sunlight
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
the types of energies in sunlight
visible light, ultraviolet and infrared light
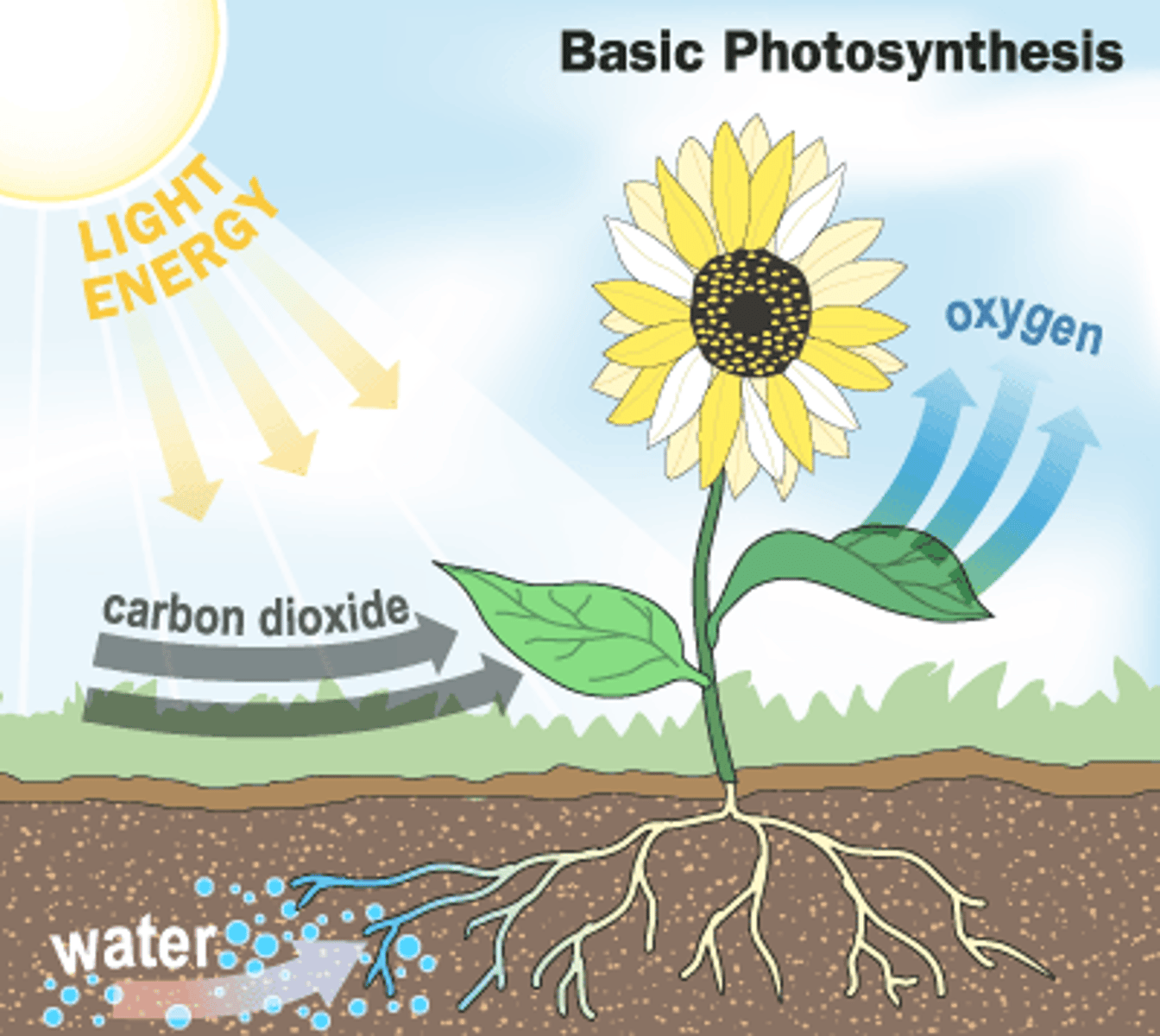
what plants use sunlight for
photosynthesis, which makes them grow and provides us with oxygen
what our bodies need sunlight for
to help produce vitamin D

why its warmer in summer
the earth is tilted towards the sun allowing the sun rays to hit earth directly
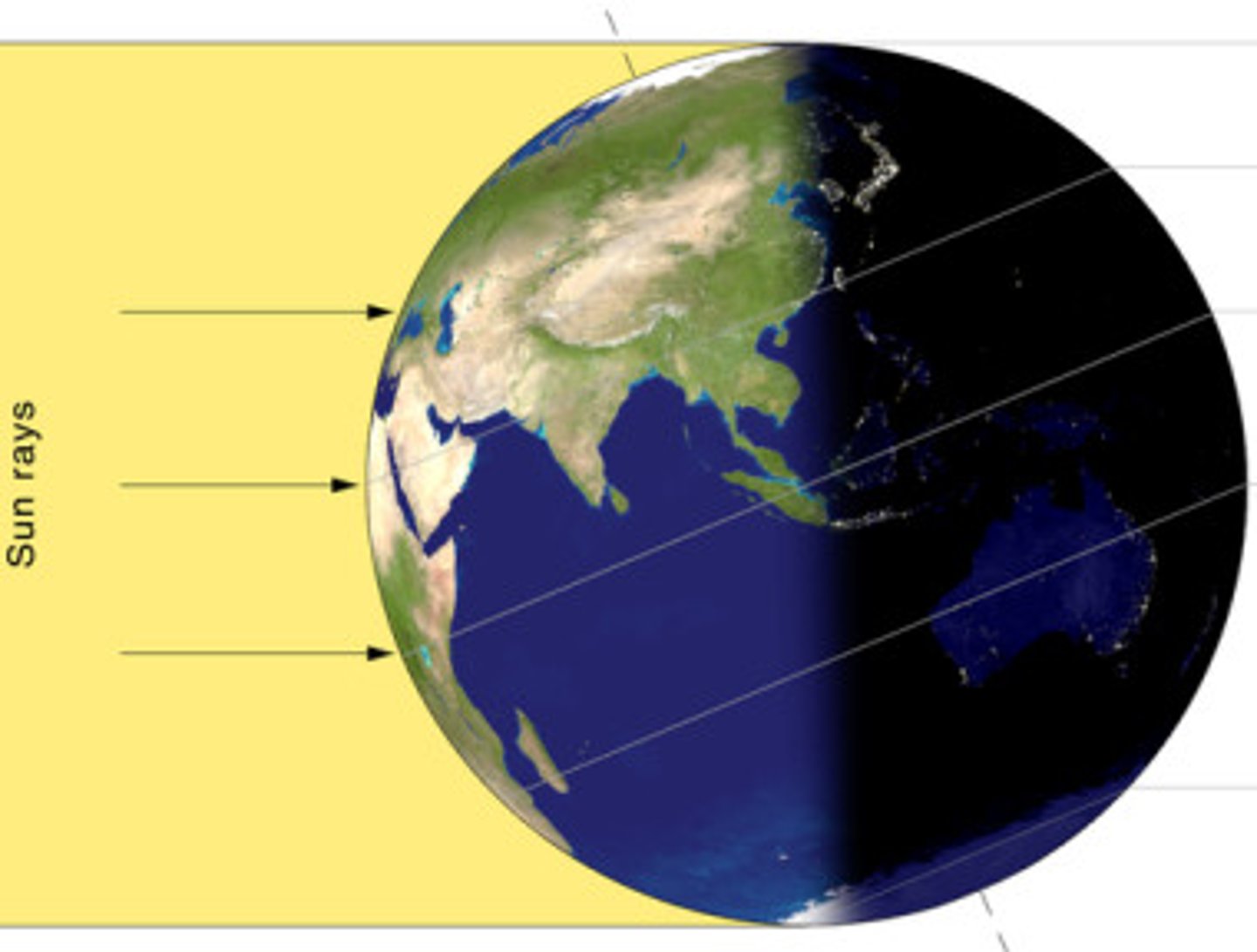
why its colder during winter
the earth is tilted away from the sun so the suns ray hit the earth at a less direct angle

what electromagnetic waves are
solar radiation
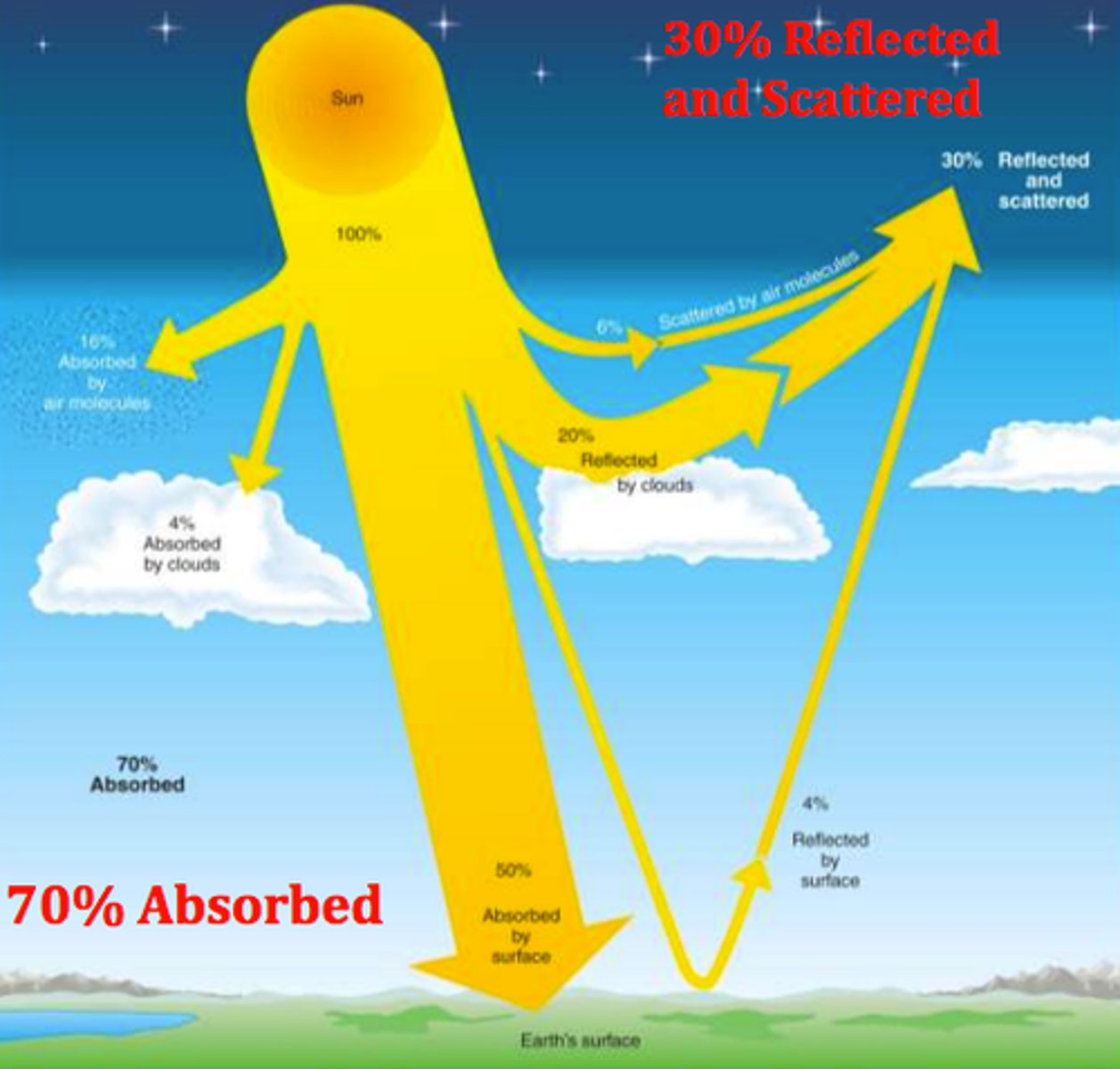
all things that can happen to solar radiation on it's way to earth
-absorption.
where gases and particles absorb the solar radiation e.g. ozone to UV ray
-reflection
caused by the solar radiation hitting things with high
albedo e.g. ice ,snow & clouds
-scattering
where solar radiation scatters in all directions by molecules and particles in the atmosphere
what albedo measures
how shiny or reflective something is
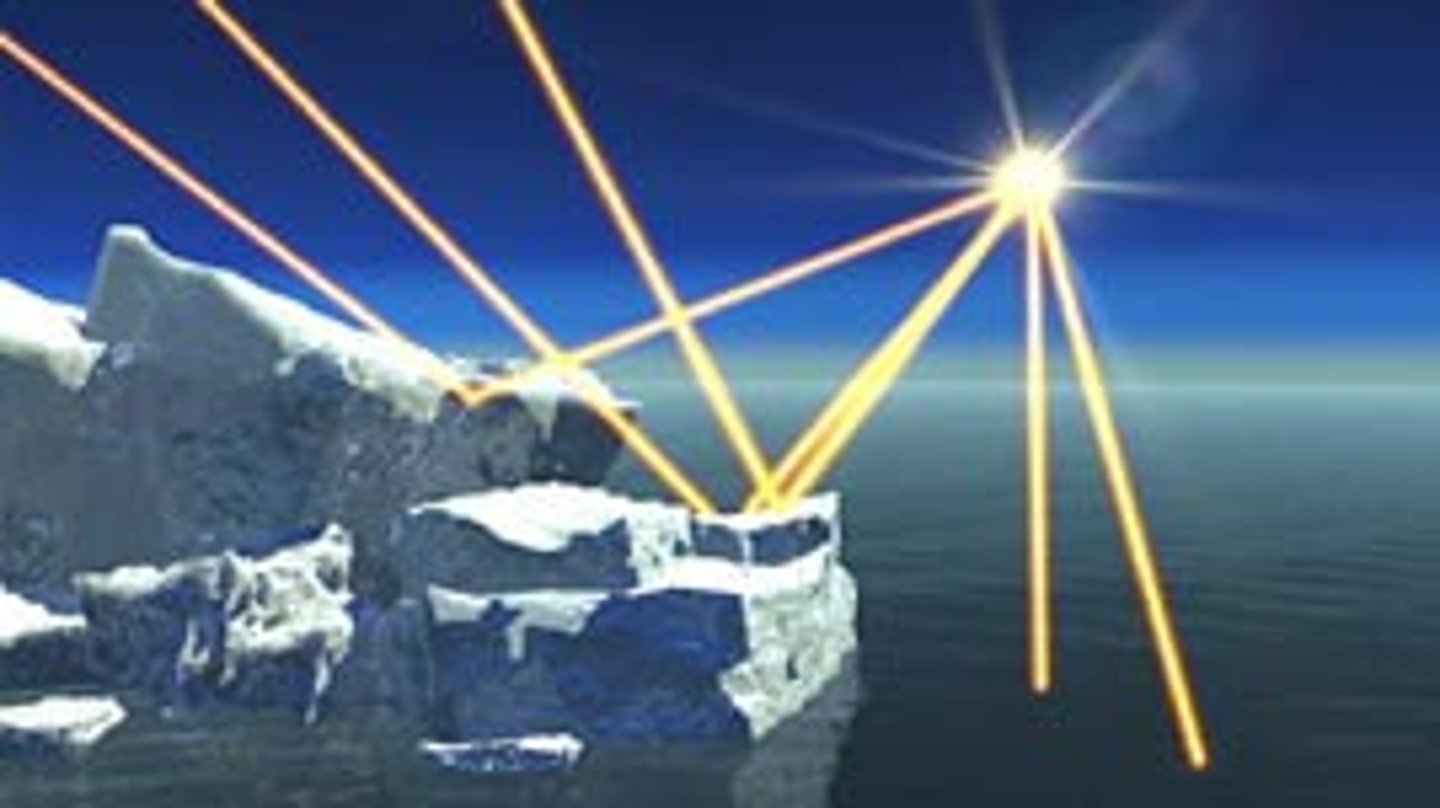

appearance and amount of reflection of something with high albedo
bright & reflects alot
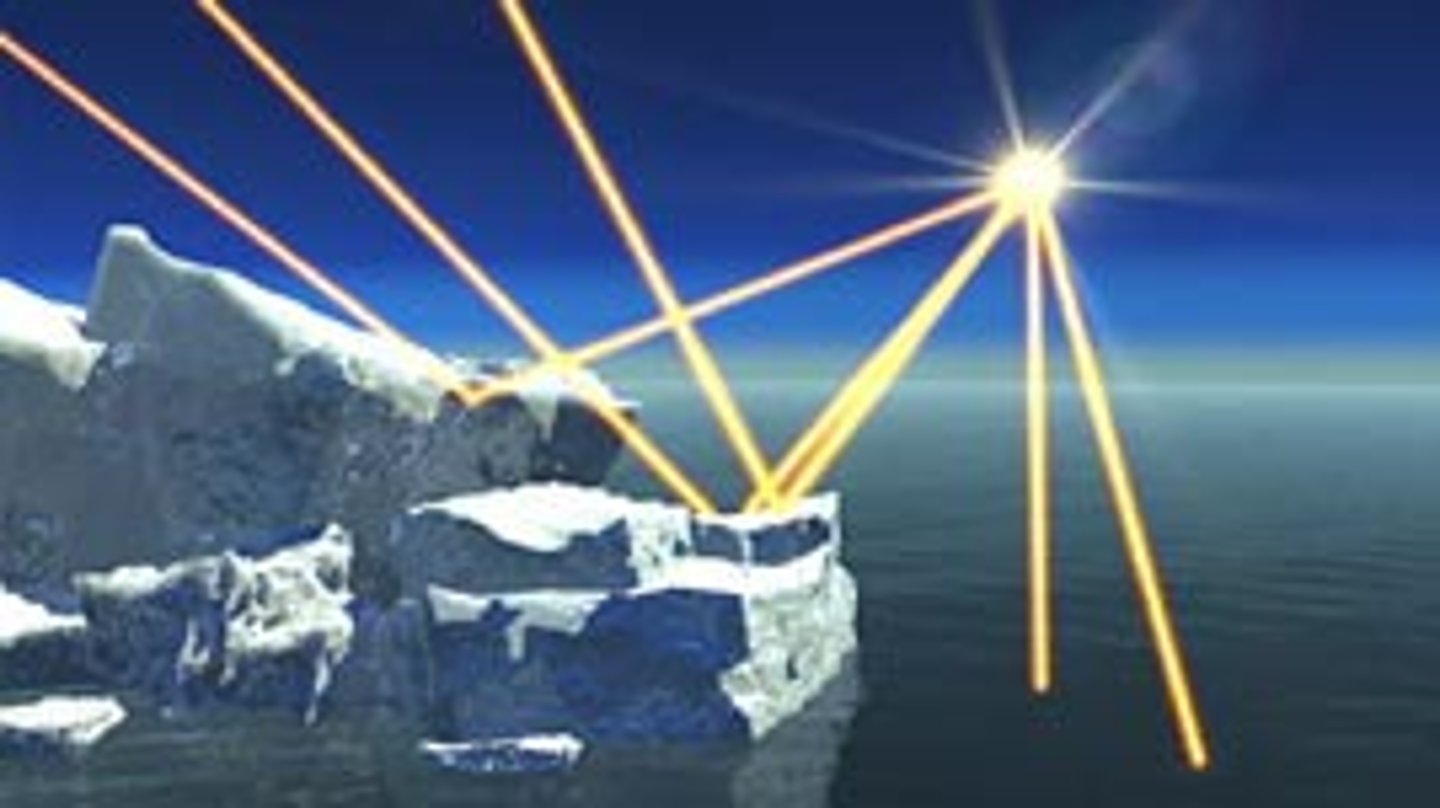

appearance and amount of reflection of something with low albedo
dark & absorbs more light (instead if reflecting)
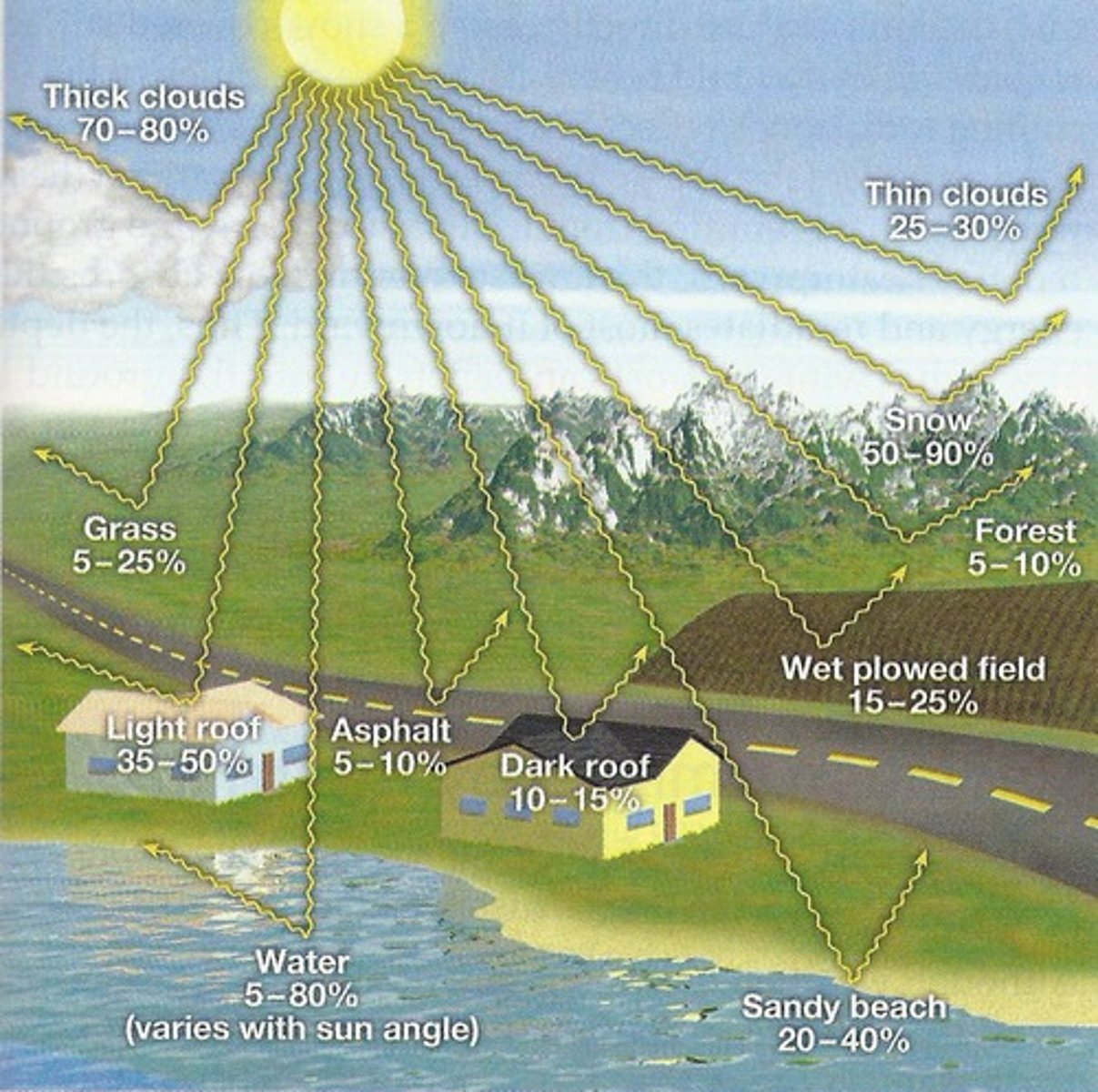
objects with high albedo
snow, ice & clouds

objects with low albedo
asphalt, forests & oceans

reason albedo is an important factor in climate science
it affects the amount of energy that the earths surface receives from the sun
Insolation definition
the amount of solar radiation that reaches the earths surface
factors that can influence insolation
latitude, season, time of day, altitude, & cloud cover
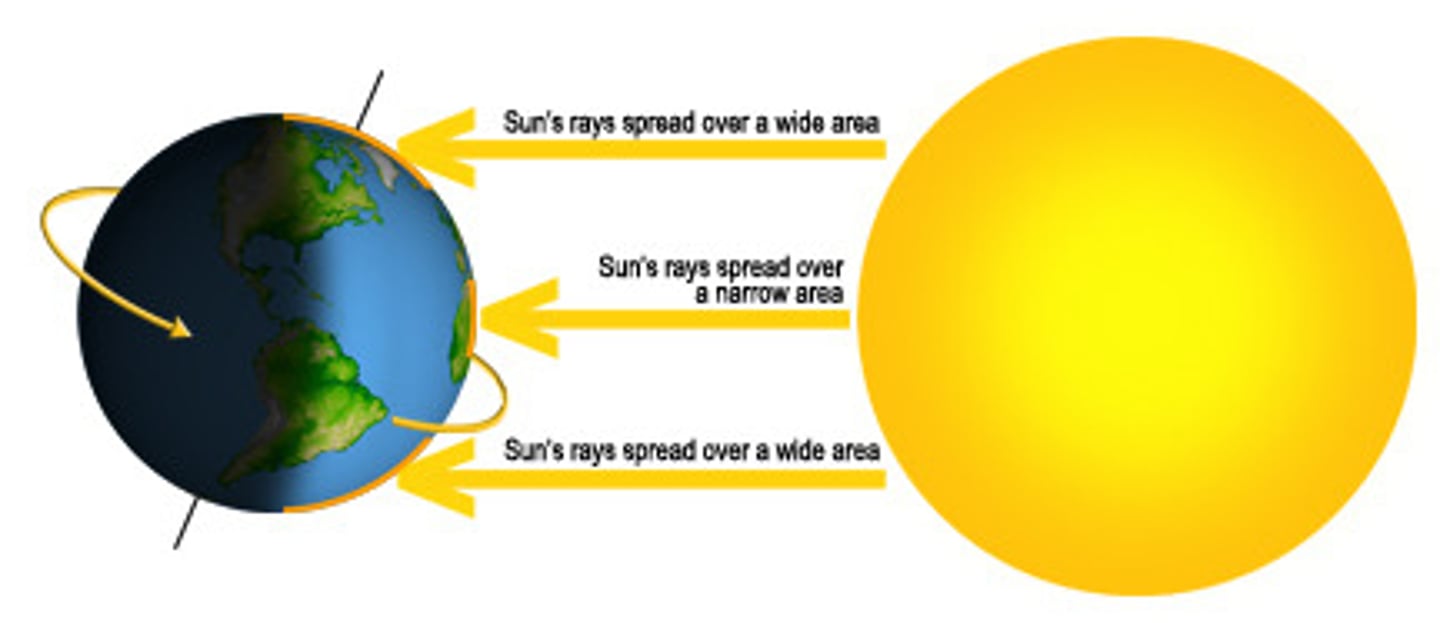
how latitude affects insolation
the sun's ray hit the equator most directly making it get hotter the close you are from it and the colder the further away you are
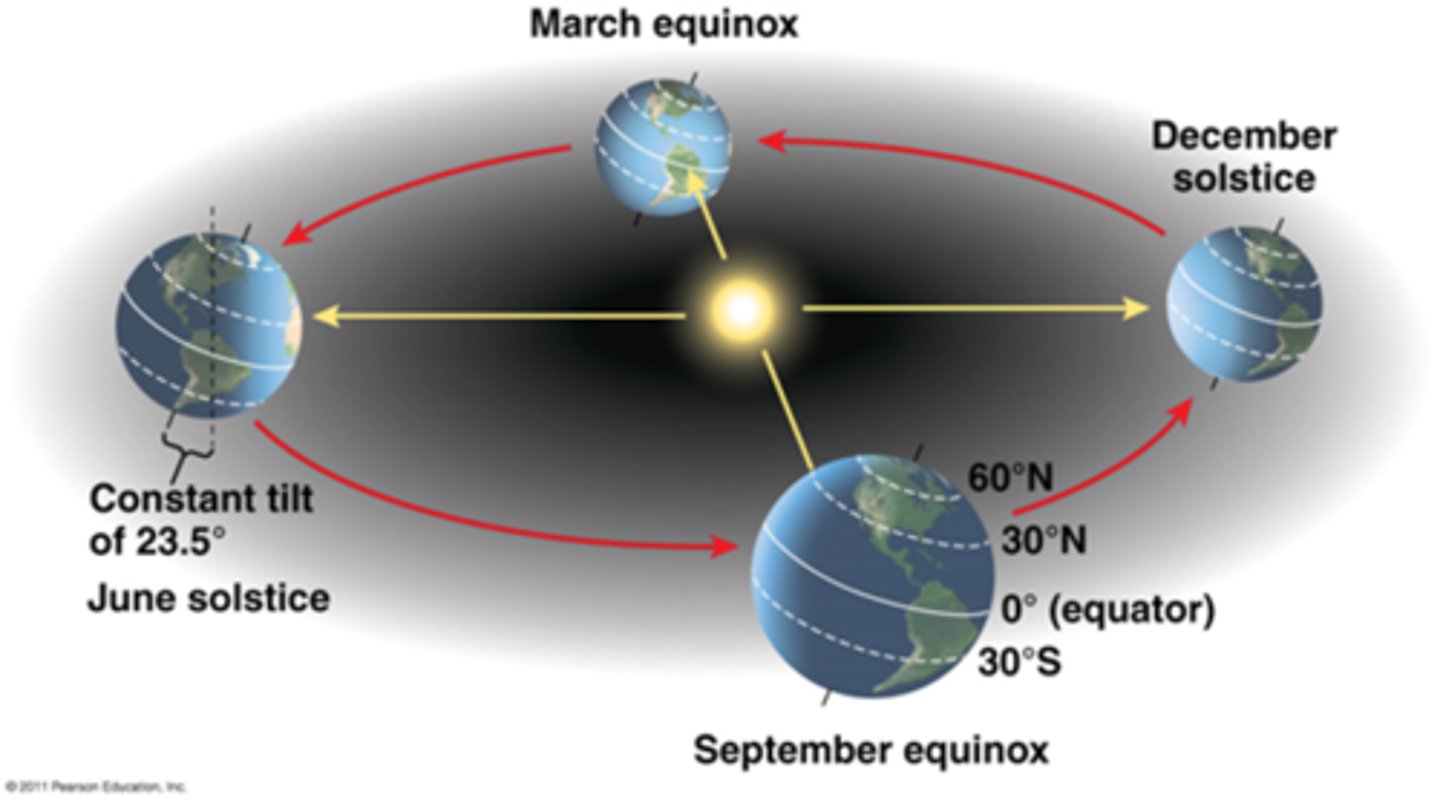
how the season affects insolation
the season (time of year) also dictates the amount of insolation an area receives
how altitude affects insolation
the areas at higher altitudes receive more insolation than areas at lower altitude. due to there being less atmosphere to scatter the insolation
how cloud cover affects insolation
clouds reflect and scatter incoming solar radiation. lowering the amount of insolation
all the factors that influence how the equator receive more insolation than other parts on earth
- it's direct angle of incidence
- it receives solar energy in a smaller area
- it high levels of moisture in the air
- the fact its closest to the sun
all the factors that influence how the poles receive less insolation than other parts on earth
- the sun's rays hitting them at oblique angles (solar radiation spread over a large area)
- them experiencing long periods of darkness during their winter
- the high albedo of the snow and ice