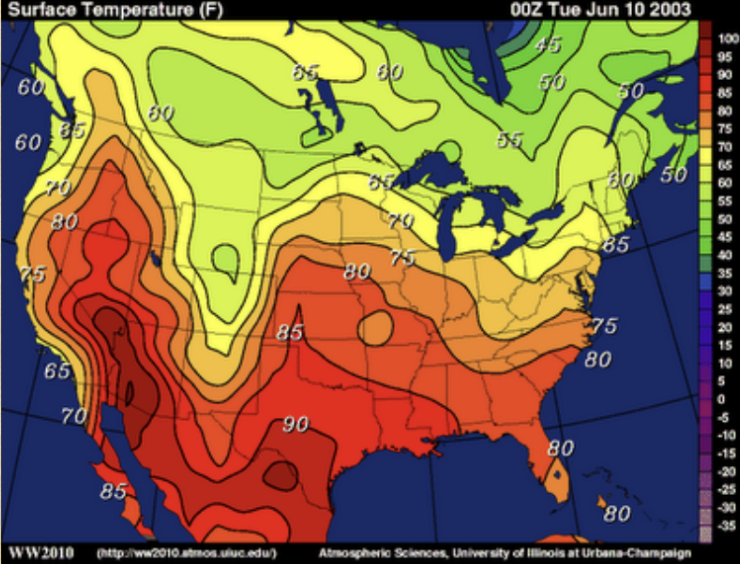
What kind of thematic map is this?
Isoline Map
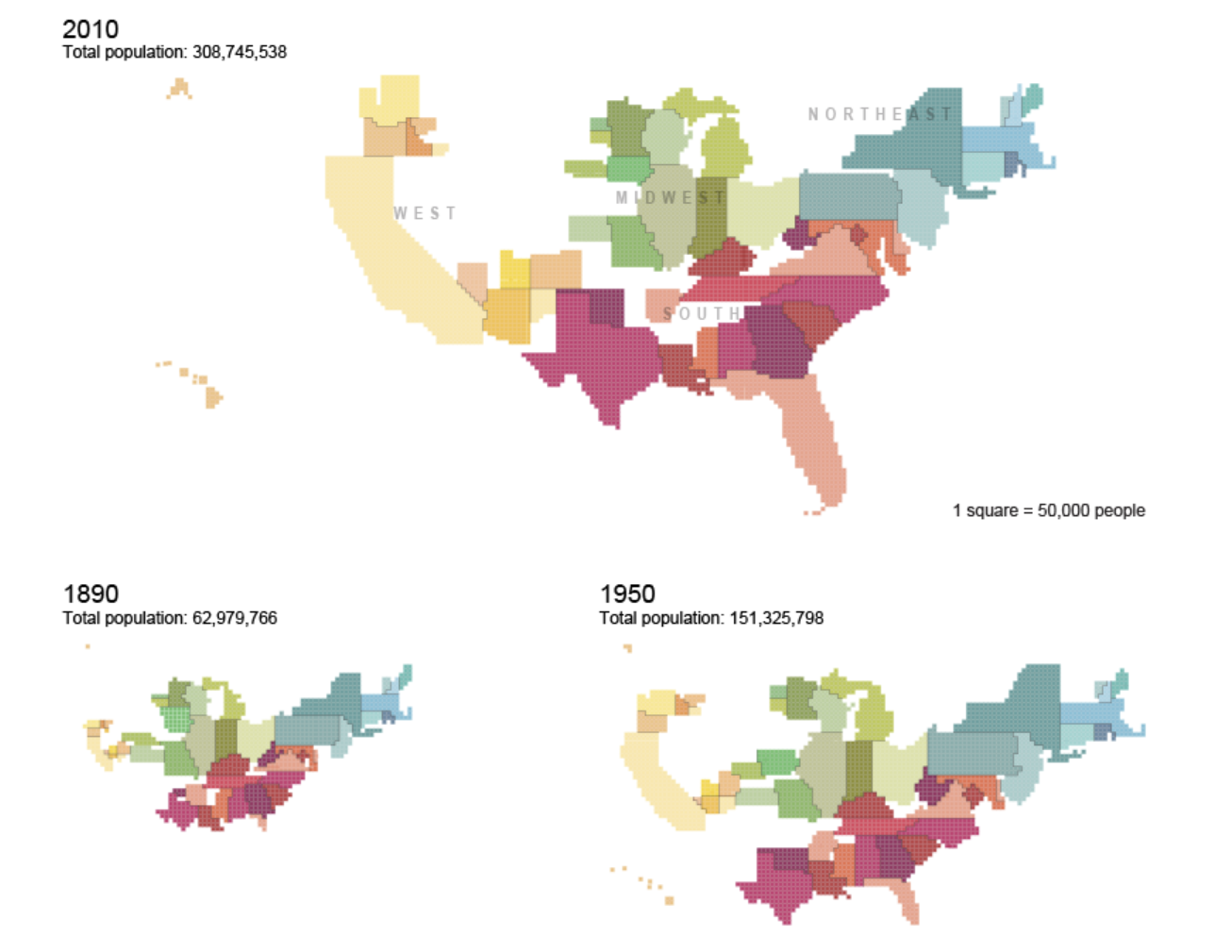
What kind of thematic map is this?
Cartogram
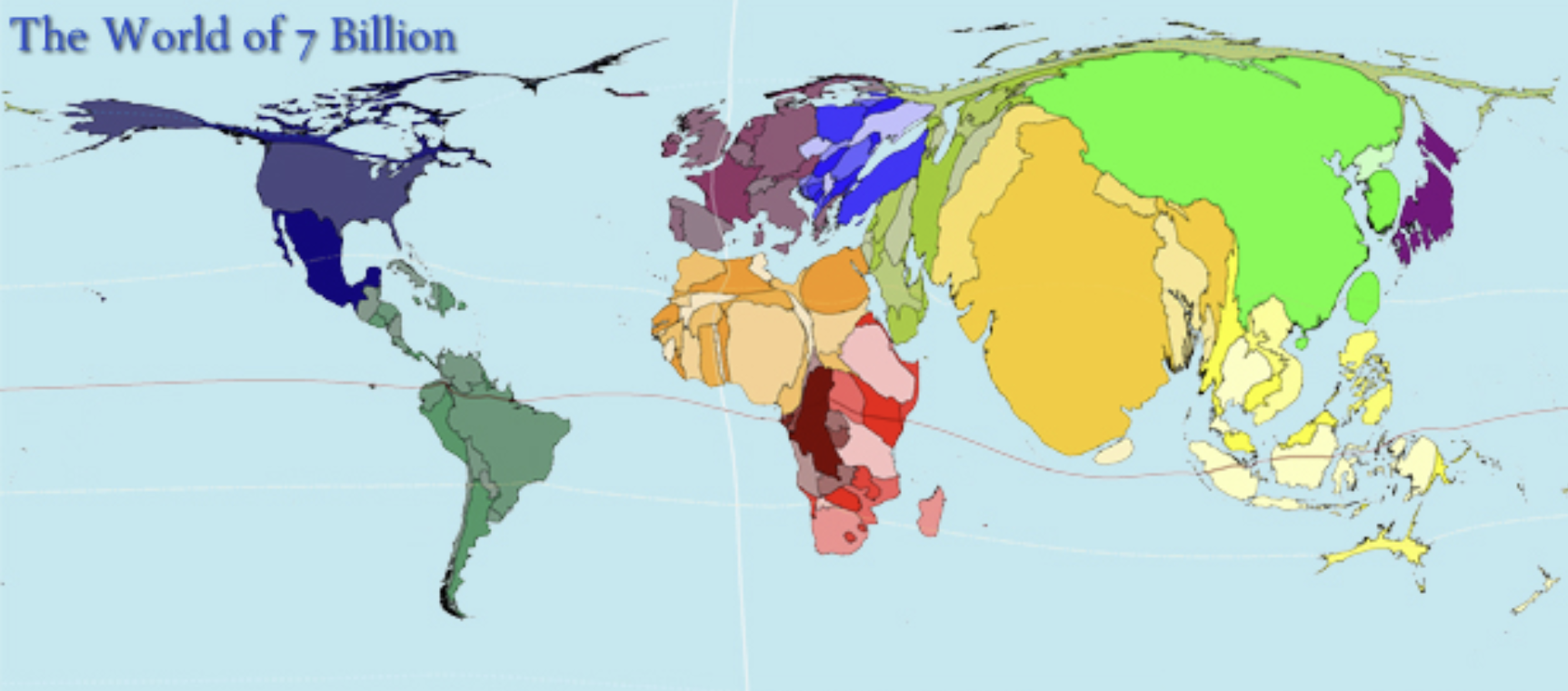
What kind of thematic map is this?
Cartogram
Reference Maps
Help identify locations of various features.
Kinds of Reference Maps (2)
Physical: shows landforms
Political: governmental boundaries
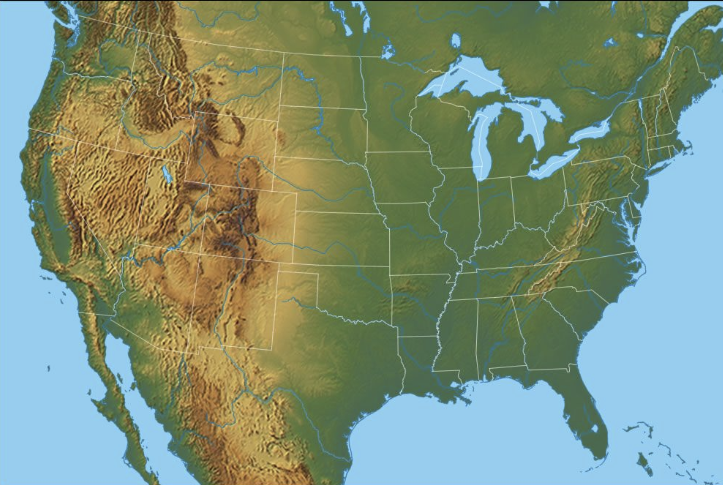
What kind of reference map is this?
Physical Map

What kind of reference map is this?
Political Map
Geographic Grid
Imaginary lines drawn on Earth’s surface for the purpose of navigation and telling time.
Meridian
Vertical lines running between the North and South poles.
Longitude
Numbering system used to identify locations of meridians. (Vertical)
Parallel
Circular lines drawn around the globe parallel to the equator and perpendicular to the meridians.
Latitude
Numbering system used to identify location of parallels. (Horizontal)
Prime Meridian
Meridian that passes through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England. Forms 0° longitude.
Equator
Line drawn around the globe. Forms 0° latitude.
Greenwich Mean Time
Master reference for all time zones
How many degrees east or west of Greenwich represent 1 hour difference.
15°
Regionalization
Dividing space into units for analysis, can be based on a number of criteria.
Region
An area on Earth defined by one or more distinctive characteristics.
Cultural Landscape
Combination of cultural features such as language, religion, agriculture, industry, and physical features.
3 Types of Regions
Formal
Functional (nodal)
Vernacular (perceptual)
Formal Region
An area where everyone shares one or more distinctive characteristics.
Functional Region
Area organized around a node or focal point, the characteristic defined by the central node decreases in importance the farther one travels from it.
Vernacular Region
An area that people believe is part of their cultural identity.
Regionalism
A group’s perceived identity with a region.
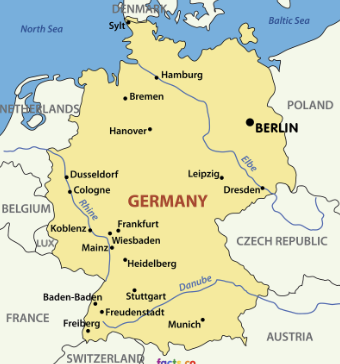
What type of region is this?
Formal Region
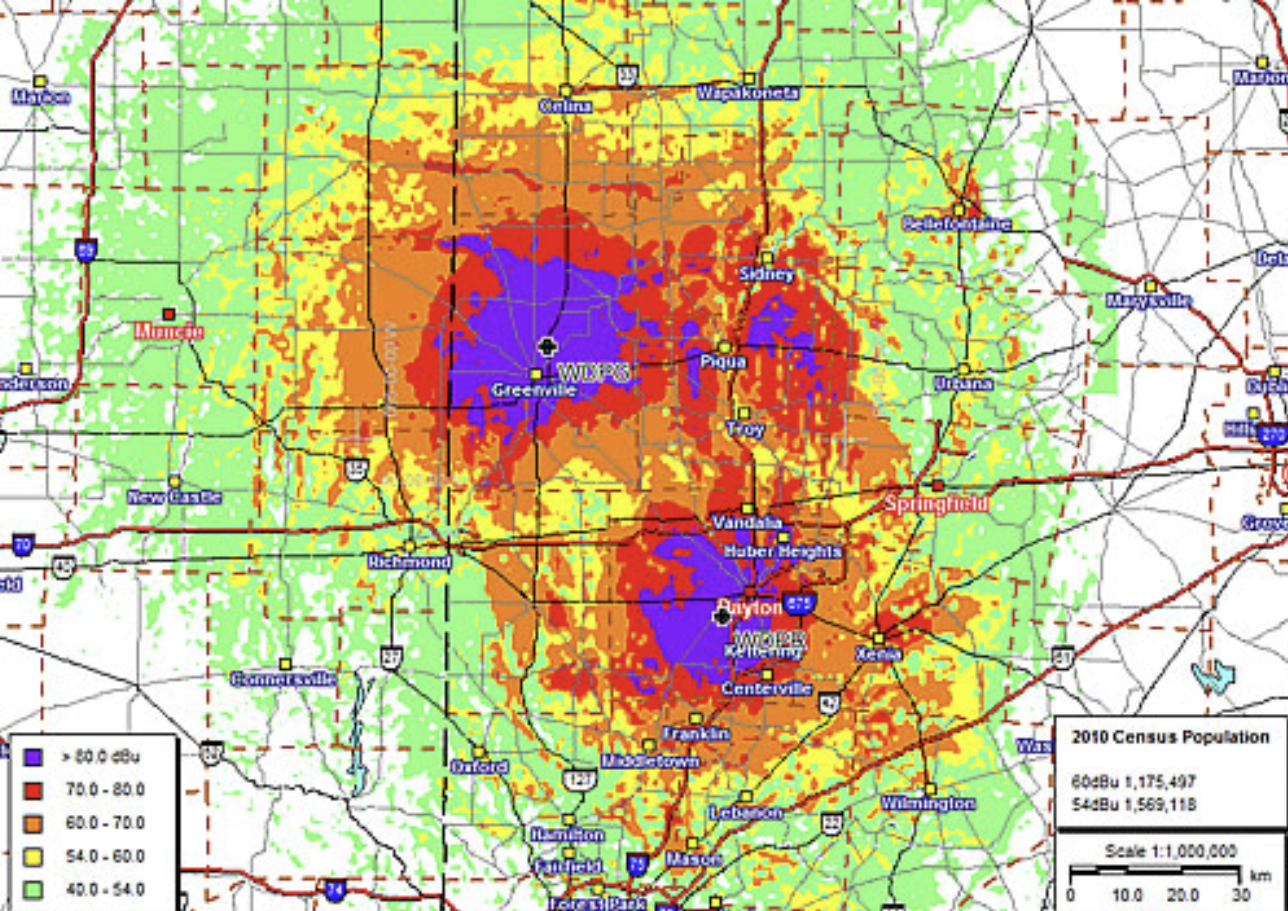
What type of region is this?
Functional or nodal region

What type of region is this?
Vernacular Region
Spatial Association
The distribution of one feature is related to the distribution of another.
Globalization
Force or process that involves the entire world and results in making something worldwide. -Certain areas are known for certain resources.
Transnational Corporations
Large companies that do business all over the world.
Density
Frequency with which something occurs in space.
Concentration
Extent of a feature spread over space.
Pattern
Geometric arrangement of objects in space.
Poststructuralist Geography
Those in power use their power to discriminate or dominate certain groups of people.
Humanistic Geography
Distribution and concentration of people in a place can be explained by the meaning that those people attach to the place.
Behavioral Geography
Emphasizes the importance of understanding the psychological basis for individual human actions in space.
Assimilation
The culture of one people comes to resemble the culture of another.
Acculturation
Cultural changes as a result of two groups interacting. Both retain their own individual cultural identity.
Syncretism
Two groups come together to form a new culture.
Diffusion
The process by which a feature spreads across space from one place to another over time.
Relocation Diffusion
Spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another.
Expansion Diffusion
Spread of a feature from one place to another in an additive process.
Contagious Diffusion
Rapid spread of an idea or trend. Think of it as something “going viral”
Stimulus Diffusion
Spread of a principle or concept without the characteristic itself spreading.
Space Time Compression
The time it takes for something to reach a place, being reduced over time.
3 Pillars of Sustainability
Environment
Society
Economy