Acid-Base Titrations (L04; chptr 10)
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHEM 310: Foundations of Analytical Chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
3 reasons why acid-base chemistry is important in medical chemistry:
to know acid-base characteristics of proteins and small molecule drugs in chemistry and biochemistry
determine how they will react with substrates due to ionization
determine solubility and permeability of small molecules
acid-base chemistry and the prodrugs of amines and amidines
amides aren’t commonly used because they’re too stable
activated amides (low basicity amines or amino acids) are effective because they limit their ability to be protonated
pKa of amines can be lowered by 3 units by converting to N-Mannich base (X = CH2NHCOAr) or Imine (Schiff base) prodrug
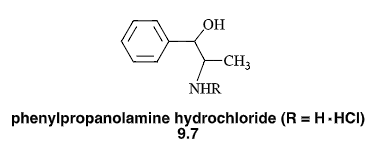
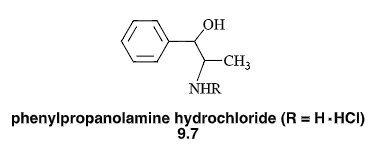
N-Mannich base (R=CH2NHCOPh)
will lower pKa of amines and make them more lipophilic
has a log D7.4 two units greater than the parent compound & has greater lipophilicity
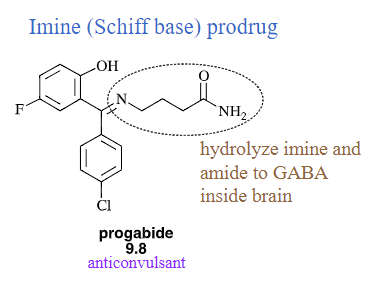
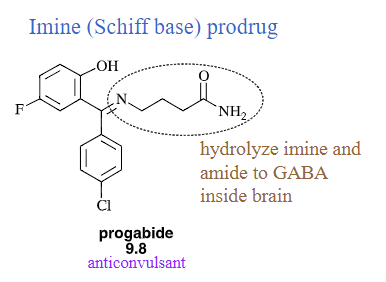
Imine (Schiff base) prodrug
will lower pKa of amines and make them more lipophilic
will improve the pharmaceutical properties of drugs because its functional group has been temporarily modifies to improve its use; easily hydrolyzed
what will lower pKa of amines and make them more lipophilic?
N-Mannich bases (R=CH2NHCOPh) & Imine (Schiff base) prodrugs
acid
substance that increases the concentration of H3O+ when added to water
base
substance that decreases the concentration of H3O+ when added to water
Brønsted-Lowry acid
proton donor
Brønsted-Lowry base
proton acceptor
salt
strong electrolytes that dissociate nearly completely into ions in dilute aqueous solutions
autoproteolysis (aka auto/self ionization)
the reaction in which two molecules of the same species transfer a proton from one to the other
protic solvents all have a reactive H+ and undergo this process
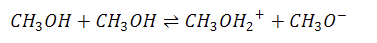
how do you calculate pH?
-log[H3O+]
![<p>-log[H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ac9faf3e-0475-479f-b8c0-e6e2892ed4f7.png)
how do you calculate pOH?
-log[OH-]
![<p>-log[OH<sup>-</sup>]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/493a5561-0fc4-4f8a-9706-ce140b890613.png)
Kw
= 1.0 × 10-14 = [H3O+][OH-]
![<p>= 1.0 × 10<sup>-14</sup><sub><sup> = </sup></sub>[H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>-</sup>]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/42016572-6bfd-4414-8f11-d57d34a364a9.png)
what is the concentration of H3O+ and OH- in pure water?
1.0 × 10-7
how can you tell whether a solution is acidic or basic?

strong acids (7)
hydrochloric acid (HCl)
hydrobromic acid (HBr)
hydroiodic acid (HI)
sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
nitric acid (HNO3)
chloric acid (HClO3)
perchloric acid (HClO4)
strong bases (8)
lithium hydroxide (LiOH)
sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
potassium hydroxide (KOH)
calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
rubidium hydroxide (RbOH)
strontium hydroxide (Sr(OH2)
cesium hydroxide (CsOH)
barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)2)
what should you know about strong acids and bases?
they will completely dissociate in an aqueous solution
weak acids (HA)
donates a proton to water
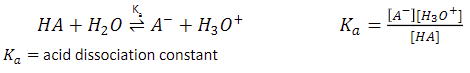
weak bases (HB)
abstracts a proton from water
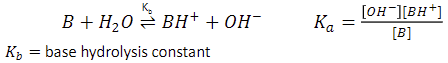
most carboxylic acids are…
weak acids
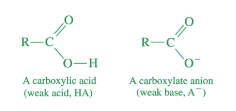
most carboxylate anions are…
weak bases
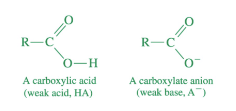
most ammonium ions are…
weak acids

most amines are…
weak bases

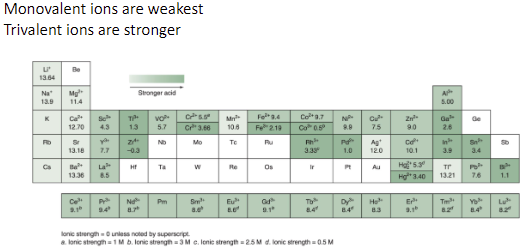
metal cations act as… by …?
weak acids; acid hydrolysis to form MOH(n-1)+ + H+
polyprotic acids and bases
can donate or accept more than one proton
example: oxalic acid is diprotic, and phosphate is tribasic
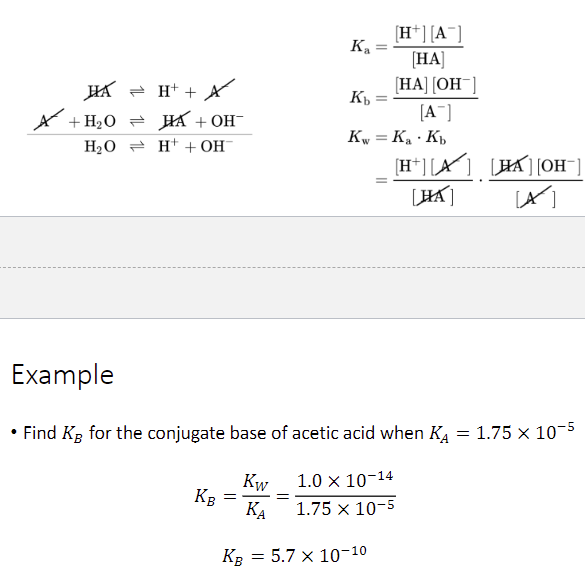
relationship between KA and KB
their product equals Kw
acid-base titrations
titrations involving acids and bases widely employed in analytical control of many commercial products
what are the 3 major types of acid-base titrations?
SA-SB
WA-SB
Diprotic Acid Titration