Electrons and Periodic Table (copy)
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
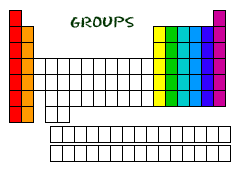
groups
vertical columns of the periodic table; also called families.
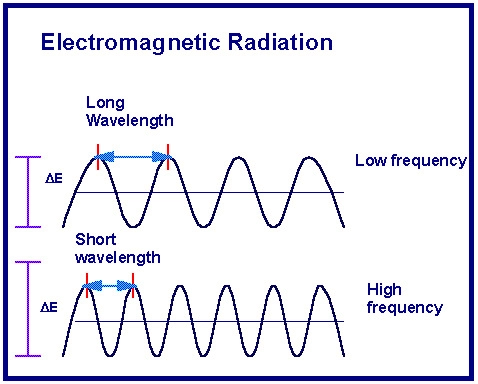
electomagnetic radiation
form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space such as light
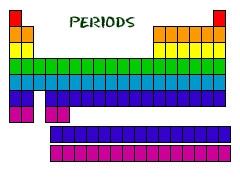
periods
horizontal rows of the periodic table.
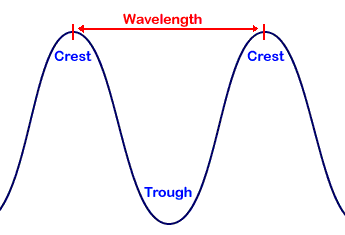
wavelength
shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave
frequency
the number of waves that pass a given point per second
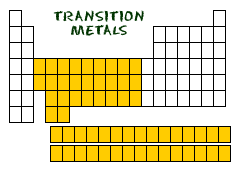
transition elements
Group B elements on the periodic table that include transition metals and inner transition metals.
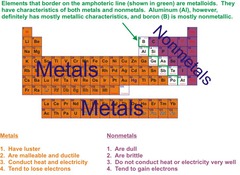
metals
Elements that are shiny and are good conductors of heat and electricity.
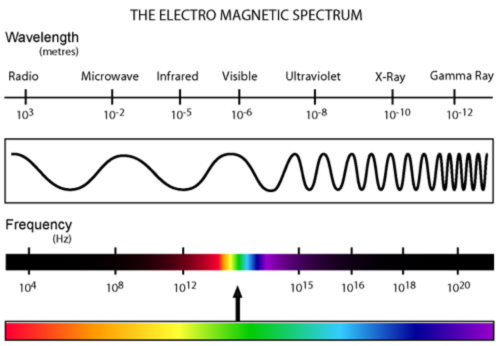
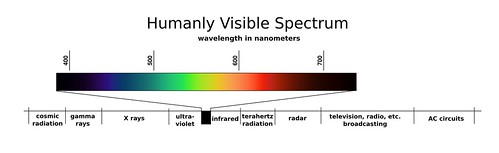
electromagnectic spectrum
includes all forms of electromagnetic radiation, with the only differences in the types of radiation being their frequencies and wavelengths
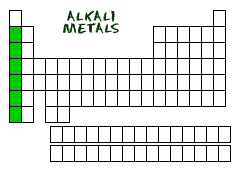
alkali metals
Most of group 1. More chemically reactive than alkaline earth metals.
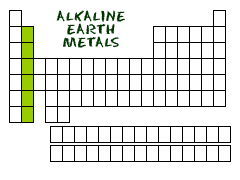
alkaline earth metals
Group 2. Harder and less reactive than alkali metals.
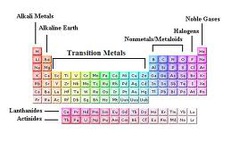
transition metals
elements that form a bridge between the elements on the left and right sides of the periodic table. The elements in groups 3-12 that are contained in the d-block of the periodic table.
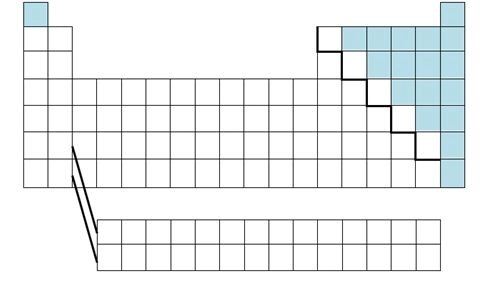
nonmetals
These elements are present in every living thing on earth and can form bonds with multiple atoms at once.
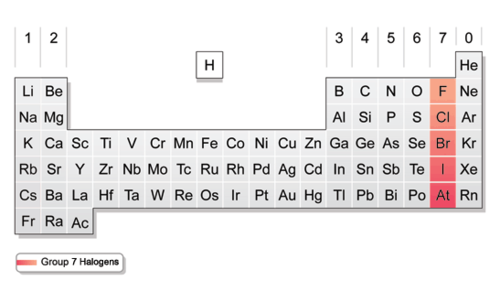
halogens
A highly reactive group 17 element.
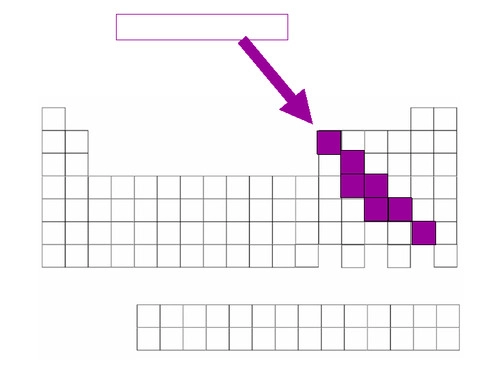
noble gases
An extremely unreactive group 18 ele- ment.

metalloids
share the same physical and chemical properties of both metals and nonmetals. silicon and germanium are the most important.
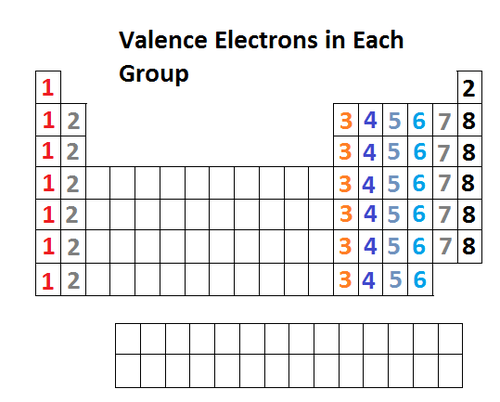
valence electrons
electrons on the outermost principal energy level of an atom.
Relationship between valence electrons and period
the energy level of the valence electrons of an element indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found.
Relationship between valence electrons and group number
the group number of a representative element is the same as its number of valence electrons. But, there are many exceptions.
atomic radius for metals
half the distance between adjacent nuclei in a crystal of the element.
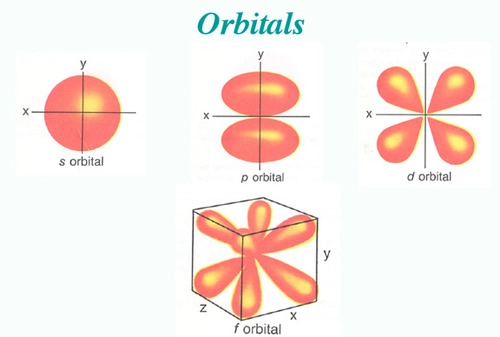
atomic orbital
wave function predicts a three-dimensional region around the nucleus
atomic radius for nonmetals
half the distance between nuclei of identical atoms that are chemically bonded together.
electron configuration
the arrangement of electrons in an atom
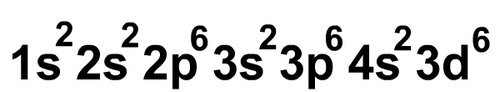
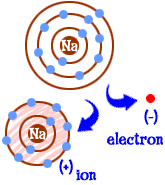
ion
an atom, radical, or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons and has a negative or positive charge.
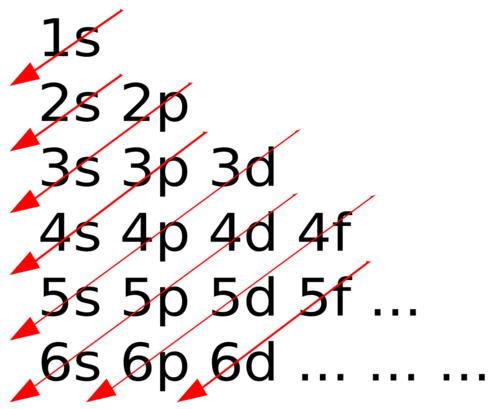
aufbau principle
states that each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available
ionic radius
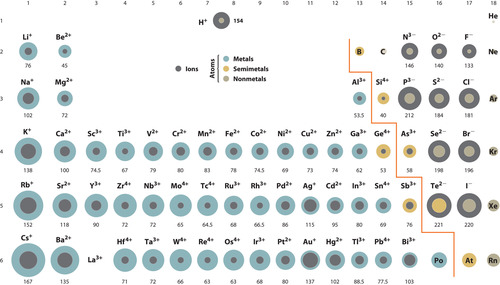
the distance from the nucleus to the outer energy level of the ion.
Pauli exclusion principle
states that a maximum of two electrons can occupy a single atomic orbital but only if the electrons have opposite spins
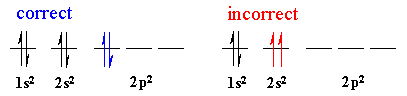
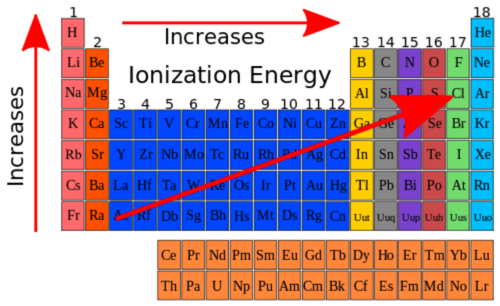
ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
Hund's rule
states the single electrons with the same spin must occupy each equal-energy orbital before additional electrons with opposite spins can occupy the same orbitals
electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract electrons in the formation of an ionic bond.
valence electron
are defined as electrons in the atom's outermost orbitals - generally those orbitals associated with the atom's highest principal energy level
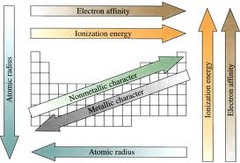
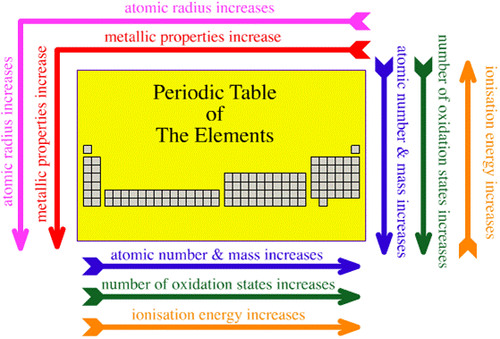
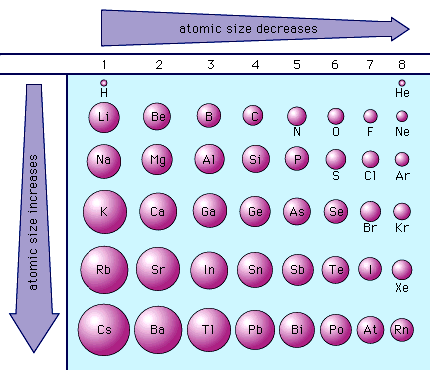
atomic radius trends
increases as you move down groups. decreases as you move right across periods.
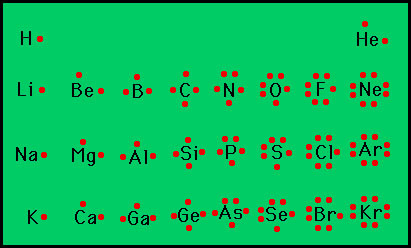
electron-dot structure
consists of the element's symbol, which represents the atomic nucleus and inner-level electrons, surrounded by dots represnenting all of the atom's valence electrons
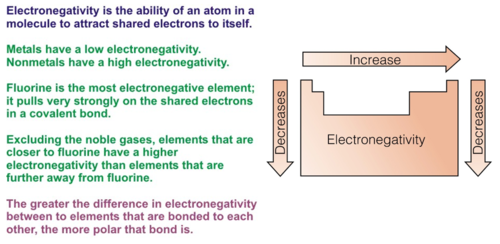
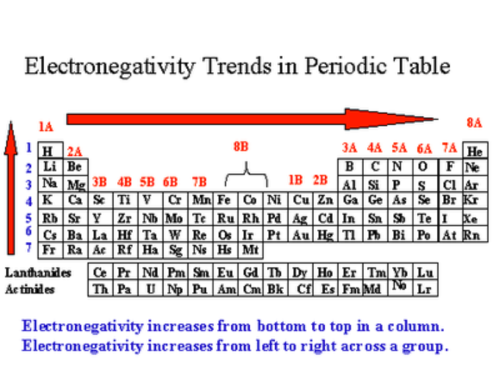
electronegativity trends
decreases as you move down groups. increases as you move right across periods. not ionization.
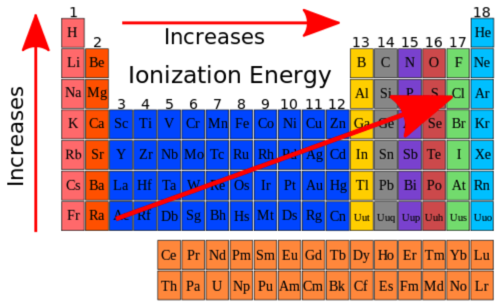
ionization energy trends
decreases as you move down groups. increases as you move right across periods. not electronegativity.
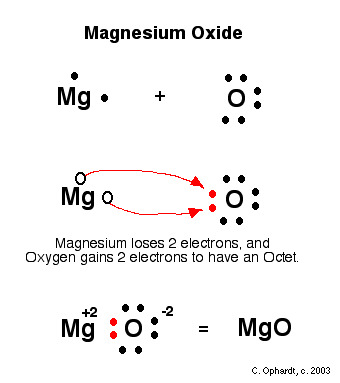
octet rule
atoms will gain, share, or give up electrons to achieve the electron configuration of a noble gas. meaning 8 valence electrons.
periodic law
the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
Mendeleev
Russian chemist who developed a periodic table of the chemical elements and predicted the discovery of several new elements (1834-1907). Arranged the table in increasing mass
Moseley
Arranged the periodic table according to atomic number instead of mass