Applied Kinesiology Quiz 4
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
hip/pelvic girlde complex is a ___ kintetic chain
forces travel up fromt he lower body and down from the upper body
closed
hip/pelvic girdle movement is necessary for ____ ___ movement
provides initiation of movement and stability/balnce
distal joint
what is the hip joint also called
acetabular femoral
hip joint is relatively stable due to
bony architecture
strong ligaments
large supportive muscles
what functions does the hip joint do
enhanced substantially by its wide ROM
weight bearing
locomotion
hip joint is a ball and socket joint connected by
head of femur connecting with acetabulum of pelvic girdle
pelvic girdle is connected by
right and left pelvic bone joined together posteriorly by sacrum
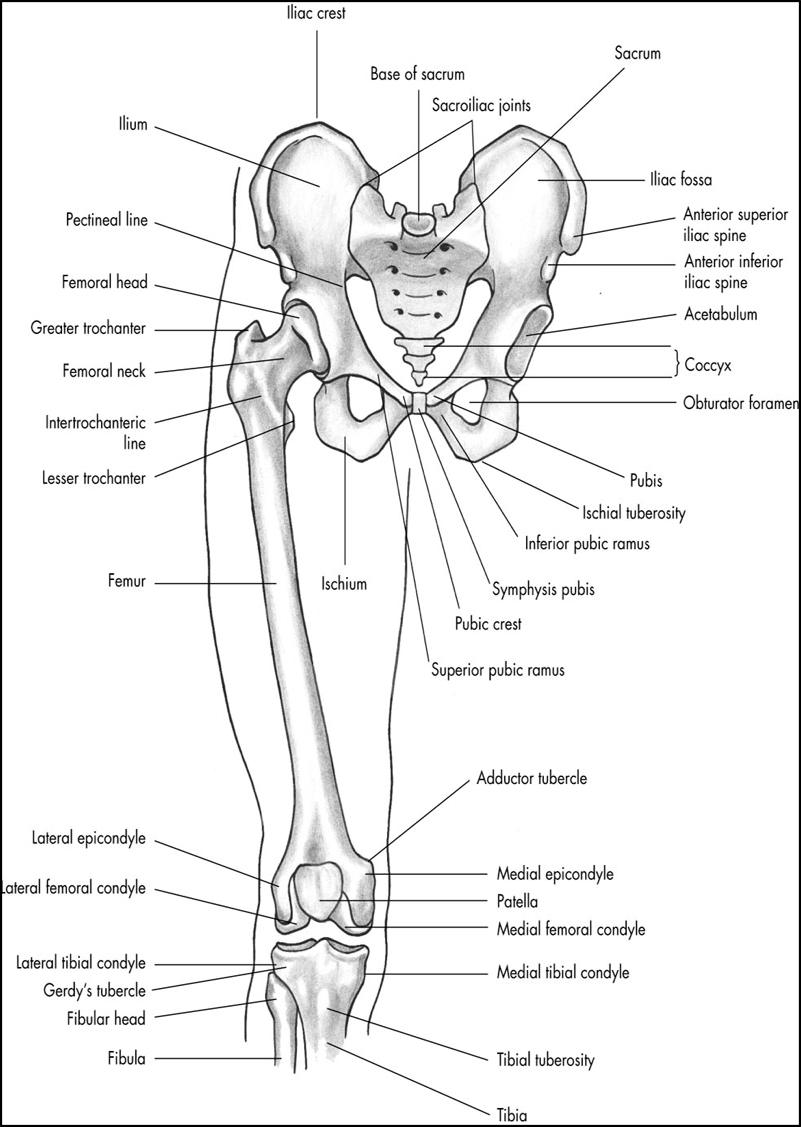
what are the pelvic bones
ilium
ischium
pubis
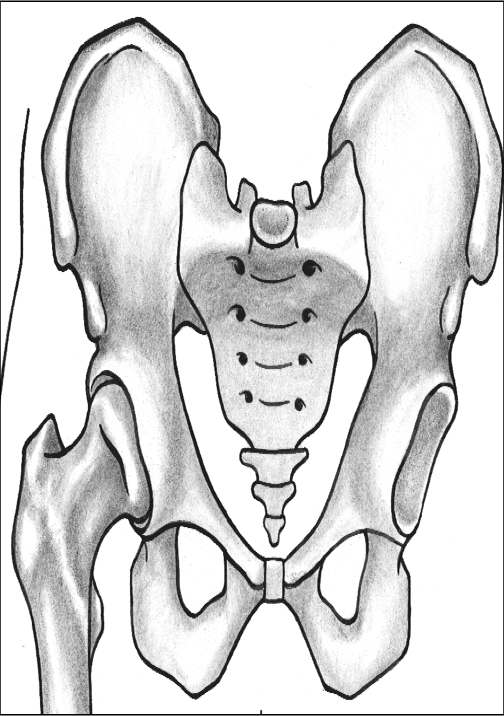
what is the sacroiliac (SI) joint
sacrum between the two pelvic bones and forms the SI joint
strong ligaments unite these bones to form rigid, slightly movable joints
synovial gliding or plane joint (limited motion)
common site for low back injury
how is the female pelvis different
lighter, thinner
wider in area
wider, flatter sacrum
two pelvic bones join to form what
amphiarthrodial articulation
cuplike area of the pelvis composed of 3 pelvic bones
similar to glenoid fossa of shoulder
lined around most of its periphery with a labrum to enhance stability and provide some shock absorption
aids in buttress effect
approximately 70 % of the head of the femur articulates with this
acetabulum
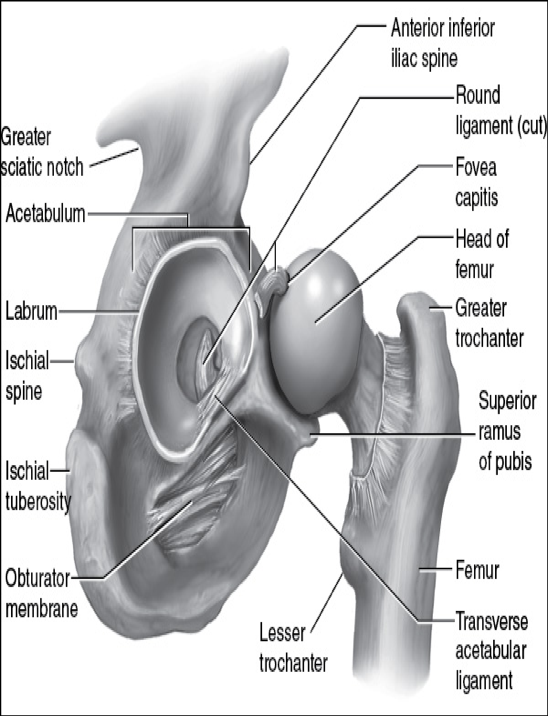
attaches from deep in acetabulum to a depression in femoral head
slightly limits adduction
ligaments of femur (round ligament or teres ligament)
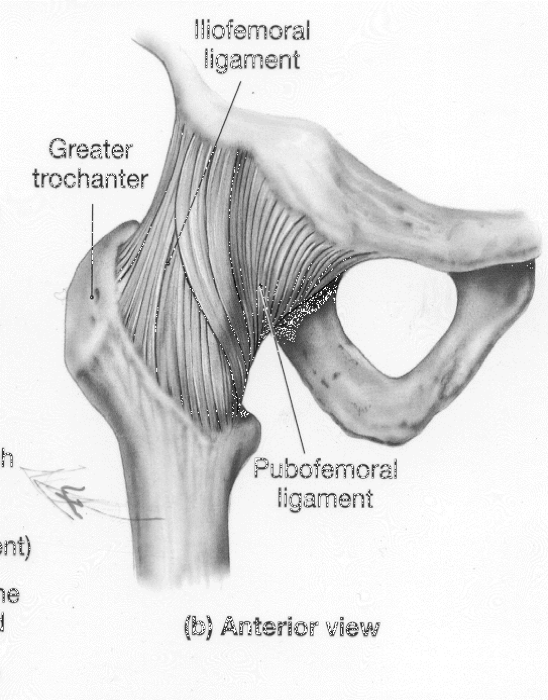
what are the structural support for the coxofemoral (hip) joint
iliofemoral ligament
pubofemoral ligament
ischiofemoral legament
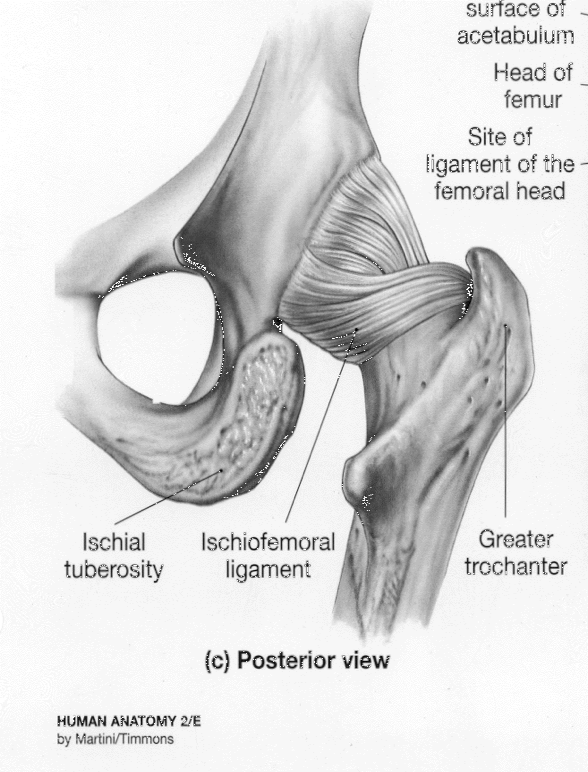
what does the neck of the femur do
holds the femur away from the pelvisw
what is the neck of the femur made of
formed by cancellous trabecular bone and reinforced with cortical bone
particularly on the inferior portion
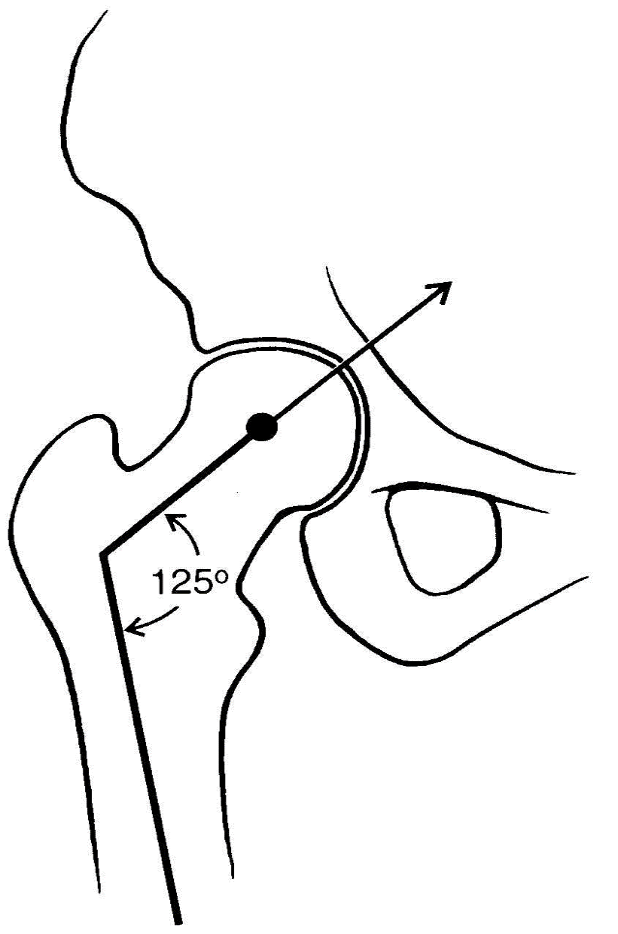
measured in the frontal place and typically ranges from 90-135 degrees with 125 considered average
angle of inclination
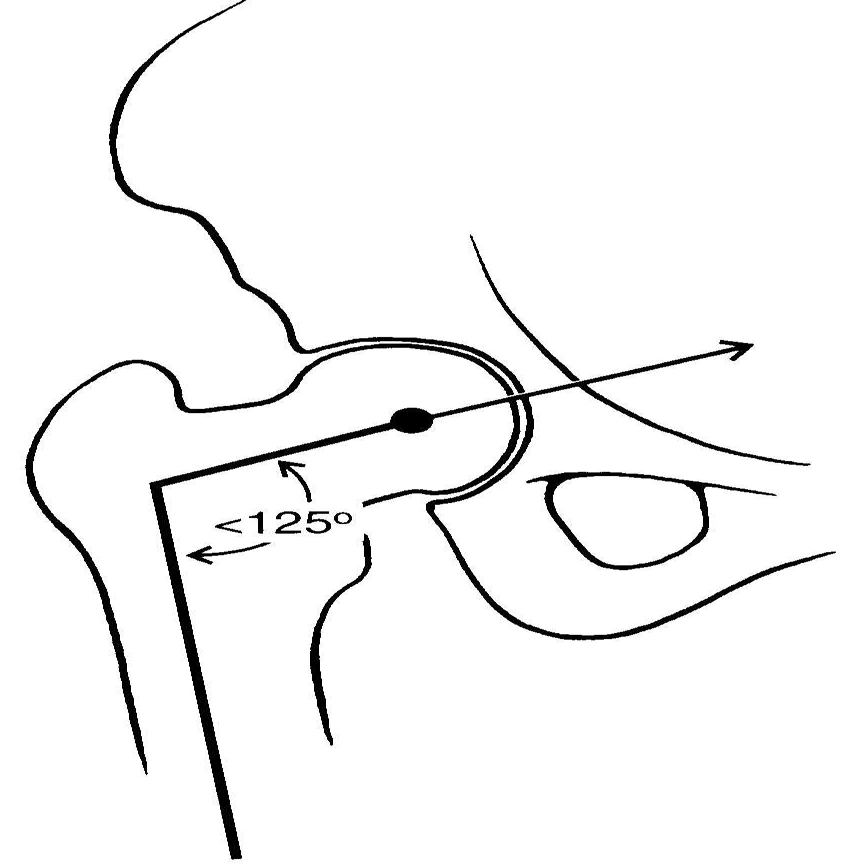
angle of femur and pelvis articulation
coxa vara
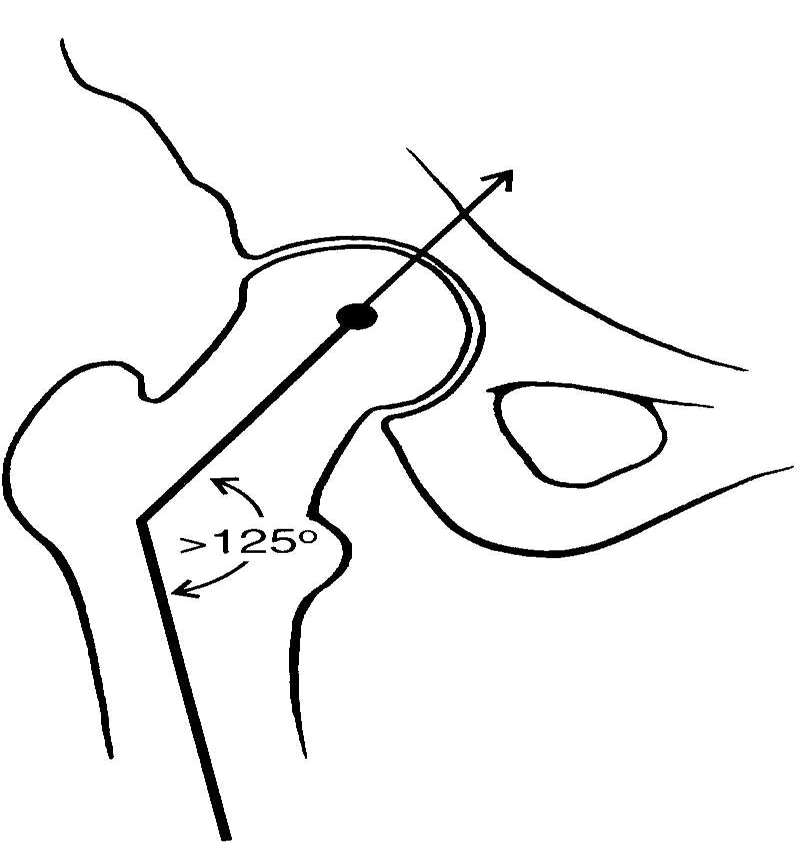
angle of femur and pelvis articulation
coxa valga
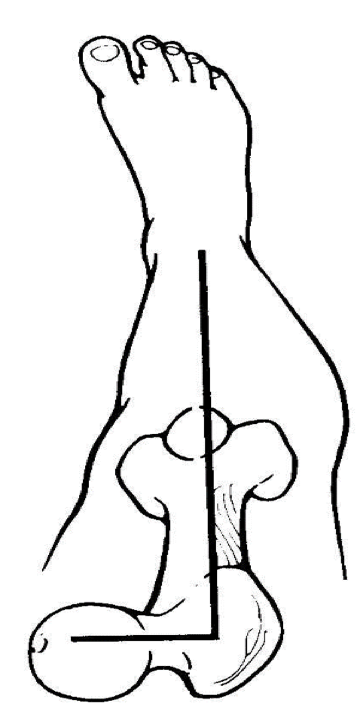
the angle of femoral neck in the transverse plane is termed the
normally the femoral neck is rotated anteriorly 12-15 degrees with respect to the femur
the varus/valgus and the anteversion/retroversion position will also influence distal joints at the knee and the ankle
angle of anteversion
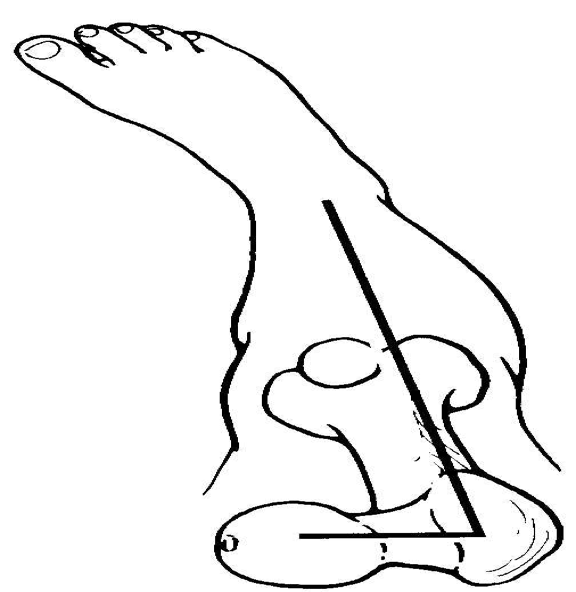
excessive anteversion
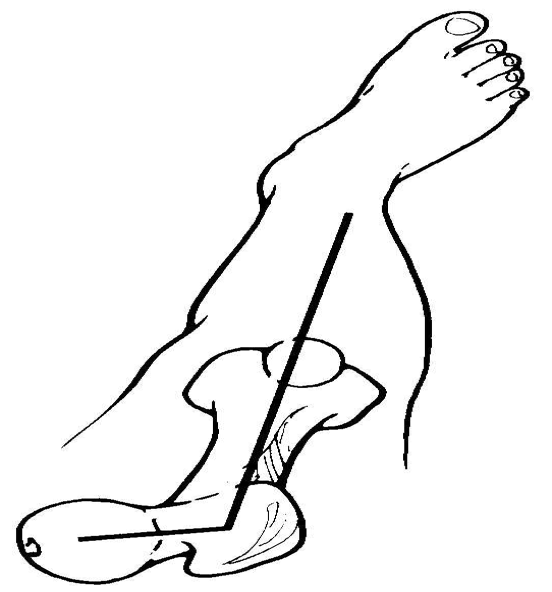
retroversion
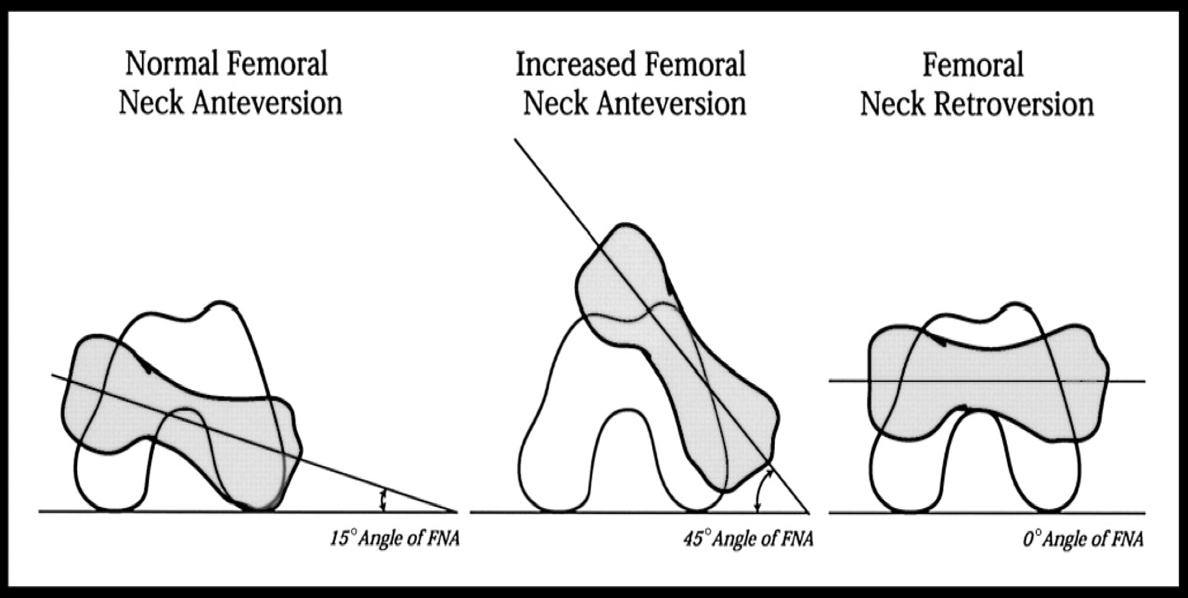
what is the normal femoral neck anteversion
what is the increased femoral neck anteversion
what is the femoral neck retroversion
15 degree angle of FNA
45 degree angle of FNA
0 degree angle of FNA
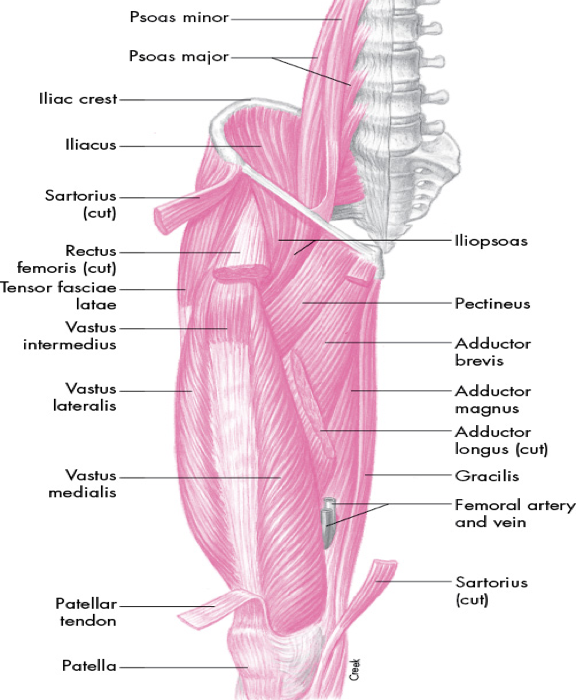
role of anterior musculature is primarily hip flexion
iliopsoas
pectineus
rectus femoris
sartorius
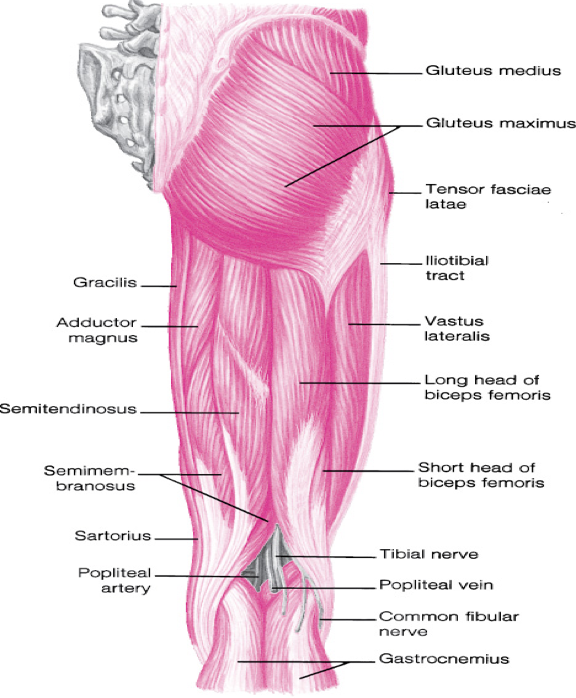
role of posterior musculature is primarily hip extension
gluteus maximus
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
external rotators
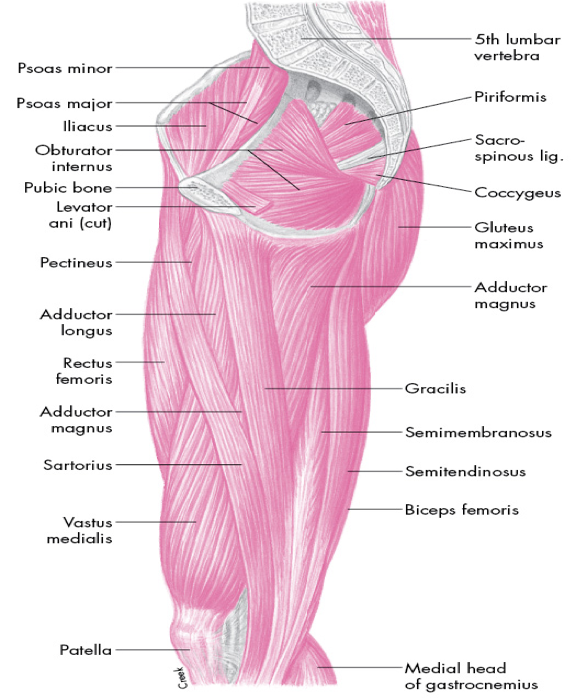
role of medial musculature is primarily hip adduction
adductor brevis
adductor longus
adductor magnus
gracilis
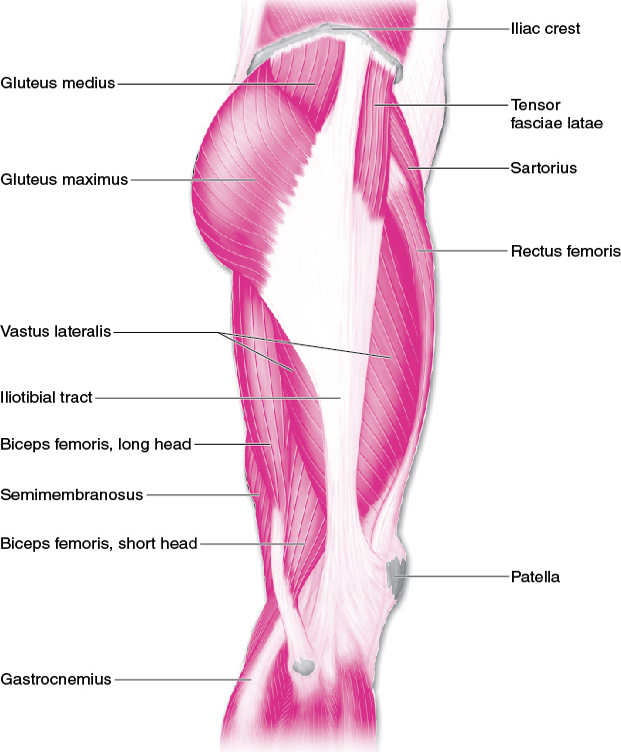
role of lateral musculature is primarily hip abduction
gluteus medius
gluteus minimus
tensor fasciae latae
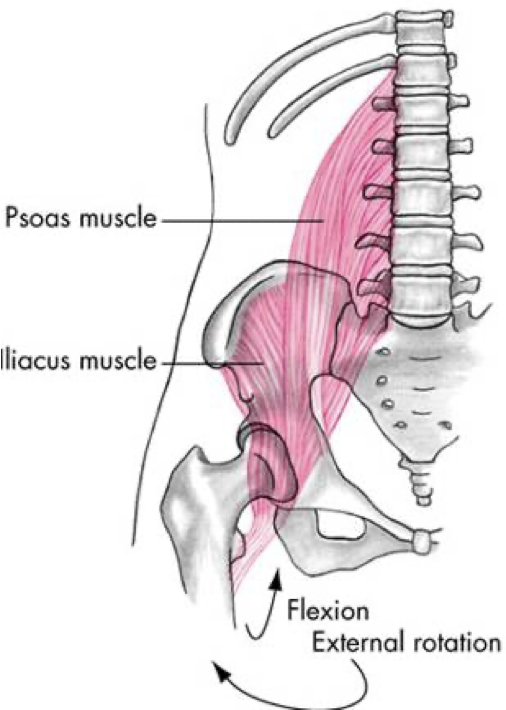
anterior compartment
iliopsoas
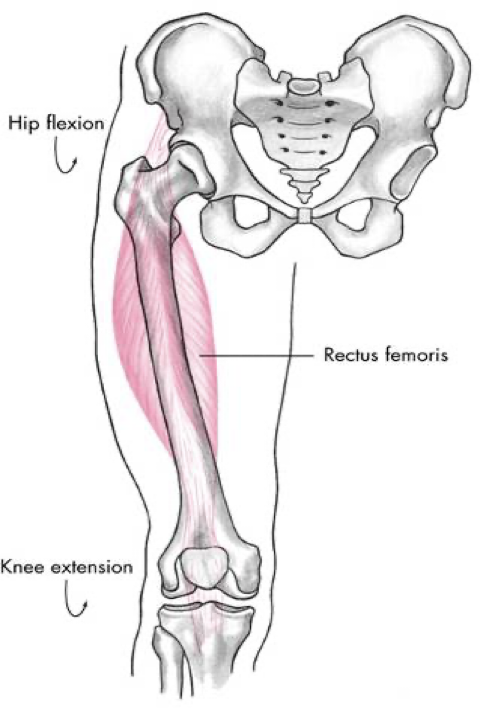
anterior compartment
rectus femoris
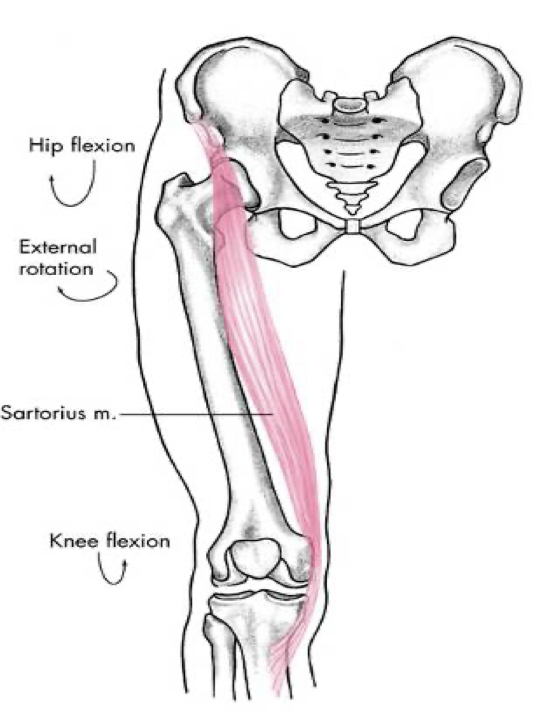
anterior compartment
sartorius
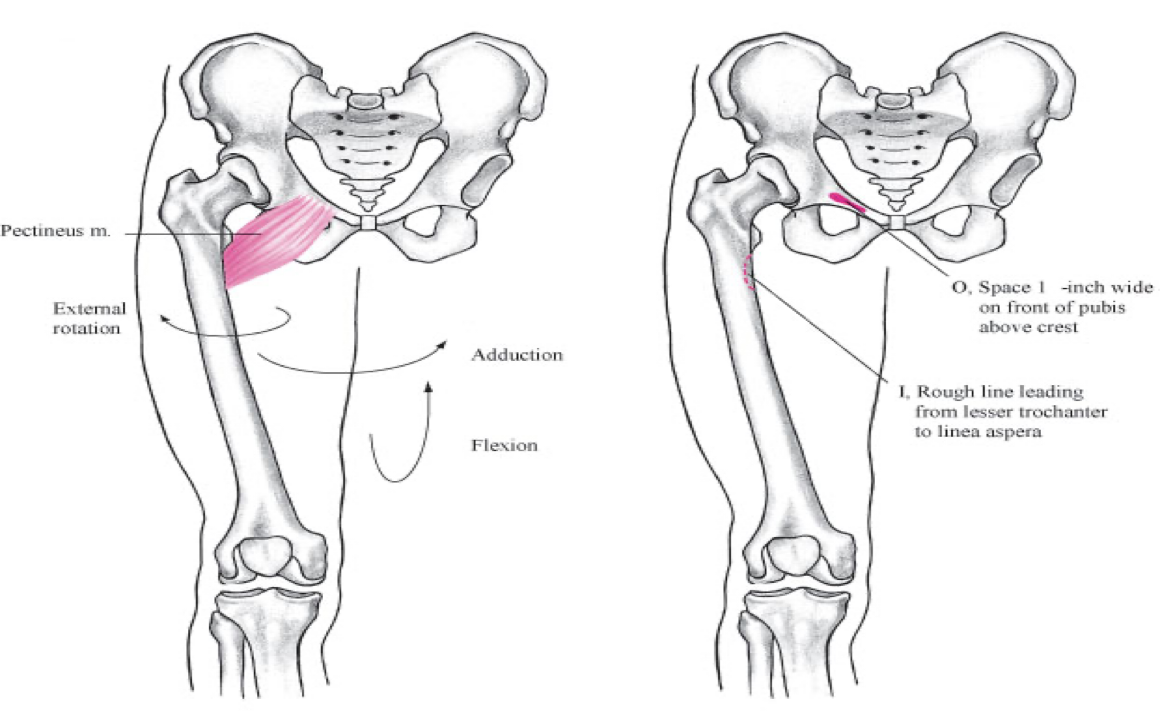
anterior compartment
pectineus
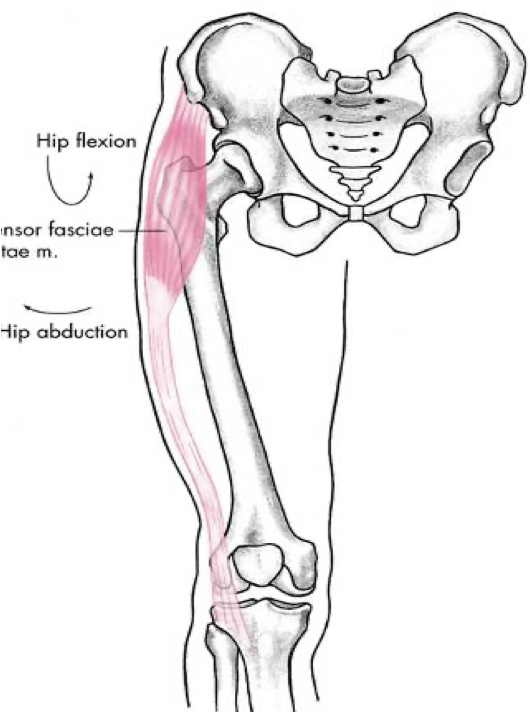
anterior compartment
tensor fascie latae
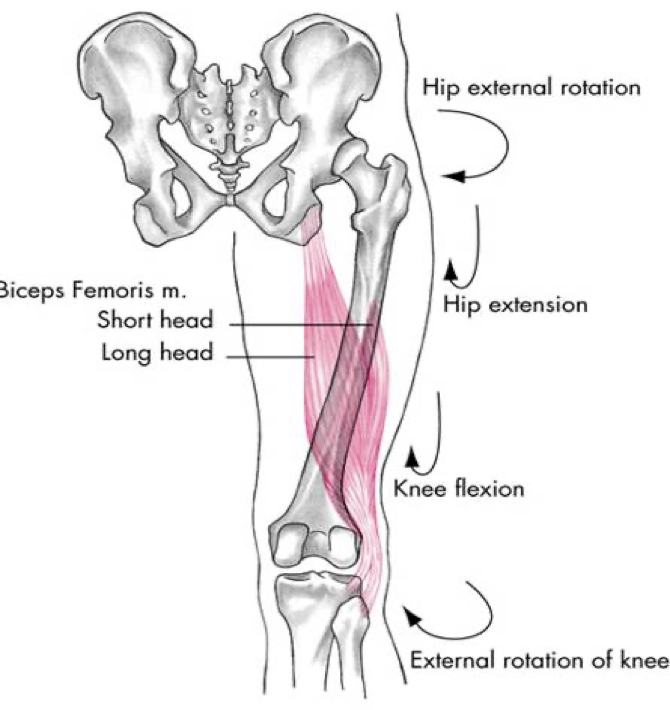
posterior compartment (hamstrings)
biceps femoris
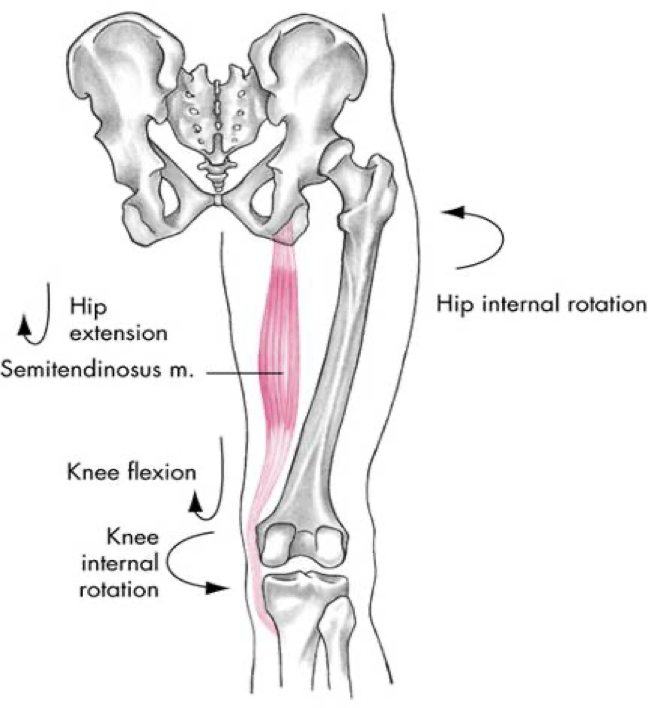
posterior compartment (hamstrings)
semitendinosus
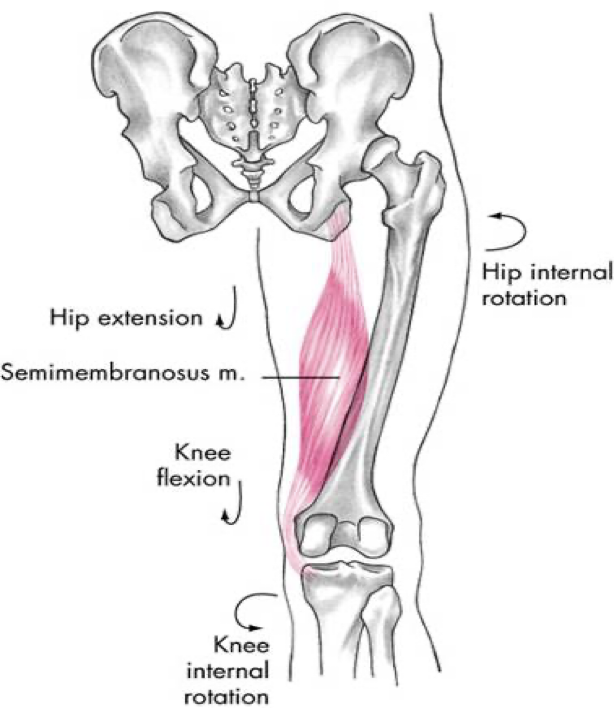
posterior compartment (hamstrings)
semimembranosus
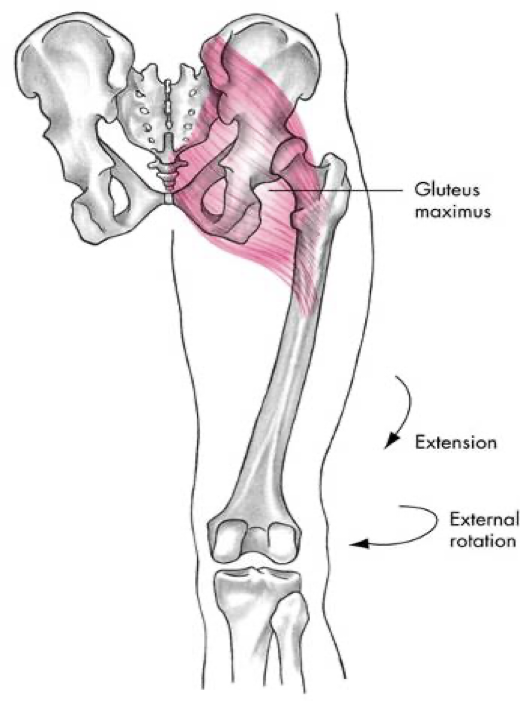
posterior compartment (gluteals)
gluteus maximus
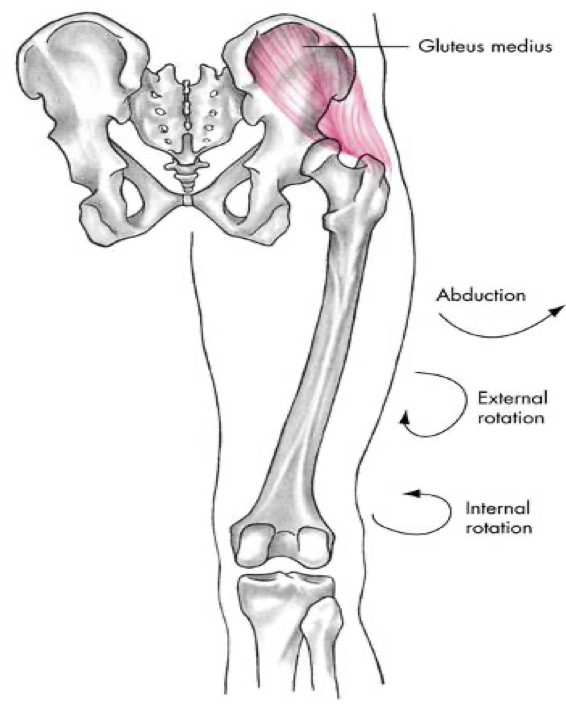
posterior compartment (gluteals)
gluteus medius
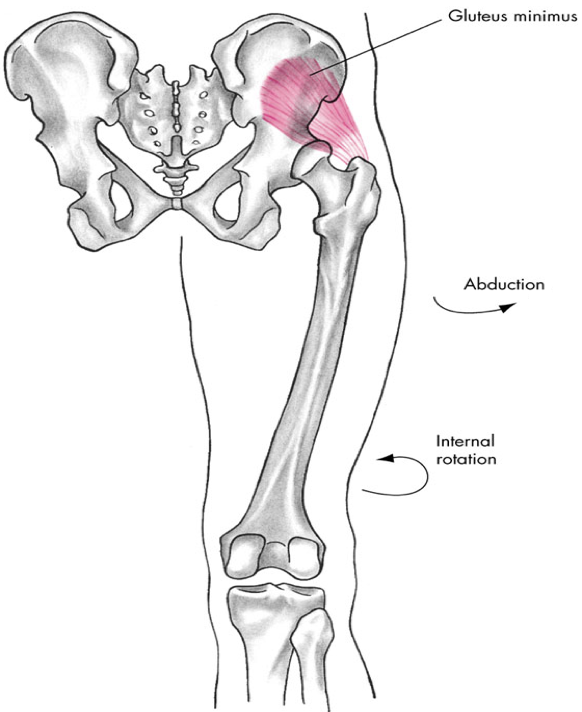
posterior compartment (gluteals)
gluteus minumus
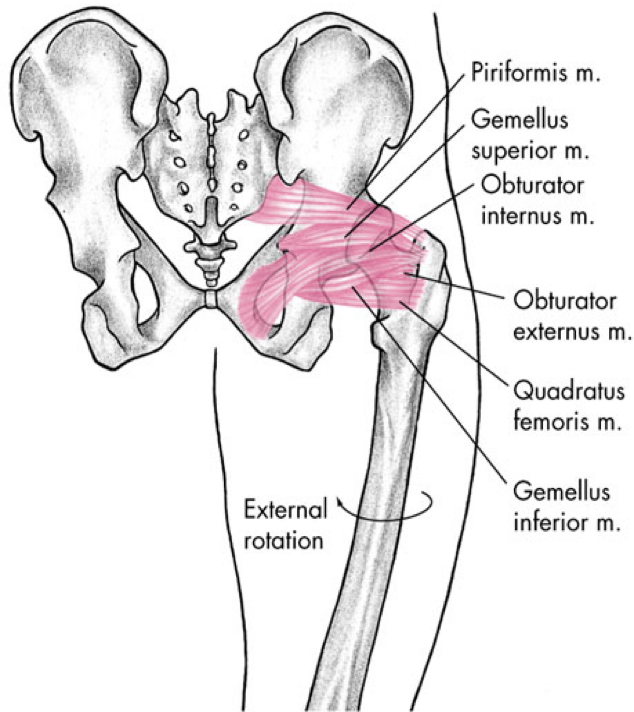
posterior compartment
deep external rotator group
piriformis m
gemellus superior m
obturator internus m
obturator externus m
quadratus femoris m
gemellus inferior m
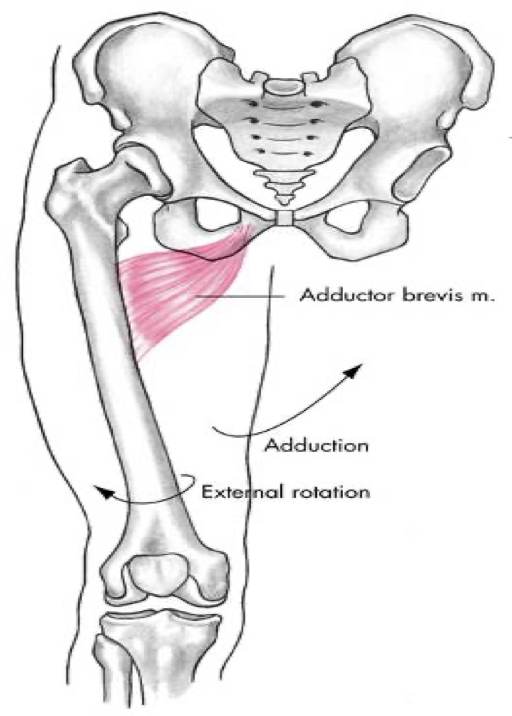
medial compartment
adductor brevis
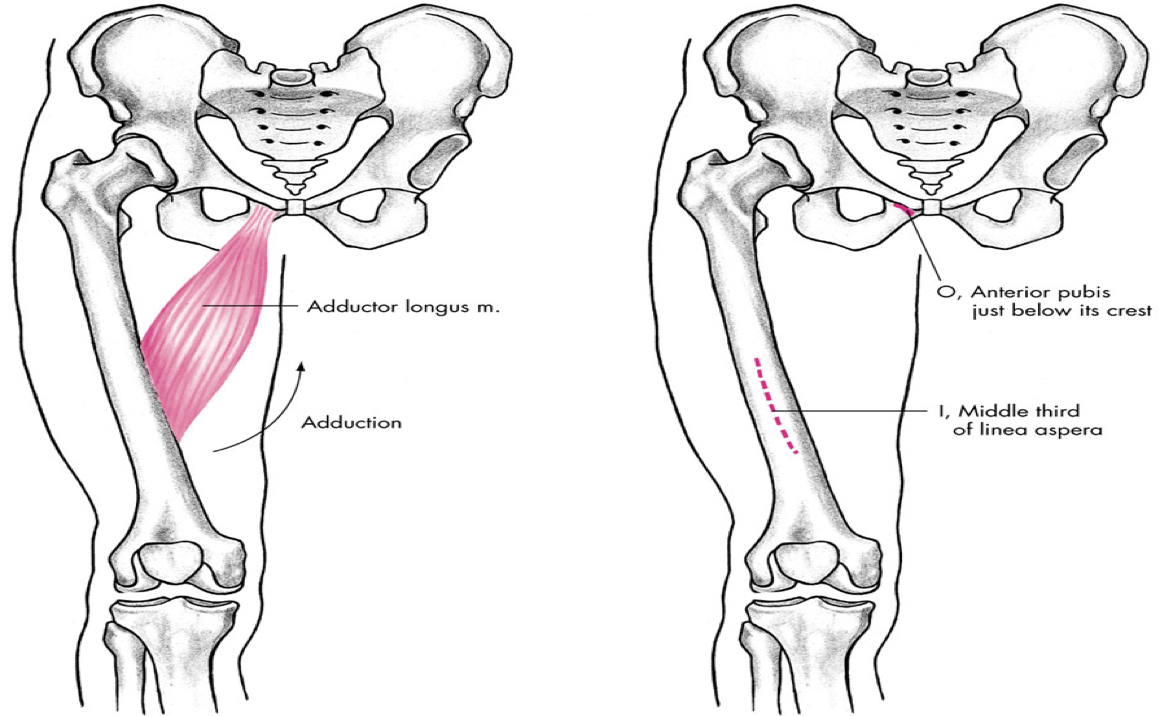
medial compartment
adductor longus
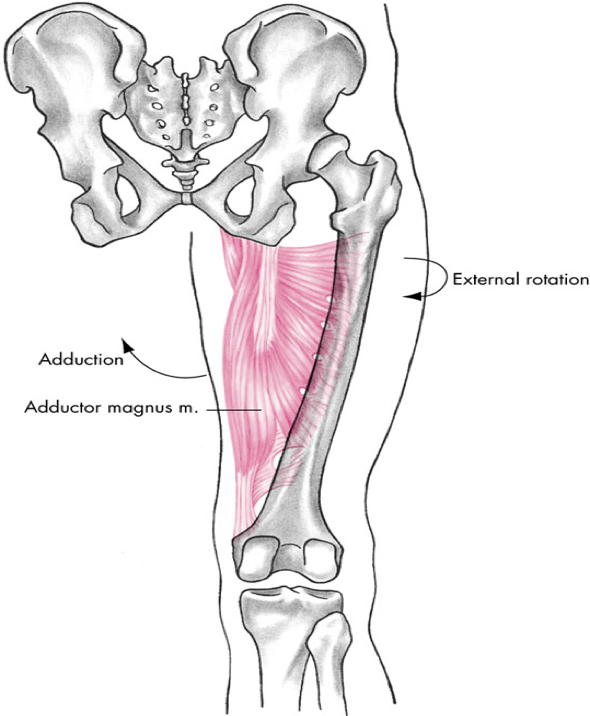
medial compartment
adductor magnus
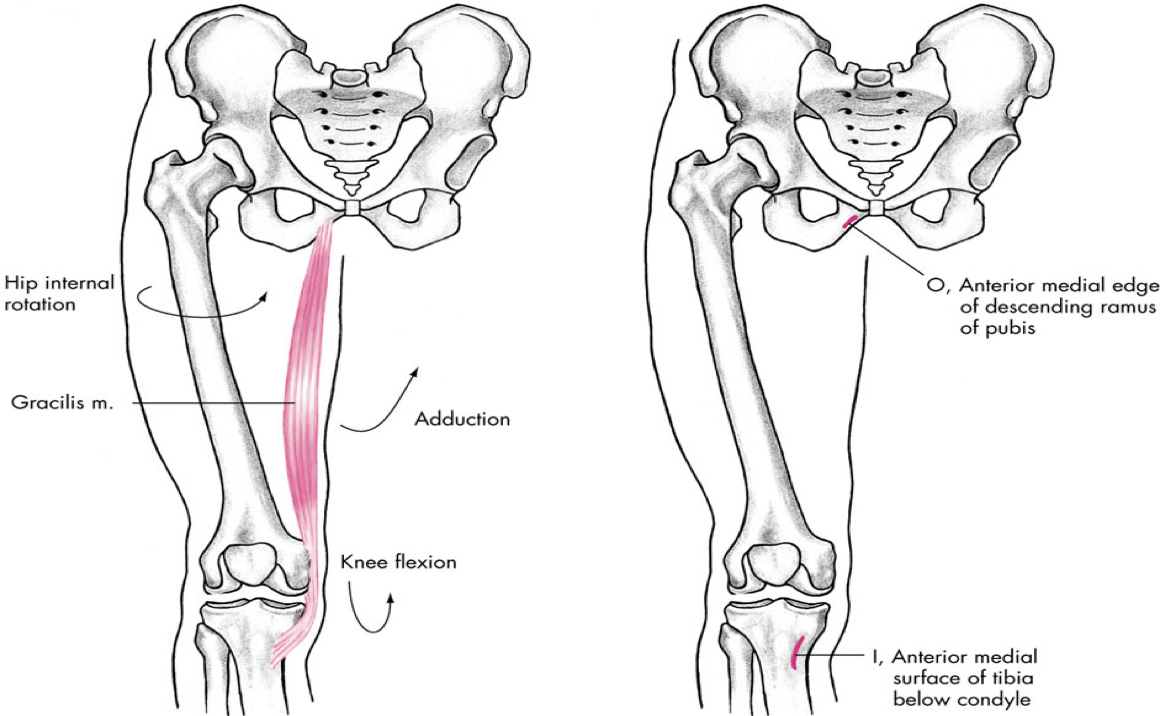
medial compartment
gracilis
pelvic girdle moves back and forth within __ planes for a total of __ different movements
3
6
all pelvic girdle rotation results from motion at one or more locations
right hip
left hip
lumbar spine
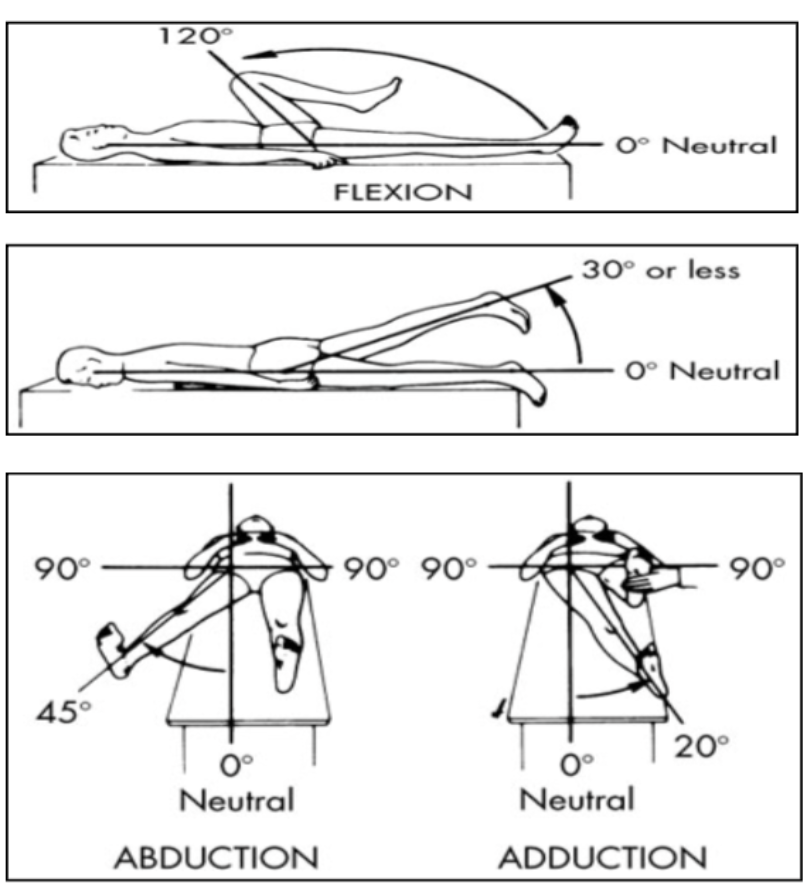
movement in the coxofemoral joint
flexion: 0-120 degrees
extension: 0-20 degres
abduction: 0-45 degrees
adduction: 0-20 degrees
internal rotation: 0-35 degrees
external rotation: 0-45 degrees
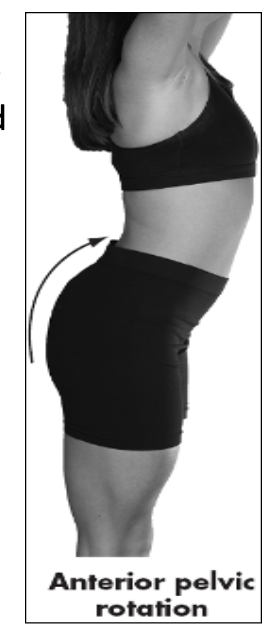
anterior movement of upper pelvis, iliac crest tilts forward in a sagittal plane, anterior tilt, downward rotation
anterior pelvic rotation

posterior movement of upper pelvis, iliac crest tilts backwards in a sagittal plane; posterior tilt; upward rotation
posterior pelvic rotation
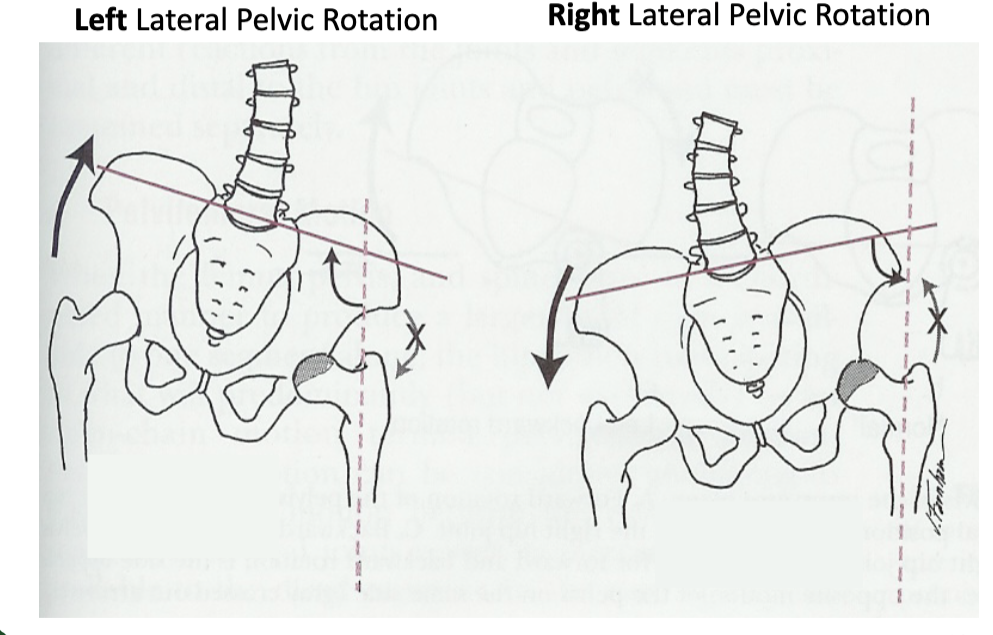
in frontal place left pelvis moves inferiorly in relation to right pelvis; either left pelvis rotates downward or right pelvis rotates upward; left lateral tilt
left lateral pelvic rotation
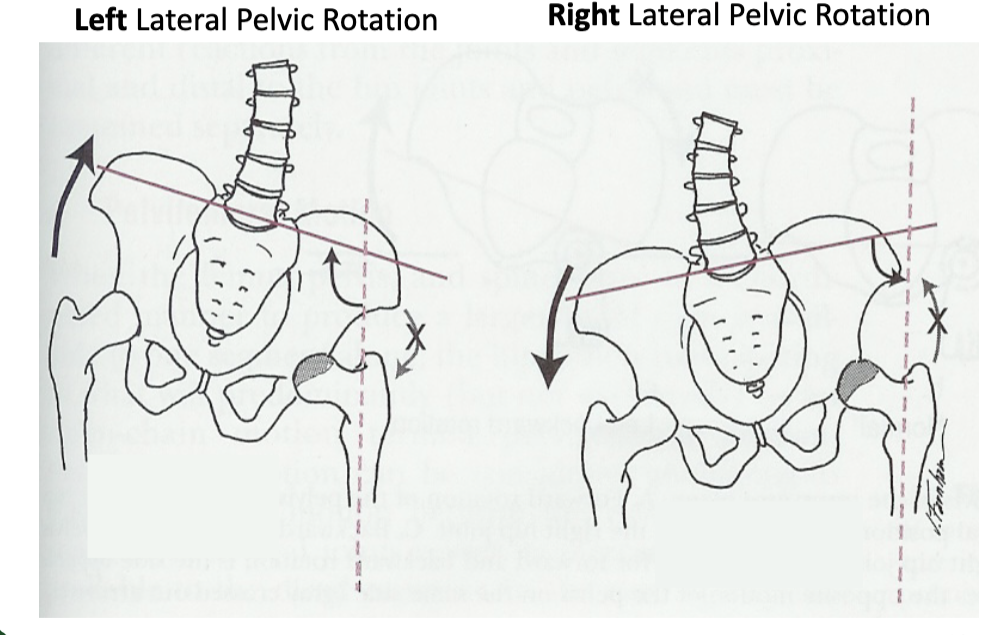
in frontal plane right pelvis moves inferiorly in relation to left pelvis; either right pelvis rotates downward or left pelvis rotates upward; right lateral tilt
right lateral pelvic rotation
in horizontal/transverse plane pelvis rotates to body’s left; right iliac crest moves anteriorly in relation to left iliac crest, which moves posteriorly
counterclockwise
left transverse pelvic rotation
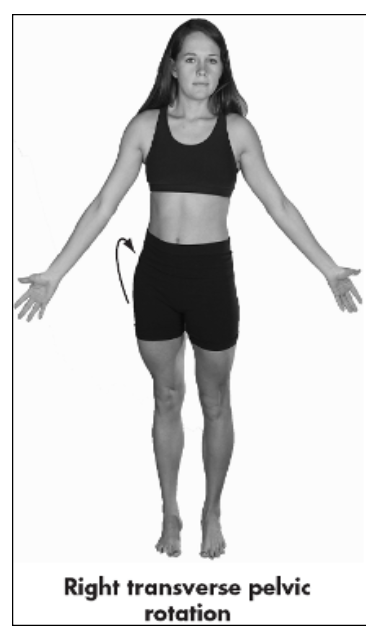
in horizontal plane pelvis rotates to body’s right, left iliac crest moves anteriorly in relation to right iliac crest, which moves posteriorly
clockwise
right transverse pelvic rotation
anterior/ posterior pelvic rotation occurs in what plane
sagittal plane
anterior pelvic rotation accomplished by hip ___ and/or lumbar ___
flexion
extension
posterior pelvic rotation accomplished by hip ___ and/or lumbar ___`
extension
flexion
standing on both feet and contracting hip flexors, the trunk and pelvis rotate ___
anteriorly
lying supine and contracting hip flexors, the thighs move ____ into ___ on the stable pelvis
forward
flexion
what are hip flexor muscles used for
moving thighs up toward trunk
in lowering to sitting position, hip extensor muscles used ___ when pelvis and trunk move downward slowly on the femur and ___ when trunk is raised on femur (rising to standing position)
eccentrically
concentrically
what muscles are used in hip flexion
iliopsoas
pectineus
rectus femoris
sartorius
what muscle assist in hip flexion
pectineus
tensor fascia latae
sartorius
rectus femoris
what muscles are used in hip extension
gluteus maximus
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
what muscles are used in hip abduction
gluteus medius
gluteus minimus
tensor fascia latae
what muscles are used in hip adduction
adductor magnus
adductor longus
adductor brevis
gracilis
pectineus
what muscles are used in hip external rotation
gluteus maximus
biceps femoris
deep external rotator group
what muscles are used for hip internal rotation
gluteus medius
gluteus minimus
tensor fascia latae
gracilis
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
what are the support ligaments
round ligament
iliofemoral ligament
ischiofemoral ligament
pubofemoral ligament
right/left hip motion
flexion
extension
abduction
adduction
internal rotation
external rotation
pelvis rotation
anterior rotation
posterior rotation
right lateral rotation
left lateral rotation
right transverse rotation
left transverse rotation
lumbar spine motion
extension
flexion
left lateral flexion
right lateral flexion
left lumbar rotation
right lumbar rotation