Review Digestion and Urinary systems test
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Digestion
The process by which the body breaks down food into smaller components that can be absorbed and utilized for energy and nutrients.
Accessory Organs
Organs that assist in digestion but are not part of the digestive tract, such as the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder.
Salivary Glands
Glands located in the mouth that produce saliva, aiding in the digestion of food and the lubrication of the oral cavity.
Liver
A vital organ that processes nutrients, produces bile for fat digestion, and detoxifies harmful substances in the body.
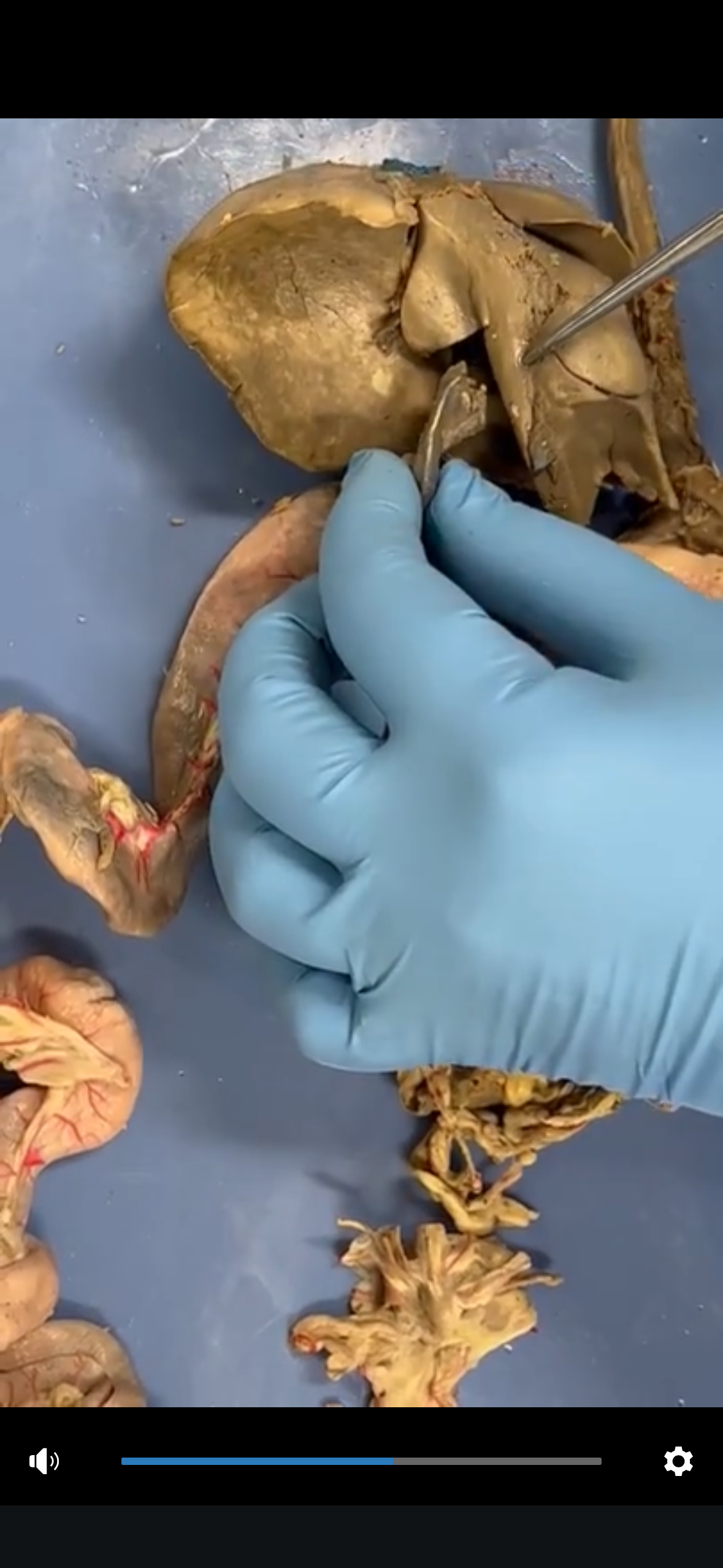
Gallbladder
A small pouch-like organ that stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver, releasing it into the small intestine to aid in fat digestion.
Pancreas
An organ that produces enzymes for digestion and hormones such as insulin that regulate blood sugar levels.
Alimentary Canal
The continuous tube that extends from the mouth to the anus, responsible for the ingestion, digestion, and absorption of food as well as the elimination of waste.
Mouth
The entry point of the digestive system, where food is ingested and the process of digestion begins through chewing and saliva.
Pharnyx
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the esophagus, playing a key role in both the digestive and respiratory systems.
Esophagus
The muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) with the stomach, transporting food and liquids after swallowing.
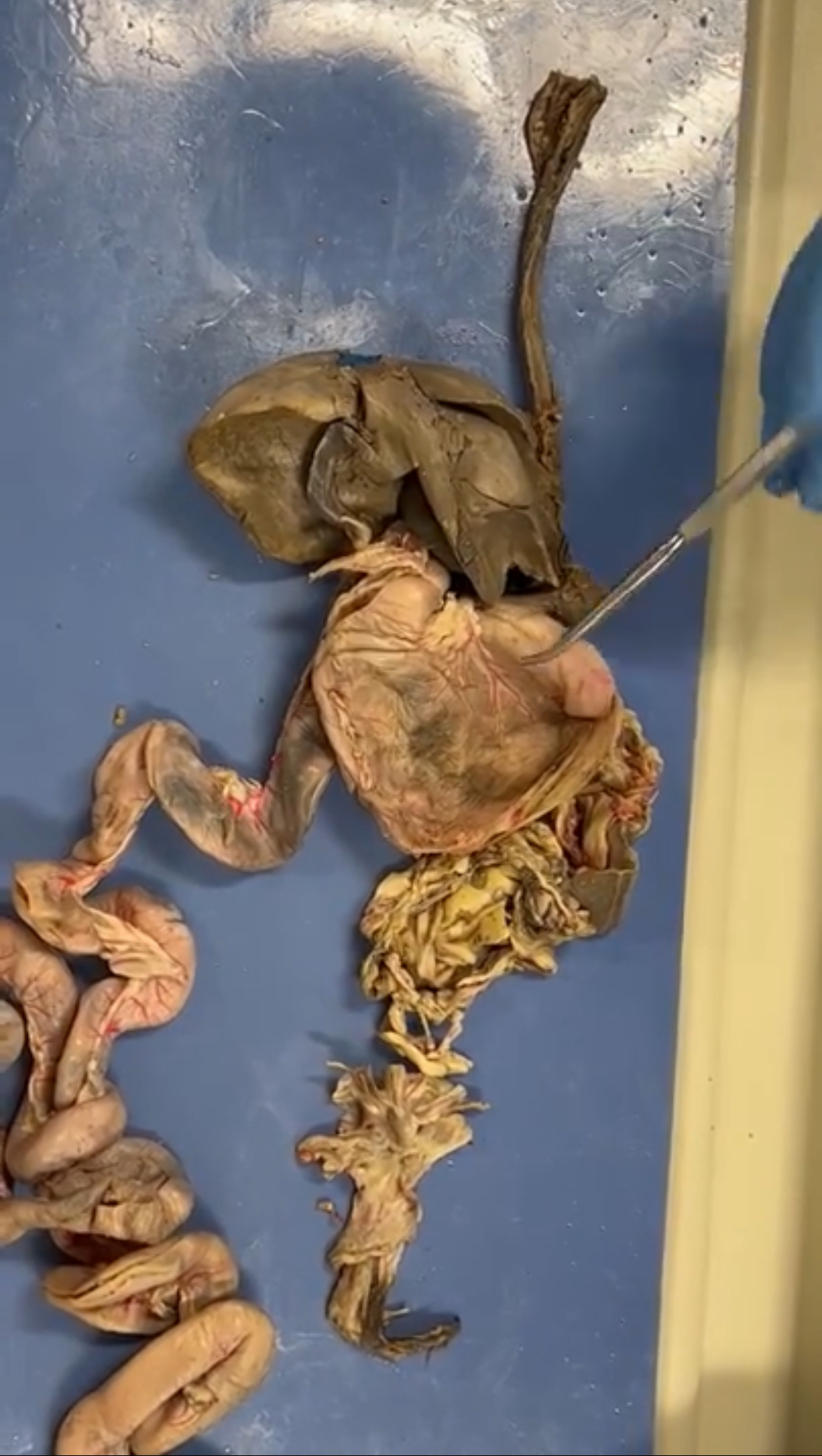
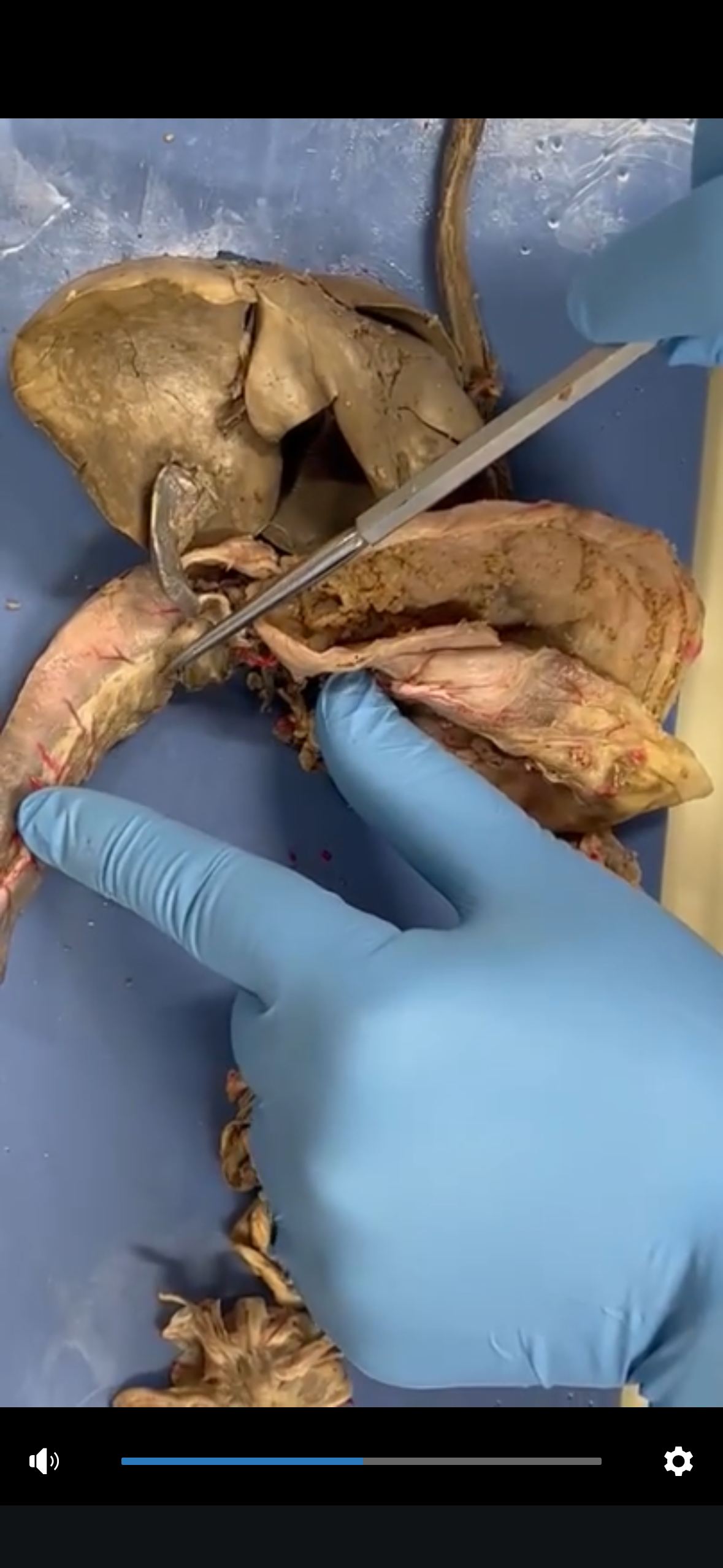
Stomach
The organ that holds food while it is mixed with stomach enzymes and acids, initiating the digestion of proteins and regulating the flow of food into the small intestine.
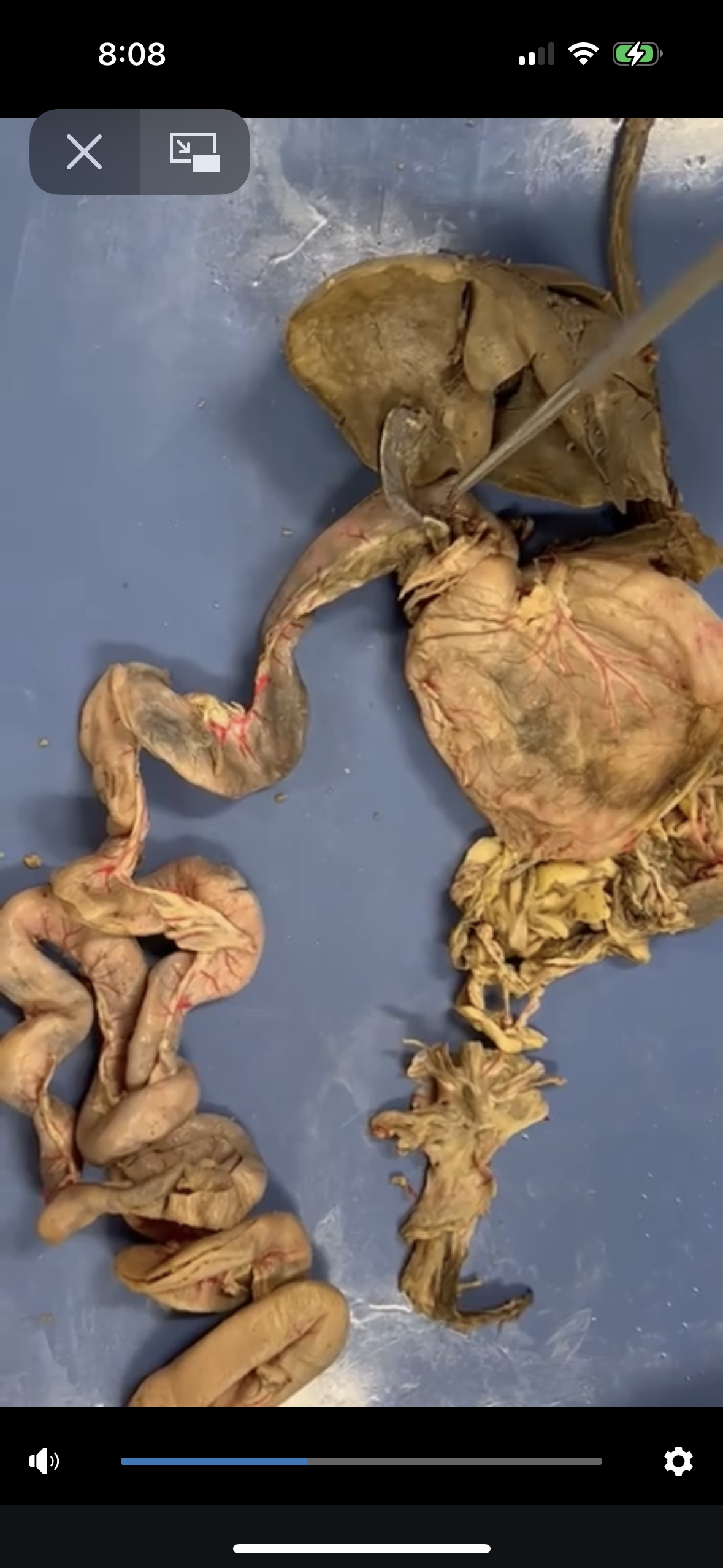
Small Intestines (duodenum, jejunum, ileum its in order)
The part of the digestive system where most of the digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs, following the stomach. It is divided into three sections: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Large intestines
Absorbs water
Large intestines have
Cecum, Ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, anus
What’s the order of the structure of the walls in the stomach
Muscosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa.
Goblet cells
Mucous-secreting cells found in the epithelium that help protect and lubricate the digestive tract.
Microvilli
Tiny projections on epithelial cells that increase surface area for absorption in the intestines.
Villi
Finger-like projections that line the intestinal walls, enhancing nutrient absorption by increasing surface area.
Lacteal
Small lymphatic vessels found in the villi of the intestine that absorb dietary fats and transport them into the bloodstream.
Simple Columnar epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue composed of a single layer of column-shaped cells, primarily involved in absorption and secretion in organs such as the intestines.
Segmentation vs. Peristalsis
Segmentation is the rhythmic contraction of circular muscles in the intestines that mixes food, while peristalsis is the wave-like muscular contraction that moves food through the digestive tract.
Tongue
A muscular organ in the mouth involved in the manipulation of food, taste sensation, and speech.
Lingual Tonsils
Lymphoid tissues located at the base of the tongue that help protect against infection and play a role in the immune response.
Uvula
A small, fleshy extension at the back of the soft palate that helps prevent food from entering the nasal cavity during swallowing.
Palatine Tonsils
Lymphoid tissues located on either side of the throat, playing a key role in the immune response by trapping pathogens.
Pharyngeal tonsils
Lymphoid tissues located at the back of the nasal cavity that help protect against infection and contribute to the immune response.
Sinuses
Air-filled cavities in the skull that help reduce its weight and produce mucus.
Hard Palate vs. Soft Palate
The hard palate is the bony front portion of the roof of the mouth, while the soft palate is the muscular back part that closes off the nasal passage during swallowing.
Salivary glands
Parotid, Sublingual, and submandibular gland
Nasopharnyx
The area of the pharynx located behind the nose and above the soft palate, playing a role in the upper respiratory system.
Oropharynx
The portion of the pharynx located behind the mouth, involved in both the respiratory and digestive systems.
Larngopharnyx
The part of the pharynx located below the oropharynx, connecting to the esophagus and larynx, serving as a pathway for both food and air.
Bolus
A mass of chewed food that is formed by the action of chewing and saliva, ready to be swallowed.
Esophagus
The muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) with the stomach, transporting food and liquids during swallowing.
Lower Esophageal
Sphincter/gastroesophageal valve
Pyloric sphincter
A band of smooth muscle located at the junction between the stomach and the small intestine, regulating the passage of chyme into the duodenum.
Pepsin
A digestive enzyme that breaks down proteins in the stomach.
Gastric Juices
A mixture of hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and digestive enzymes secreted by the stomach to aid in food digestion.
Chyme
A semi-liquid mixture of partially digested food and digestive juices found in the stomach.
Pancreas
An organ that produces digestive enzymes and hormones, including insulin, to regulate blood sugar levels.
Pancreatic Juices
The digestive fluids produced by the pancreas, containing enzymes that aid in the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Common Hepatic Duct
The duct that carries bile from the liver to the gallbladder and small intestine for digestion.
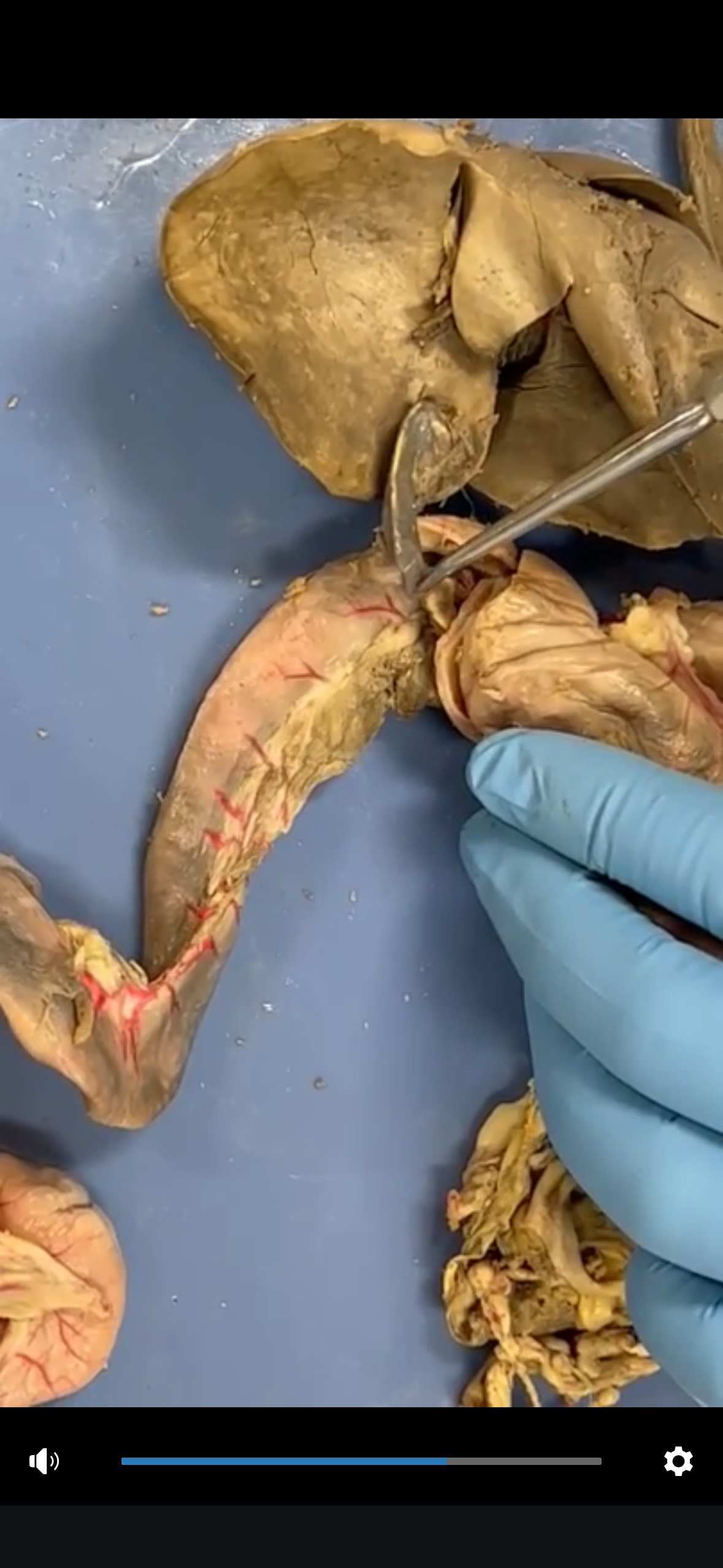
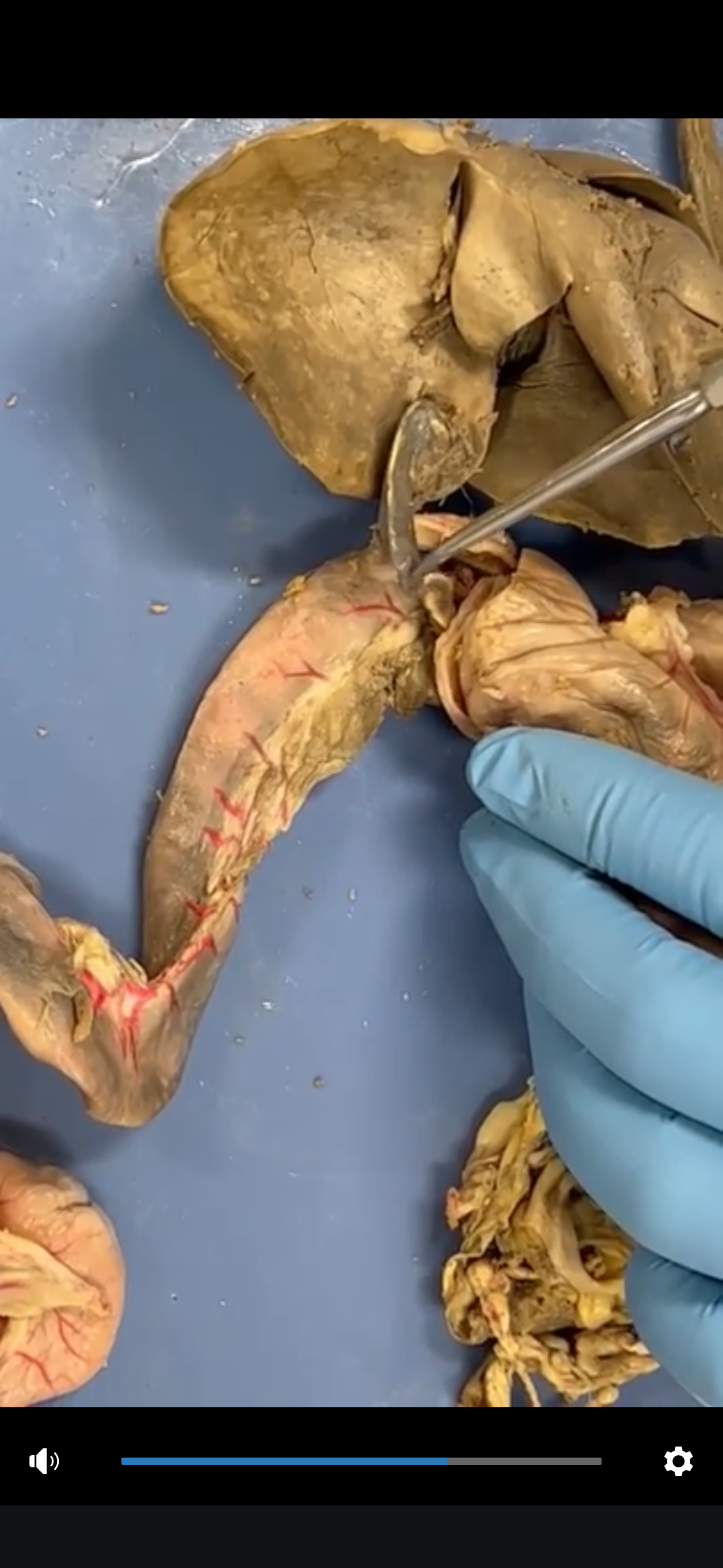
Cystic Duct
The duct that transports bile to and from the gallbladder, connecting it to the common hepatic duct.
Bile Duct
The duct that carries bile from the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum in the small intestine.
Heptapancreatic duct
The duct that carries bile and pancreatic juices from the liver and pancreas to the duodenum, facilitating digestion.
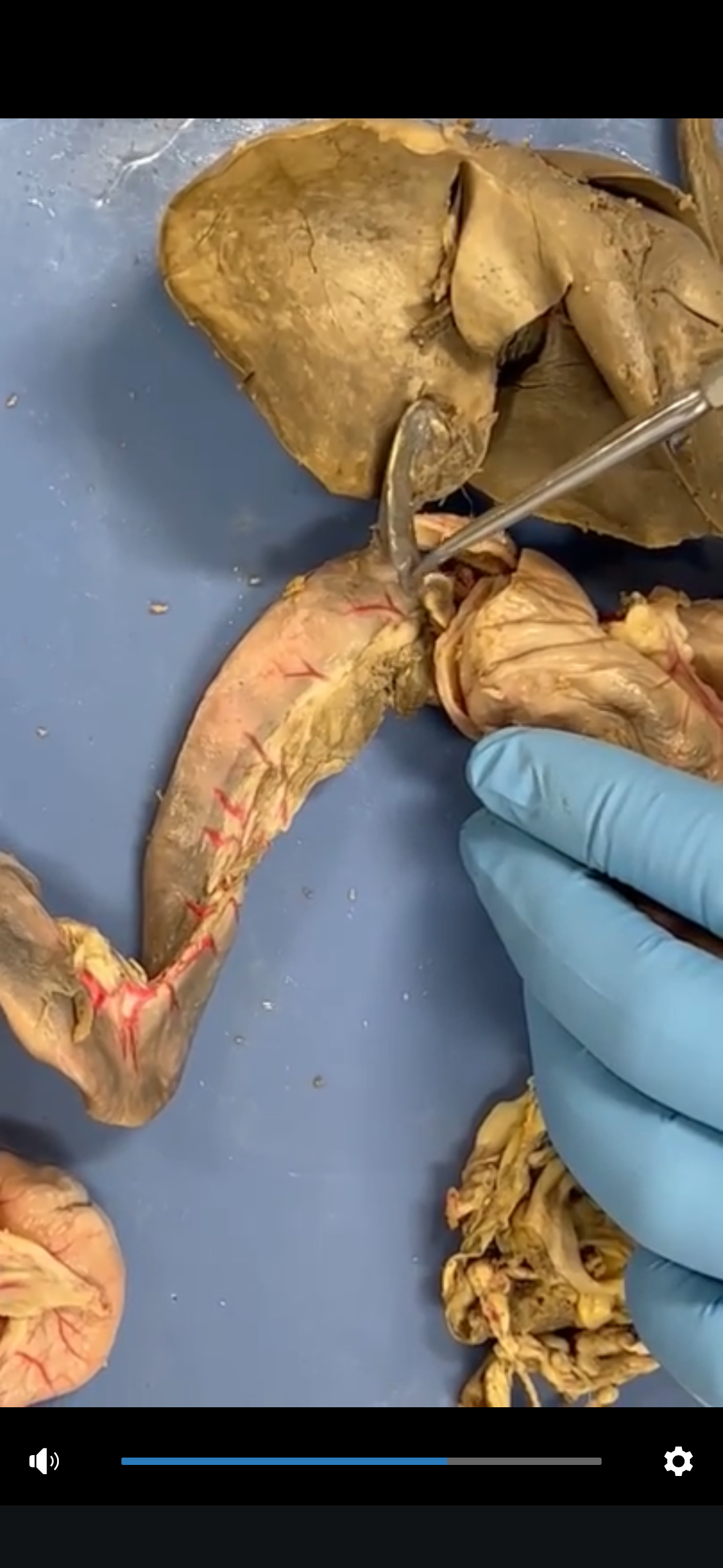
Sphincter of Oddi
A muscular valve that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juices through the hepatopancreatic duct into the duodenum.
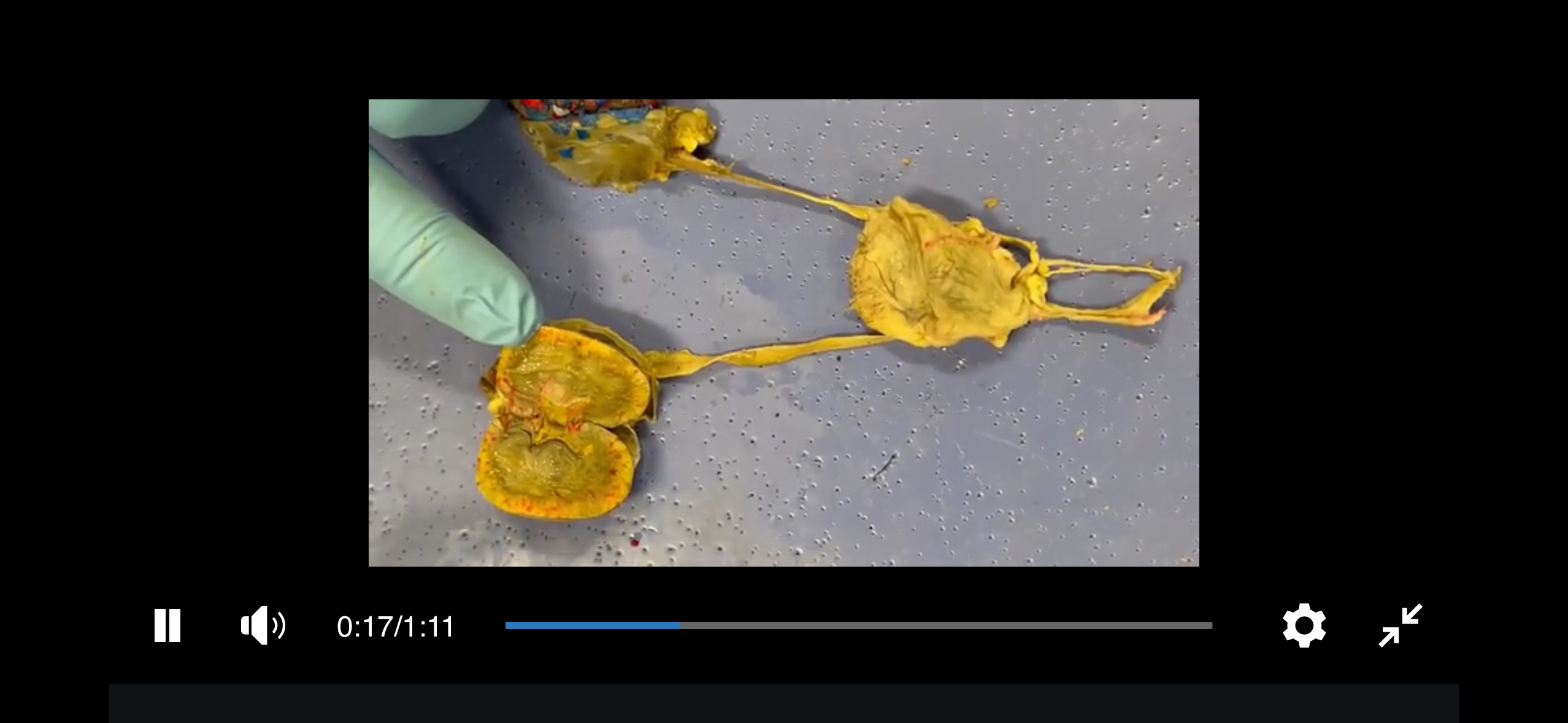
Liver
The organ that produces bile, metabolizes nutrients, detoxifies substances, and plays a critical role in digestion and metabolism.
Bile
A greenish-yellow fluid produced by the liver that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats.
Messentary
A fold of tissue that attaches the intestines to the abdominal wall, supporting the blood vessels and nerves that supply the intestines.
Mesocolon
A fold of peritoneum that attaches the colon to the posterior abdominal wall, helping to support its position.
Lacteal
A lymphatic vessel in the small intestine that absorbs dietary fats and transports them to the bloodstream.
Villus
A tiny, finger-like projection in the lining of the small intestine that increases surface area for absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
Macronutrients
Nutrients required in large amounts, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, essential for energy, growth, and overall health.
Retroperitoneal
Referring to the anatomical space behind the peritoneum, where the kidneys and adrenal glands are located.
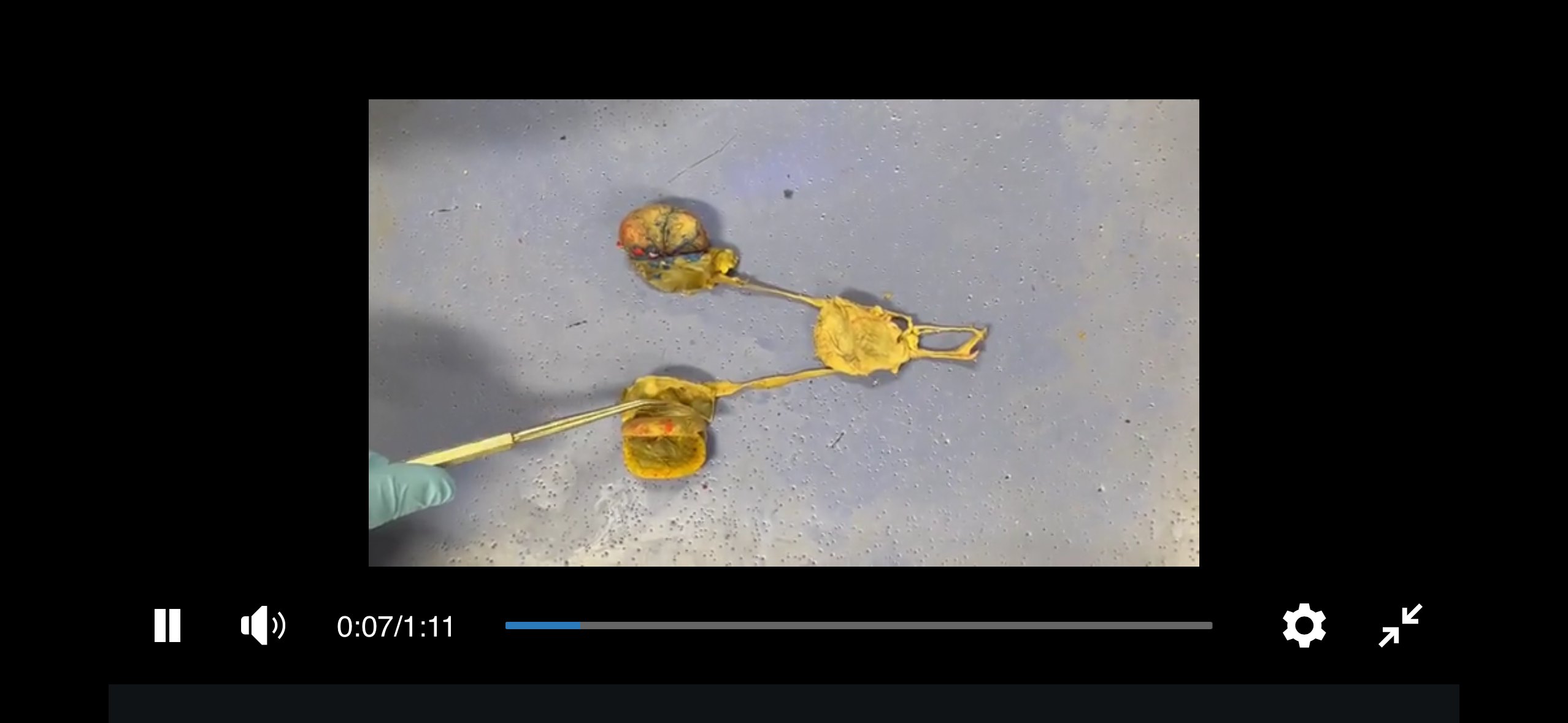

Kidney
An essential organ that filters waste products from the blood, regulates fluid and electrolyte balance, and produces urine.
Adrenal Gland
An endocrine gland located on top of each kidney, responsible for producing hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol that regulate metabolism, immune response, and stress.
Ureter
A tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
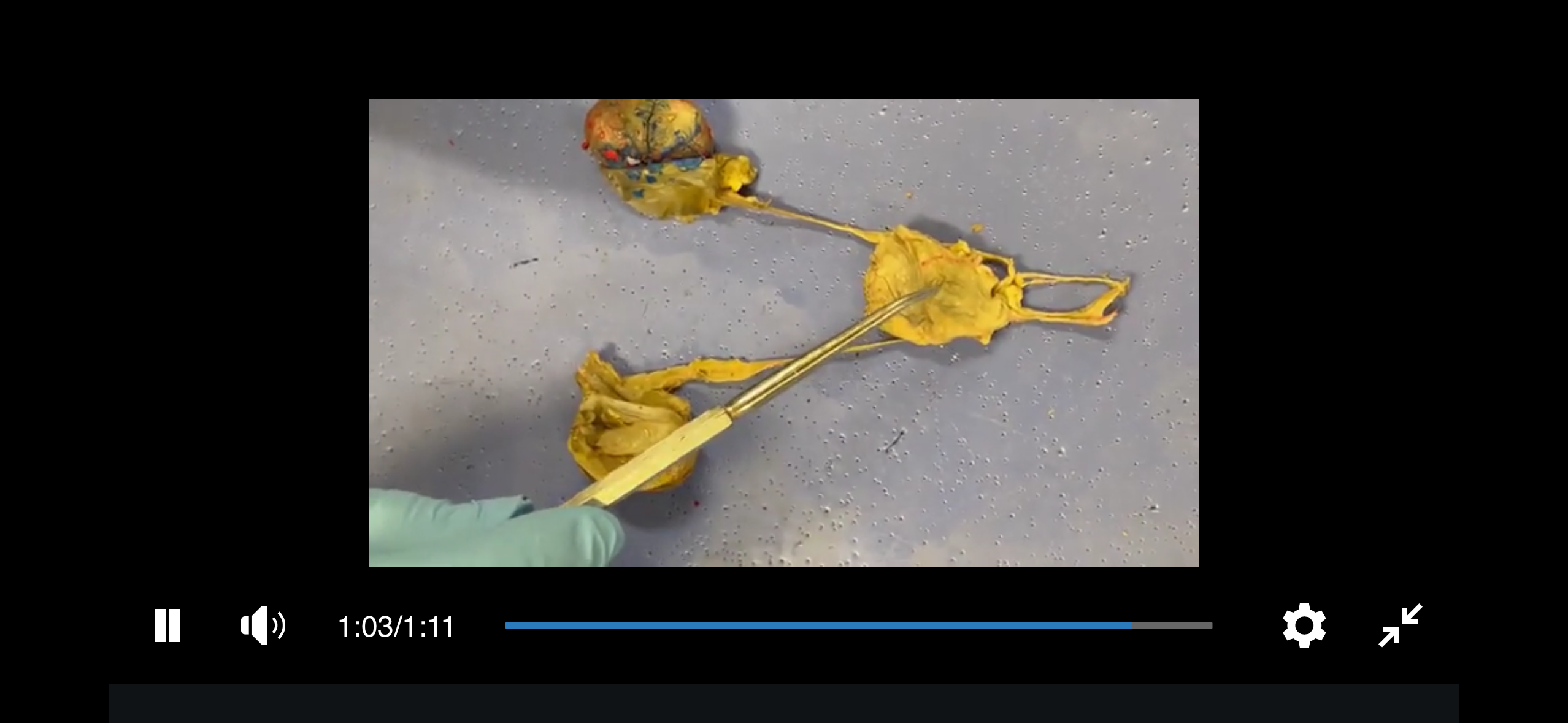

Urethra
A tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Renal Capsule
The fibrous membrane that surrounds and protects the kidney, providing structural support and helping to maintain its shape.
Renal Cortex
The outer part of the kidney, involved in filtration and urine production.
Renal Medulla
The inner region of the kidney which contains the renal pyramids, plays a crucial role in the concentration of urine, and contains structures like the loop of Henle and collecting ducts.
Renal pyramid
Triangular structures within the renal medulla that contain the nephrons and collecting ducts, facilitating urine passage to the calyces.
Renal Pelvis
The funnel-shaped structure in the kidney that collects urine from the renal calyces and channels it into the ureter.
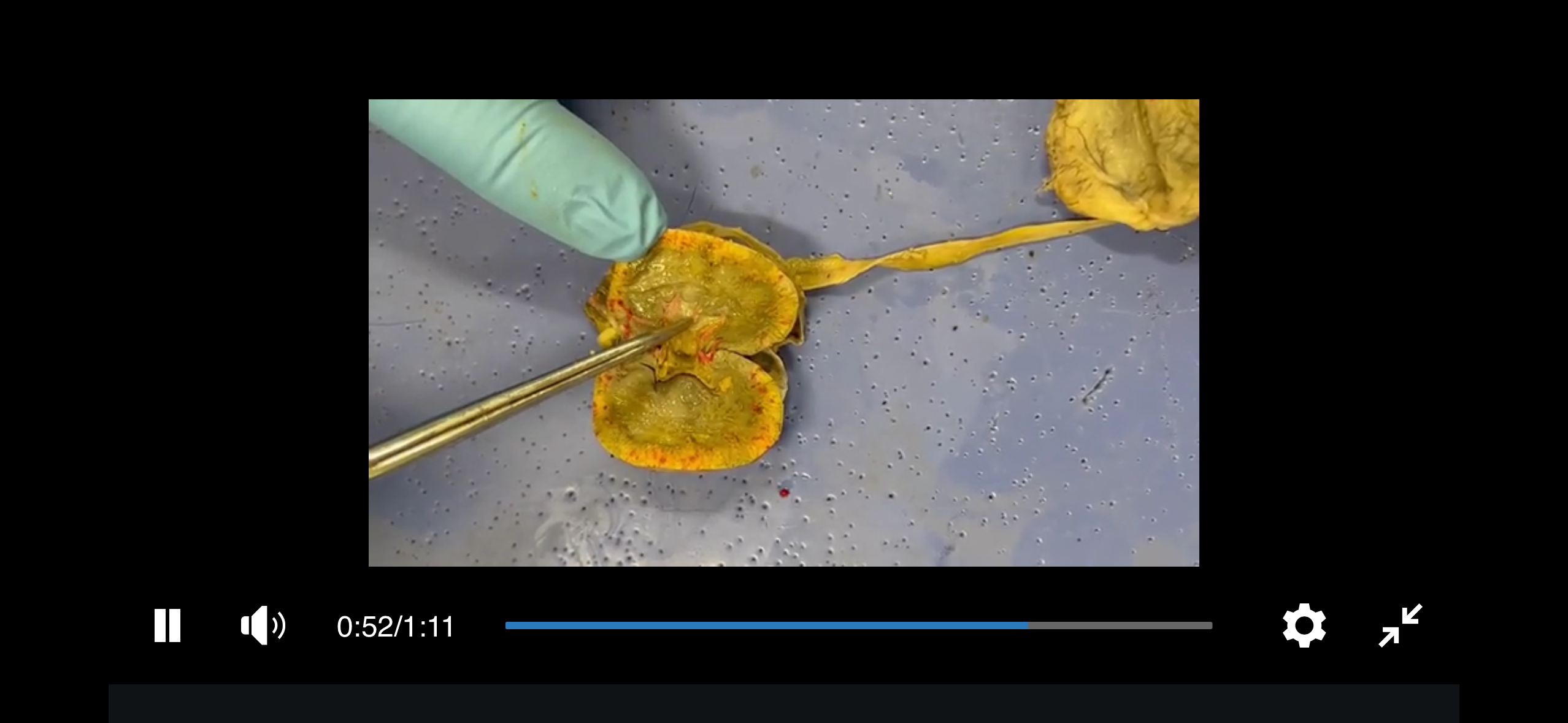
Nephron
the functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood, reabsorbing essential substances, and producing urine.
Glomerulus
The functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. It consists of a glomerulus and a renal tubule.
Filtration
The process by which the kidneys remove waste and excess substances from the blood, forming urine.
Kidney stone
A solid mass formed from crystals that develop in the kidneys, often causing pain and blockage in the urinary tract.
GFR
Glomerular filtration rate, a measure of how well kidneys filter blood.
Micturition
The process of expelling urine from the bladder through the urethra.
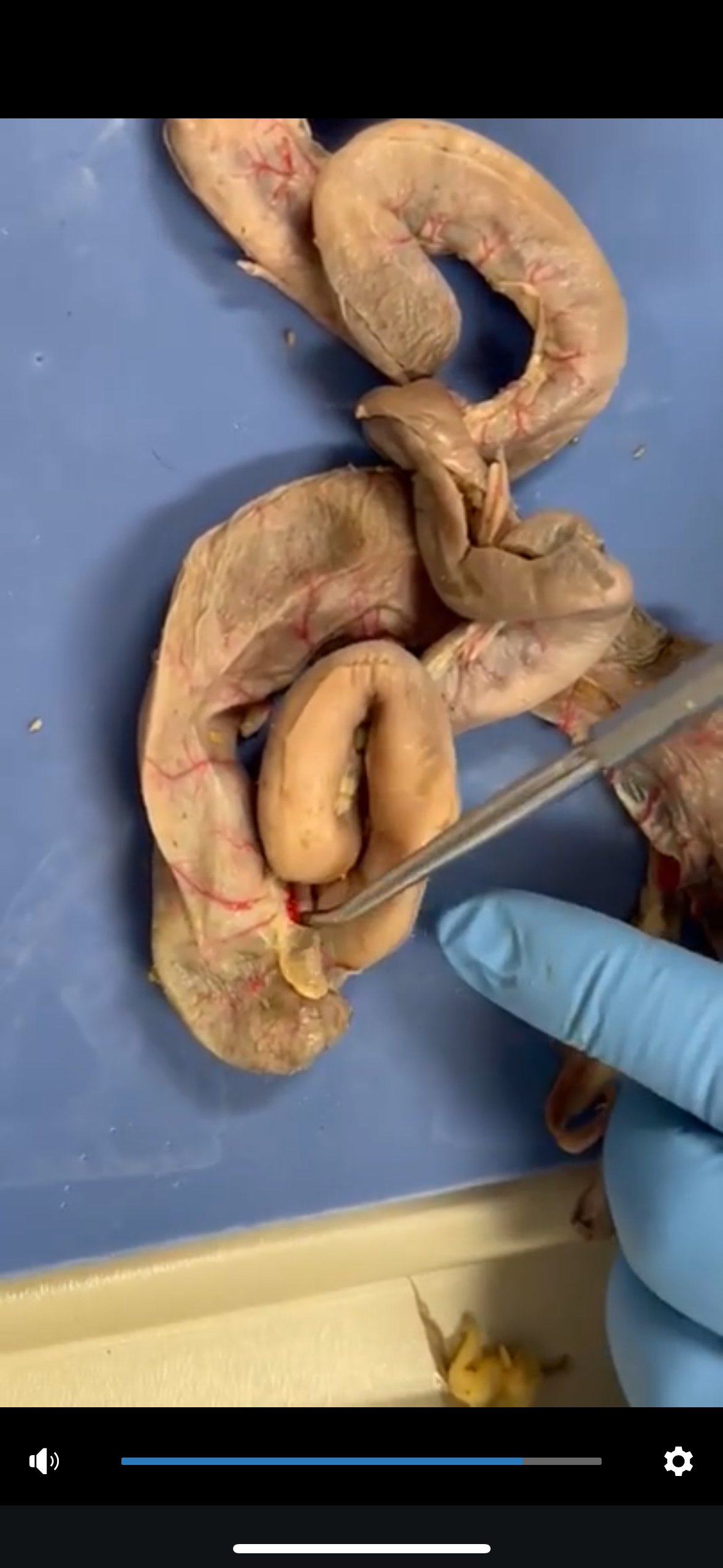
What is this
ileocecal valve and it is between the cecum and ileum
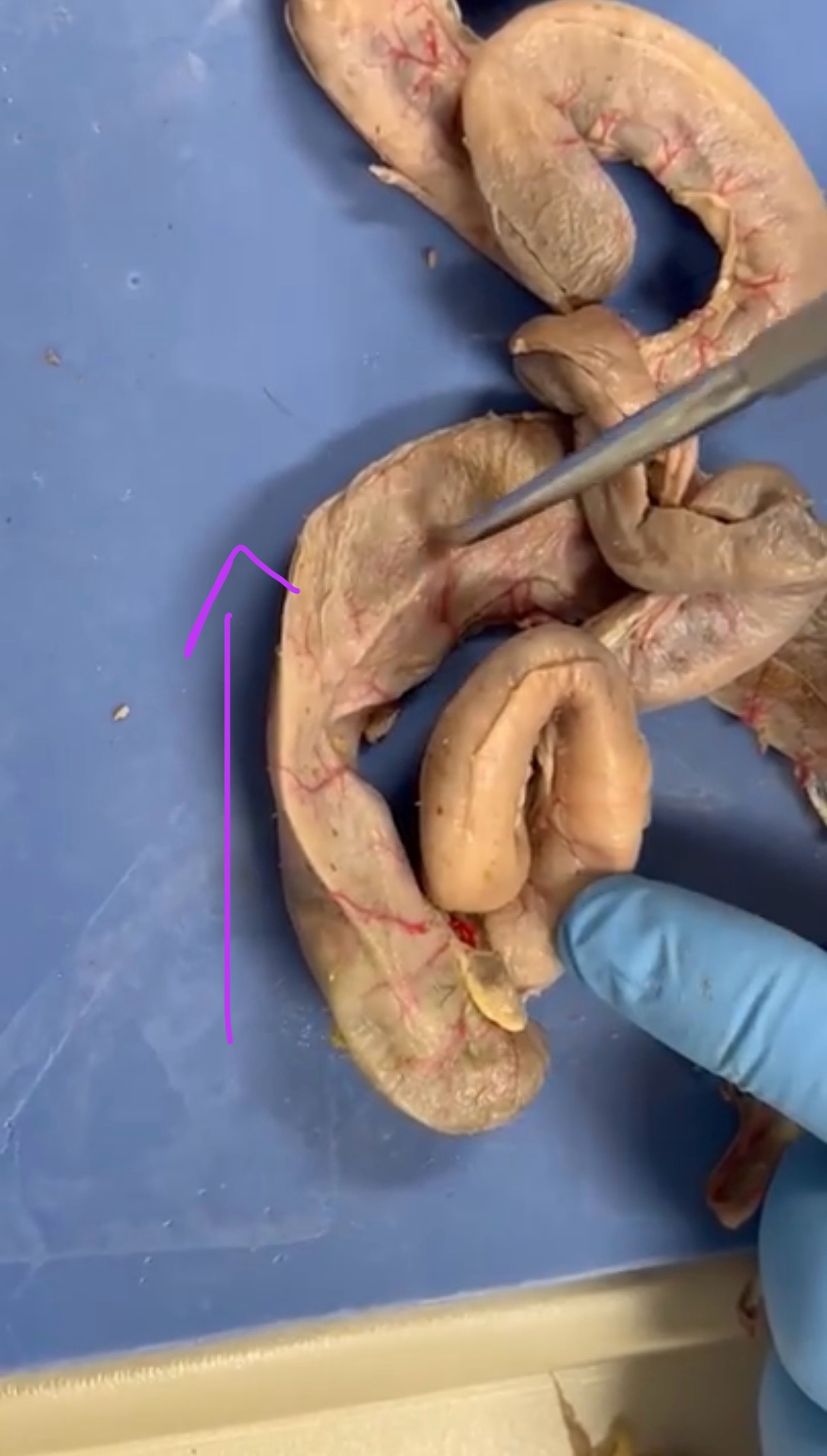
What is this?
Ascending Colon

What is this?
Transverse colon
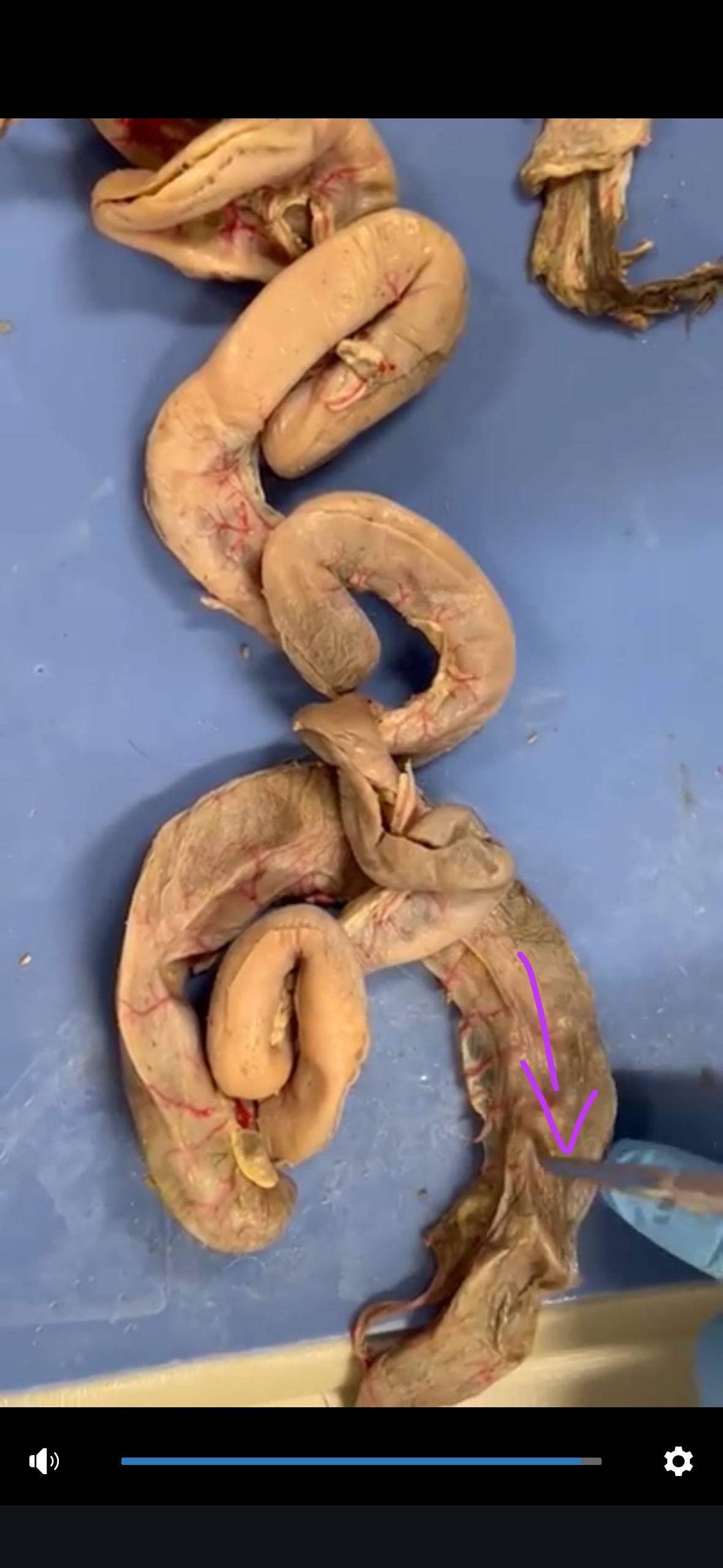
What is this?
Descending colon
Cats don’t have a ____ colon
Sigmoid