Term 1 Exam Review (Honors Physical Science)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What is physical science?
A combination of physics and chemistry

scientifc theory
a possible explanation for repeatedly observed patterns in nature supported by observations and results from many investigations

scientific law
A statement that describes what scientists expect to happen every time under a particular set of conditions

Precision
a measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another

Accuracy
how close a measurement is to the true value

area
The number of square units required to cover a surface.
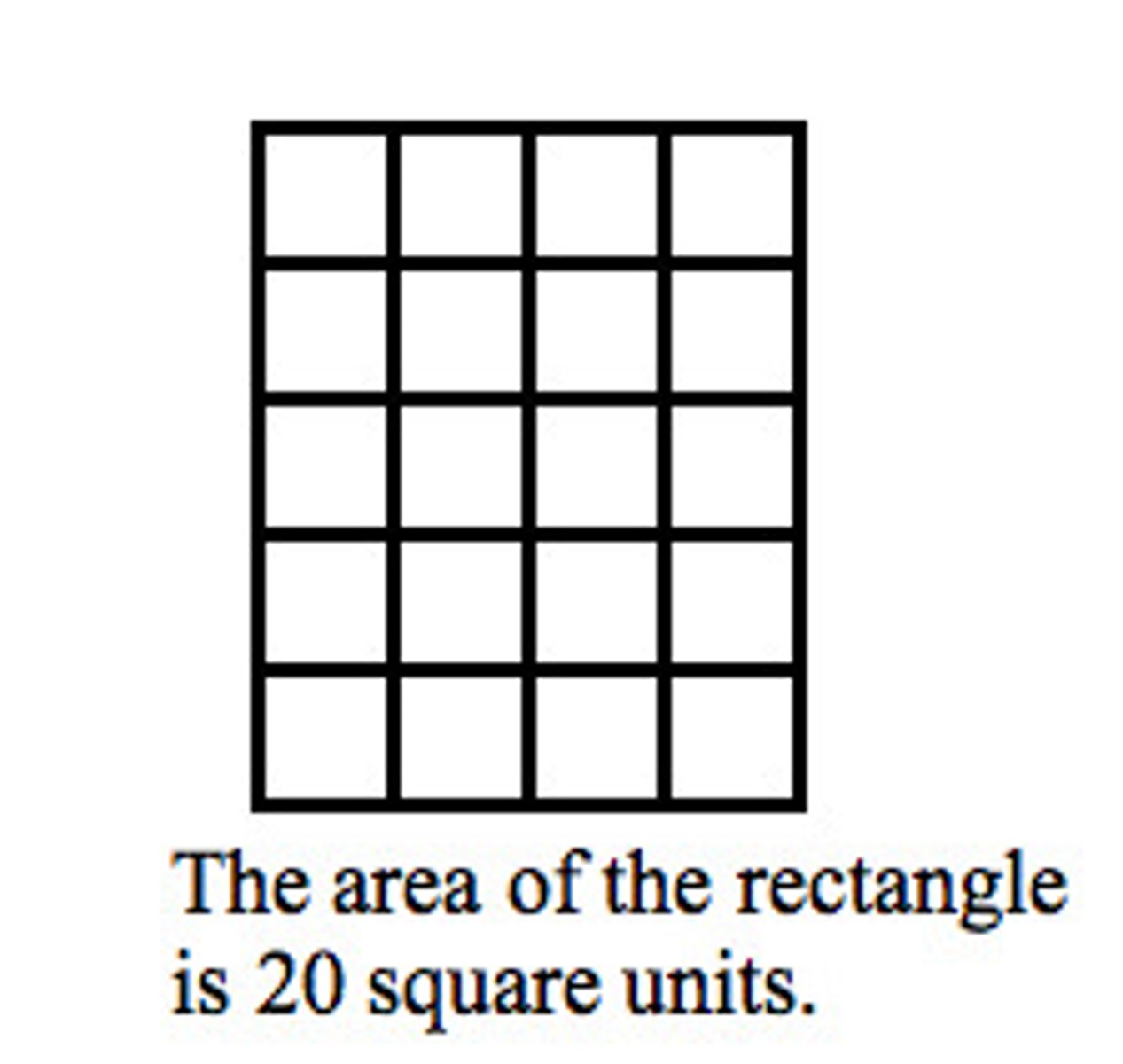
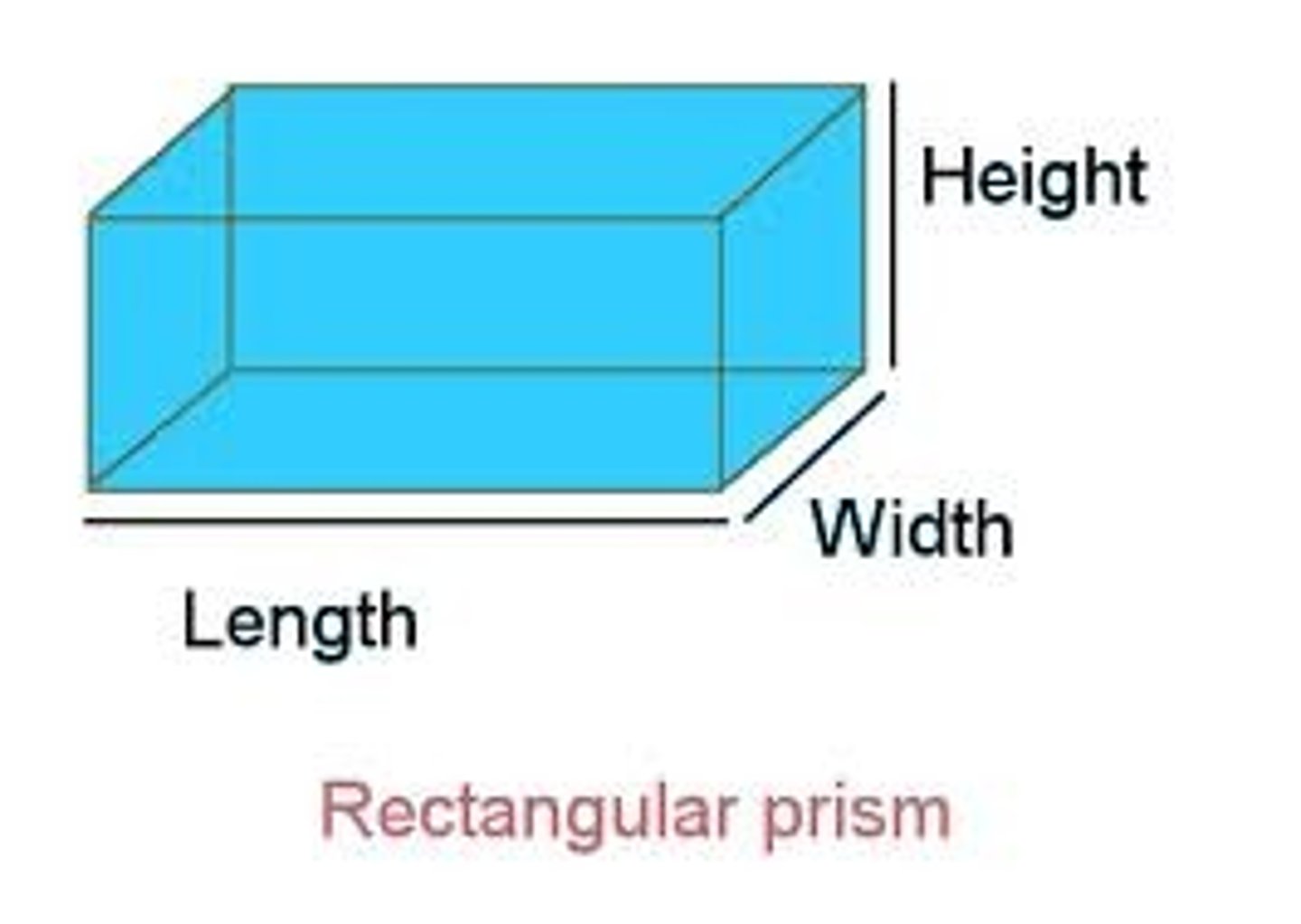
Volume
The amount of space an object takes up
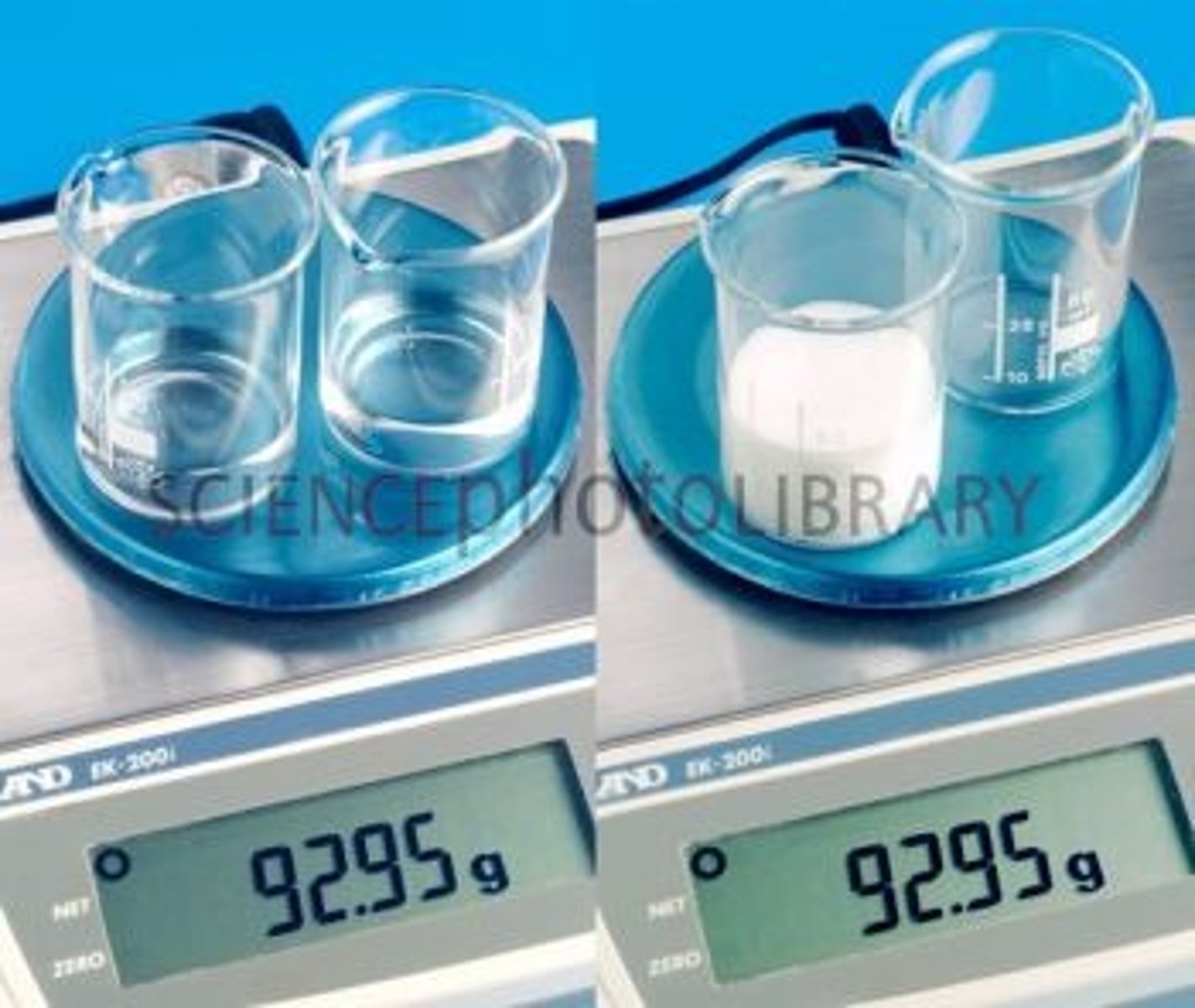
Mass
the amount of matter in an object

Scientific Method Steps
Question, Research, Hypothesis, Experiment, Analyze the Data, Conclusion

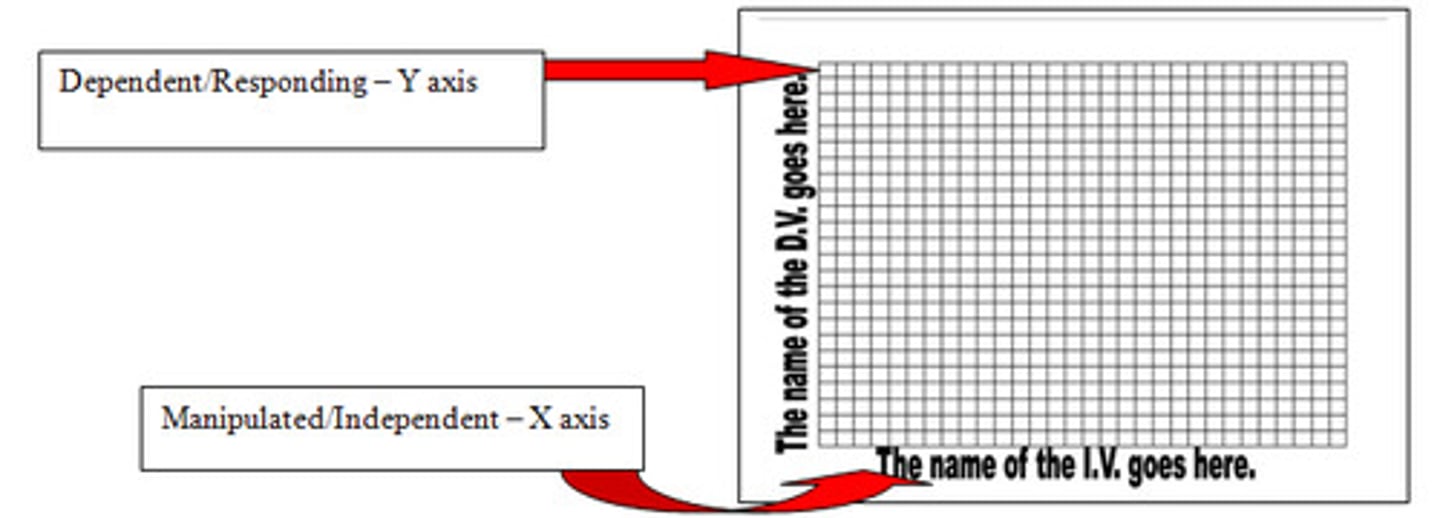
independent variable
variable that is manipulated

dependent variable
The measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested.

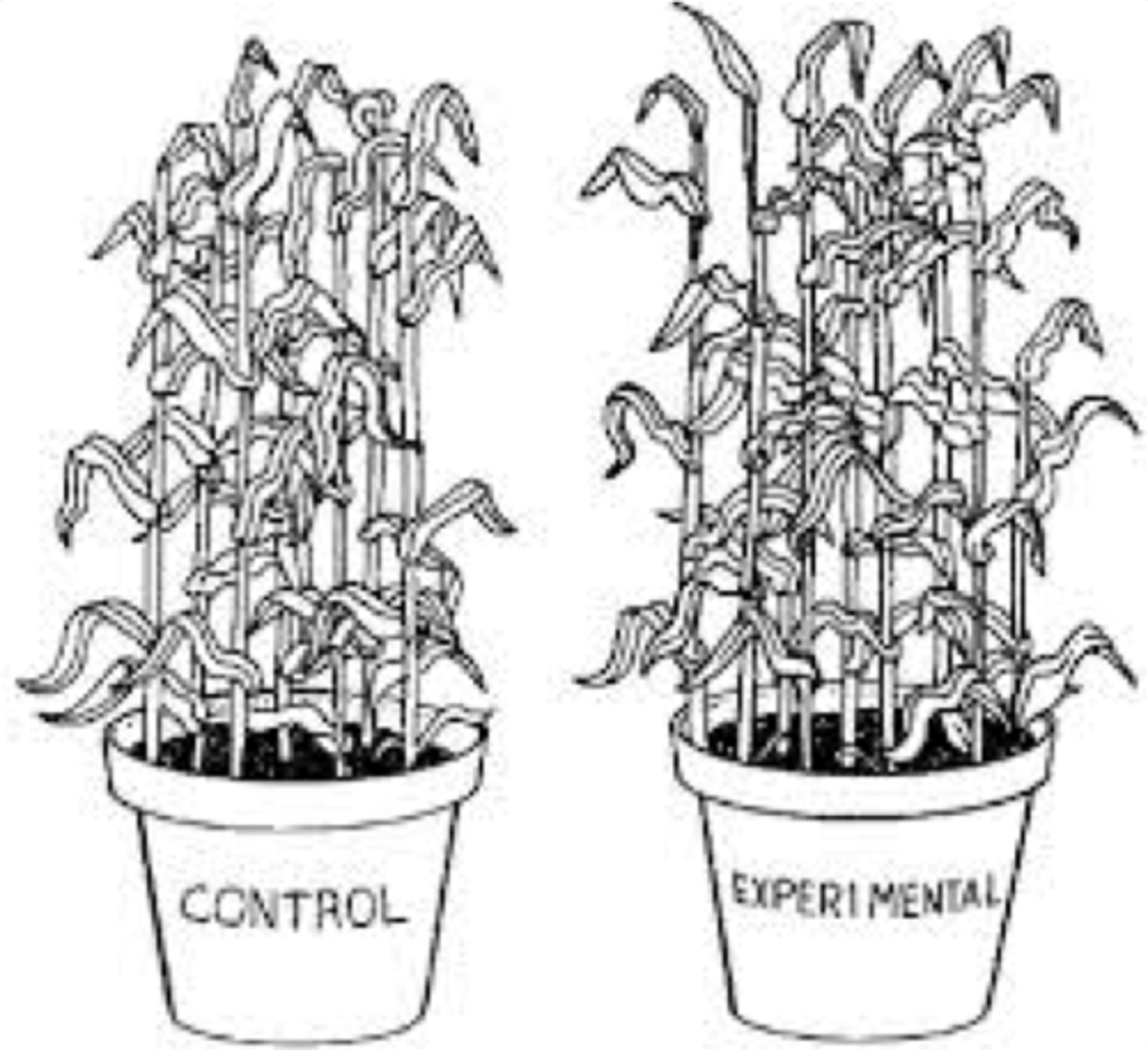
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
qualitative data
descriptive data

quantitative data
numerical data

What is an SI unit?
International System of Units
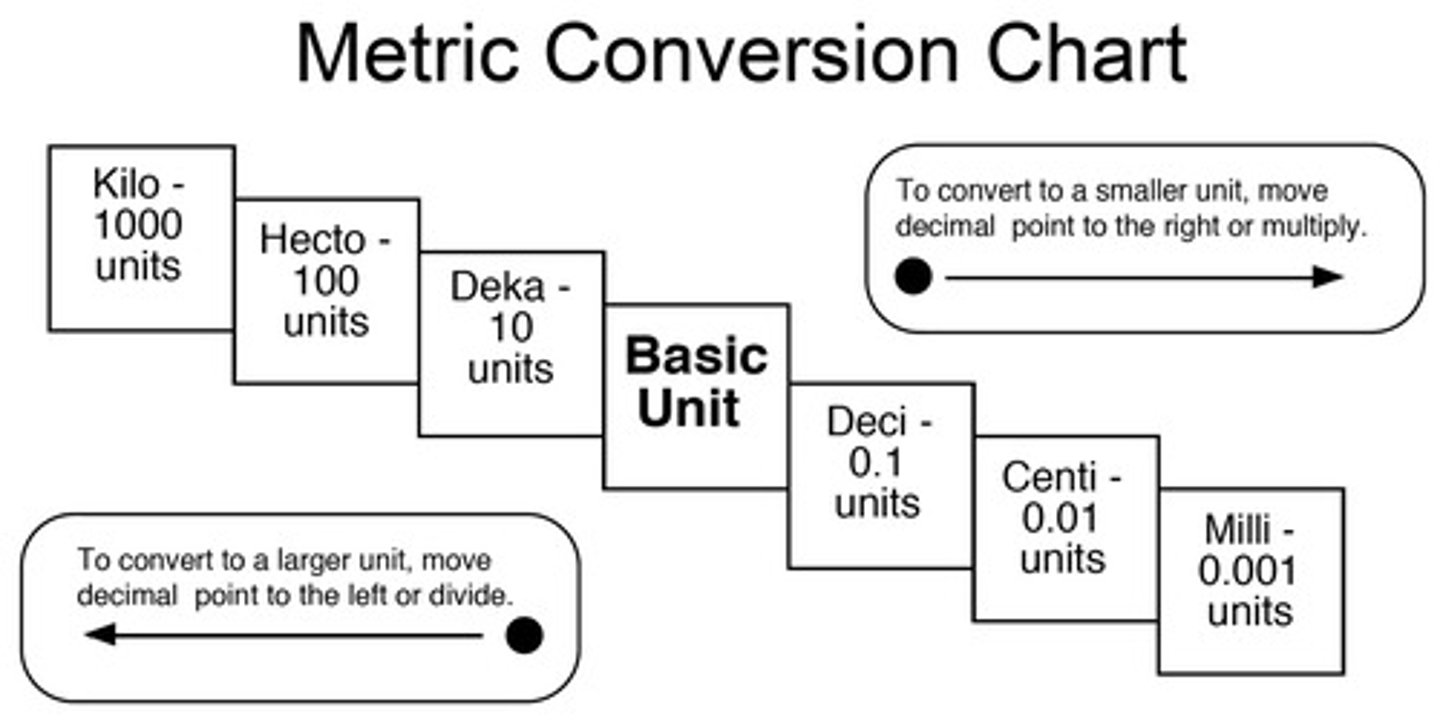
What are the metric units?
Kilo, Hecto, Deca, Base, Deci, Centi, Milli, Micro (Kings Hate Dragons Because Dragons Can't Make Money).
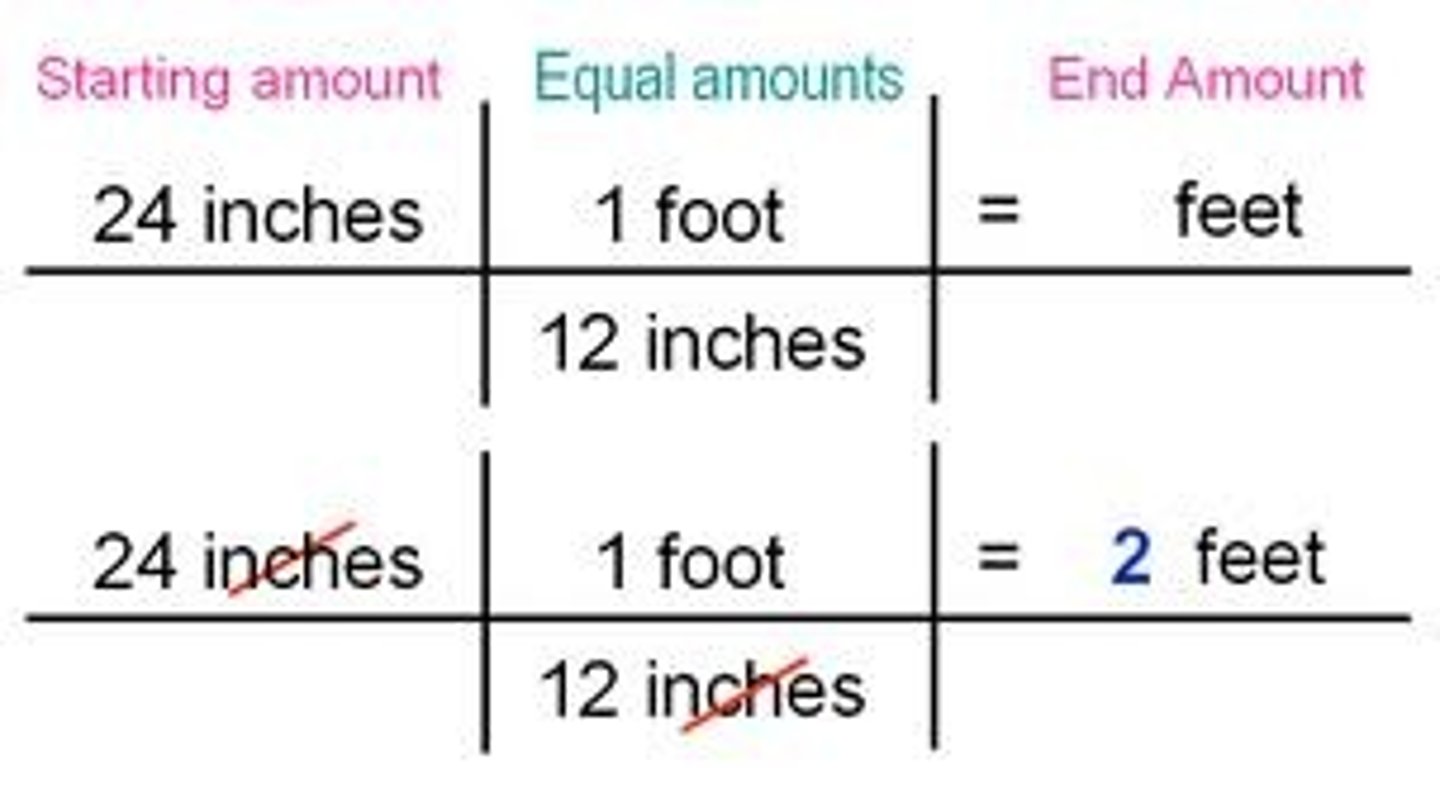
Dimensional analysis
a technique of problem-solving that uses the units that are part of a measurement to help solve the problem
DRY MIX
Dependent
Responding
Y Axis
Manipulated
Independent
X Axis
scientific notation
A mathematical method of writing numbers using powers of ten.

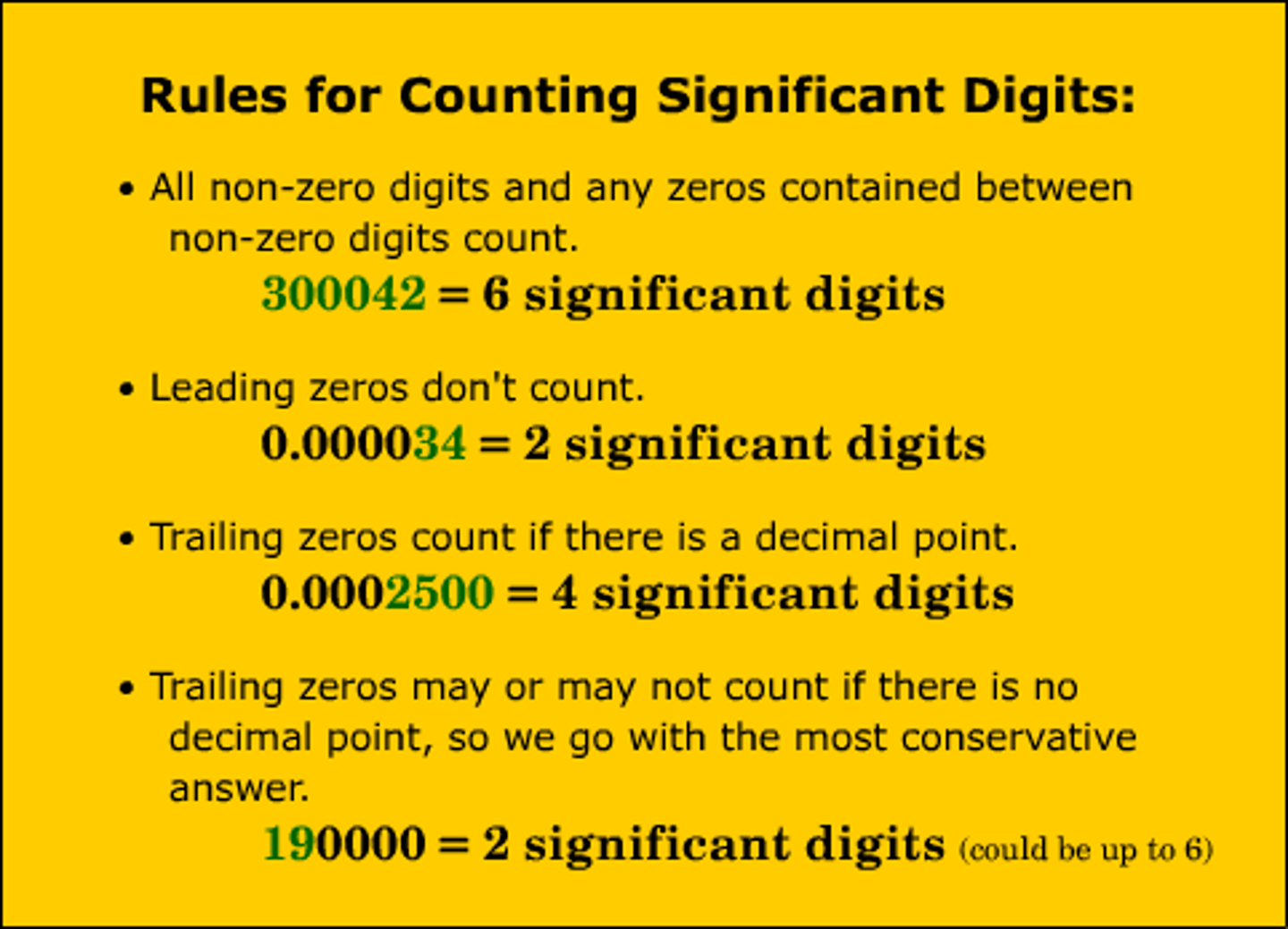
significant figures
All the digits that can be known precisely in a measurement, plus a last estimated digit
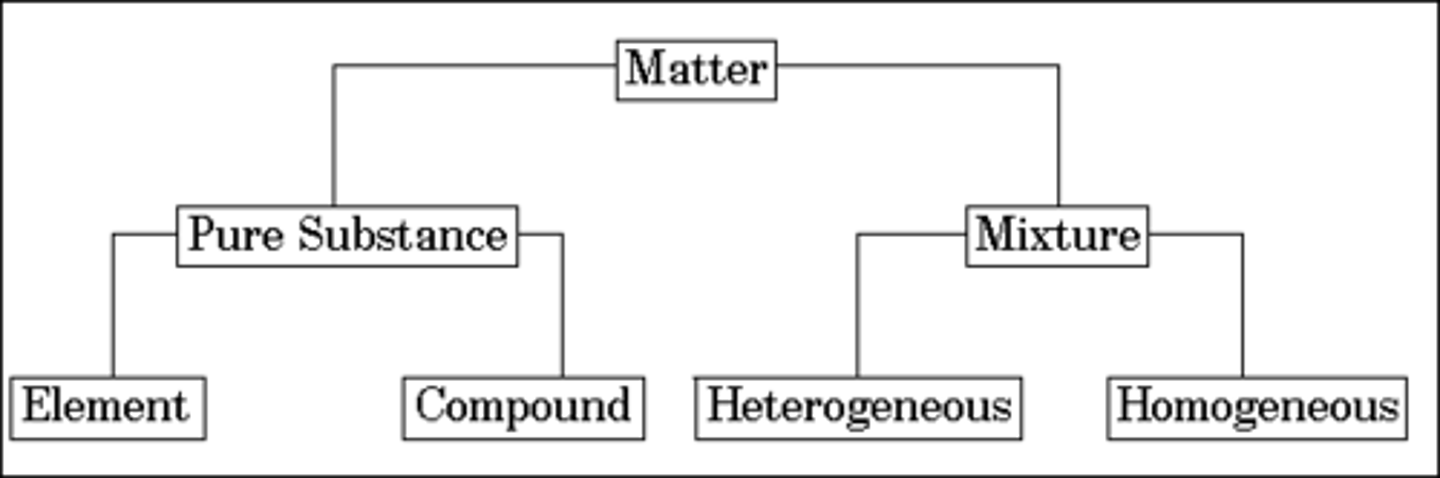
matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom

Atom
Smallest particle of an element
Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
molecule
smallest unit of most compounds
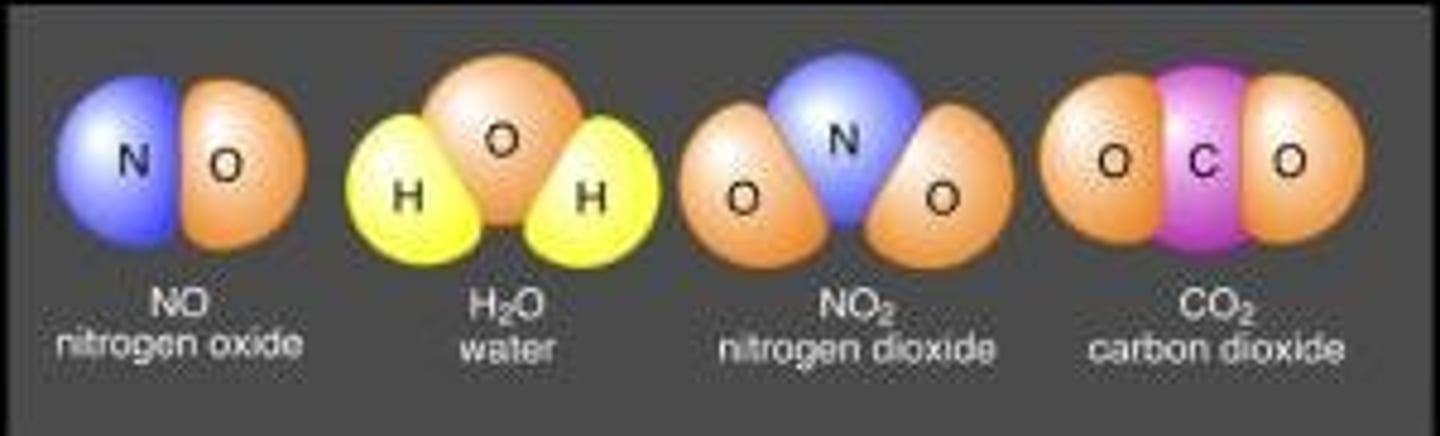
chemical formula
A combination of chemical symbols and numbers to represent a substance
pure substances
elements and compounds
Mixtures
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined

melting point
the temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid
boiling point
The temperature at which a liquid boils

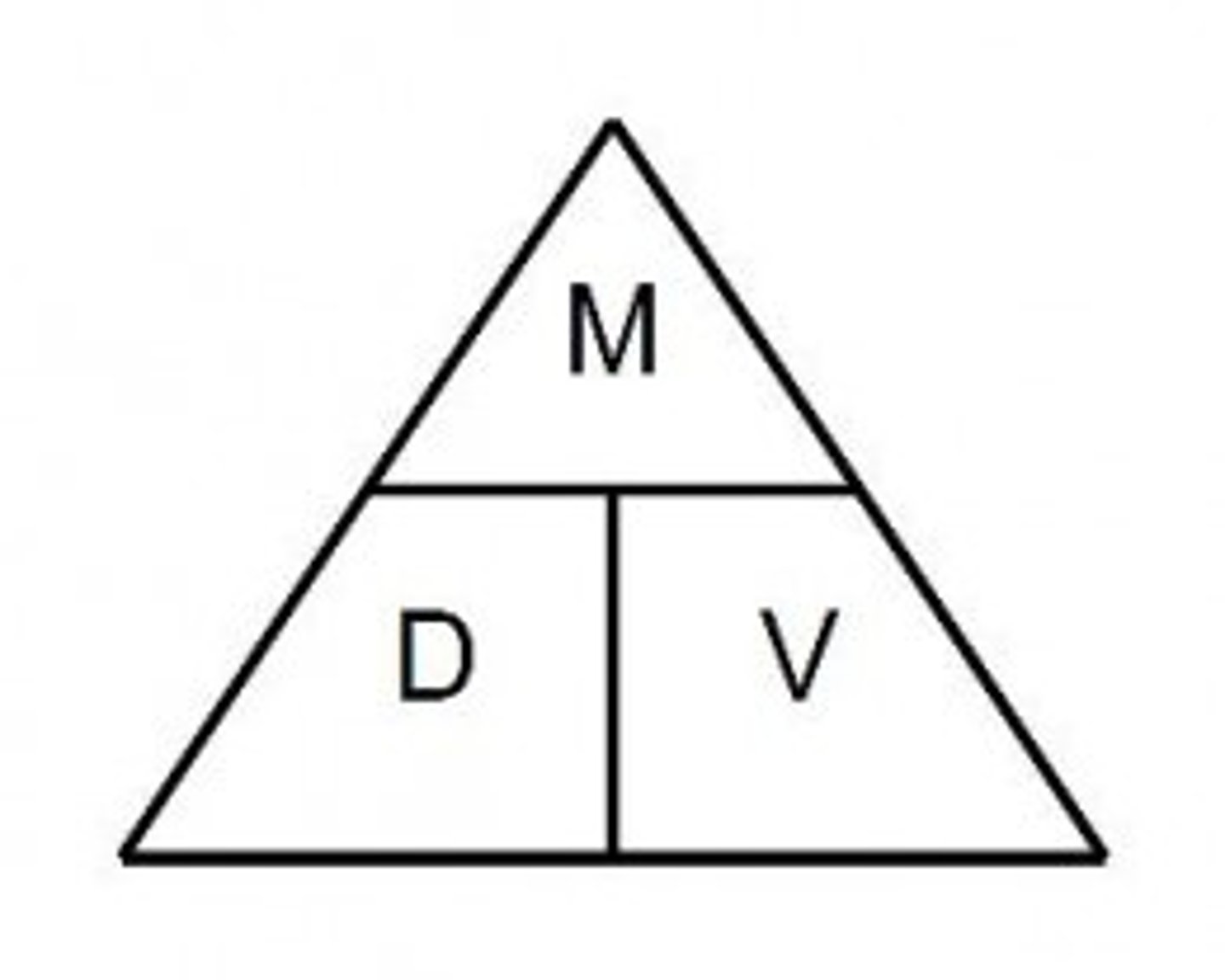
Density
mass/volume
Reactivity
How readily a substance combines chemically with other substances.

Flammability
the ability to burn

heterogeneous mixture
A mixture in which different materials can be distinguished easily
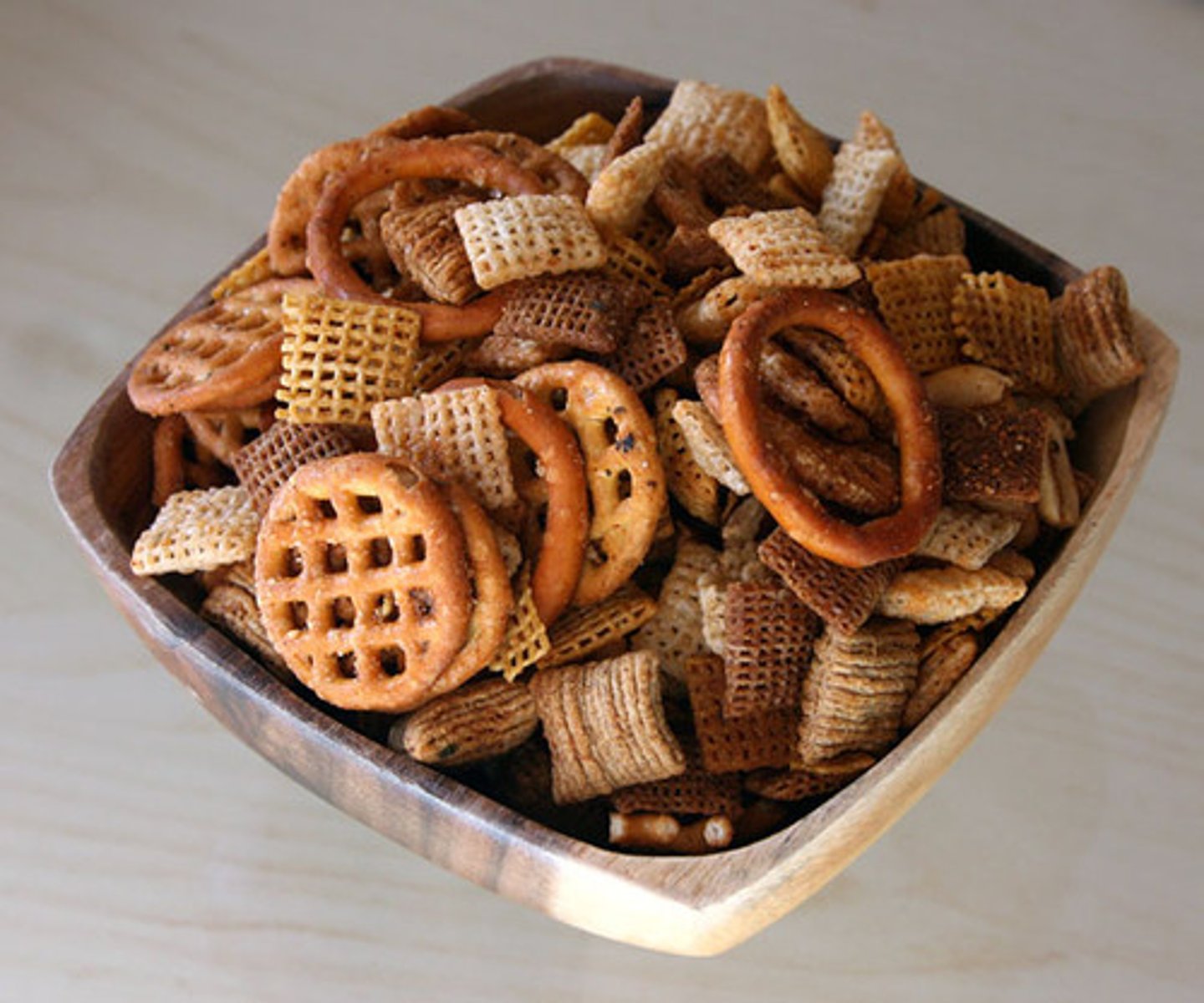

homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture

Miscible
Describes two liquids that are soluble in each other

Immiscible
liquids that are not soluble in each other

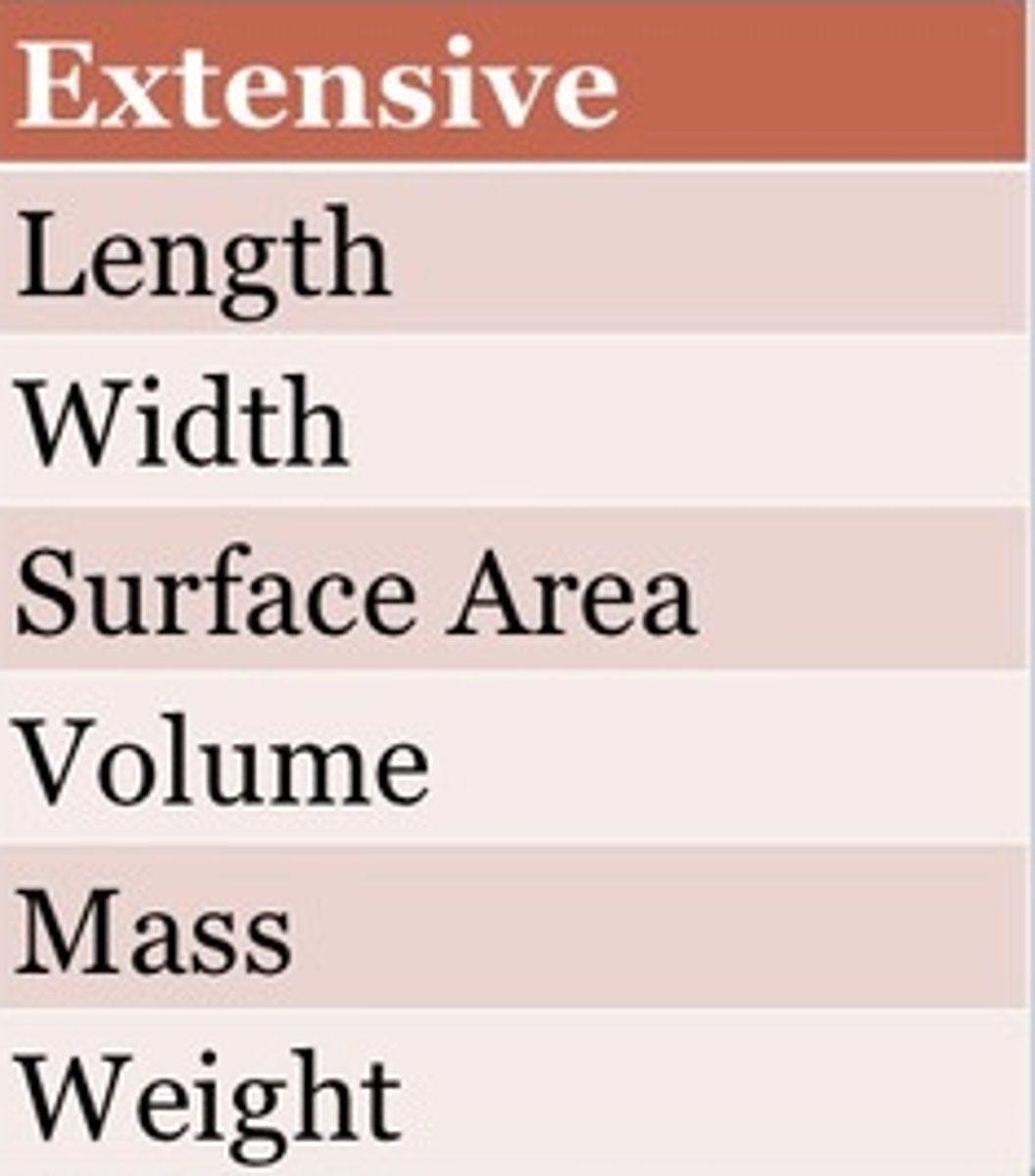
extensive property
a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample
intensive property
a property that depends on the type of matter in a sample, not the amount of matter
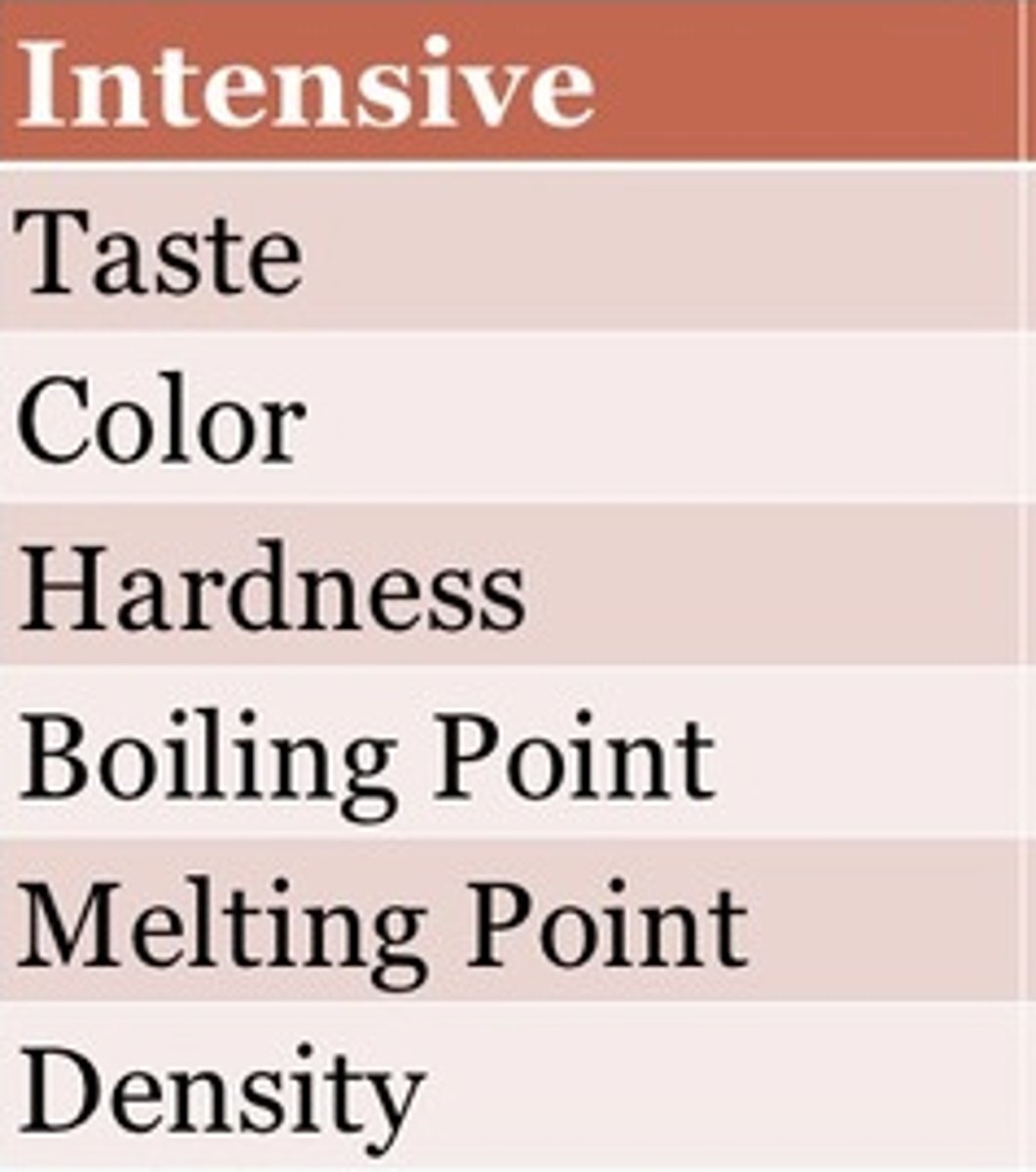
chemical propety
a characteristic that describes how a substance changes into a different substance

physical change
A change in a substance that does not change its identity

chemical change
A change in matter that produces one or more new substances

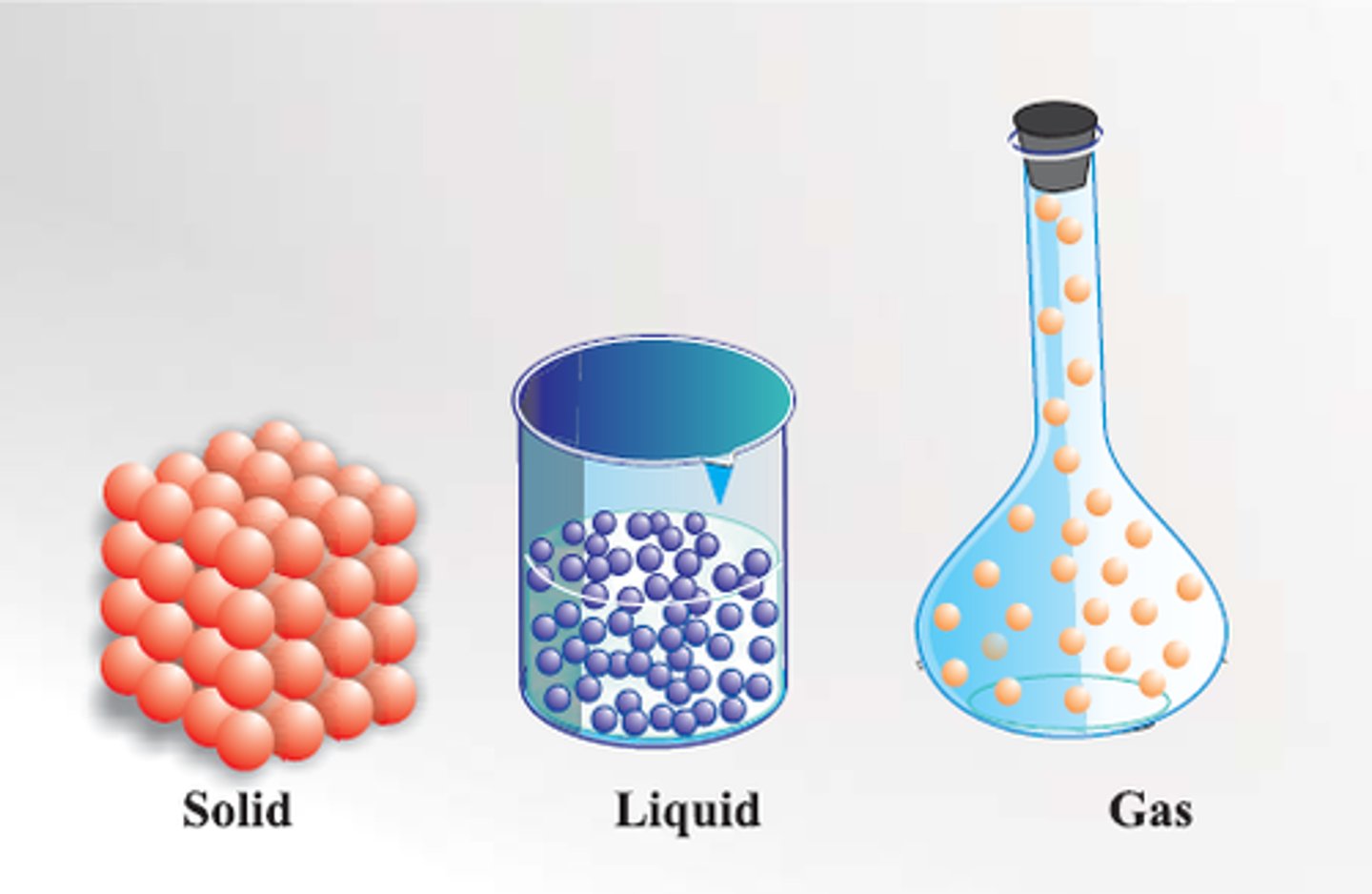
Kinetic Molecular Theory
based on the idea that particles of matter are always in motion

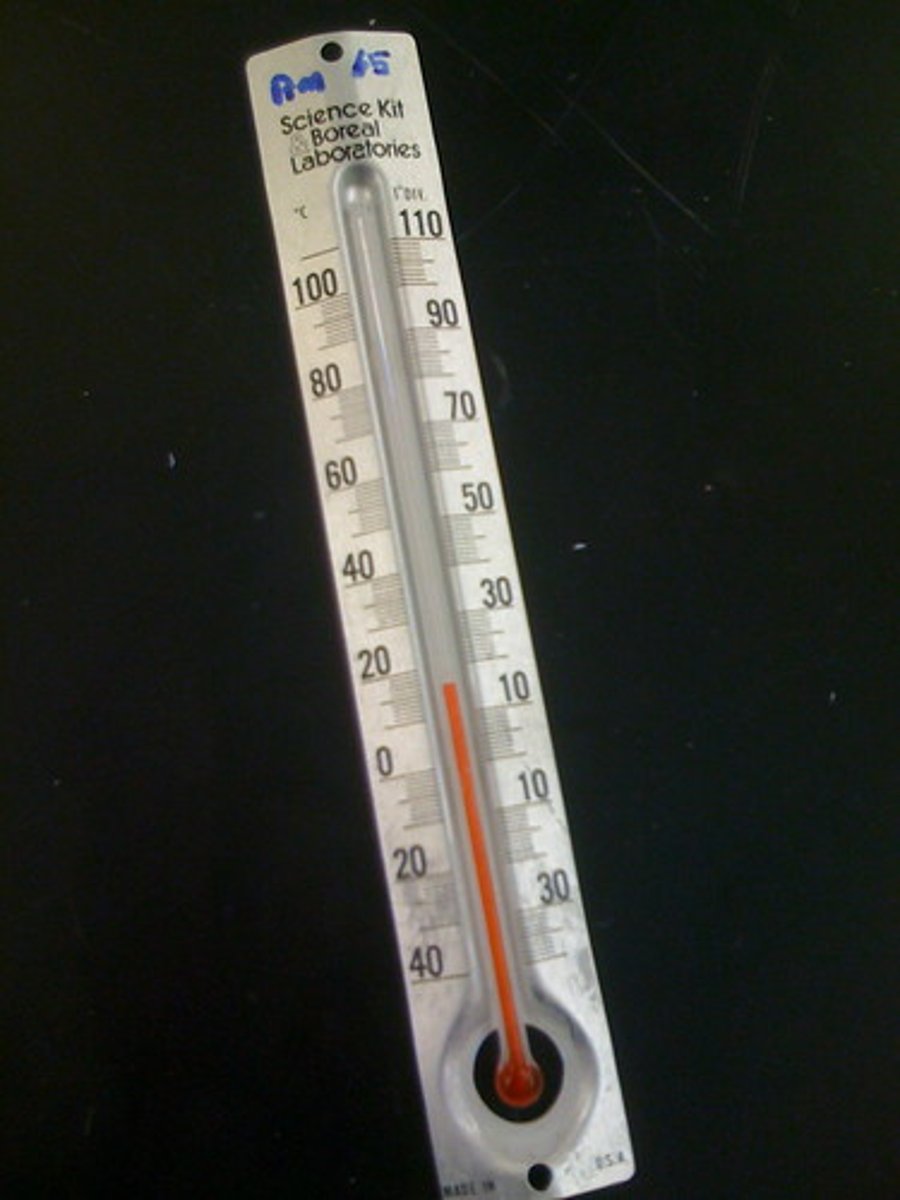
temperature
A measure of how hot or cold something is.

thermal energy
Heat energy
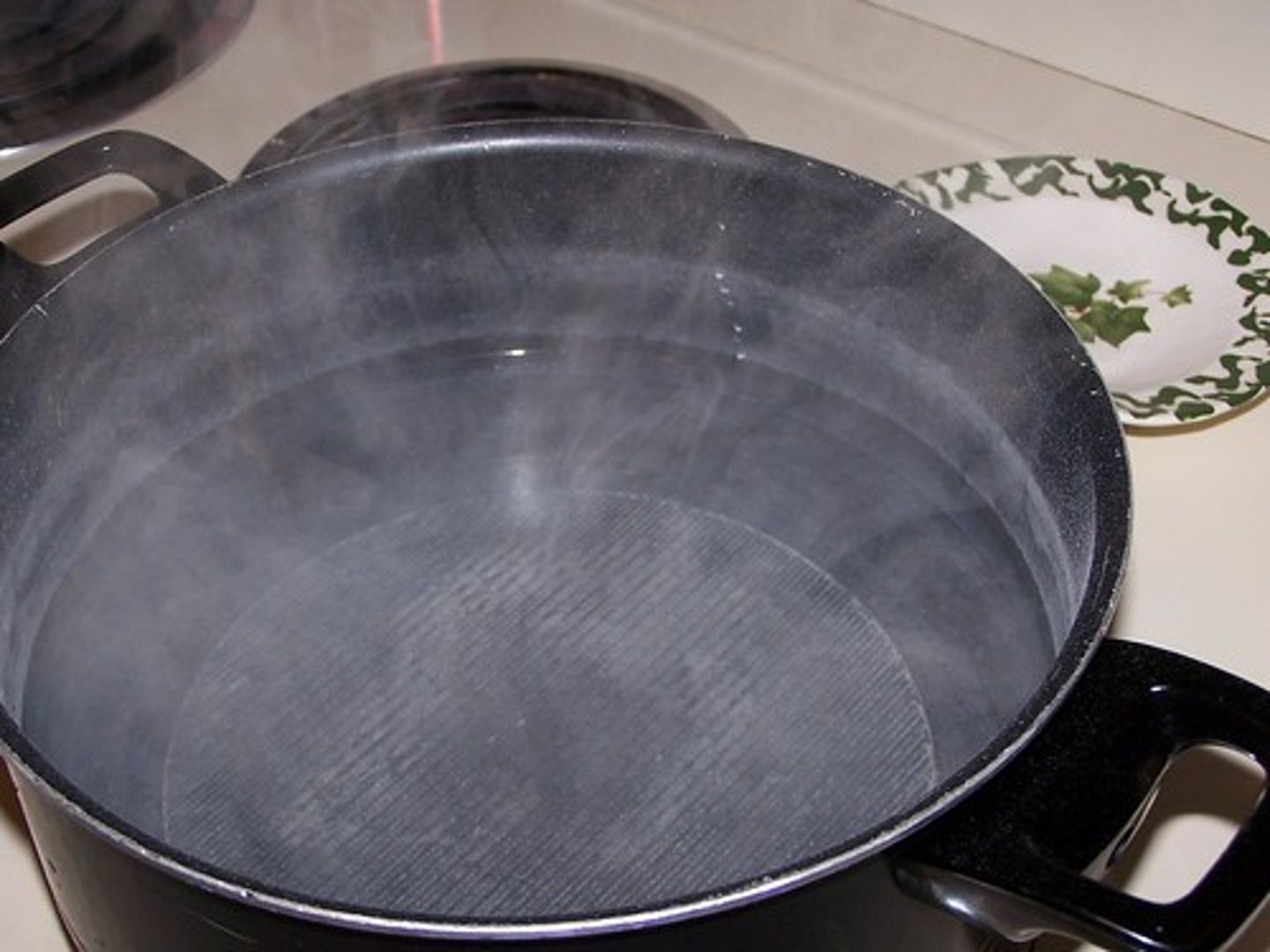
Evaporation
Liquid to gas

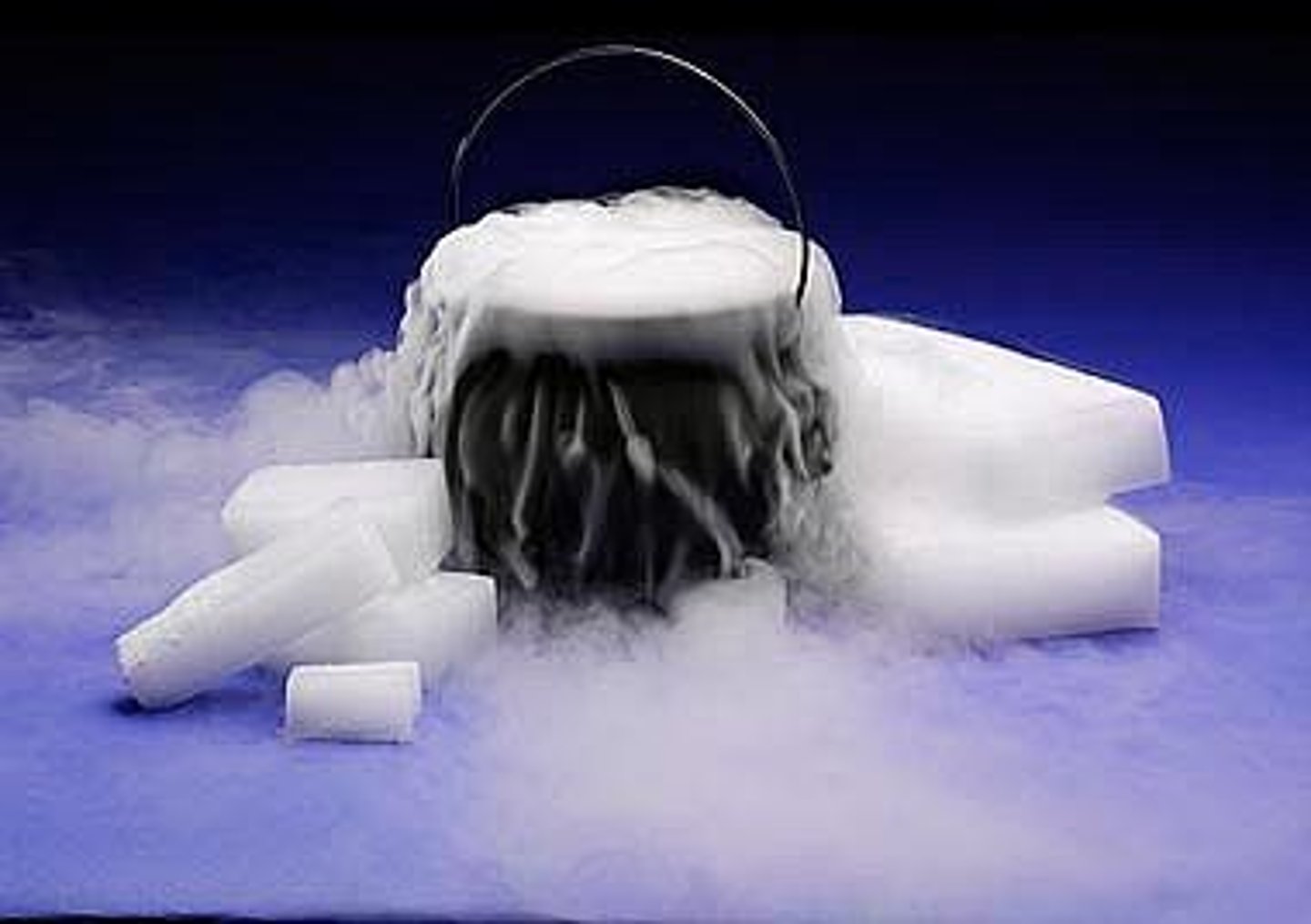
Sublimation
solid to gas

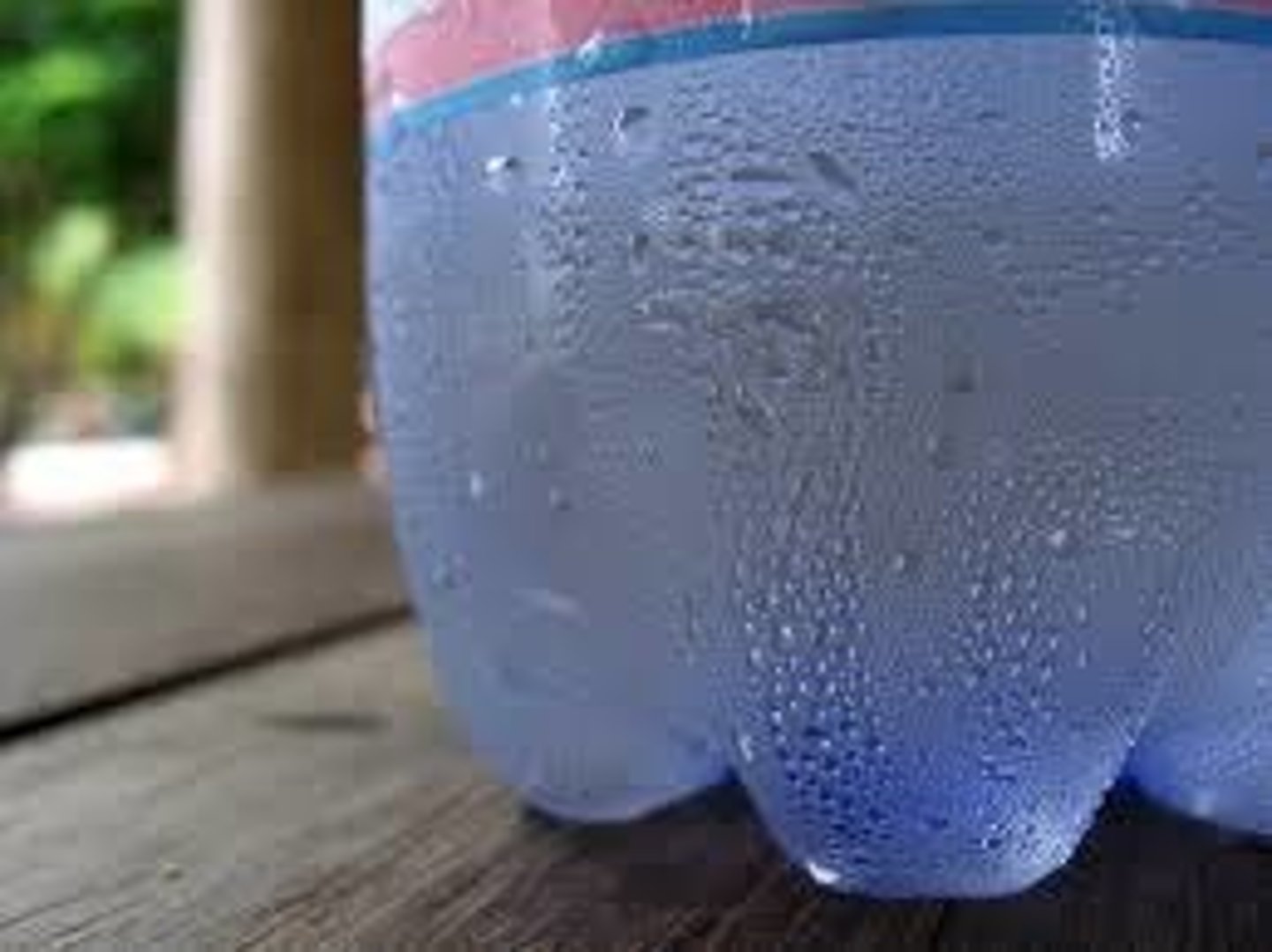
Condensation
Gas to liquid

Freezing
liquid to solid
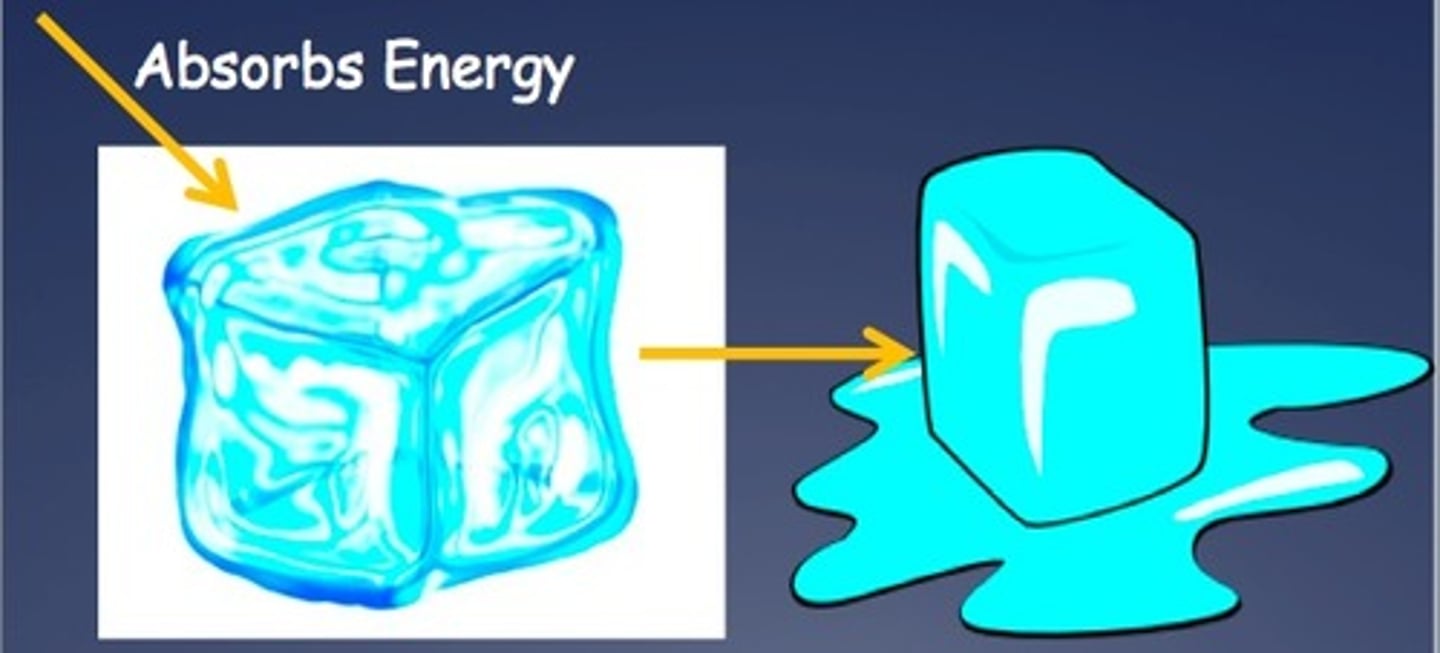
Endothermic
Absorbs heat
Exothermic
Releases heat

How can matter be classified?
elements, compounds, mixtures
Celsius to Kelvin
K=C+273
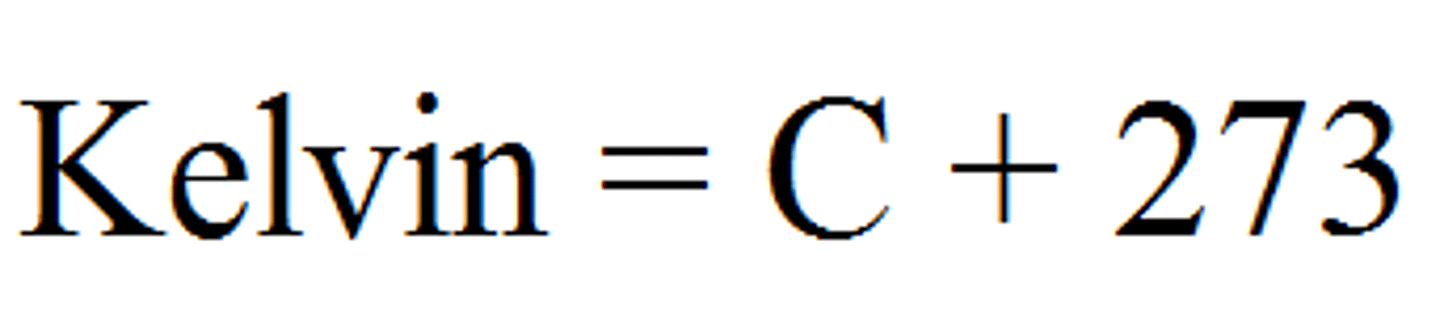
mass volume and density triangle
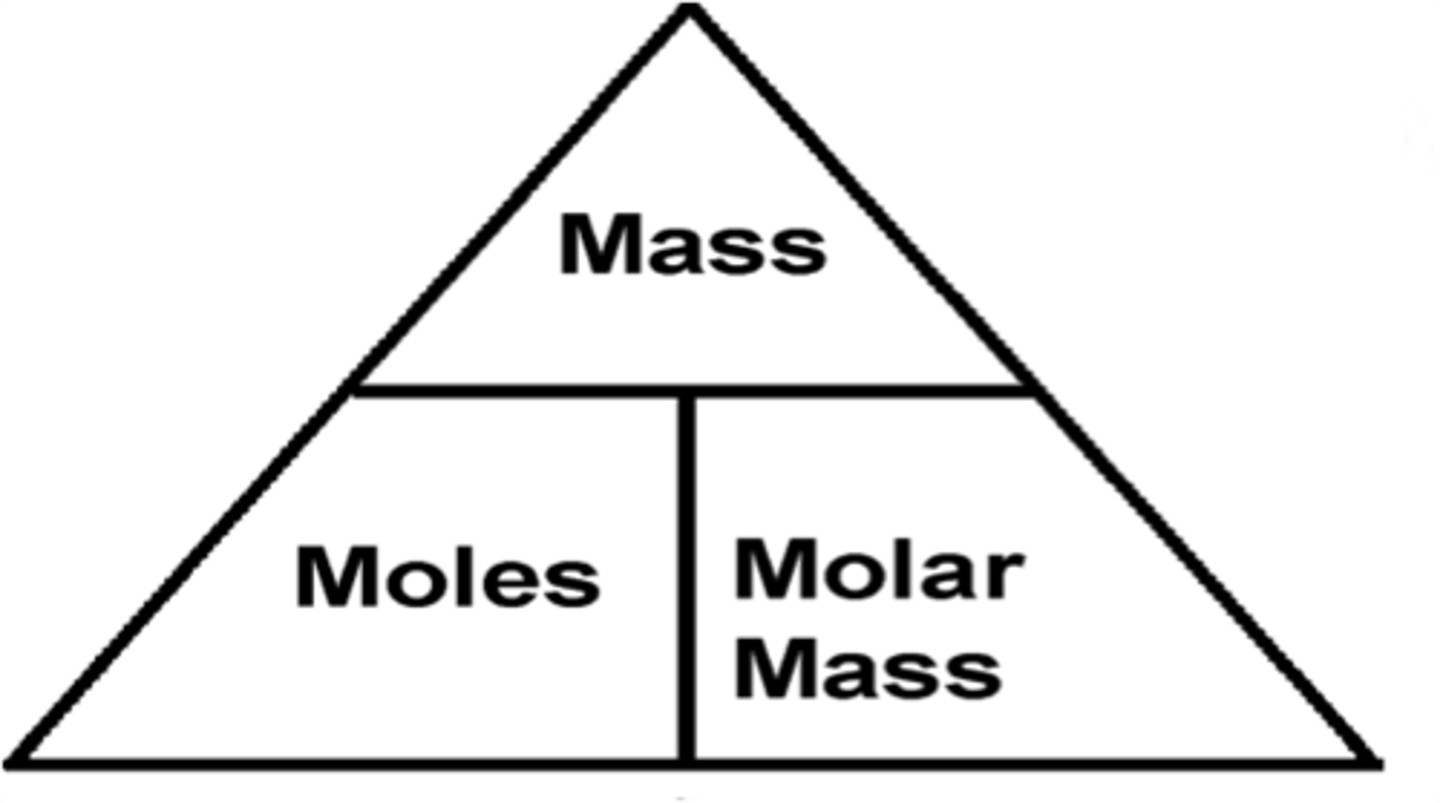
Mole Calculations formula
Number of moles = given mass / gram-formula (molar) mass
Democritus
Original idea of the atom

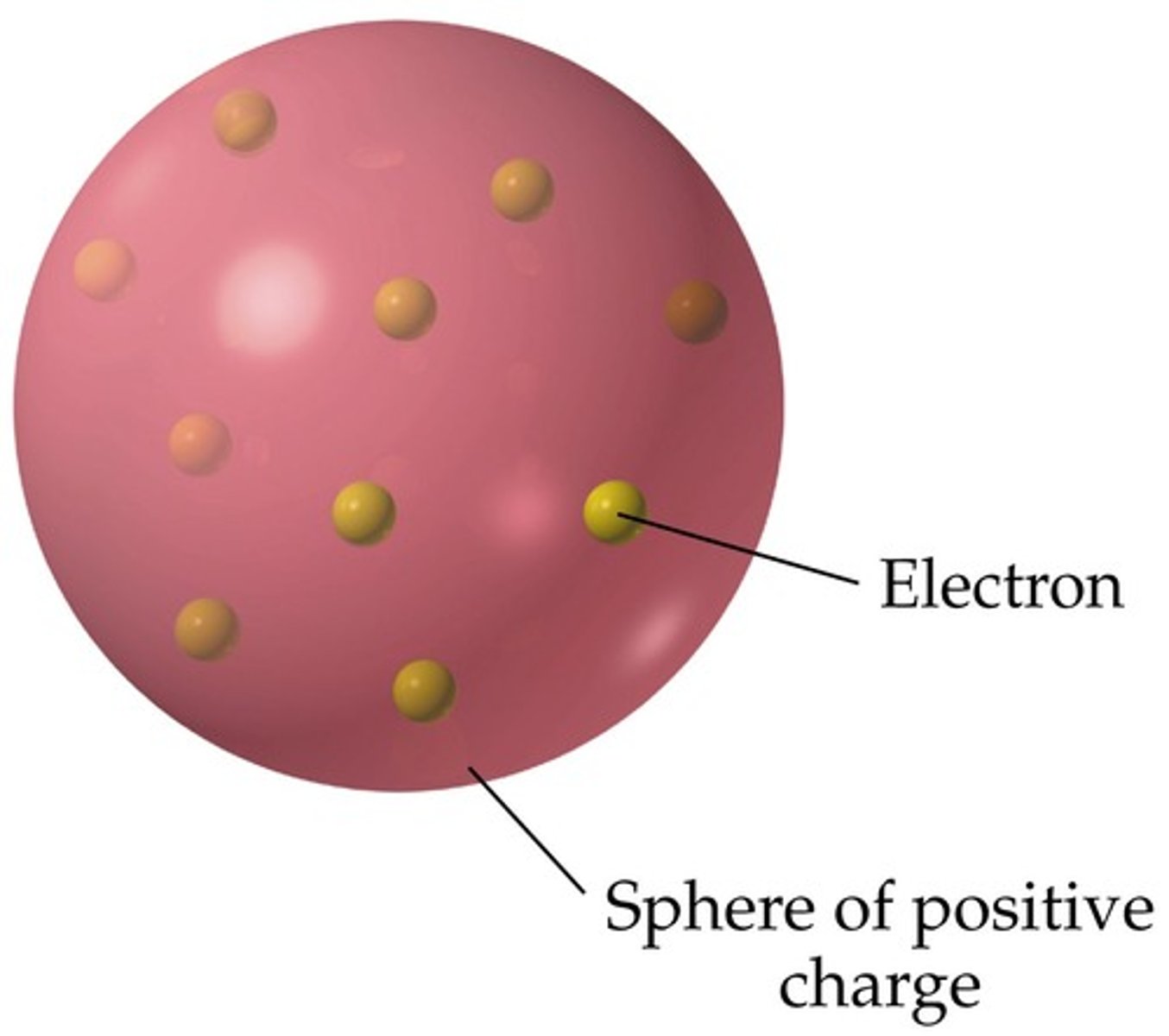
Dalton's Atomic Theory
1) elements are composed of atoms. 2) atoms of same element are identical, but differ from other elements. 3) elements can mix together 4) atoms only change when mixed with other elements

Rutherford
Gold foil experiment, discovered nucleus
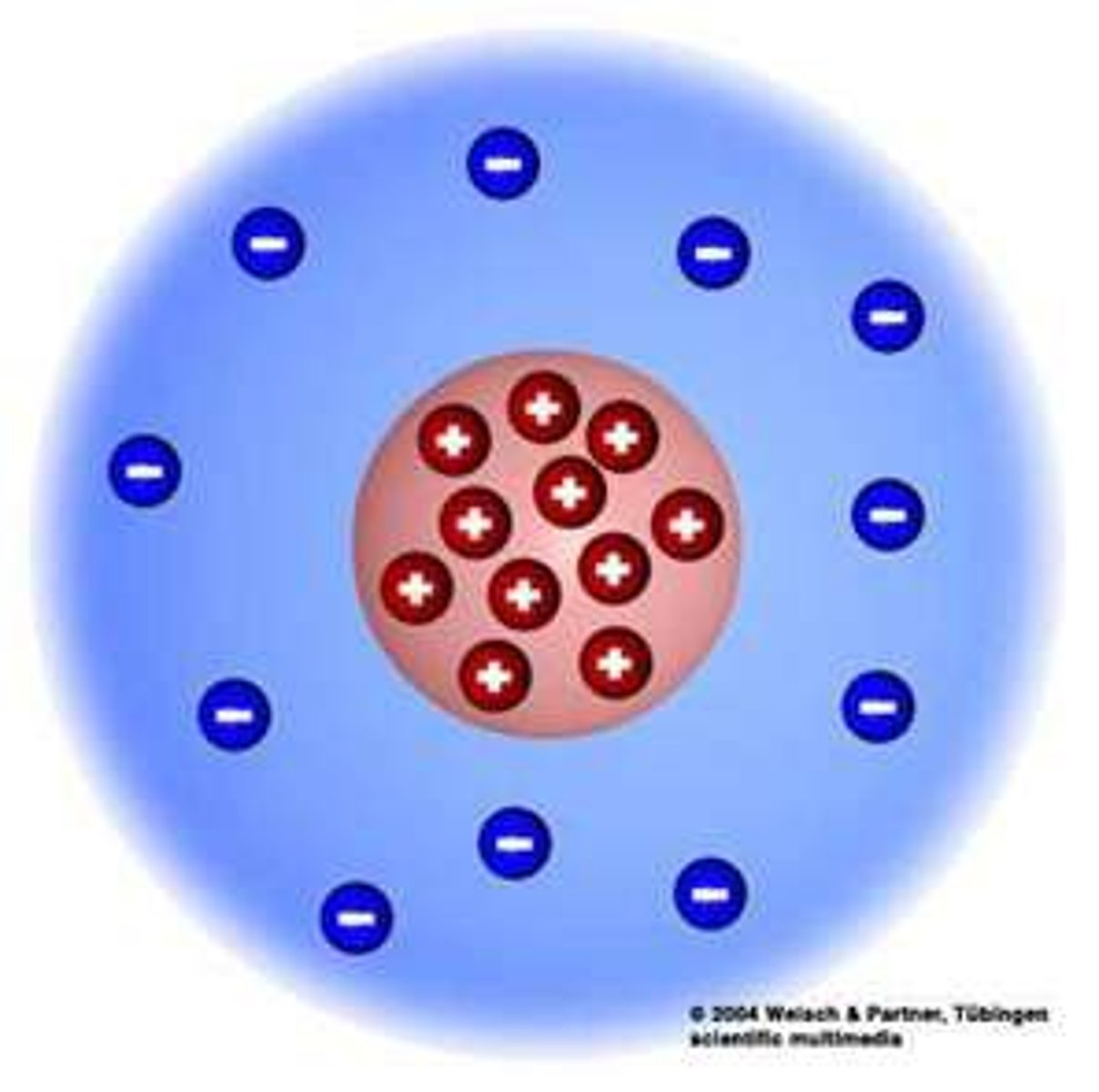
Thomson
discovered the electron
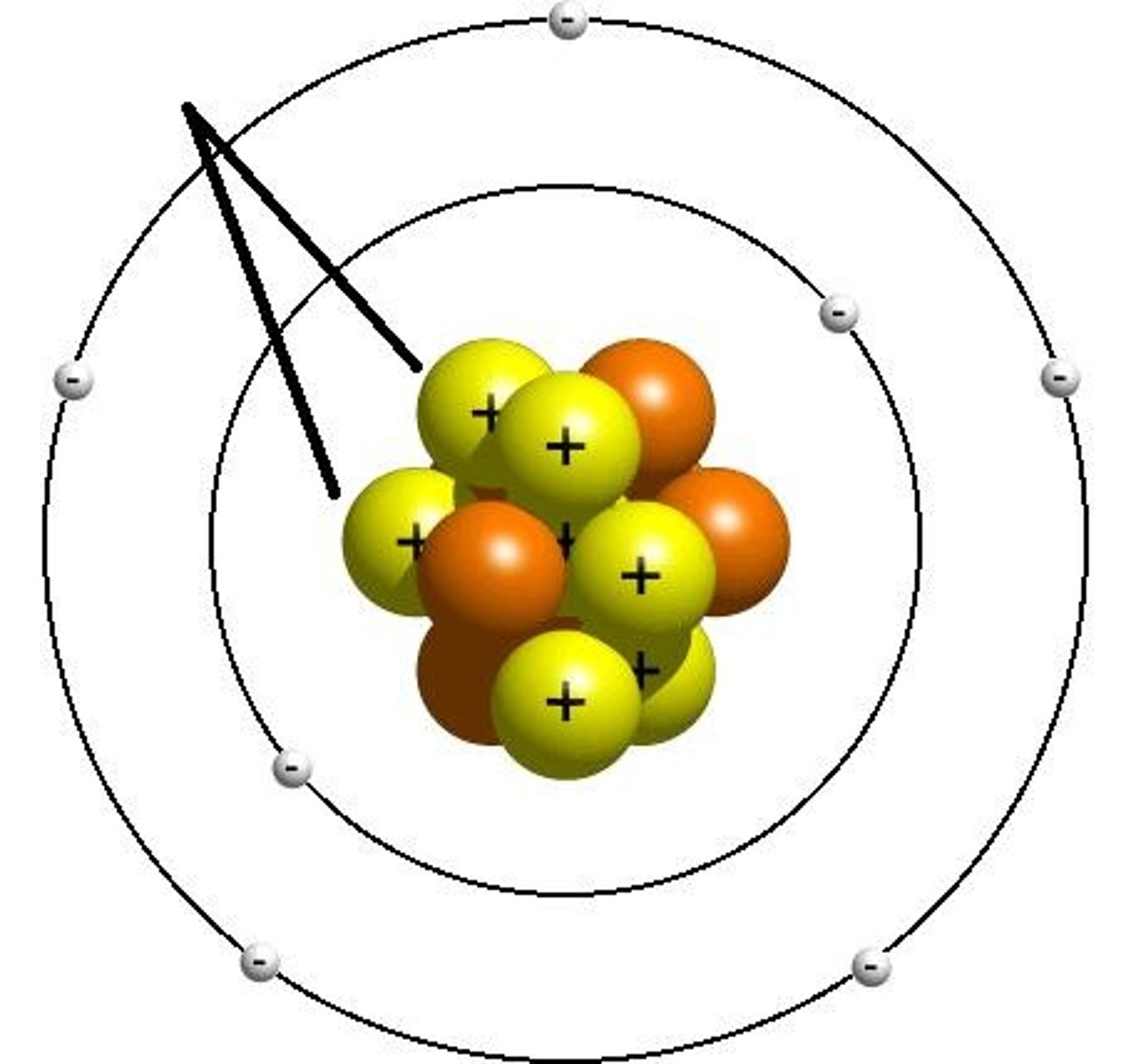
Proton
positively charged particle
Neutron
no charge
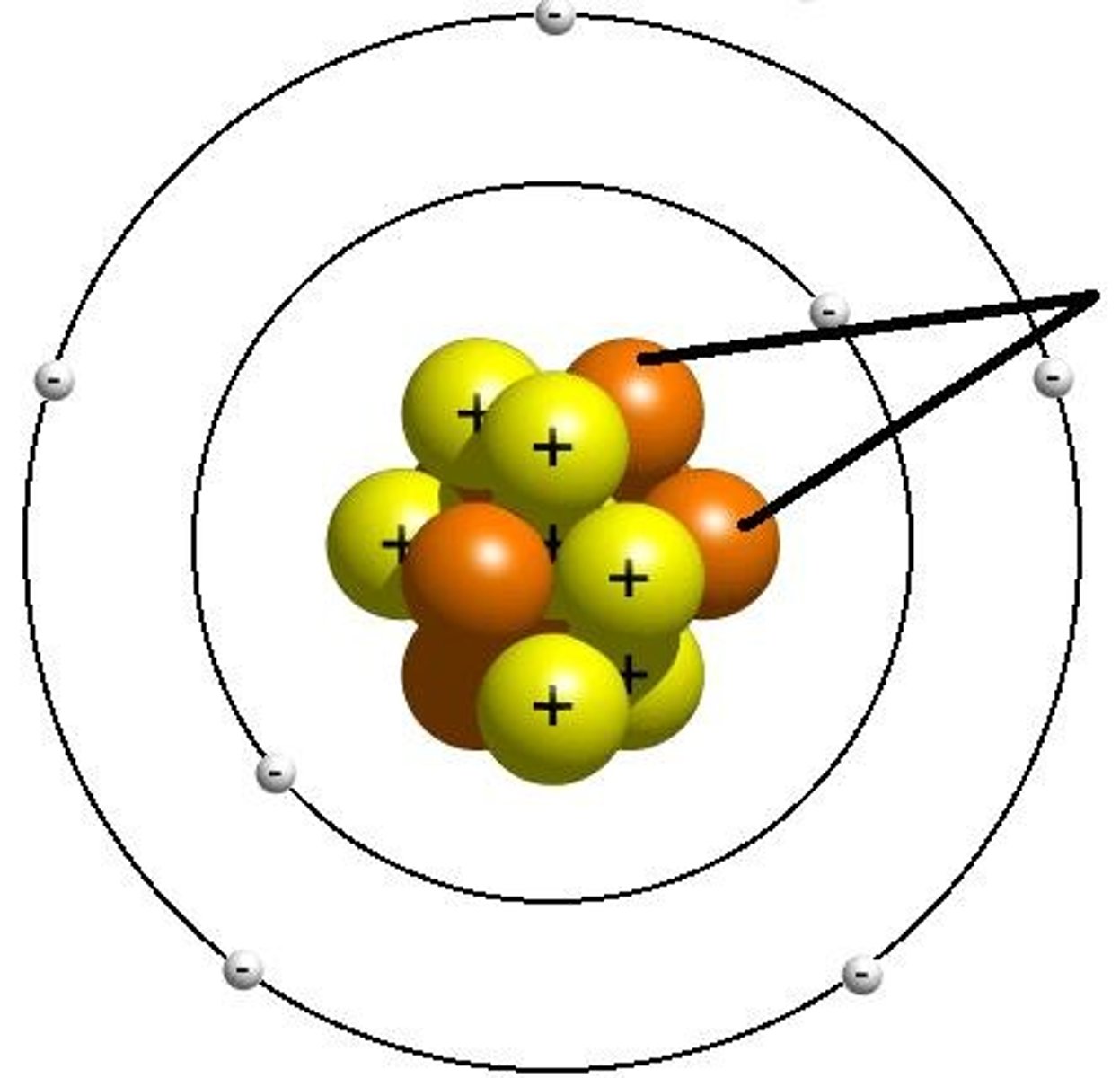
Electron
negatively charged particle
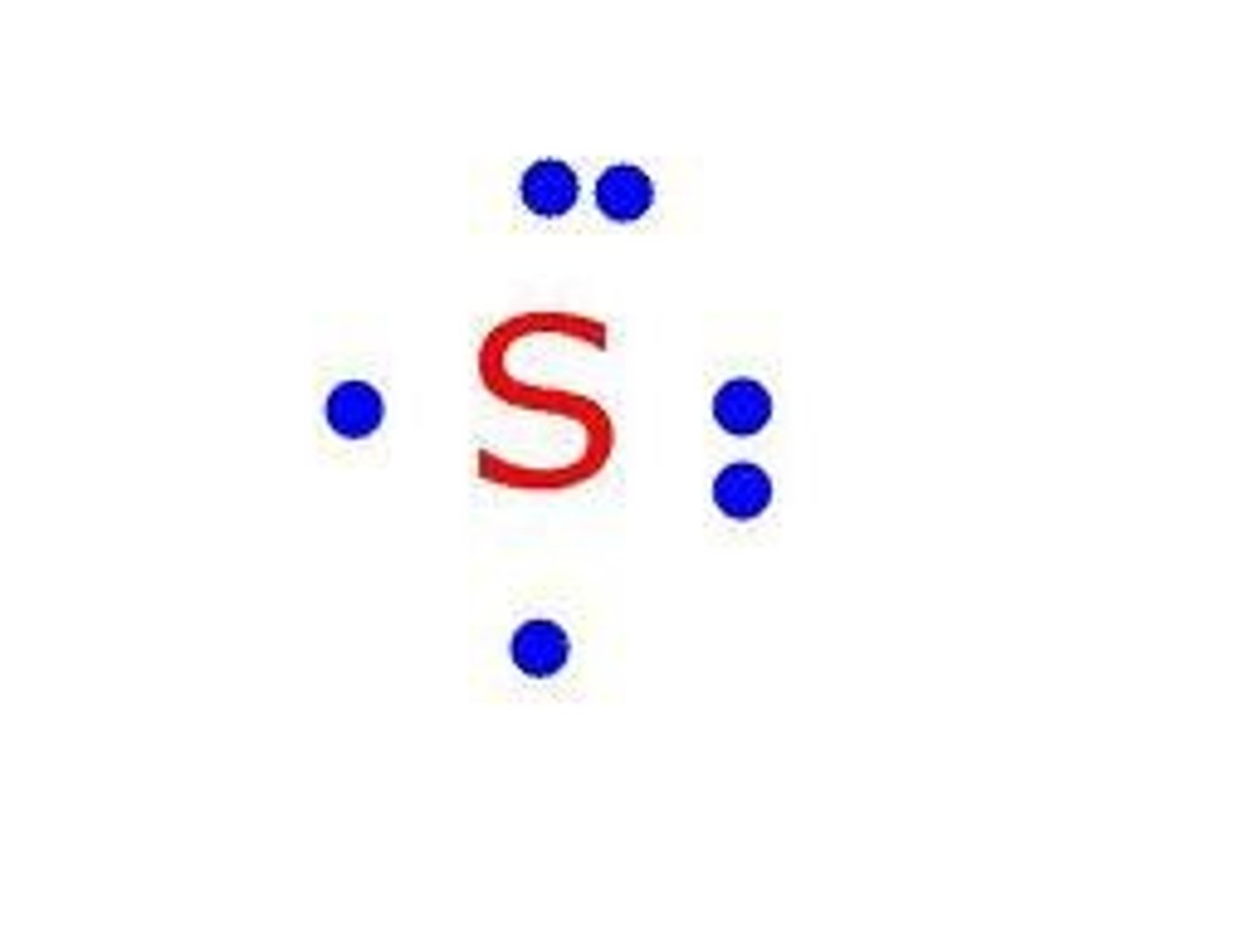
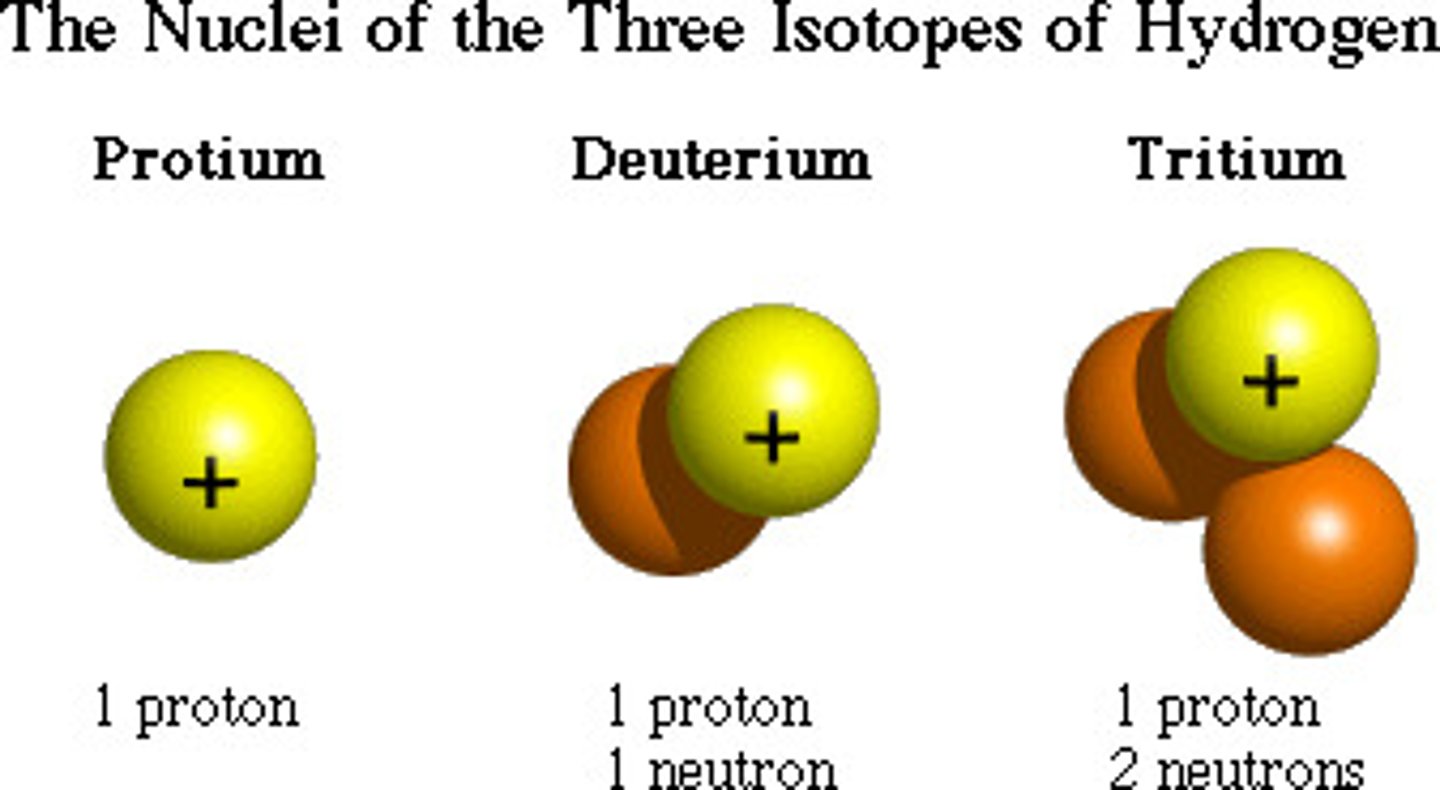
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
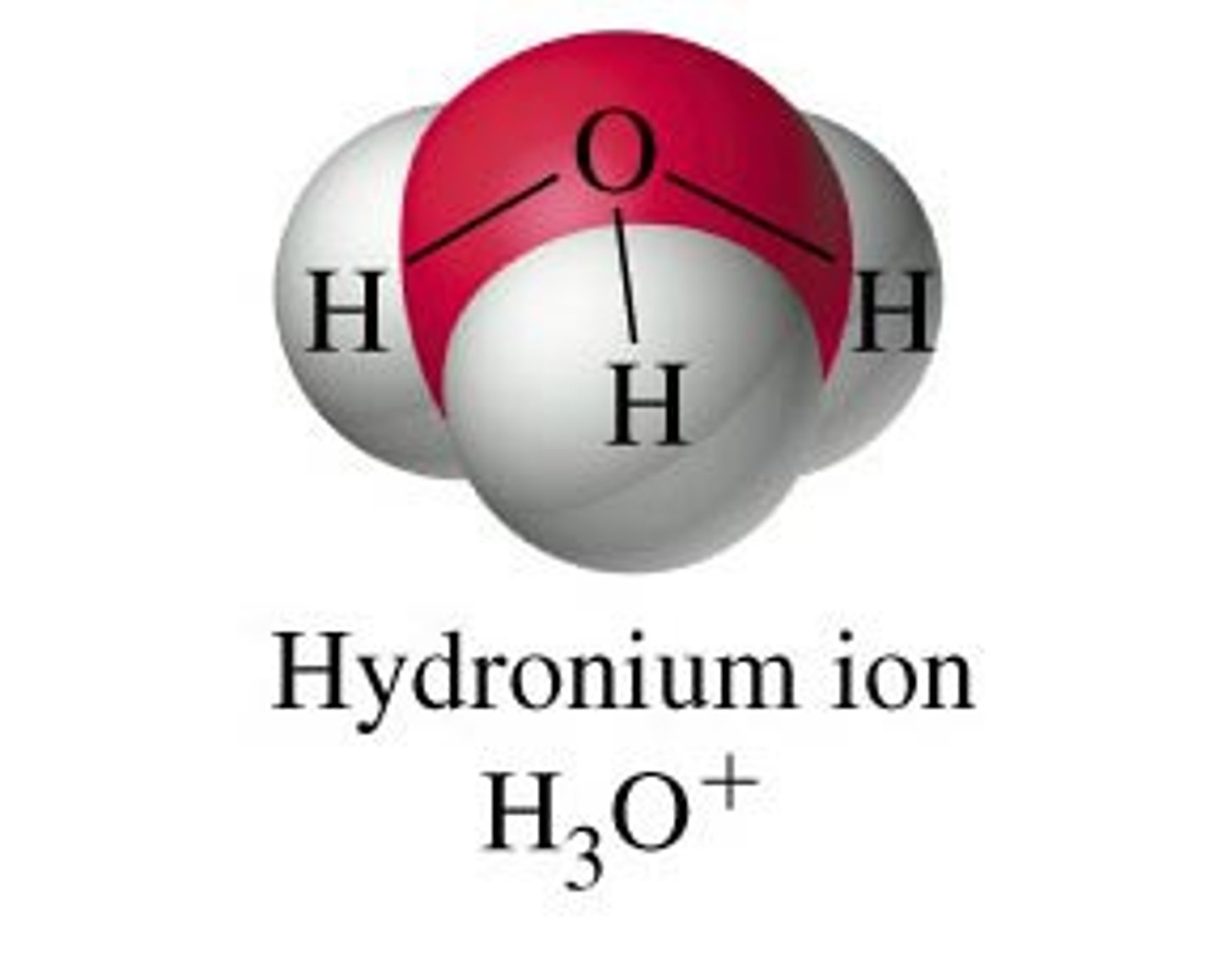
Ions
positively and negatively charged atoms
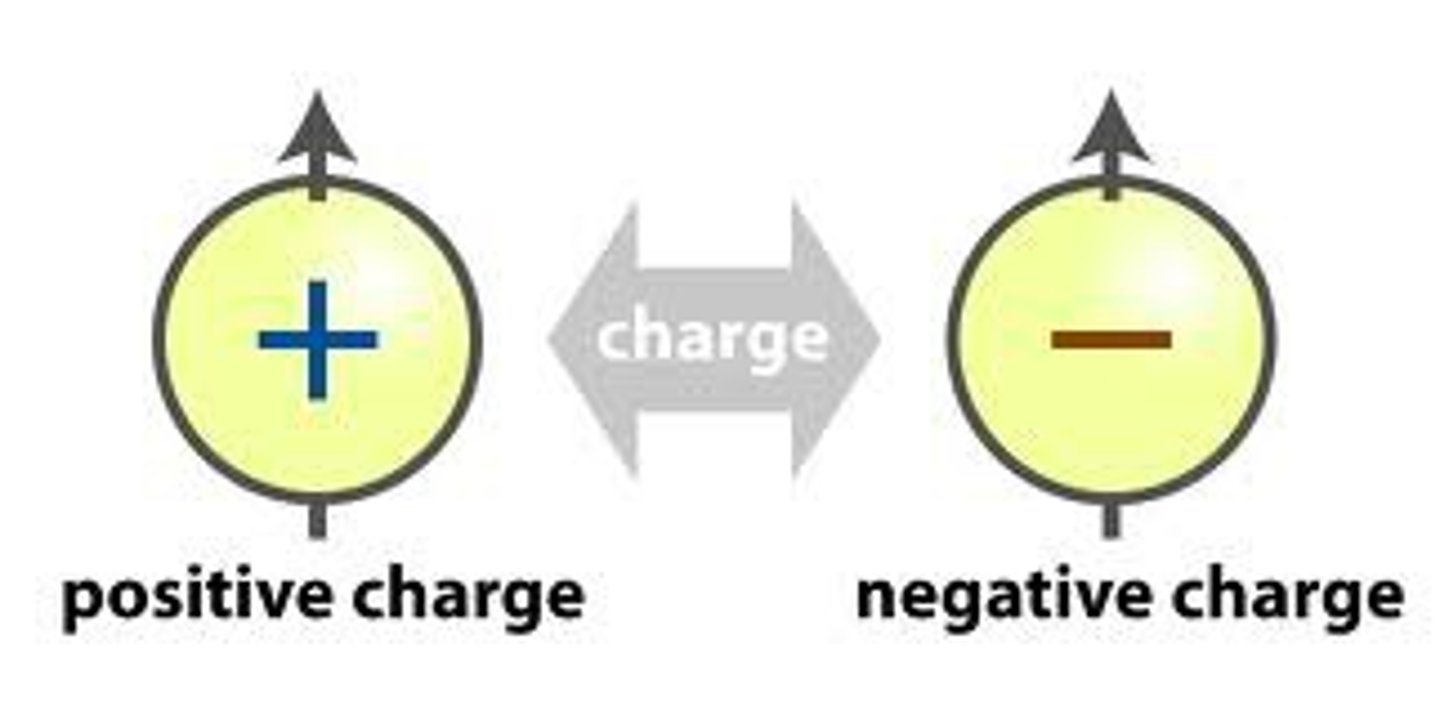
charge
protons-electrons
Mass of an atom
protons + neutrons

atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
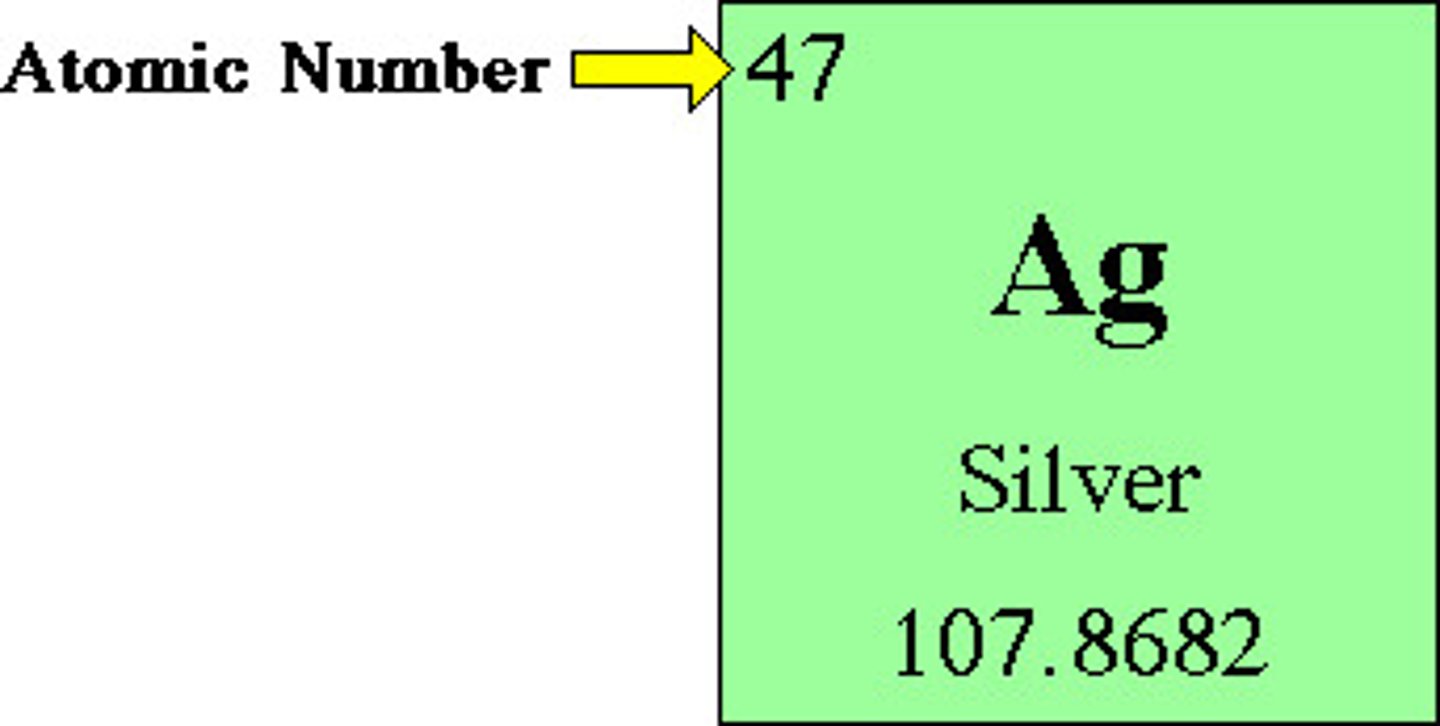
atomic mass
Number of protons and neutrons
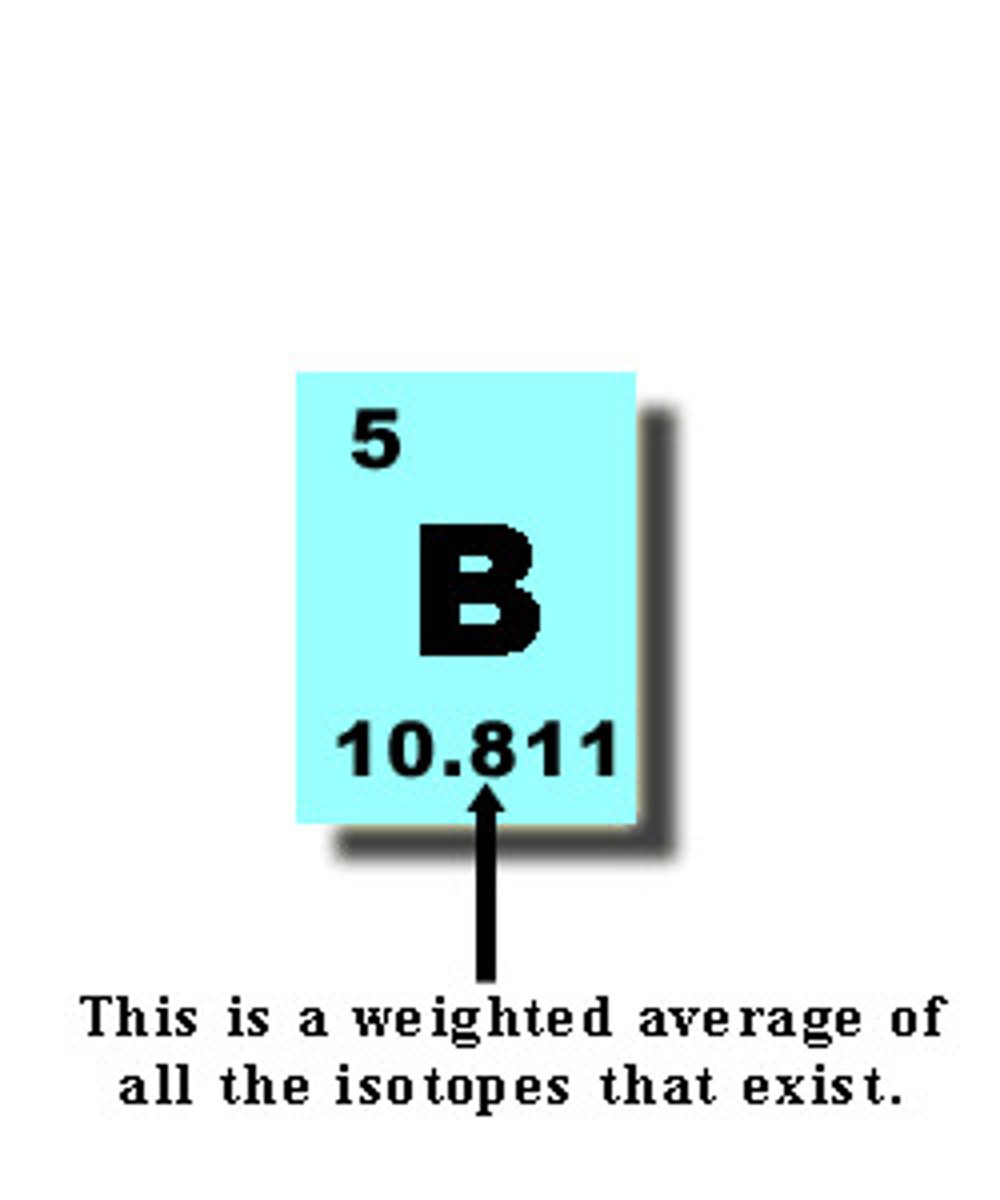
average atomic mass
the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element

average atomic mass formula
(Percent to decimal)(mass) + (percent to decimal)(mass)
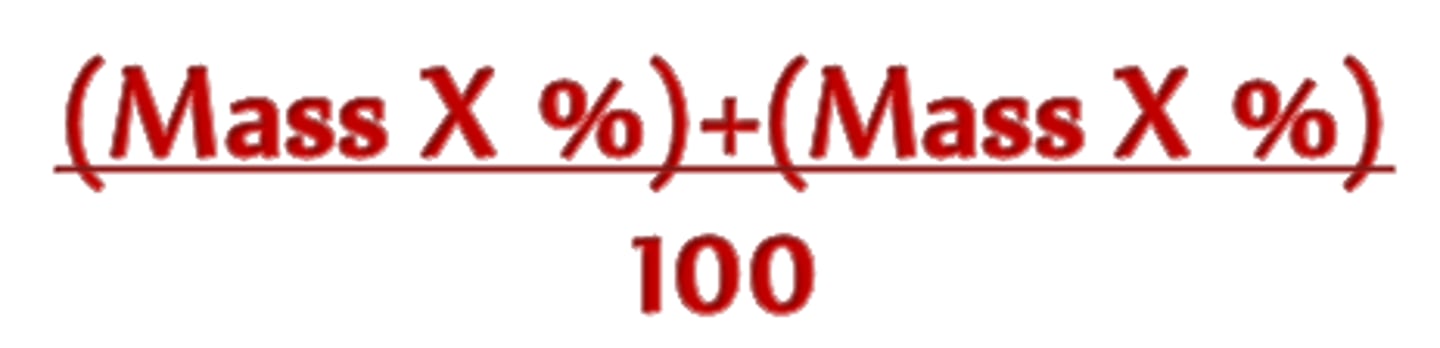
1 mole=
6.02x10^23
