2 Endocrine System
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
What is the main function of the endocrine system?
Controls and regulates metabolic processes in the body.
Why is the endocrine system called the “powerhouse” of the body?
Because it regulates key processes that keep the body functioning properly
Which endocrine gland produces thyroid hormones?
Thyroid gland
What is another name for the pituitary gland?
Hypophysis
What is the main role of the pituitary gland?
Regulates other endocrine glands in the body.
How many lobes does the pituitary gland have
Two lobes—anterior and posterior
Which lobe of the pituitary is called the “master gland”?
Anterior pituitary
What controls the anterior pituitary gland?
The hypothalamus
What is hypopituitarism (GH deficiency)?
pituitary gland doesn’t produce enough growth hormone → inhibiting growth in all cells of the body.
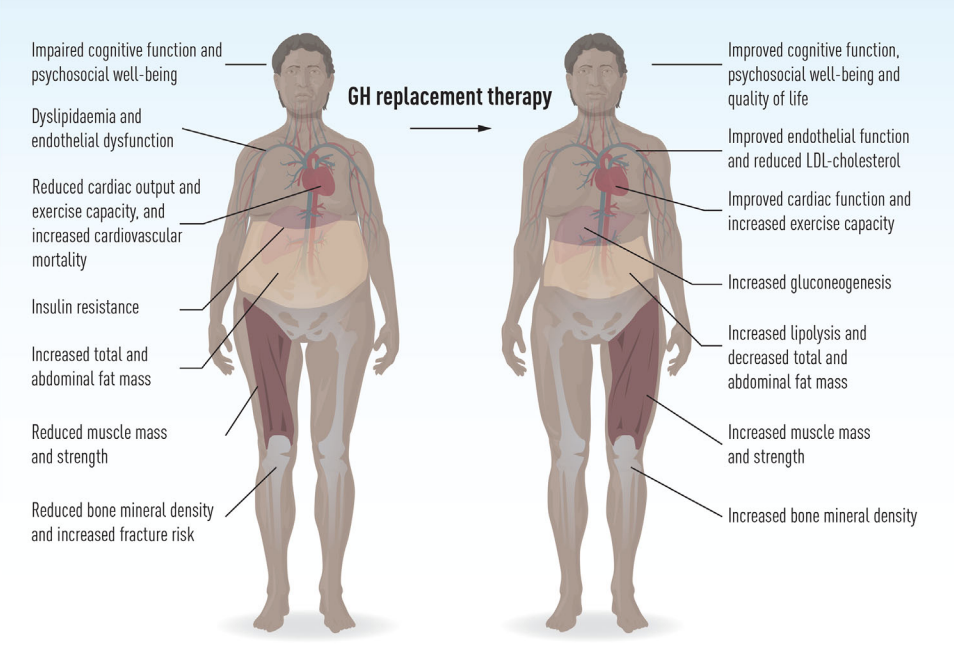
What is the primary site of dysfunction in GH deficiency?
The hypothalamus
How is GH deficiency diagnosed in children?
evaluating child, parental, and familial growth patterns
checking pituitary GH reserves
skeletal surveys (<3 yrs)
hand–wrist x-rays for ossification centers
What is the main treatments for GH deficiency?
MAIN - Biosynthetic growth hormone (injections)
Other hormone replacements as needed
Thyroid extract
Cortisone
Testosterone or estrogens and progesterone
What are key nursing considerations for children with GH deficiency?
Identify growth problems early
support the family
address body image concerns
prepare the child for daily injections
consider cost and insurance coverage
What happens in pituitary hyperfunction before epiphyseal closure?
Excess GH → overgrowth of long bones
Physical characteristics in children with pituitary hyperfunction?
Very tall (up to 8 ft)
rapid vertical growth
increased muscle development
Head changes in pituitary hyperfunction?
Enlarged head circumference
delayed fontanel closure
When does acromegaly occur?
Excess GH after epiphyseal closure
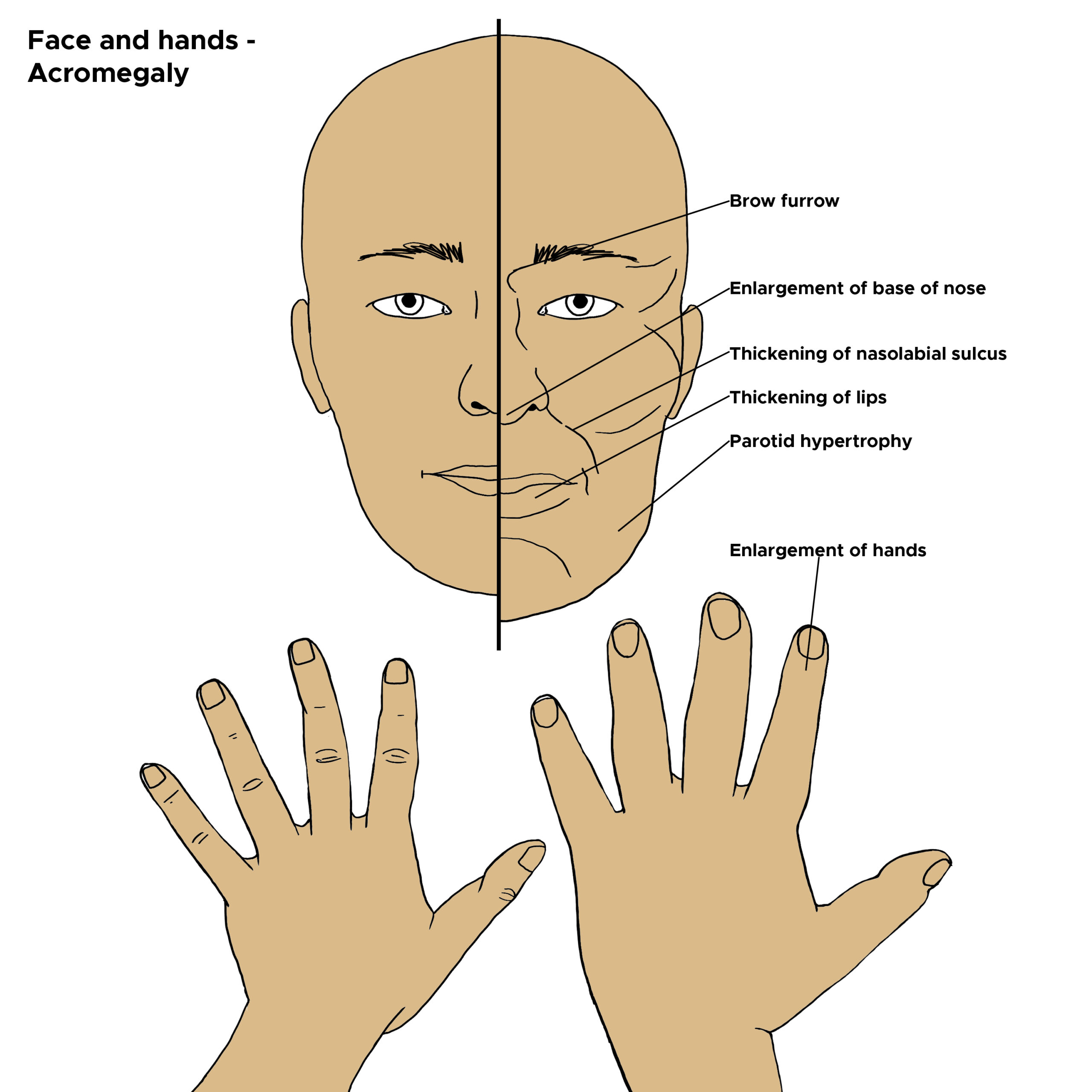
Typical facial features of acromegaly
Enlarged head, lips, nose, tongue, jaw
enlarged paranasal & mastoid sinuses
facial disproportion to skull
separation and malocclusion of teeth
Thickened, deeply creased skin
increased facial hair
Diagnostic Evaluation of Acromegaly
Radiologic studies
X rays
Endocrine studies
Therapeutic Management Acromegaly
Surgical treatment to remove the tumor
Irradiation and radioactive implants
Hormone replacement therapy after surgery in some cases
Why might hormone replacement be needed after surgery?
Removing the tumor can lead to hypopituitarism (decreased hormone production).
Nursing Management Acromegaly
Early identification of children with excessive growth rates
Use plot chart
Early treatment for improved outcomes
Emotional support
Body image concerns
What is Precocious Puberty
Defined as sexual development
before age 9 years in boys
before age 7 years in Caucasian girl
before 6 years in African-American girls
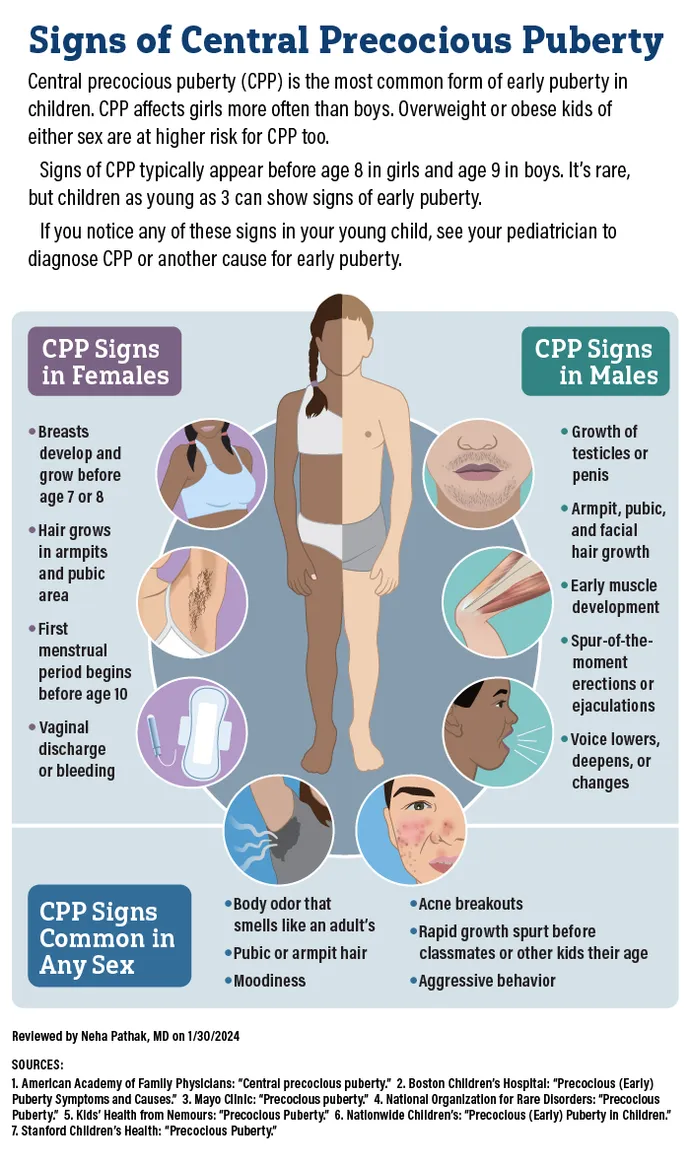
Three types of Precocious Puberty
Central precocious puberty (CPP) (80%)
Peripheral precocious puberty (PPP)
Incomplete precocious puberty (IPP)
Central Precocious Puberty (CPP)
Brain starts puberty too early (HPG axis turned on early).
Everything develops in normal order, just too soon.
Most common type (80%).
🧠 Think: “Central = brain’s fault.”
Peripheral Precocious Puberty (PPP)
Hormones come from somewhere else (like ovaries, testes, or adrenal glands).
Brain NOT involved.
Caused by tumors, cysts, or adrenal problems.
💥 Think: “Peripheral = problem outside the brain
Incomplete Precocious Puberty (IPP)
Only one sign of puberty shows up early (like breast buds or pubic hair).
Doesn’t keep progressing.
Usually benign and just monitored.
🌱 Think: “Incomplete = starts but doesn’t finish.”
What is the main goal of treating precocious puberty?
To slow early sexual development and help growth return to normal rates.
What medication is used to treat central precocious puberty?
Leuprolide acetate (Lupron Depot).
How does leuprolide acetate work?
suppresses gonadotropin release, slowing puberty progression to a normal rate
When is treatment for precocious puberty discontinued?
When the child reaches the normal age for puberty to begin.
What do thyroid hormones regulate?
The basal metabolic rate (BMR) — how fast the body uses energy.
What two main hormones are secreted by the thyroid gland?
T3 (Triiodothyronine) and T4 (Thyroxine)
calcitonin
Which thyroid hormone is more potent?
T3 is stronger, but there’s more T4 in circulation
What hormone controls thyroid hormone release?
TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) from the pituitary gland
What does calcitonin do?
Lowers blood calcium by storing calcium in bones
What happens in hypothyroidism?
Thyroid is underactive → low metabolism, fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation

What happens in hyperthyroidism?
Thyroid is overactive → high metabolism, weight loss, heat intolerance, anxiety, tachycardia

What might cause thyroid hormone imbalance?
Either too much or too little TSH or direct thyroid dysfunction
Lab pattern in Graves disease (hyperthyroidism)?
↑ T3 + ↑ T4 + ↓ TSH
(thyroid is overactive, pituitary slows TSH release).
What are the two main types of juvenile hypothyroidism?
Congenital
Acquired
Congenital Juvenile Hypothyroidism
Congenital hypoplastic thyroid gland
Born with it and there's a problem with the thyroid gland
Underactive hypothroid
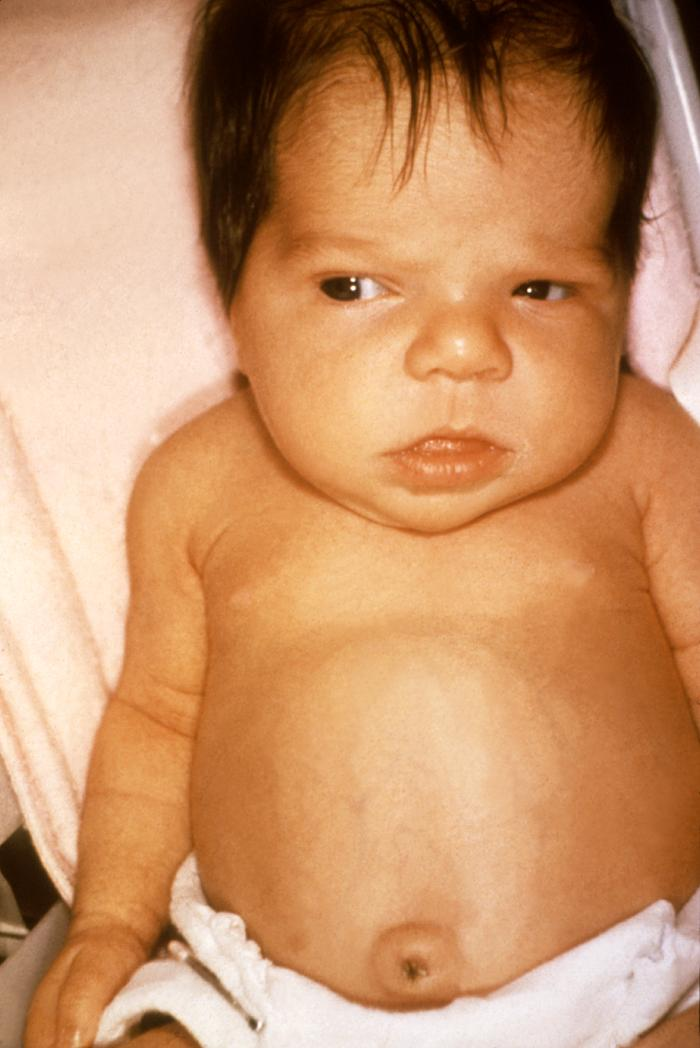
Acquired Juvenile Hypothyroidism
Partial or complete thyroidectomy for cancer or thyrotoxicosis
Following irradiation for Hodgkin disease or other malignant disease
Obtained accidentally maybe from getting cut from a tumor
Can dietary iodine deficiency cause juvenile hypothyroidism in the U.S.?
Rarely — it’s uncommon because most foods are iodized
Clinical Manifestations of Juvenile Hypothyroidism
Decelerated growth
Myxedematous skin changes
Dry skin
Sparse hair
Periorbital edema
Constipation
Sleepiness
Mental decline

What is a goiter?
Hypertrophy (enlargement) of the thyroid gland → making it swollen
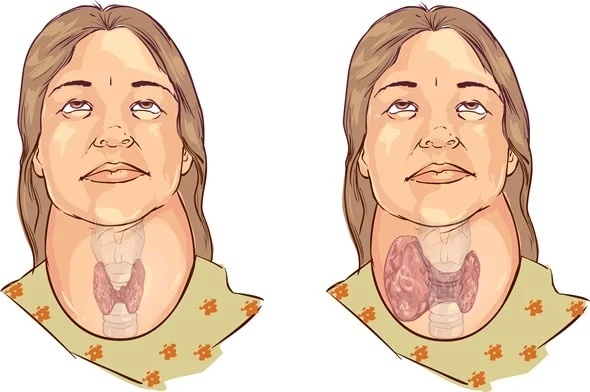
Congenital Goiter
Usually results from maternal ingestion of antithyroid drugs during pregnancy
Acquired Goiter
Result of
neoplasm
inflammatory disease
dietary deficiency (but rarely in children)
increased secretion of pituitary TSH
Why is thyroid enlargement at birth a concern?
may compromise the newborn’s airway
How can goiters present in newborns?
Large goiters are obvious
smaller nodules may only be felt on palpation
How is hypothyroidism with thyroid enlargement treated?
Thyroid hormone (TH) replacement
What is lymphocytic thyroiditis also called?
Hashimoto disease or chronic autoimmune thyroiditis
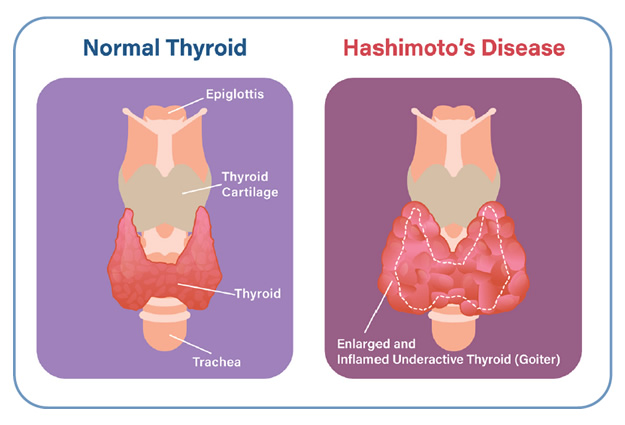
Who is most affected by lymphocytic thyroiditis
Children and adolescents, usually after age 6
How does lymphocytic thyroiditis present?
Often as a goiter, which may be transient and asymptomatic
How long might lymphocytic thyroiditis take to resolve spontaneously?
1 to 2 years.
What treatment can decrease goiter size in lymphocytic thyroiditis
Oral thyroid hormone (TH) replacement.
Is surgery recommended for lymphocytic thyroiditis?
No, surgery is contraindicated.
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in children?
Graves disease AKA diffuse toxic goiter
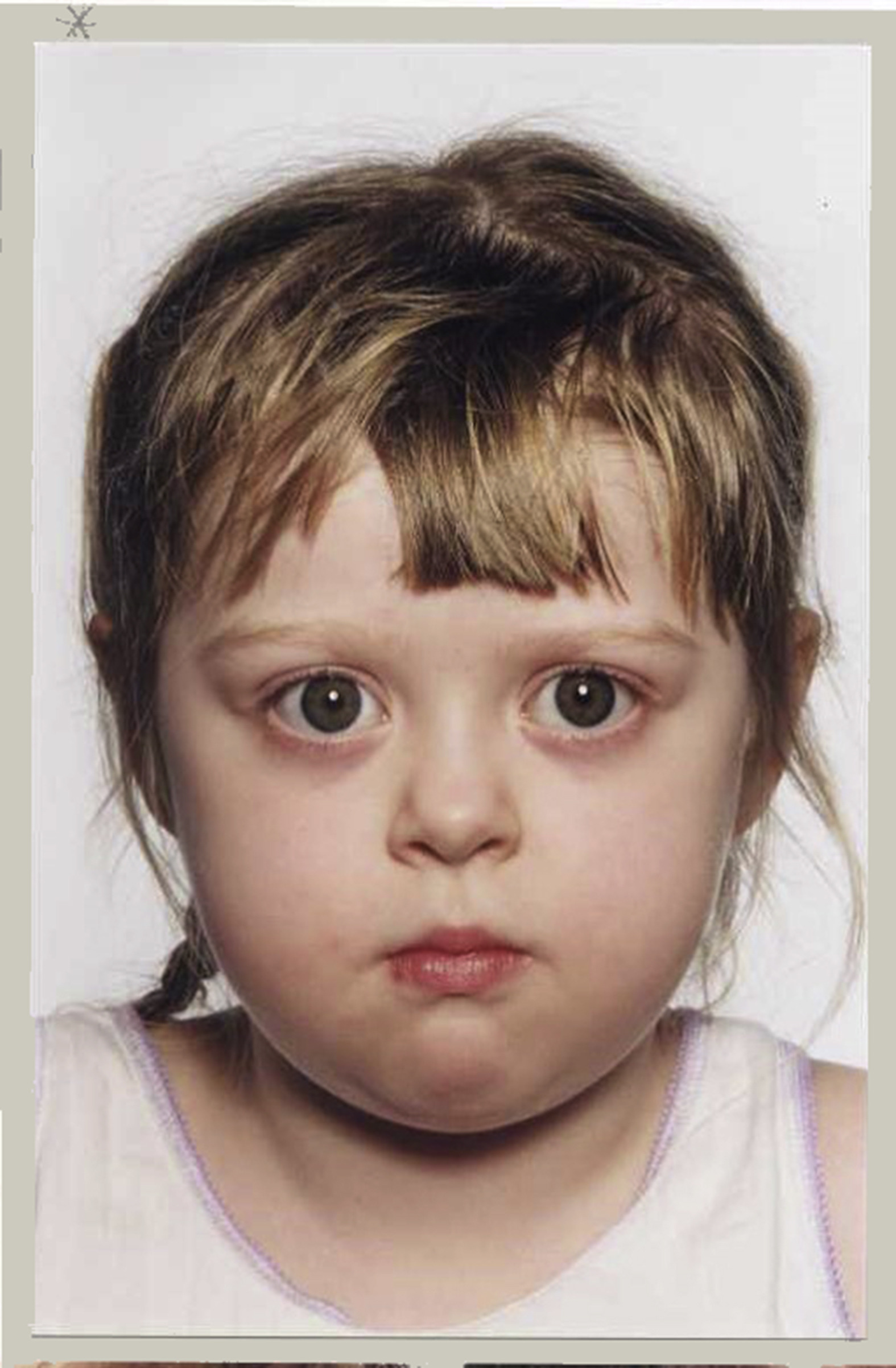
What causes Graves disease?
Autoimmune response to TSH receptors (exact cause unknown)
Typical signs of Graves disease in children?
Enlarged thyroid (goiter) and exophthalmos
Peak age for Graves disease onset in children?
12–14 years, but it can occur at birth
How is Graves disease diagnosed?
High T4 and T3 levels, with suppressed TSH.
What is the goal of therapy for Graves disease?
Slow hormone secretion to reduce hyperthyroidism symptoms
Treatments for Graves disease in children?
Antithyroid drugs: propylthiouracil (PTU) or methimazole (give with food).
Subtotal thyroidectomy.
Radioactive iodine ablation
What is thyrotoxicosis?
Thyroid “crisis” or “storm”
sudden, extreme release of thyroid hormones

Is thyrotoxicosis common in children
unusual but can be life-threatening
What can trigger a thyroid storm in kids?
Infection
surgery
stopping antithyroid meds suddenly
Treatment for thyroid storm?
Antithyroid drugs + propranolol
What’s the first step in nursing care for pediatric thyroid disorders?
Identify children with hypothyroidism
How should the environment be for a child with thyroid issues?
Quiet with rest periods
Dietary needs for children with thyroid disorders?
Meet increased metabolic requirements
What should nurses teach about thyroid medications?
Explain medications and their side effects
What does the adrenal cortex secrete?
Glucocorticoids
mineralocorticoids
sex steroids
What do glucocorticoids do?
Regulate metabolism and stress response
(cortisol, corticosterone)
What do mineralocorticoids do?
Control sodium and water balance
(aldosterone).
What do adrenal sex steroids do?
Influence sexual development and characteristics
(androgens, estrogens, progestins)
What does the adrenal medulla secrete?
Catecholamines: epinephrine and norepinephrine for energy
What is the main cause of adrenal medulla hyperfunction?
Catecholamine-secreting tumors (e.g., pheochromocytoma)
What happens if the adrenal medulla tumor is present?
Overproduction of catecholamines → hyperactivity, high blood pressure, other symptoms
What is acute adrenocortical insufficiency also called?
Adrenal crisis
What are common causes of adrenal crisis?
Trauma with adrenal hemorrhage
severe infection
abrupt withdrawal of cortisone
failure to increase cortisone during stress
What are clinical symptoms of adrenal crisis?
Low blood sugar
lethargy
nausea
muscle weakness
headache
sometimes infection
How is adrenal crisis treated?
Emergency stress dose of corticosteroids (e.g., Solu-Cortef IM)
What is chronic adrenocortical insufficiency in children called?
Addison Disease
What usually causes Addison disease in children?
Adrenal neoplasm
adrenal lesion
idiopathic (unknown) cause.
When do symptoms typically appear?
Gradually, after ~90% of adrenal tissue is nonfunctional
How is Addison disease diagnosed?
Blood tests
urine tests
ACTH stimulation test
MRI
CT scan
How is Addison disease treated?
Corticosteroid replacement therapy (replace what is missing).
What are key nursing considerations for Addison disease?
Chronic illness management
patient/family education
monitoring for adrenal crisis
What is Cushing Syndrome?
group of symptoms caused by too much circulating cortisol
What are common causes of Cushing Syndrome in children?
Adrenal tumor
prolonged/excessive steroid therapy
pituitary ACTH excess
ectopic tumors
food-dependent adrenal response (polypeptide)
What can abrupt steroid withdrawal cause in Cushing Syndrome?
Acute adrenal insufficiency
What is a typical “Cushingoid appearance”?
Moon face
red cheeks
weight gain
pendulous abdomen with red striae
excessive hair
poor wound healing
ecchymosis
How is Cushing Syndrome diagnosed?
Confirm excess cortisol
lab tests (glucose, electrolytes, 24-hour urine)
X-rays (osteoporosis, sella turcica)
What is the treatment for Cushing Syndrome?
Surgery if tumor present
hormone replacement (GH, ADH, TH, gonadotropins, steroids).
Nursing considerations for Cushings Disease
Body image support
chronic disease management
multiple medications
monitoring for complications
How do hormones work in children?
Secreted by endocrine glands (pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, ovaries) → travel in blood to organs/tissues to regulate functions
Most common endocrine disorders in children?
Diabetes
thyroid disorders
early/delayed puberty
growth hormone deficiency
Turner syndrome
tumors