3.2 - CompTIA A+ Core 1
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Category 5 (Cat 5)
Uses the 1000BASE-T (1Gbit/s) ethernet standard, with a supporting distance of up to 100 meters.
Category 5 enhanced (Cat 5e)
Uses the 1000BASE-T (1Gbit/s) ethernet standard, with a supporting distance of up to 100 meters.
Category 6 (Cat 6)
Uses the 10GBASE-T (10 Gbit/s) ethernet standard, supporting distances of up to 55 meters (unshielded) or 100 meters (shielded).
Category 6 augmented (Cat 6A)
Uses the 10GBASE-T (10 Gbit/s) ethernet standard, with a maximum supporting distance of up to 100 meters.
Coaxial cable
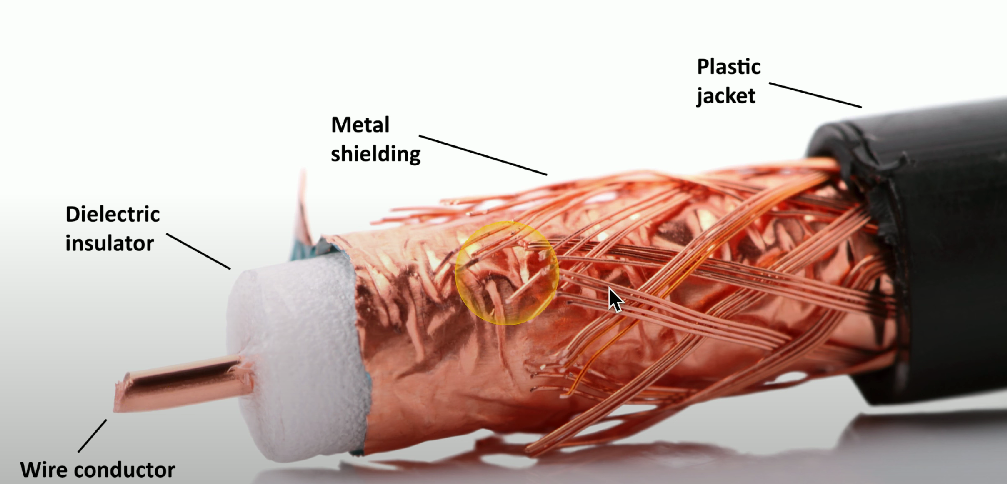
Typically used for cable modems and cable television; RG-6 is the most common form.
Shielded twisted pair (STP)

Balanced wire pair with additional shielding to protect against interference, wires MUST BE TWISTED
Why STP wires should be twisted
Twisting wires minimizes electromagnetic interference and crosstalk between pairs, enhancing signal integrity.
Plenum
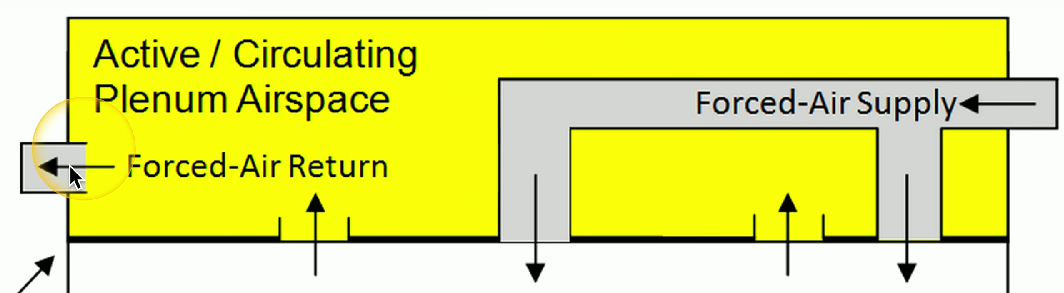
An area inside a commercial building designated for storing warmer air; network cables in this area may produce smoke in case of fire.
Example plenum-rated cables
Fluorinated ethylene polymer (FEP) or low-smoke polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Twisted pair shielding types
U = unshielded
S = braided shielding
F = foil shielding
Format for classifying STP wire shielding
[overall shielding]/[wire shielding]TP
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
Cables that have no additional shielding; the most common type of twisted pair cabling.
Direct burial STP
Network cable placed underground as an alternative to overhead cabling.
T568A/T568B standard
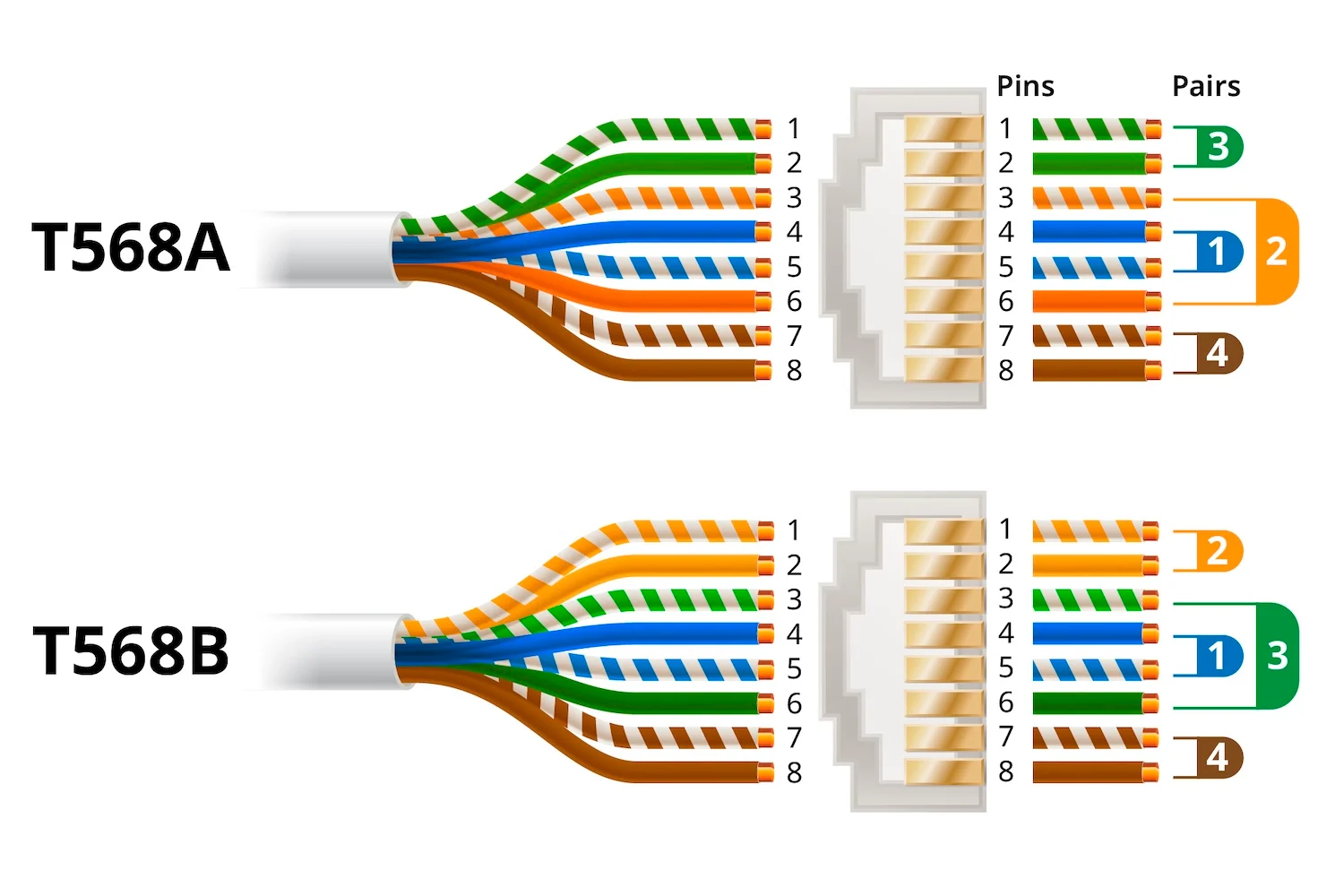
Cabling standard for pin/pair assignments in twisted pair cabling, with T568A for residential and T568B for commercial applications.
Single-mode optical fiber
Type of optical fiber designed for long-distance communication; uses a single light path.
Multimode optical fiber
Type of optical fiber ideal for short distances; allows multiple light paths for greater bandwidth.
Peripheral Cables
Used to simplify connections to peripherals, such as printers, storage devices, keyboards, and mice.
Universal Serial Bus (USB)
A high-speed wired communication standard that connects devices to peripherals, other devices, or power sources.
USB 1.1
Low speed of 1.5 Mbit/s throughput and max length of 3 meters; full speed of 12 Mbit/s throughput and max length of 5 meters.
USB 2.0
Offers 480 Mbit/s transfer throughput with a max length of 5 meters.
USB 3.0
Also known as SuperSpeed USB, it provides 5 Gbit/s (5000 Mbit/s) throughput with typically a length of 3 meters.
USB 3.1 Gen 1
An updated name for USB 3.0 following USB 3.1 release, supports the same 5 Gbit/s throughput as USB 3.0.
USB 3.1 Gen 2
Released in July 2013, also known as USB SuperSpeed+, offers 10 Gbit/s throughput, double compared to USB 3.1 Gen 1.
USB 3.2
Released in September 2017, doubles the bandwidth/throughput compared to USB 3.1, and can use a second “lane” of communication to double bandwidth
USB 3.2 Gen 1
Name update for USB 3.0 following USB 3.2 release - throughput of 5 Gbit/s as before.
USB 3.2 Gen 2

Name update for USB 3.1 following USB 3.2 release - throughput of 10 Gbit/s.
USB 3.2 Gen 2 × 2

Name for USB 3.2 that offers a throughput of 20 Gbit/s by using two lanes for data transfer.
Serial Communication
Utilizes DB-9 and DB-25 connectors and the RS-232 standard for transmitting data between computers and peripheral devices.
Thunderbolt
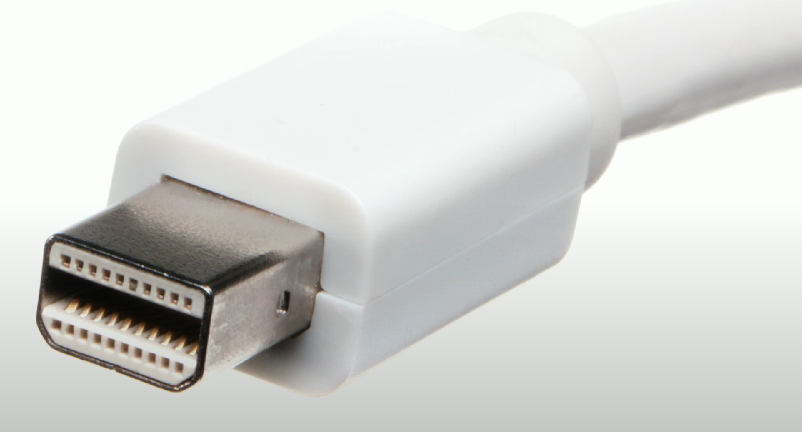

High-speed serial connector that uses the Mini DisplayPort (MDP) standard. Can transmit data and power on the same cable.
Thunderbolt v1
Features two transmission channels with 10 Gbit/s per channel, totaling 20 Gbit/s throughput.
Thunderbolt v2
Provides 20 Gbit/s total throughput via aggregated channels, using the same Mini DisplayPort connector.
Thunderbolt v3
Has 40 Gbit/s aggregated throughput, uses a USB-C connector, and can daisy-chain up to 6 devices.
Video Graphics Array (VGA)

Uses a 15-pin DB-15/DE-15 connector, blue color, for video only, and carries an analog signal.
HDMI

High-definition Multimedia Interface that supports both video and audio, with a digital-only connection and a range of about 20 meters.
DisplayPort

Digital-only connection that sends information in packetized form, supporting both audio and video, available in two distinct formats.
Digital Visual Interface (DVI)

Primarily a digital connection with single and dual link options, offering different types: DVI-A (analog), DVI-D (digital), and DVI-I (integrated).
USB-C

A reversible connector that enables power and data transmissions, supports audio and video in a digital format.
Hard drive cables
Interface for connecting storage devices (HDDs, SSDs, optical drives) to the motherboard, allowing data transfer and power delivery.
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
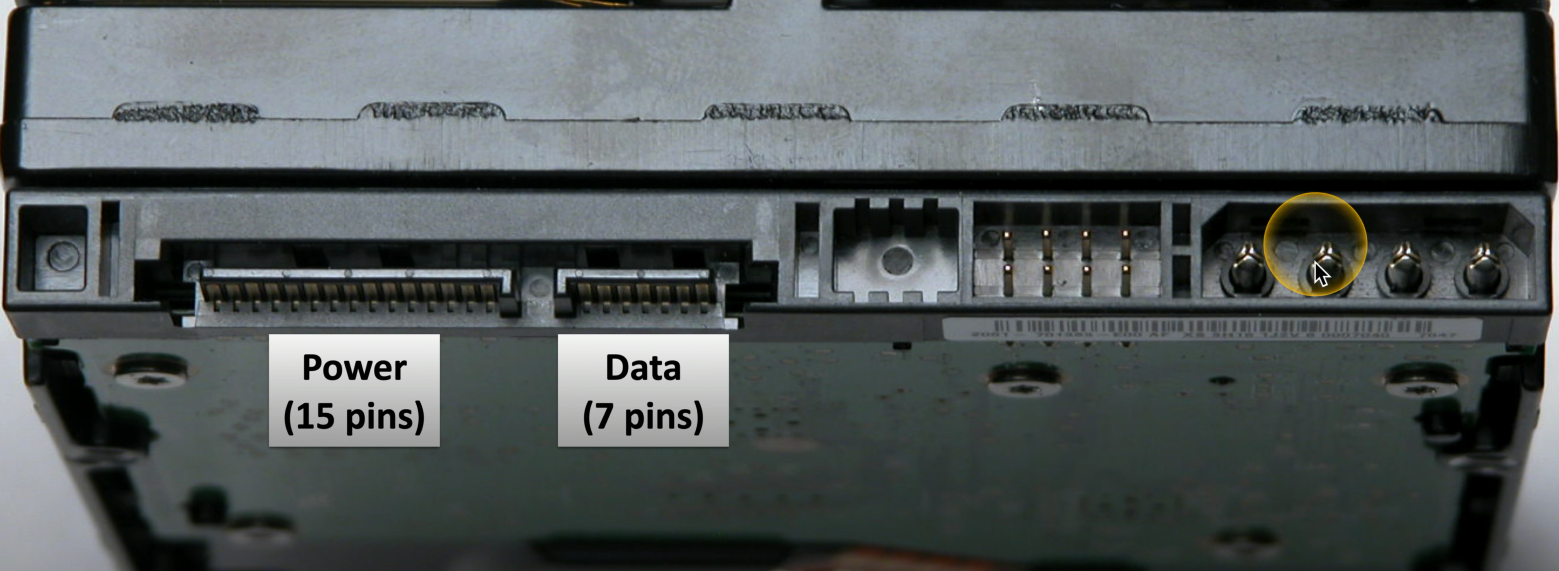
Uses a 15-pin interface for power transfer and a 7-pin interface for data transfer.
SATA Revision 1.0
SATA 1.5 Gbit/s, supports cable lengths up to 1 meter.
SATA Revision 2.0
SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, supports cable lengths up to 1 meter.
SATA Revision 3.0
SATA 6.0 Gbit/s, supports cable lengths up to 1 meter.
SATA Revision 3.2
SATA 16 Gbit/s, supports cable lengths up to 1 meter.
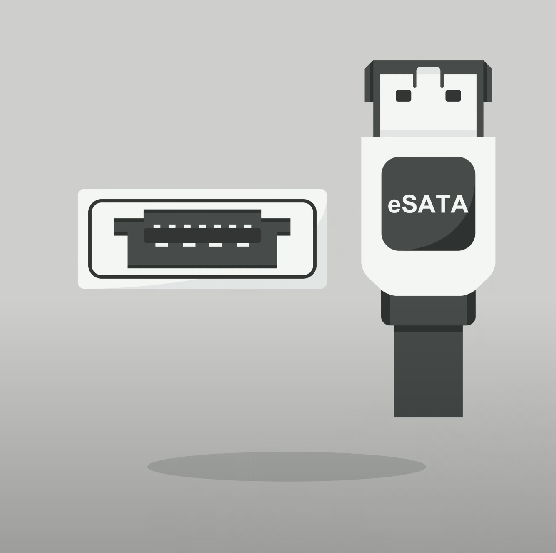
External SATA (eSATA)
Matches SATA standard but allows a cable length of 2 meters with different connector shapes.
Adapters
Devices that convert interfaces from one format to another, enabling compatibility between different connectors.
DVI-D to HDMI
An adapter that connects an HDMI interface to a DVI-D interface.
DVI-A to VGA
An adapter that connects a VGA interface to a DVI-A interface.
USB to Ethernet
An adapter that connects USB interfaces to Ethernet interfaces.
USB hub
A peripheral device that connects to a computer via USB, allowing multiple interface connections.
RJ11
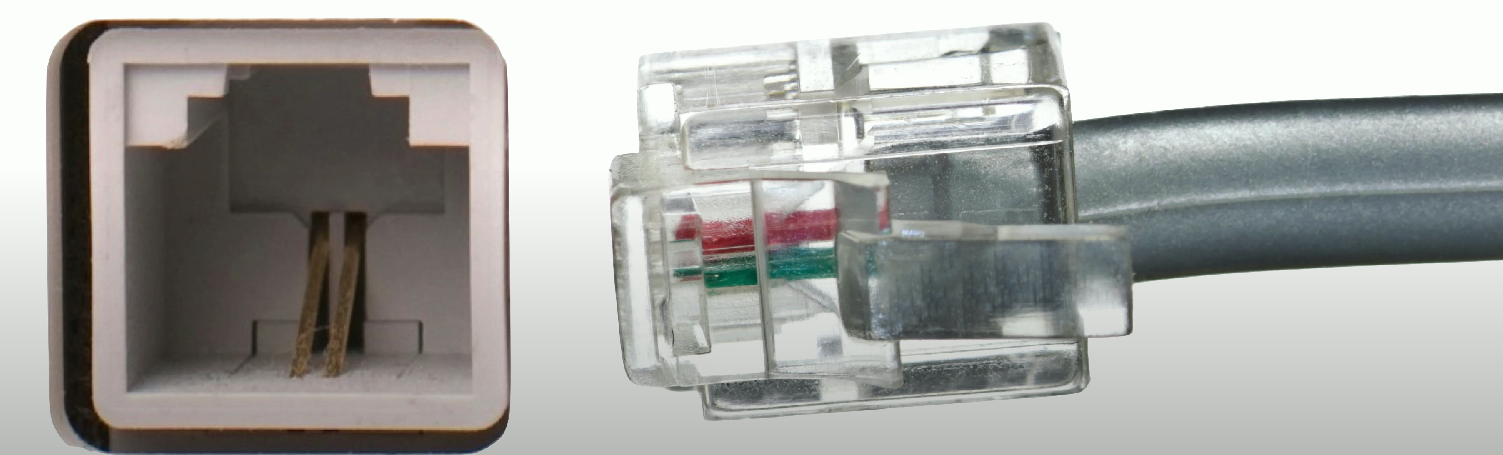
A connector type that is 6-position, 2 conductor (6P2C) typically used in telephone and DSL connections.
RJ45
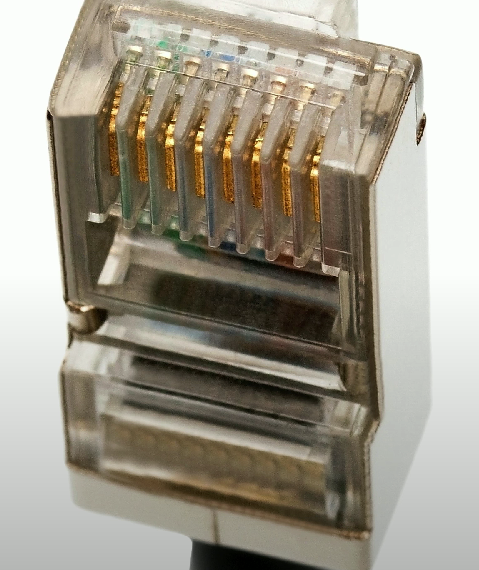

Registered jack type 45, which is an 8 position, 8 conductor (8P8C) connector used in modular connections and Ethernet.
F-type connector
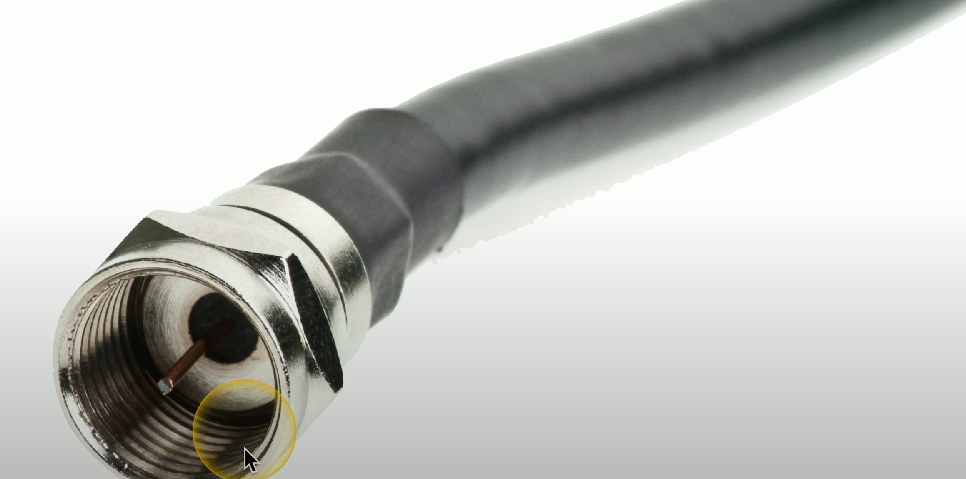

Used in cable modem internet connections (via DOCSIS) and cable television.
Straight-tip (ST) connector

A fiber optic connector type that uses a bayonet-style (twist-on, twist-off) attachment mechanism, commonly used for multimode fiber networks.
Subscriber connector (SC)
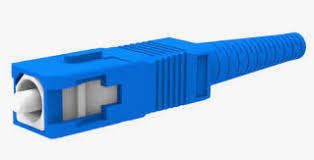
Fiber optic connector that uses a push-pull latching mechanism - widely used in single-mode and multimode fiber optic applications.
Lucent connector (LC)
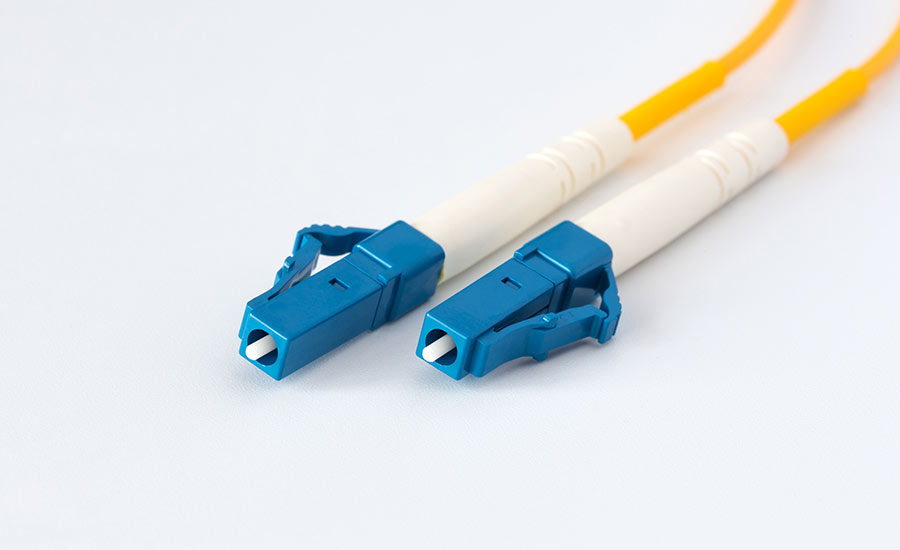
A fiber optic connector that is similar in size to a standard RJ45 connector and commonly used in high-density applications (e.g., data centers). Features a push-pull design for connections.
Punchdown block
A wire-to-wire patch panel where wires are 'punched' to be permanently attached.
USB Standard A-Plug
The most common USB connector type.
USB Standard B-Plug
A common USB connector type for printers.
USB Mini-B Plug
An older USB connector used for cell phones.
USB Micro-B Plug
A newer USB connector used for cell phones.
USB 3.0 Standard-B Plug
A newer standard-B plug for printers over USB 3.0.
USB-C
A 24-pin double-sided USB connector used for data and power transfer in various devices.
Molex connector
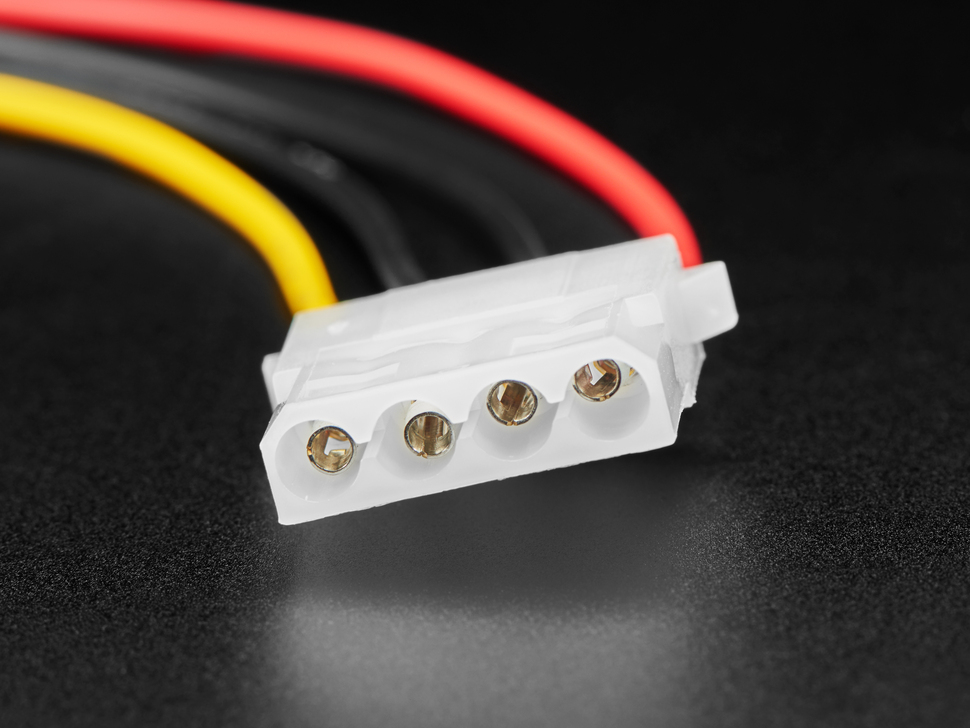

A 4-pin peripheral power connector providing +12V and +5V voltage for devices inside a computer.
Lightning connector

An 8-pin proprietary cable from Apple for digital data transfer, offering advantages like higher power output.
DB-9
A connector primarily used for serial communications and network device configurations via the RS-232 protocol.