Cell membranes
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
three primary body cavities
cranial cavity
thoracic cavity
abdominopelvic cavity
Physical isolation
physical barrier separating ICF and ECF
Regulation of exchange with the enviornment
controls entry, elimination and release of things into/out of the cell
Communication
contains proteins that allow for responding or interacting with the external environment
structural support
proteins in the membrane are used to make cell to cell connections and to anchor the cytoskeleton
What is the rule for how much protein a cell membrane contains
the more metabolically active the membrane is the more protein in contains
What are the three types of lipids in the cell membrane
phospholipid
sphingolipids
cholestrol
Phospholipids
form bilayers, micelles or liposomes
tails are hydrophobic and heads are hydrophillic
amiphipathic
having one region that is hydrophobic and one region that is hydrophillic
Cholestrol
increases viscosity (holds it together, strength)
decreases permeability (doesn’t allow as much in)
what is the current model of membranes
the fluid mosaic model
intergral protiens
transmembrane protiens
lipid anchored protiens
protiens cannot be removed without disrupting the membrane
integral protiens role
membrane receptors
cell adhesion molecules
transmembrane movement
Peripheral protiens
usually attached to integral protiens
loosely attached to phospholipid heads
Peripheral Protien roles
participate in intracellular signaling
form submembraneous cytoskeleton
lipid rafts
groups of protiens and sphingolipids that stay together with a high cholestrol content
glycoprotiens
protein with a carbohydrate attached, always extracellular
forms a protective coat and helps with cell-cell recogntion/interaction
glycolipid
lipid with a carbohydrate attached, always extracellular
forms protective coat and helps with cell to cell interactions
cell to cell recognitions
identifying whether or not cells are foreign
what % of the human body is made up of water
60%
adipose tissue
90% lipids, majority triglycerides
small fraction water
skeletal muscle
75% water
18% protein
what can change total water content
age, sex and body fat composition can alter total water content in the body
osmotic equalibrium
fluid concentration are equal, the amount of solute per volume of solution
osmosis
the movement of water across a membrane in response to a solute concentration gradient
moves from a low concentration to a high concentration
aquaporin channels
proteins in membranes that have a small pore to allow water to move in and out of the cell freely
What ions are high in extracellular fluid
Na+
Cl-
Ca2+
HCO3 -
what ions are high in intracellular fluid
K+
Anions
Protiens
Osmotic pressure
means of quantifying the driving force of water to move to a higher concentration
Osmolarity
describes the number of particles in solution
isoosmotic
solutions have identical osmolarities
hyperosmotic
solution with the higher molarity
hyposmotic
the solution with the lower osmolarity
tonicity
describes a solution and how that solution would effect cell volume if a cell were placed in a solution
hypotonic solution
solution has a low concentration, causing the cell to swell
isotonic solution
solution has an identical concentration as the cell, causing the cell to stay the same
hypertonic solution
solution has a higher concentration, causing the cell to shrink
what is the difference between osmolarity and tonicity
osmolarity depends on the nature of the solutes, the overall solute concentration of a compartment
tonicity depends on the concentration of non penetrating solutes, solution concentration relative to a cell
Osmoality
osmoles per kg of solvent
selectively permeable
what crosses depends on the properties of the cell membrane and the substance
diffusion
the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration g
general properties of diffusion
uses kinetic energy of molecular movement
continues until concentrations come to equilibrium
can take place in an open or closed system
what makes diffusion faster
along higher concentration gradients
over shorter distances
at higher temperatures
for smaller molecules
what makes the rate of diffusion across a membrane faster
the membranes surface area is larger
the membrane is thinner
the concentration gradient is larger
the membrane is more permeable to the molecule
what does membrane permeability depend on
the molecules lipid solubility
the molecules size
the lipid composition of the membrane
what is simple diffusion used for
small uncharged lipophilic molecules such as O2 CO2 NH3 Lipids and steroids
ficks law
rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the surface area x concentration gradient x membrane permeability
Protien mediated transport
for molecules that cannot cross the membrane via simple diffusion
Channel protiens
mad of membrane spanning protien subunits that create a cluster of cylinders with a pore through the center
gated channel types
chemically gated
voltage gated
mechanically gated
what is selectivity determined by
the size of the pore and the charge of the amino acids lining the pore
Carrier proteins
large complex proteins that change formation to move molecules. they can move small organic molecules that cannot pass through channels
uniport carriers
carrier protiens that only transport one kind of substrate
symport carriers
carrier protiens that move two or more substrates in the same direction
antiport carriers
move substrates in opposite directions
Facilitated diffusion
diffusion that is facilitated by the use of a protein
Active transport
move molecules against their concentration gradients from an area of low concentration to high concentration
always by carrier proteins
primary active transport
energy to move molecule comes directly from hydrolyzing ATP (ATPase)
secondary active transport
uses the potential energy stored in the concentration gradient of one molecule to push another molecule against their concentration gradient
High affinity binding
means that the binding sites are very sticky and will grab on to an ion no matter how hard it is
Low affinity binding
binding sites that dont care as much to grab onto ions and will only do so if the ions bump into them
specificity
the ability of a transporter to move one molecule or a closely related group of molecules
Competition
a carrier may move several members of a related group of substances but these substances compete with eachother
saturation
rate of transport depends on concentration and number of transporters. when the transporters are completely full
transport maximum
where saturation occurs. all of the carriers are in use and they cannot move any more
Phagocytosis
creates vesicles by rearranging the cytoskeleton
steps for phagocytosis
encounters a bacterium
phagocyte uses cytoskeleton to push its cell membrane around the bacterium
the phagosome separates from the membrane and moves into the cytoplasm
the phagosome fuses with lysosomes containing digestive enzymes
bacterium is killed by the enzymes
pinocytosis
allows ECF to enter freely, non selective type of endocytosis
receptor mediated transport
wants a specific substance in the cell, selective type of endocytosis
steps for endocytosis
ligand binds to membrane receptor
migrates to clathrin-coated pit
pit begins to close and move into the cytosol
vesicle loses clathrin coat
receptors and ligands seperate
ligands go to lysosomes or golgi for processing
transport vesicle with receptors moves to the cell membrane
Exocytosis
transport vesicle and cell membrane fuse, then the pit opens and releases substances
can occur continuously or intermittantly
epithelial transport
substances entering and exiting the body or moving between compartments often must cross a layer of epithelial cells
absorption
things moving from the lumen of the organ to the extracellular fluid
secretion
things moving from extracellular fluid to lumen of the organ
transcellular epithelial transport
across the epithelial wall, either freely diffusing or protien mediated
paracellular epithelial transport
between tight junctions, depends on how tight the junctions are. does not require ATP
transcytosis epithelial transport
for larger substances that need to pass the epithelial wall. uses endocytosis, vesicular transport and exocytosis
apical surface
outer membrane of the epithelial layer, facing the lumen
basolateral membrane
mix between the basal and lateral membranes
major ions
intracellular: K+ and phosphate ions and protiens
extracellular: Na+ and Cl-
the law of conservation of electrical charge
net amount of charge produced in any process is zero, for every positive charge on an ion there is an electron on another ion
conductor
the material through which positive and negative charges can move towards one another
insulator
the material separating the charges
membrane potential
the electrical disequilibrium that exists between the ECF and ICF
electrochemical gradient
the combination of electrical and concentration gradients
equilibrium potential
the membrane potential that directly opposes the concentration gradient
nernest equation
measures the equilibrium potential for a single ion. assumes that ions can cross the membrane freely
resting membrane potential
the membrane potential of a cell when it is not active
voltmeter
measures the difference between two electrodes in teh CIF and the ECF
resting membrane potential range in excitable cells
ranges from -40 to -90 mV
Sodium Potassium pump
sets up concentration gradients that determine membrane potential
3 Na+ out/ 2 K+ in
maintains the concentration gradients
pump is considered electrogenic as it generates a negative intracellular charge
disturbance of membrane potential
the concentration gradients of different ions across of the membrane
the permeability of the membrane to those ions
depolarization
if the membrane potential becomes less negative than the resting potential
repolarization
returning from a depolarized state
hyperpolarization
if the membrane potential becomes more negative
Hyperkalemia
increased blood K+ concentration that brings the membrane closer to the threshold
hypokalemia
decreased blood K+ concentration, hyperpolarizes the membrane
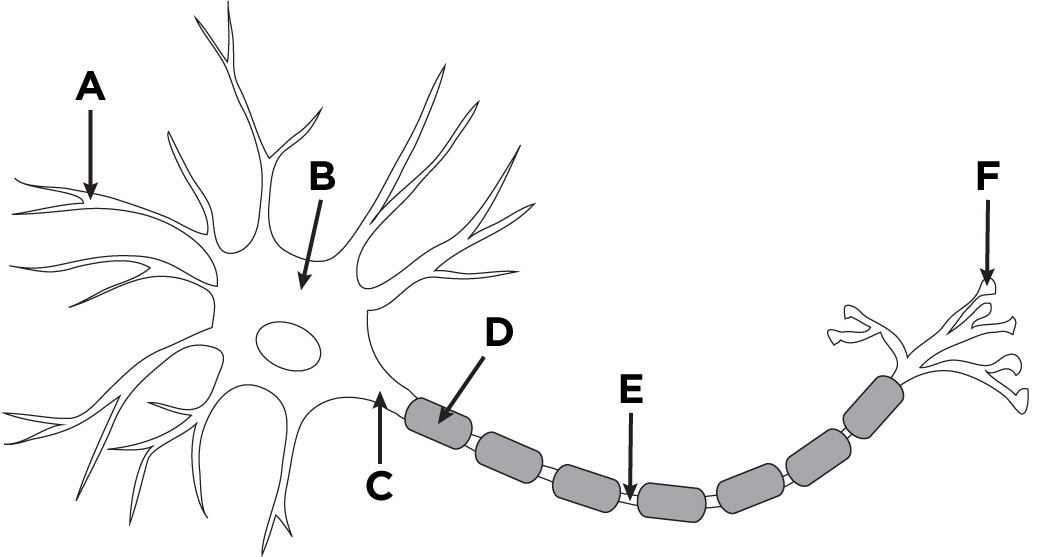
Label the things on this neuron
A - dendrite
B - soma
C- axon
D- myelin
E - gap between myelin sheaths
F - axon terminal