Radiographic Quality Assurance & Processing
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What does acceptance testing typically involve?
Vendors, biomedical engineers, and the PACS administrator
What are the three tests that need to be performed for acceptance testing?
image erasure test
phantom image test
visual check
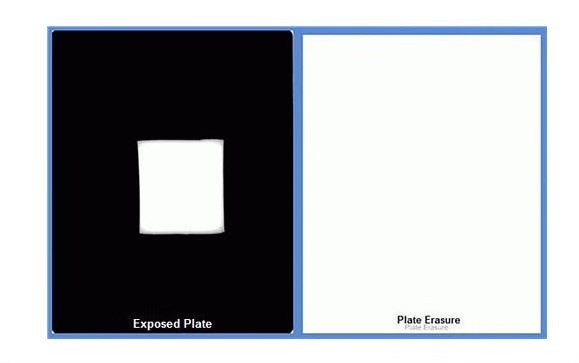
Image Erasure Test
ensures the photostimulable phosphor plate (PSP) is completely erased
shouldn’t see any residual or ghost image on the PSP
appear as a uniform, blank image
Phantom image test
wide variety of phantoms are available (easy way to test equipment without exposing a real person)
digital imaging processor codes/software requires phantoms have to be more anthropomorphic (true anatomic shape similar to human characteristics)
allows for more accurate histogram and image data set
What other tests are also included in phantom image testing?
contrast evaluation
laser jitter (evaluates transport system)
measurements tool evaluation
exposure indicator calibration
linearity
noise
brightness uniformity
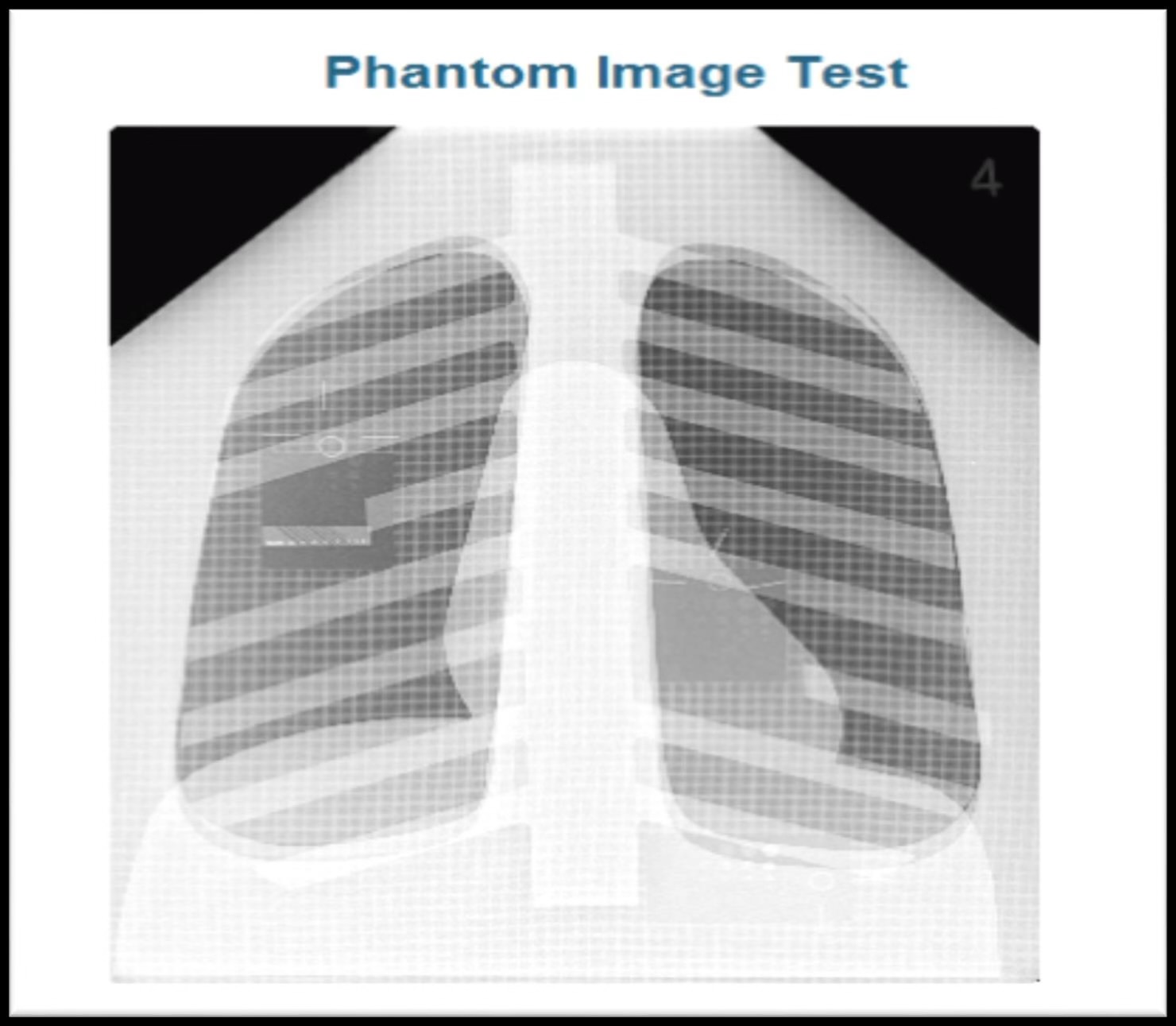
Found within this Phantom Image test of a chest x-ray are test tools that can also evaluate and measure _____ and _____
Contrast, noise
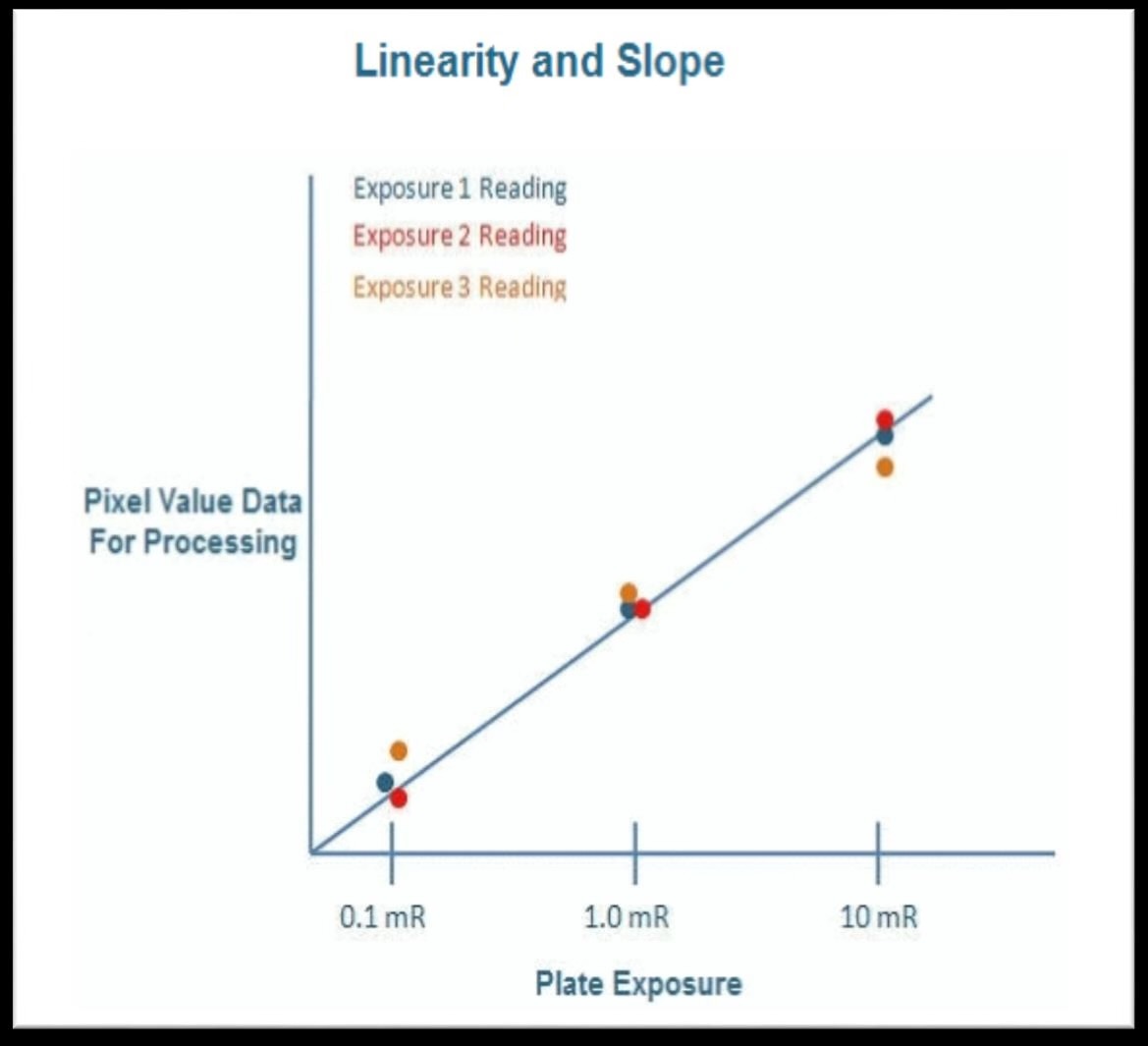
For linearity response, why must you use properly calibrated x-ray tibe along with filtration?
Ensures consistancy of tube output and qulaity of the x-ray beam (also use the same PSP plate thought the test)
What does linearity response measure?
The pixel values produced by separate exposures
What is the equiptment needed for exposure indicator calibration?
calibrated x-ray source and ionization chamber
assorted types and thickness of beam filtration materials
time
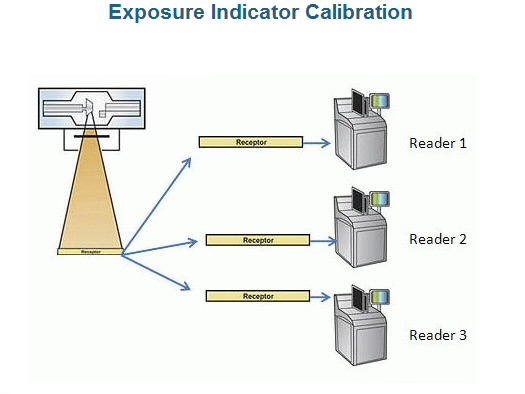
What is the best way to effectively monitor that patient dose is consistent?
By using exposure indicator calibration (PSP and readers)
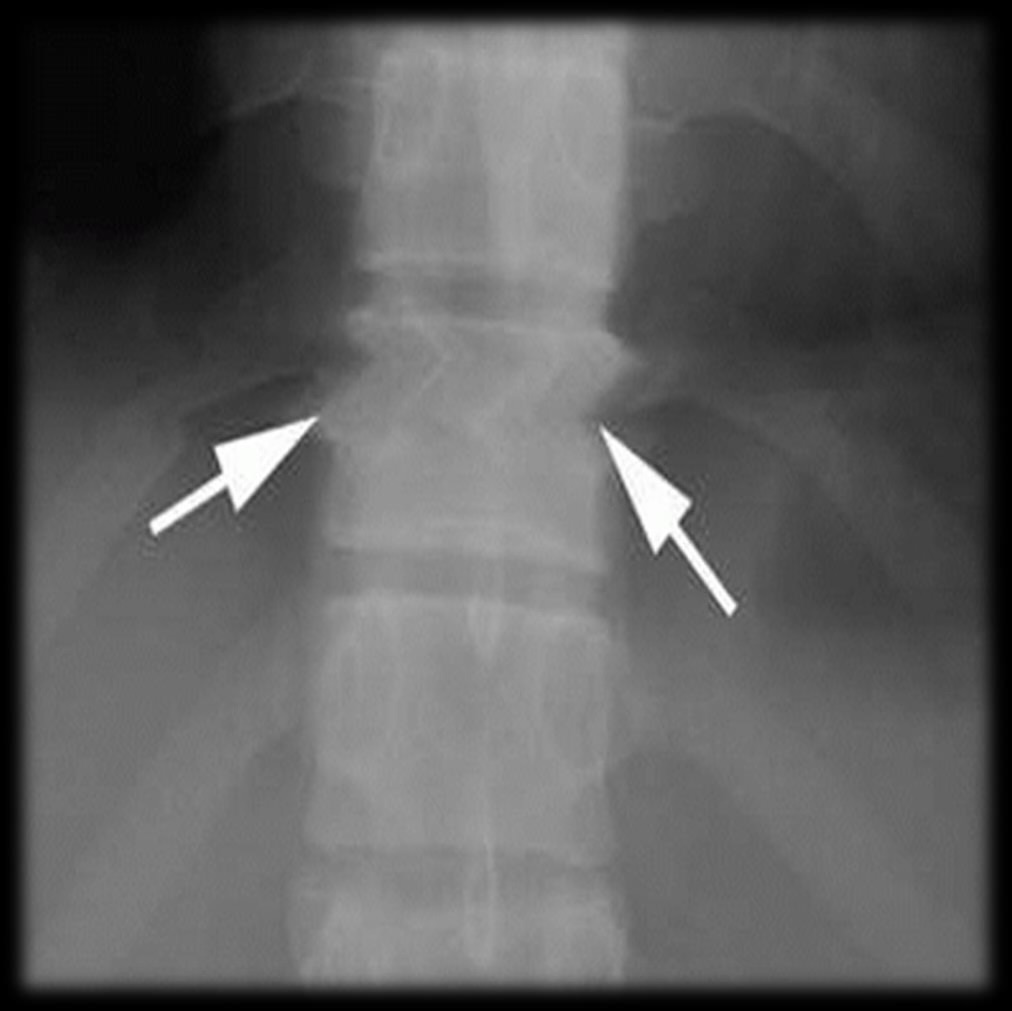
Laser jitter test
evaluates the transport system of a PSP plate reader
caused by artifacts when PSP is pulled into the plate reader
problem exists with the transport system
seen as a wavy band perpendicular to the direction of travel
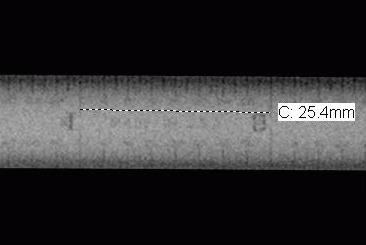
Measurement tool evaluation
evaluates how accurately the measurement tools are on either a diagnostic or technologist’s workstation
evaluates the measurements recieved at the workstation and those of the test tool located inside the phantom

Brightness uniformity (shading test)
ensures that the plate reader is functioning properly
measures pixel values across the plate
a variation of 10% (+/ -) in pixel value is allowed
Visual check
final check to be performed (PSP) plates
visually inspect PSP’s for cracks, scratches, etc

Besides radiographic equiptment and PSP plates, what else might need to undergo initial acceptance testing?
PACS
laser printers
Besides upon initial start up, QA tests should also be performed ______ or whenever you are having problems with image quality
Yearly
Test the modality wordlist to ensure that all required patient data is being transferred from radiology information system to the ___________ (DOB, referring physician, MRN, accession #)
Hospital information system (HIS)

What does acceptance testing of laster printers require?
initial calibration
QC tests
For acceptance testing of laser printers initial calibration, you print the range of densities and a ______ is used to compare this printed film to the expected outcomes
Densitometer
What components of a digital imaging system require routine evaluation?
monitor
technologist workstation
PACS workstation
PSP plate
PSP plate reading device
flat-panel receptor/detector
What are the other QA test tools?
light-field-radiation congruency
timer accuracy
beam allignment
focal spot
resolution
reproducibility, reciprocity, linearity
Light-field radiation congruency
light-localized, variable aperture rectangular collimators should be provided
cones and diaphragms may replace the collimator for special exams
the radiation field and the light field must coincide to within 2% of the SID

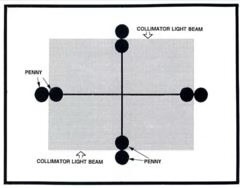
What can you test light-field radiation field congruency with?
collimator test tool
penny test
Timer accuracy QC
Exposure time directly affects the total quantity of radiation emitted from tube. Must have accurate exposure time
Maximum allowable variation for the exposure timer is:
± 5% for exposures over 10 ms
± 20% for exposures less than 10 ms
What is the timer accuracy QC determined by?
manual spinning top test
synchronous spinning top test
digital x-ray timer (1 or 3)
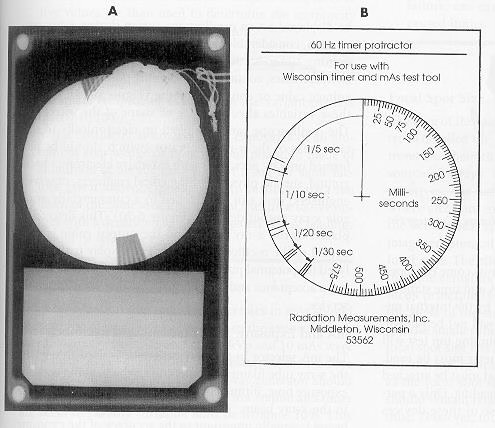
Spinning top test on single-phase equipment
dots are compared to the number that the particular time station should produce for that exposure
half wave: exposure time (seconds) x 60
full-wave: exposure time (seconds) x 120
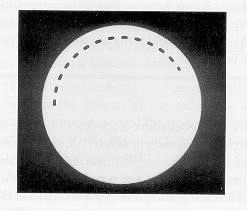
Synchronous spinning top test (left), protractor to measure film (right)
What all should be evaluated for beam alignment?
perpendicularity
must be within 1 degree of perpendicular
otherwise image is distorted
x-ray beam Bucky tray alignment/ central ray congruency
must be wishing 1% of SID
risk clipping important anatomy or grid cut off
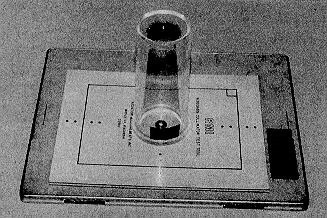
What is evaluated with a beam alignment tool?
Beam alignment
Focal spot size QC is used to measure focal spot _________
Blooming
What measures focal spot QC?
pin hole camera
resolution test tool (star pattern, line pairs test etc)
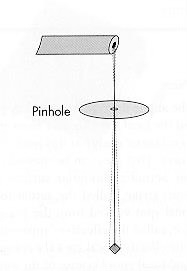
Pin hole camera
plate of gold platinum alloy with a small hole in the center
places over IRS on stand
image of focal spot produced on film and can be measured by comparing to manufactures guidelines for machine
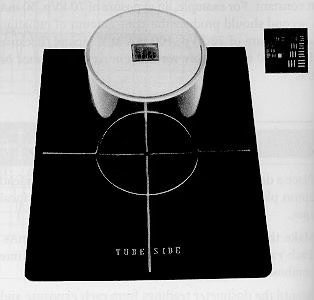
Focal spot test tool
test tool places on film, radiograph taken, test tool imprint compared to manufactures guidelines for machine
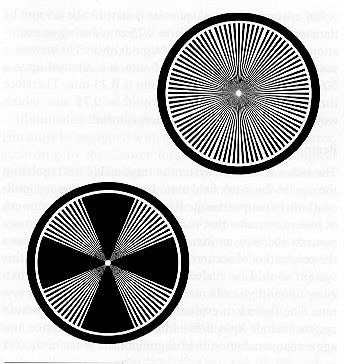
Star test pattern
used to measure resolution
resolution measured by blur zone
facial spot size in mm = angle radius/ (magnification factor - 1)
Magnification may be determined using formula:
M = Di/Do (image diameter/ actual diameter)
If the stated focal spot size is 0.8 mm or less, what is the percent of blooming allowable?
50%
If the stated focal spot size is 0.8 mm to 1.5 mm, what is the percent of blooming allowable?
40%
If the stated focal spot size is 1.6 mm or greater, what is the percent of blooming allowable?
30%
Reproducibility
the output exposure should be constant from one exposure to another
the variation in x-ray intensity should not exceed 5%
Reciprocity
the amount of x-ray intensity should remain constant at a specific mAs value despite the different combinations of mA and exposure time
maximum acceptable variation is ± 10%
Linearity
adjacent mA stations are utilized
exposure time remains the same
the maximum acceptable variation is 10% from one mA station to an adjacent mA station
What are the units for radiation intensity?
mR/mAs