Lipids 5- Metabolism and Fatty Acid Synthesis Flashcards
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering lipid metabolism, fatty acid synthesis, and related concepts from biochemistry lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Fatty Acid Synthesis Location
Occurs in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and adipocytes, and liver cells of eukaryotes.
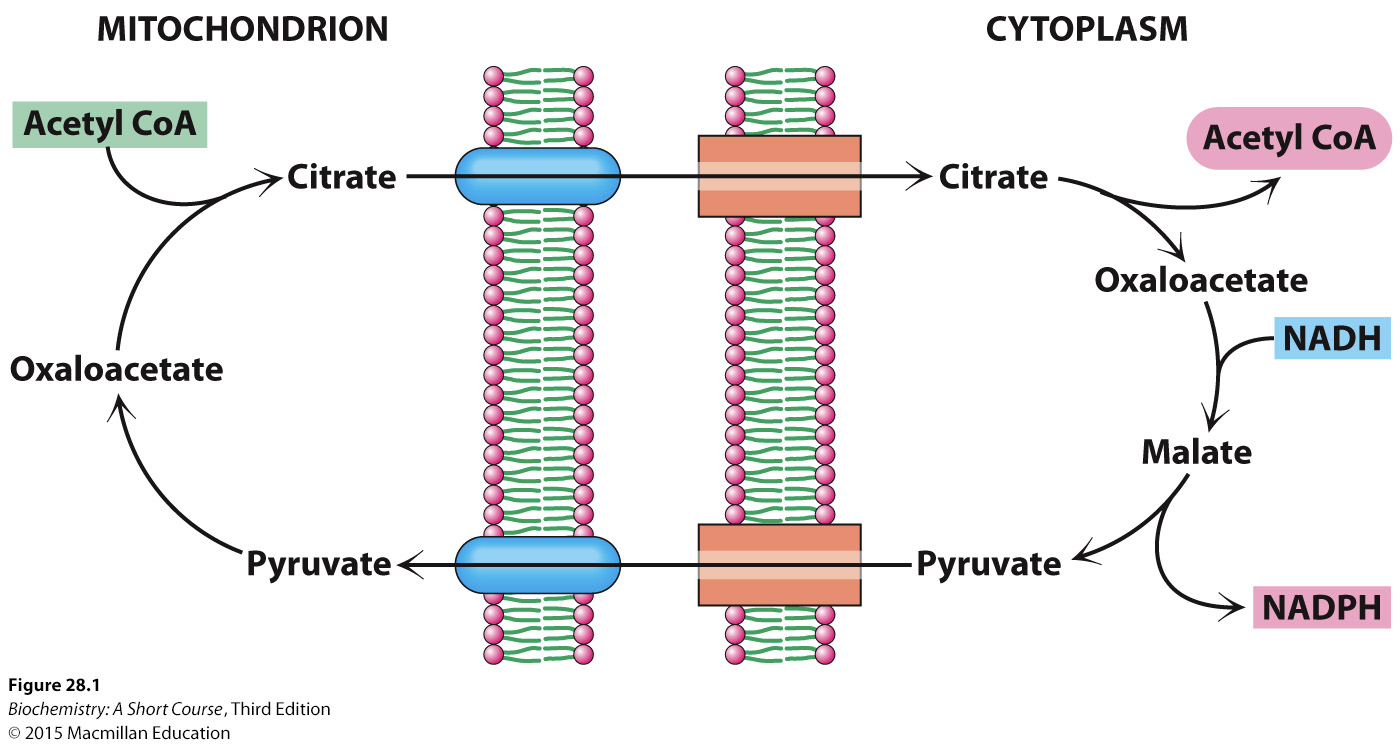
Citrate-Malate Shuttle
Transports Acetyl CoA from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm for fatty acid synthesis because the inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to Acetyl CoA.
Acetyl CoA Carboxylase I (ACC)
The enzyme that catalyzes the committed step in fatty acid synthesis, converting acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA.
Requires ATP hydrolysis to proceed
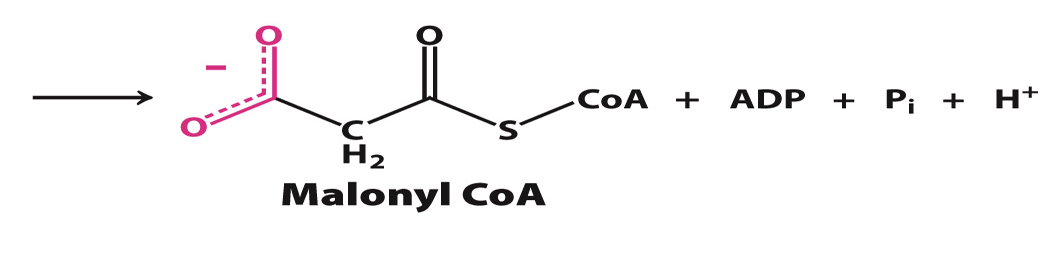
Malonyl CoA
Formed when Acetyl CoA is condensed with bicarbonate, catalyzed by acetyl CoA carboxylase I (ACC).
malonyl CoA is the actual carbon donor for all but two of the carbon atoms of palmitic acid
ACC Regulation: Covalent Modification
Insulin stimulates phosphatase, leading to dephosphorylation and activation of Acetyl CoA carboxylase. Glucagon/Epinephrine stimulates protein kinase, leading to phosphorylation and inactivation.
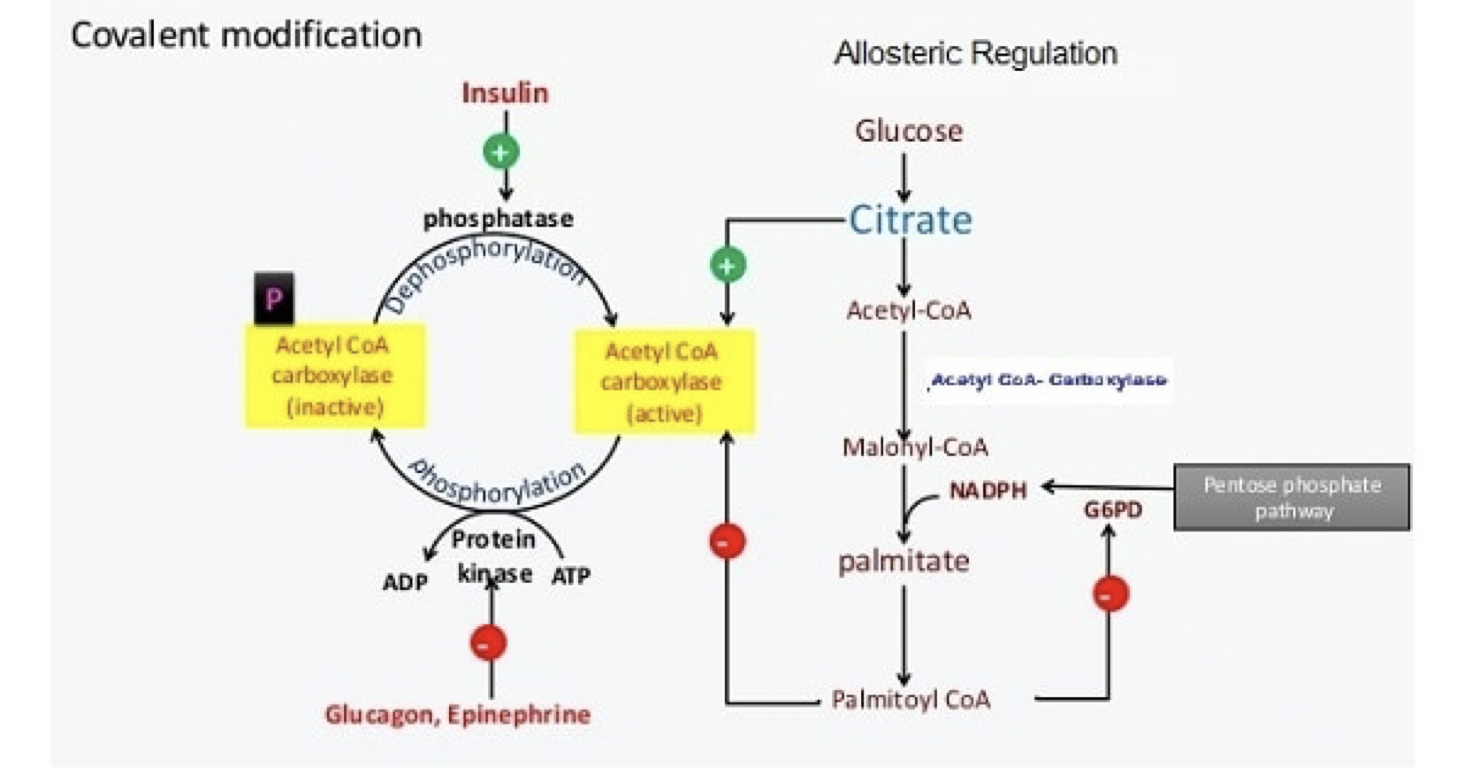
ACC Regulation: Allosteric
Citrate activates Acetyl CoA carboxylase; Palmitoyl CoA inhibits.
Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP)
Serves as a scaffold in fatty acid synthesis, with intermediates attached to the sulfhydryl end of an ACP group
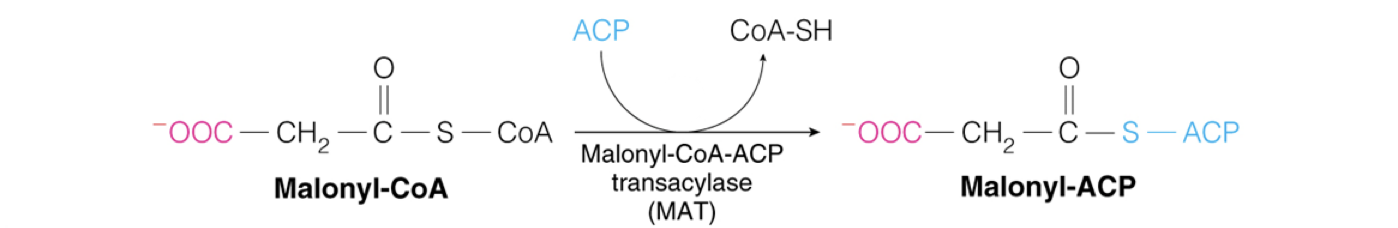
Malonyl-CoA-ACP Transacylase (MAT)
The enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the malonate group to Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP).
generates malonyl ACP upon which the fatty acid is built
Fatty Acid Synthesis Steps
- Condensation, 2. Reduction of the carbonyl group, 3. Dehydration, 4. Reduction of the double bond.
β-ketoacyl synthase
The enzyme that catalyzes the condensation of malonyl ACP with acetyl ACP, extending the acyl group by two carbons.
3-ketoacyl-ACP reductase
The enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of the carbonyl group using NADPH as the electron donor.
β-hydroxyacyl ACP dehydratase
The enzyme that catalyzes the dehydration of D-3-hydroxybutyryl ACP, generating a trans double bond.
Enoyl ACP reductase
The enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of the C=C bond, using NADPH as the electron donor.
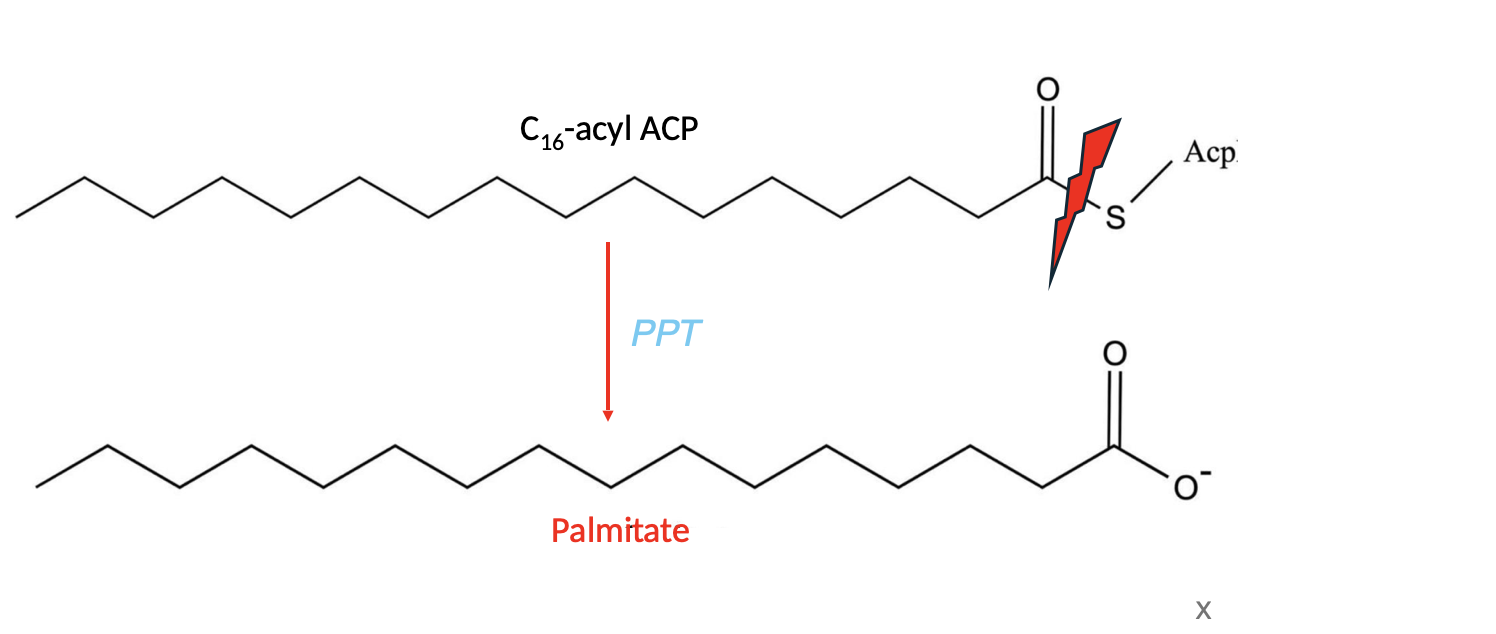
Palmitoyl-protein thioesterase (PPT)
The enzyme that cleaves the thioester linkage connecting the 16C acyl group with ACP, releasing palmitate.
Elongases
Anabolic enzymes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane that are involved in generating products with more than 16 carbons.
Desaturases
Enzymes that introduce cis double bonds at particular locations in fatty acids to generate an unsaturated fatty acid
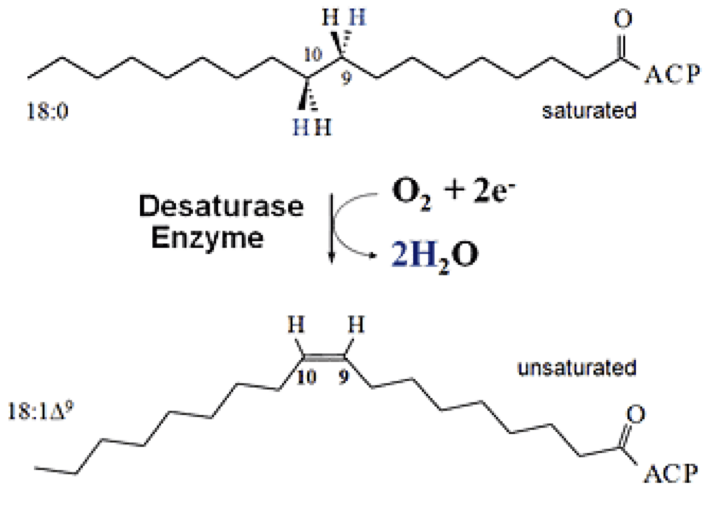
Essential Fatty Acids
Linolenic acid (ω3) and linoleic acid (ω6) which cannot be synthesized by humans and must come from the diet. Humans cannot introduce double bonds beyond carbon-9.
Odd chain saturated fatty acid synthesis location
Cytoplasm via same anabolic pathway
How many acetyl CoA must be transported?
Depends on hydrocarbon length; actyl CoA a 2-carbon carrier
Synthesis of palmitate (16:0)
Would need 8 acetyl CoA
Acetyl CoA
The end product of fatty acid degradation and is the precursor for all fatty acids
Biochemical Challenge
Link the 2-carbon units together and reduce the carbon atoms to produce palmitate, a C16 fatty acid that serves as a precursor for a variety of fatty acids
Fatty acid synthase
Enzyme system that catalyzes the synthesis of saturated long-chain fatty acids from acetyl CoA, malonyl CoA and NADPH is called
Steps in fatty acid synthesis repeat until
Palmitate (16:0) is made
Generation of a saturated, even chain fatty acid
Pathway extends the hydrocarbon chain two carbons at a time
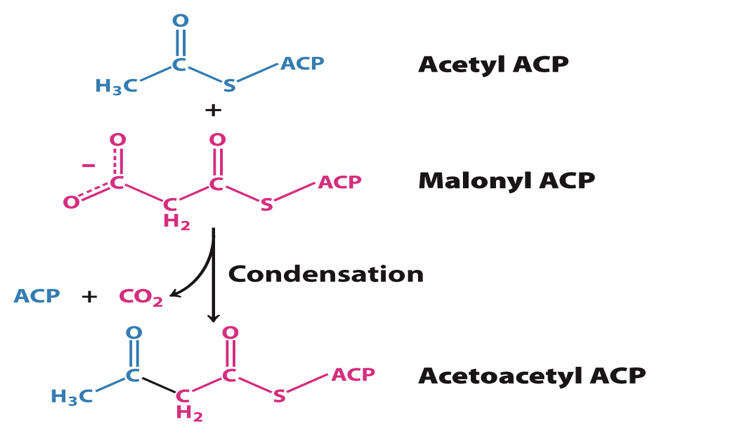
Step 1: condensation
First reaction is the condensation of malonyl ACP with acetyl ACP
enzyme= B-ketoacyl synthase
Reaction extends acyl group by 2 carbons
products: acetoacetyl ACP and CO2
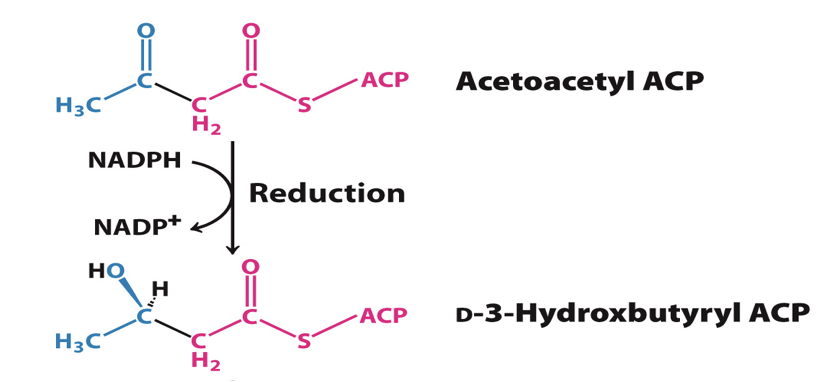
Step 2: Reduction of carbonyl group
The second reaction is the reduction of the carbonyl group by a reductase
enzyme= 3-ketoacyl-ACP reductase
NADPH is the electron donor
reaction converts keto group to hydroxyl group at carbon-3
product: D-3-hydroxybutyryl ACP
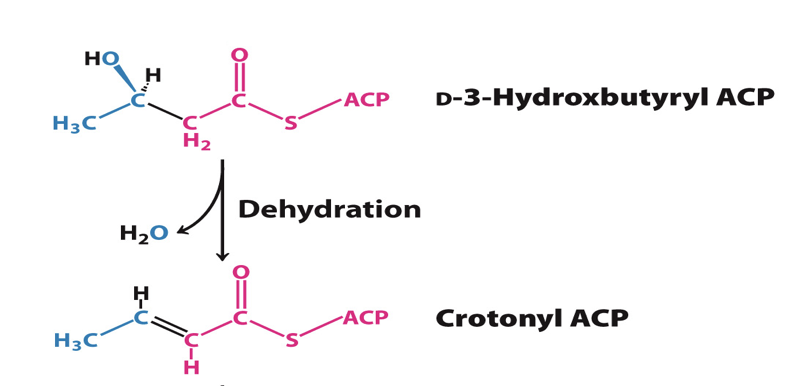
Step 3: Dehydration
The third reaction is the dehydration of D-3-hydroxybutyryl ACP by a dehydrogenase
enzyme= B-hydroxyacyl ACP dehydratase
reaction generates trans double bond between carbon 2 and 3
Product: crotonyl ACP and H2O
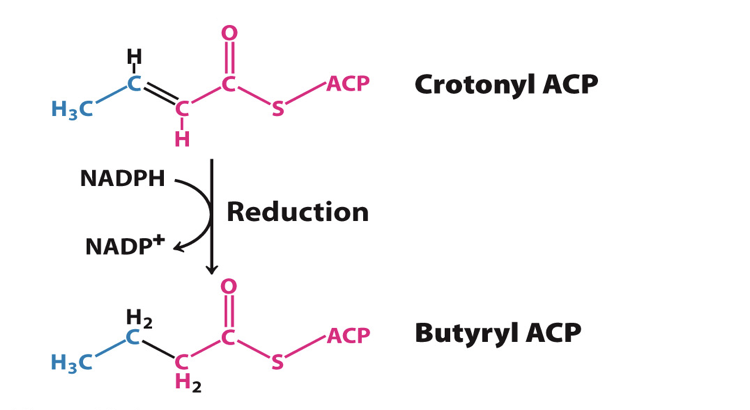
Step 4: Reduction of the double bond
The fourth reaction is reduction of the Carbon carbon double bond by a reductase
enzyme= Enoyl ACP reductase
NADPH is the electron donor
reaction generates single bond between carbon 2 and 3
product: butyryl ACP
Final product: Butyryl ACP
Condenses with a new molecule of malonyl ACP (step 1)
forms C6-B-ketoacyl ACP; acyl group now contains 6 carbons
reduction, dehydration, and reduction (steps 2-4) then follow
repeats until C16-acyl ACP is formed

Front-end desaturases
Humans have these specifically at delta 4, delta 6, and delta 9 positions. But have no methyl-end desaturases (like omega-3 and omega-6)
Propionate (contains 3-carbons)
Transferred to an ACP and condensed with malonyl ACP which generates a 3-oxovaleryl ACP (has 5 carbons)
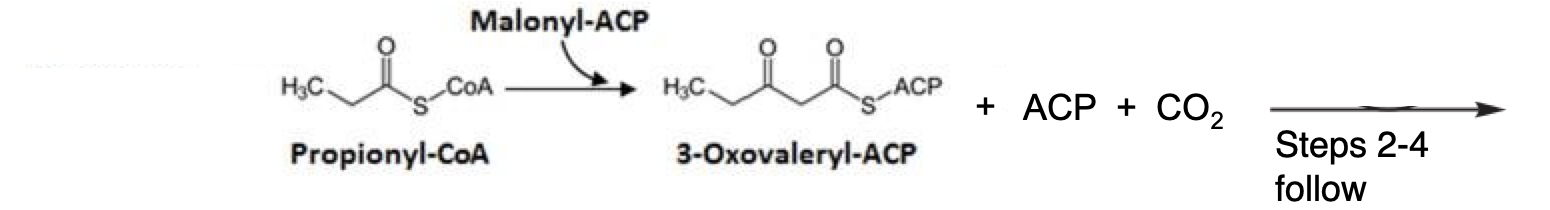
Odd chain fatty acid synthesis rounds
each round will add 2 carbons to acyl group (7, 9, 11)
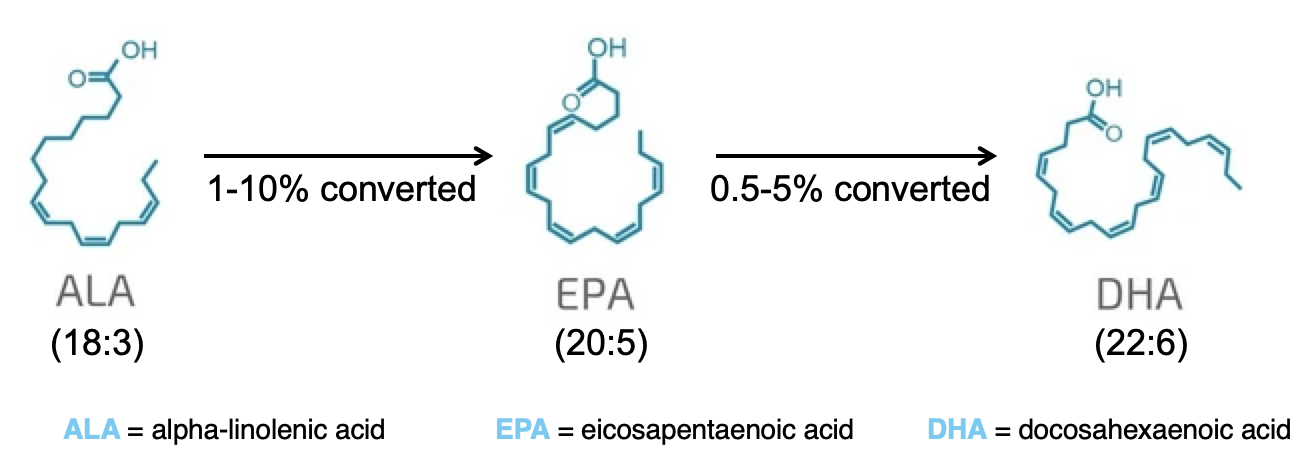
PUFAs
polyunsaturated fatty acids
Acyl chain extension and front-end desaturates process
Humans have enzymes to convert PUFAs within a family
Comparison of beta oxidation and fatty acid synthesis
FA metabolism | FA synthesis | |
Location for repeating steps | Mitochondria | Cytoplasm |
Carbon number altered via | Thiolysis (step 4) | Condensation (step 1) |
Rate-limiting step | Yes with CAT1 | No / None |
Committed step | No / None | Yes with ACC |
Coenzyme(s) involved | NAD+ and FAD | NADPH |
Acyl group attached to | CoA | ACP 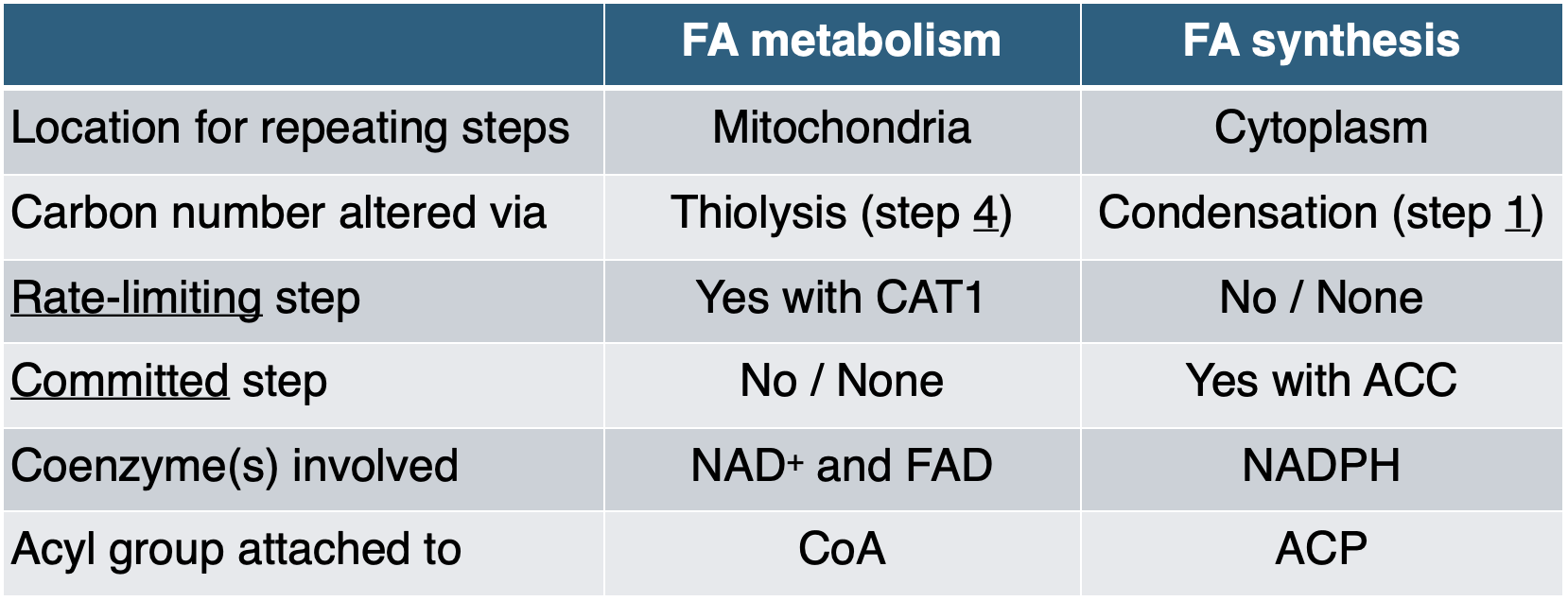 |