Lecture 3 – Neuroimaging, Computational Methods and Thresholds
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Electrophysiological recording
Methods used to study the nervous system by measuring electrical activity in neurons.
Intracellular recording
(A technique that measures voltage changes across the cell membrane by comparing the voltage inside versus outside; 1-100mV
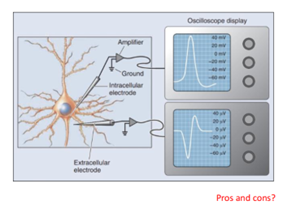
Extracellular recording
A method that measures voltage changes just outside a cell to assess activity near the cell compared to a distant inactive location; 10-500 uV
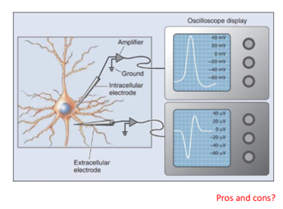
Pros and cons of electro-physiological recording
Intra does smaller potentials and has very high temp. and sp. resolution but is very invasive and damages the cell, and only one at a time
Neuroimaging
A set of methods that generate images of the structure and/or function of the brain, allowing examination of thousands or millions of neurons at once.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
A technique that measures electrical activity in the brain through electrodes placed on the scalp, to roughly locate activity at low sp. resolution but high temp.
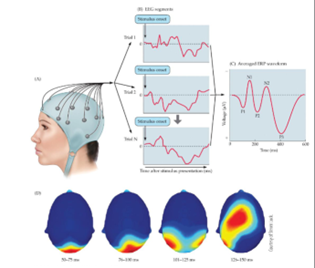
Event-related potential (ERP)
The average activity resulting from many EEG responses to the same stimulus.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
A method that measures changes in tiny magnetic fields produced by neuronal activity, providing information about populations of neurons.
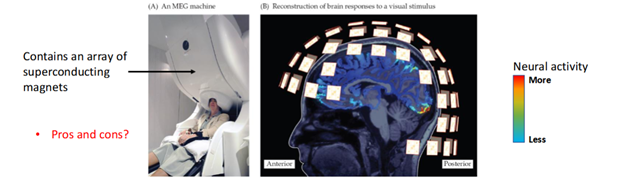
SQUID
Superconducting quantum interference device, used for MEG
Pros and cons of MEG
very costly, but better sp. res especially for deeper sub-cortical structures
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
A radiofrequency current produced by a strong magnetic field causes atoms to spin out of equilibrium, sensor detect energy released as atoms realign with field when pulse turned off
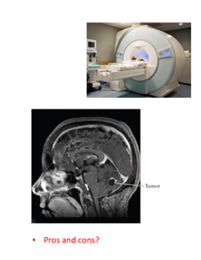
Functional MRI (fMRI)
Magnetic pulses pick up evidence of demand for more oxygen in the brain, creasting a blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signal
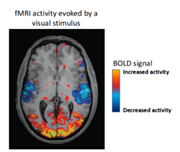
Pros and cons of fMRI
low temporal resolution (because blood flow → delay), indirect measure, good for subcortical strucutures and non-invasive
Pros and cons of MRI
provides structural information, not activity; better for soft (i.e. water-rich) tissues, cannot be used for audition (loud), uncomfortable, no radiation, costly
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Detects metabolic activity in the brain by using an injected radioactive tracer (e.g. 2-deoxy-D-glucose)
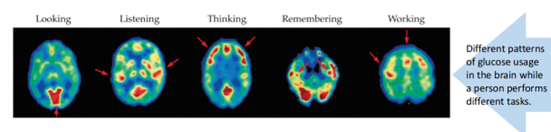
Pros and cons of PET
poor spatial resolution, but good for auditory stimulus (vs fMRI) and can look at deep structures
Efficient coding models
Models that assume sensory systems tune to predictability in natural environments to economically encode predictable information. while highlighting inputs that are less predictable; cpress redundant information
Bayesian models
Statistical models that use prior observations to bias expectations for future events and adjust based on prediction errors.
Artificial neural networks
Computational models consisting of interconnected, weighted units that simulate neuronal connections and learning.
Thresholds
Minimum levels of stimulus required for detection by the sensory system.
Psychophysics
study of quantitative relationships between physical stimuli and psychological experiences, pioneered by Gustav Fechner
Why relate physical stimuli to perceptual experiences using mathematical models?
If we can quantify what the standard is, we can identify when people may be experiencing deviations