Biology - Unit 10: Protein Synthesis
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
DNA vs. RNA Base pairing rules
DNA: A-T C-G
RNA: A-U C-G
RNA: A-U C-G
2
New cards
DNA vs. RNA strand numbers
DNA = Double Stranded
RNA = Single Stranded
RNA = Single Stranded
3
New cards
mRNA Structure
Single stranded and linear
4
New cards
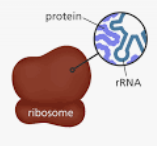
rRNA Structure
Single Stranded and Globular
5
New cards
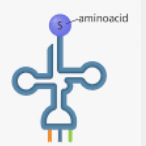
tRNA Structure
Single stranded and clover leaf
6
New cards
Why do we need to do Transcription?
DNA cannot leave the nucleus but the mRNA can, so an mRNA takes its place.
7
New cards
What is the product of Transcription?
RNA transcript
8
New cards
Where does transcription happen?
Euk-Nucleus
Prok-Cytoplasm
Prok-Cytoplasm
9
New cards
Helicase
unzips DNA
10
New cards
Transcription Factors
look for promoter region
11
New cards
Promoter Region
DNA Nucleotides sequence flag down RNA Polymerase so it can bind
12
New cards
TATA Box
Region where transcription begins; place where RNA Polymerase binds to DNA
13
New cards
RNA Polymerase
Transcribe genetic information from DNA to RNA sequence; 3’ to 5’
14
New cards
Complementary Base Pairing Rules
(A→U, T →A, C→G, G→C)
15
New cards
Termination Sequence
AAUAAA;
16
New cards
How quickly after the termination sequence does transcription end?
10-35 nucleotides after termination sequence
17
New cards
Where does translation happen?
Cytoplasm (More specifically the ribosomes)
18
New cards
What is the product of translation?
Proteins
19
New cards
How do we read and process mRNA?
Read in sets of triplets called codons
20
New cards
tRNA in translation
carries amino acids to ribosome based on mRNA
21
New cards
Anticodons
sequence at end of transfer RNA
22
New cards
Peptide Bonds
the bonds responsible for attaching amino acids to the polypeptide chain
23
New cards
Ribosomes
Big and small ribosomal subunit attach where tRNA attaches connect amino acids
24
New cards
5’GTP Cap
Attach to small ribosomal subunits
25
New cards
Small Ribosomal Subunit
Attaches to Large Ribosomal Subunit
26
New cards
Start anticodon
Part of tRNA that had complementary nucleotides for codon
27
New cards
Large Ribosomal Subunit
Attaches to Small Ribosomal Subunity
28
New cards
A Site
tRNA attaches here and takes amino acids from P site
29
New cards
P Site
tRNA from A Site moves here and P tRNA moves to next site
30
New cards
E Site
tRNA from P site moves here to exit
31
New cards
Methionine
AUG - Start codon amino acid
32
New cards
Stop Codon
Sequence that signals stop: UAA, UGA, UAG
33
New cards
Release Factor
protein that recognizes stop codon and ends translation
34
New cards
Point Mutations
Change only one base pair; most mutations fit under this category
35
New cards
Substitution definition
Swap out base pairs for a different base pair
36
New cards
Types of Substitution
Silent, Missense, Nonsense
37
New cards
Silent
Has no effect on the amino acid; inserted at wobble position
38
New cards
Wobble position
third base pair in codon
39
New cards
Missense
Change the amino acid being created (can change shape or function of entire polypeptide); 1st or 2nd base pair in codon
40
New cards
Nonsense
Creates a stop codon and ultimately creates a nonfunctional polypeptide
41
New cards
Frameshift definition
Changing the reading frame of the code
42
New cards
Frameshift types
Insertion and Deletion
43
New cards
Insertion
Nucleotide is added to the gene and changes all amino acids after that; shifts reading frame to the right
44
New cards
Deletion
Nucleotide is removed from the gene; all amino acids change after that; shifts reading frame to the left