Gravitational and Electric Fields
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
What is a force field?
A region in which a body experiences a non-contact force
What is the difference between geostationary and geosynchronous orbits?
Both have a orbital period equal to the rotational period of the planet they are orbiting, but geostationary means it orbits around the equator (it is stationary relative to observers on the earth) whereas geosynchronous don’t have to orbit around equator.
Explain why astronauts in an orbiting space vehicle experience the sensation of weightlessness. (2 marks)
Idea that both astronaut and vehicle are travelling at same (orbital) speed or have the same (centripetal) acceleration / are in freefall (Not falling at the same speed)
B1 No (normal) reaction (between astronaut and vehicle)
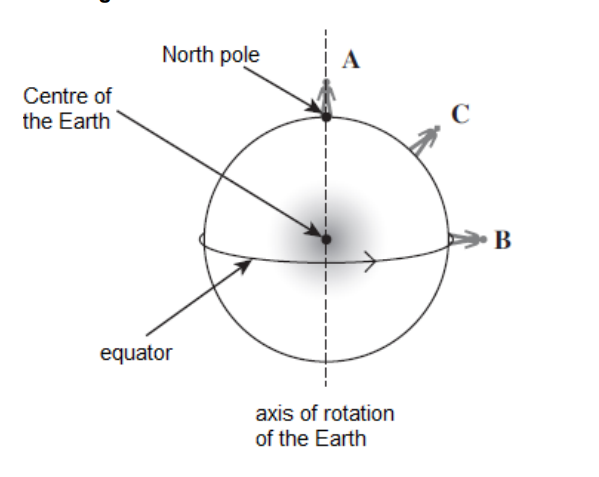
Show, on Figure 1, an arrow showing the direction of the centripetal force acting on student C.
(Perpendicular to and toward the axis of rotation) NB – not towards the centre of the earth
HAS to be towards centre of sphere not the centre of earth!!!
Student B stands on a bathroom scale calibrated to measure weight in newton (N). If the Earth were not rotating, the weight recorded would be equal to the force calculated in part (a)(i). State and explain how the rotation of the Earth affects the reading on the bathroom scale for student B. (VERY IMPORTANT (3 marks)
Draw a diagram of boy standing, with mg and mv²/r pointed downwards and normal upwards. using F = ma, re arrange to make a positive (mg - R = mv²/r) since a = V²/r in circular motion.
Without Earth rotation, no mv²/r so R = mg
With rotation, R = mg - mv²/r so the scales reading (which is the normal reaction) is less than when Earth isn’t rotating.
This is because some of the weight of the boy is supplying the centripetal force. The "missing" weight is actually being converted into centripetal force that is required to keep the student moving in their circular path.
(Since state and explain question, do a calculation - there is one in this case)
What is the distance used to calculate gravitational potential from the surface of the Earth?
NOT 0!!! Its the radius of the Earth…
Compare the uses and principal features of low and high orbiting satellites.

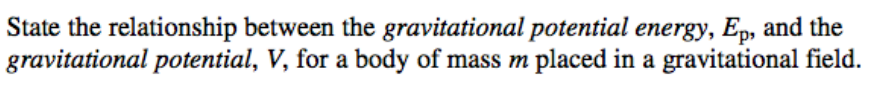
Ep = m Δv
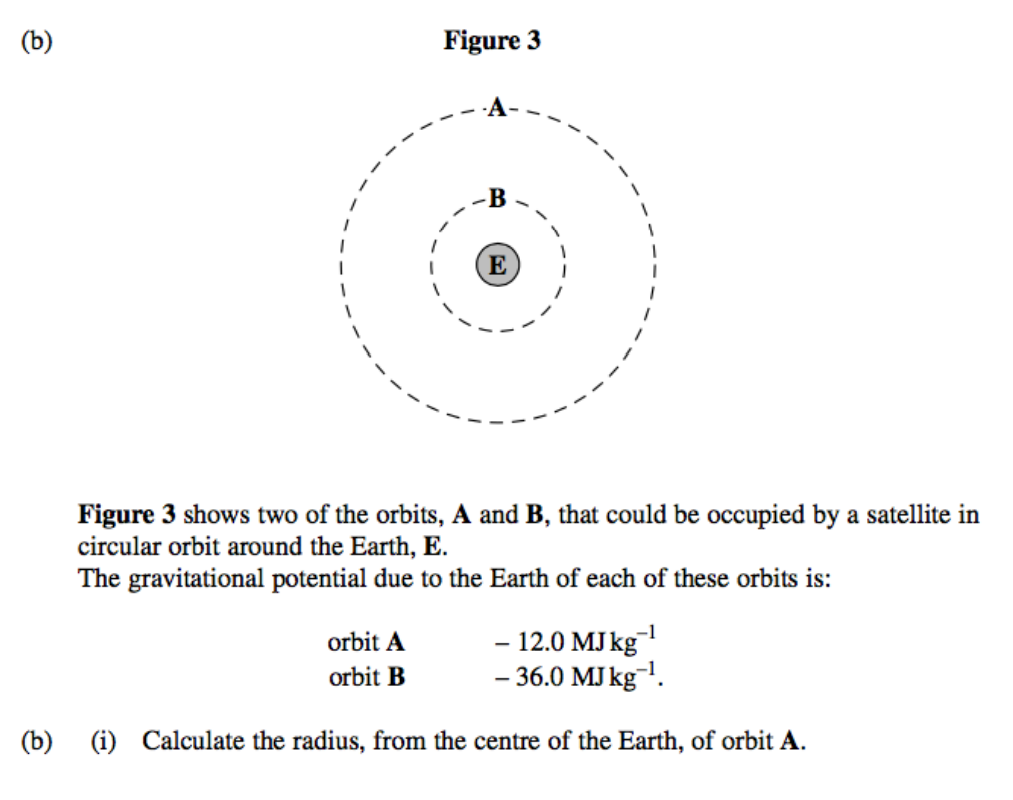
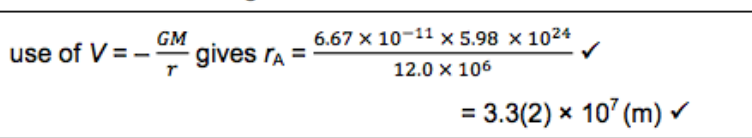
What is true about localised fields?
They are equally spaced out and parallel (almost).
State and explain 3 uses of Low-Orbiting satellites
Monitoring Weather & Surveillance - can scan whole Earth and information can be updated regularly)
GPS - GPS receiver calculates its distance from a satellite using the time it takes for the satellite's signal to reach it. So multiple required
Does gravitational potential increase with distance from object?
Yes, since r is the distance from the centre of the object, and so the further away the less negative the value is getting so the larger the number is. (larger r, closer V gets to 0, therefore its getting larger!)
What is an advantage to using geo-synchronous satellites in communications?
Offers uninterrupted communications between transmitter and receiver.
What is meant by gravitational field strength and is it a scalar or vector quantity?
Force per unit mass, vector.
Does the centripetal acceleration equal g (gravitational field strength)?
Yes
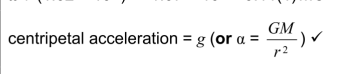
State, in words, Newton’s law of gravitation. (3 marks)
The attractive force between point masses
Is directly proportional to the product of the masses and
inversely proportional to the square of distance apart.
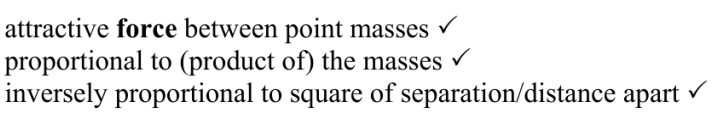
What is meant by Earths “mean orbit radius”
It is the radius from the centres of Earth to the SUN! (the thing the earth ORBITS
If you work out T² of Earth, what must you do?
Square root!!!!!
What is the equation to find the speed of an orbital?
Mass of orbital not required…
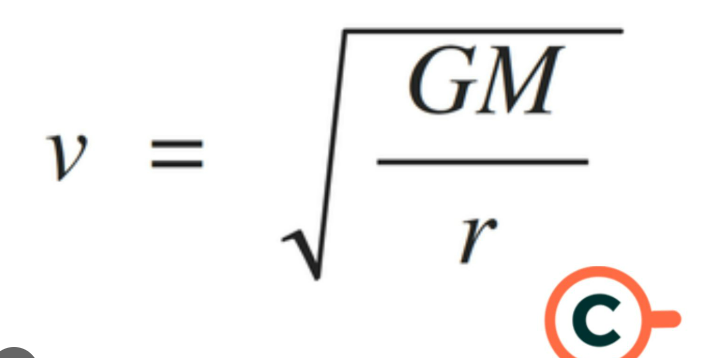
Can the change in work done equation also be used to find the change in grav potential energy?
Yes, Ep = m x (change in gravitational potential)
Why is no work done by the gravitational force that acts on the moon to keep it orbiting earth? (3 marks)
work done = force x distance moved in direction of force (cos theta)
Since in circular motion, the force acts perpendicular to displacement, there is no component of the force that acts in the direction of the distance moved
Therefore, no work is done and KE and Ep remain constant since speed and radius are constant.
Definition of Gravitational Potential (2 marks)
Work done per unit mass
In moving a small mass from fto that point.

Don’t need to use any extra data….
What does gravitational potential graph look like from Earth to Moon?
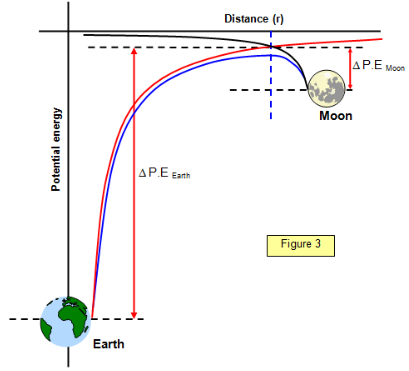
What is Gravitational potential energy (Ep) equation?
Ep = (-) GMm/r
Why does gravitational potential increase as you move further from the centre of the field?
The equation is - GM/r so as r increases, the potential will increase since it is getting closer to 0 (-1/100 is closer to 0 than -1/10).
Gravitational potential is defined as the work done per unit mass to move a mass from infinity to that point, so when it is at infinity, the Gravitational potential is 0 (because no work is needed to move a mass to this point from itself) . As you move closer to object, this then becomes more negative.
How can you find the speed of an orbiting satellite given its gravitational field strength and distance from centre of earth?
g = v²/r
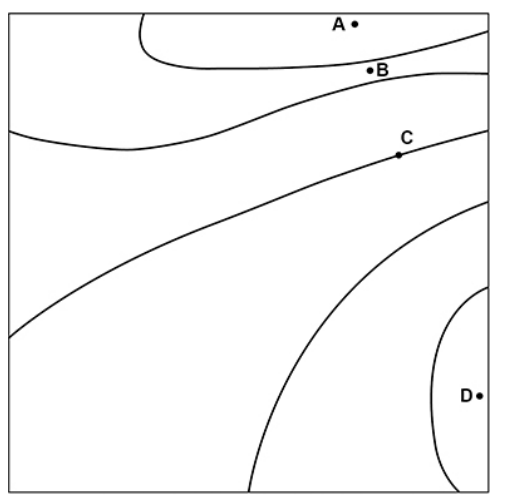
Which point has the greatest gravitational field strength?
B, since the field lines are closest here.
Why is gravitational potential negative?
Gravitational potential is defined as the work done per unit mass to move an object from infinity to a point in a gravitational field. Since gravity does the work as an object moves toward a massive body, the potential energy becomes negative because no energy is required to bring the object closer; instead, energy is released. As the object moves closer to the source, this negative potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, causing the object to accelerate, making the overall potential energy more negative (further away from 0)
As an object moves closer to the source of the gravitational field (like a planet), the gravitational force does the work to pull the object in, decreasing its potential energy. This energy is not from the object itself but from the gravitational field created by the massive body, and the negative sign reflects that the system loses potential energy as the object moves closer (since it is gaining kinetic energy)
What is the difference between Geostationary and Low Orbiting Satellites?
A geostationary satellite is a synchronous satellite and has an orbital radius of 42000km (36000km above surface)
Low orbiting (180 and 2000km above earth), cheaper to launch, use less powerful transmitters but require many of them to achieve full coverage - since they don’t stay above a fixed point
What are low orbiting satellites good for?
Imaging high definition of Earth, monitoring the weather. ISS is a low orbiting satellite.
Why do Geostationary satellites have to orbit in the plane of the equator?
So they are always above the same point on the equator (synchronous orbit)
What are the 3 properties of a geo-synchronous satellite?
An object that has an orbital period equal to the rotation period of the objects its orbiting (e.g Object around Earth would be orbital period 24 hours - which is a Geostationary orbit)
What is true about Radial Fields?
Their “line of force” meet at the centre of the circle.
What is the “line of force”?
Another way of saying “Gravitational field lines”
What 2 quantities do lines of forces present?
Direction (Arrow)
Strength (Density of how many lines)
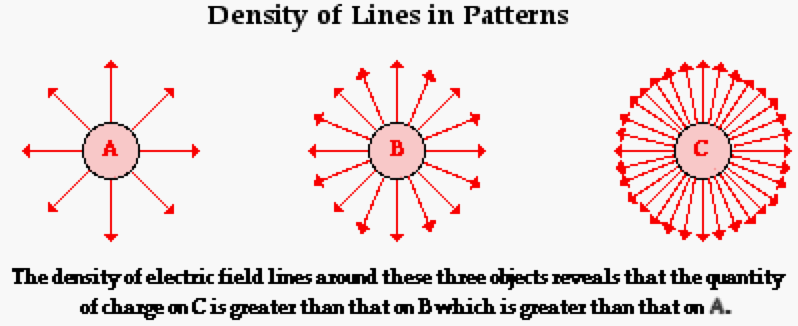
What is Newton’s law of gravitation?
F = Gm1m2/r²
F = magnitude of force experiences by an object in a gravitation field
G = Gravitational constant (6.67×10^-11)
m1 and m2 = Masses of 2 different objects
R = Distance between 2 centre of masses being the 2 objects.
Why does an object being launched at the equator have more kinetic energy rather than an object being launched at the poles?
Earth has a non-perfect sphere shape, making it slightly flattened at the poles and bulges at the equator due to its rotation. Since w = v/r, and w is the same everywhere on earth (24hour time period), v is directly proportional to r, so a larger radius (distance from Earth) means a larger velocity, resulting in a larger kinetic energy.
What is the gravitational potential energy equation? What must the answer always have if it is potential energy?
-GMm/r
MUST ALWAYS BE NEGATIVE SINCE IT REQUIRES ENERGY!
What is a useful equation to find the radius of an object (earth), given only the mass and angular speed of it?
GMm/r² = mw²r (where w is angular speed (2 pi f = 2 pi /T)( (since both are equal to the centripetal force of the object, the mass of the other object (m) cancels out and rearranging for radius gives:
(GM/w²)^1/2 = r³
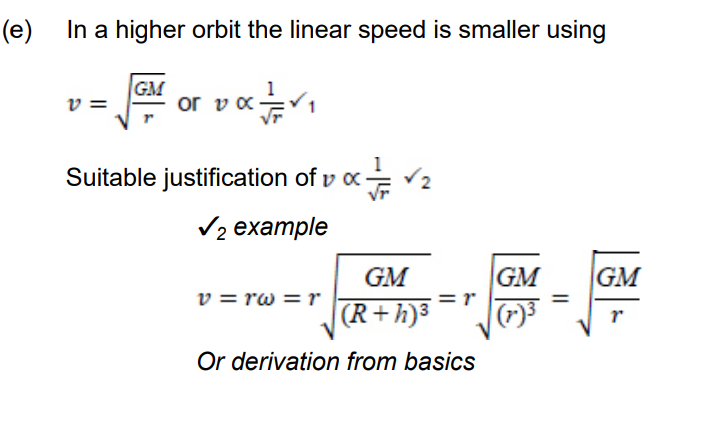
A different satellite is in a higher circular orbit. Explain how the linear speed of this satellite compares with the linear speed of the satellite.
Since now it is in orbit, and not on Earth, cannot simply use w = v/r since now the gravitational pull G is in use, not g, as well as circular motion. We can refer to equation mv²/r = GMm/r, rearranged for v = (GM/r)^1/2. Here now we can see that v is proportional to 1/ r^1/2, so the higher the object is, the slower its linear velocity.
What must be true about the masses in Newton’s law of gravitation?
They must be point masses
What are point masses?
Where all the objects mass acts as if its in the centre (uniform spheres)
What is the inverse-square law?
F is proportional 1/r²
What are the 2 equations to find gravitational field strength (g)?
g = F/m
g = GM/r²
What is gravitational field strength?
Force per unit mass
What are the units for gravitational field strength?
Nkg^-1
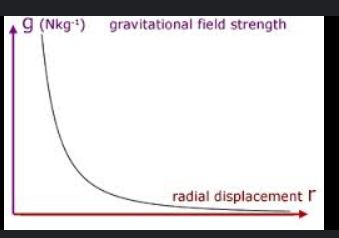
What does the graph r-g look like (radius of earth against g) ?
1/x² graph
What is the definition of gravitational potential?
The amount of work required to move 1 unit mass from infinity to the point.
(The gravitational potential energy that a unit mass would have at a point)
Is gravitational potential always negative? Why?
Yes, since it is the work you have to do against the gravitational field to move the object out of it (think of energy levels)
Are both gravitational potential and gravitational potential energy negative?
Yes.
Does potential energy become less negative as you move upwards?
Yes, since r gets bigger, v gets smaller
What is the difference between g and V?
g is gravitational field strength
V is gravitational potential
What is the potential gradient?
Gradient taken from the potential- radius graph
(change in V)/(change in distance from the centre of the object)
Wat does the potential radius graph look like?
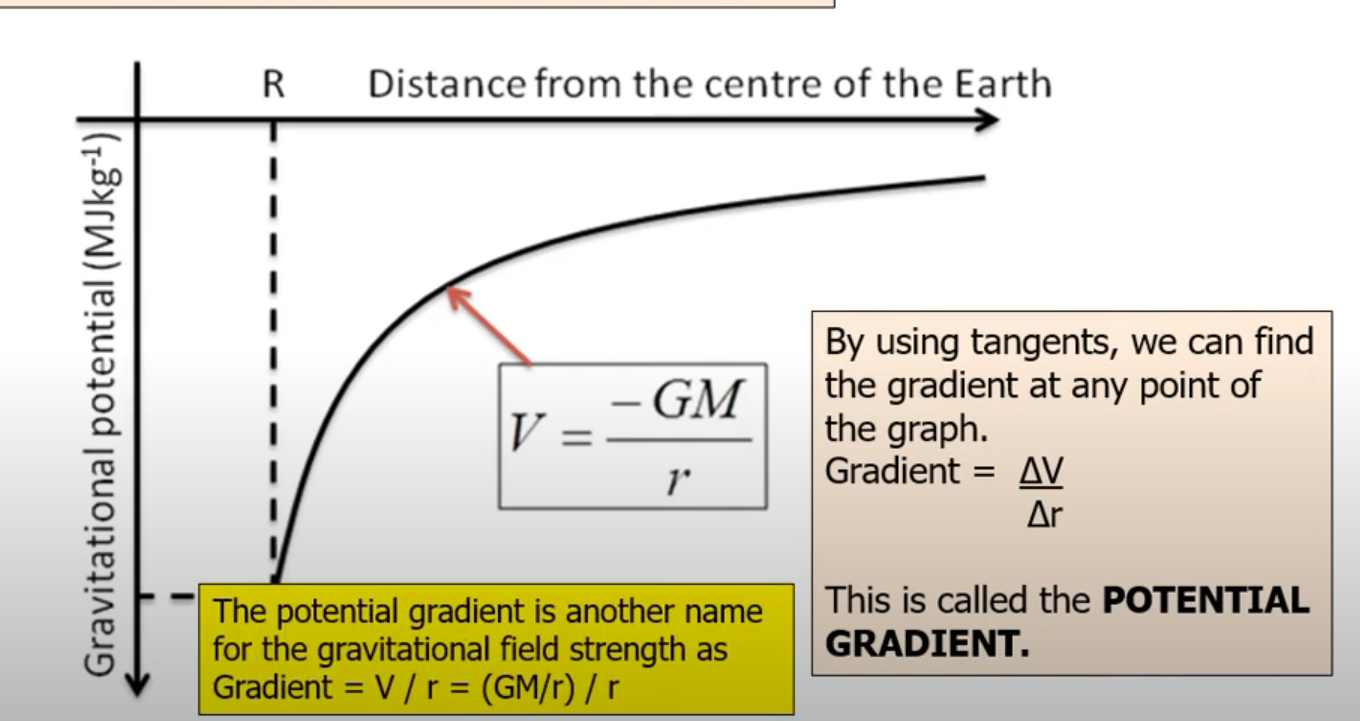
Is the potential gradient negative?
Yes.
What does the area under a g-r give you?
Change in gravitational potential.
What is gravitational potential difference?
The energy needed to move a unit mass
What is the work done equation involving mass and gravitational potential?
W = m V
What is the equation to work out gravitational potential energy?
Ep = m (change in) V
What is (change in) V equation?
V = Vfinal - Vintial
What are equipotentials?
Lines that join together all the points with the same gravitational potential.
What happens when you move along equipotentials?
You don’t lose or gain energy, No work is done when moving along an equipotential surface since the gravitational potential difference is 0
What are the units for gravitational potential?
Jkg^-1
What are the units for grativational constant?
Nm²kg^-2 (given on datasheet)
What is the gravitational potential equal to at point infinity?
0
What does the gradient of the V-r graph give you?
The NEGATIVE gravitational field strength.
What 2 equations can you use to find Keplers law?
F = mw²r = Gmm/r²
(mw²r = mv²/r)
What is the important piece of information that Kepler’s law tells us?
T² = r³
(time period is directly proportional to radius)
Will a satellite travel faster or slower with a larger or smaller radius?
Faster with smaller radius
Slower with larger radius.
What is Keplers equation?
T = (4pi²3r³/GM)^1/2
Can you use ratios involving Keplers law?
Yes, since if 2 objects are orbiting the same planet, the time period and radius of 1 object will be proportional to another’s, since 4pi²/GM is a constant
Giving: Ta²/Ra³ = Tb²/Rb³
What are the 2 types of energy all satellites have?
Kinetic and Potential
Is a satellites energy always constant?
Yes.
What are the 3 things that are constants in satellites in circular orbit?
Total energy, orbital speed and distance from mass its orbiting.
What is the difference between circular and elliptical orbits?
A satellite speeds up as its orbital decreases in elliptical orbits compared to circular orbits which have a constant orbital speed. (Meaning its kinetic energy increases and its potential energy decreases).
What is the definition of escape velocity?
The minimum speed required for an unpowered object to leave the gravitational field of a planet and not fall back towards the it due to gravitational attraction.
What are the 2 equations required to find an equation for escape velocity?
½ mv² = GMm/r
Where does GMm/r come from?
The equation ΔW = mΔV is also used to describe gravitational potential (Ep) through ΔEp = mΔv
Meaning the ΔEp = m(GM/r) = GMm/r
What is the equation for escape velocity?
v = (2GM/r)^1/2
Where r is the radial distance from the centre of the planet to the object! So if it was above the surface it would be r +h!
Is the escape velocity a velocity or speed?
What does it mean if an object has a synchronous orbit?
The orbiting object has an orbital period equal to the rotational period of the object its orbiting.
What is the name of a satellite that has a synchronous orbit?
Geostationary (they are always above the same point on Earth)
What distance makes an orbiting object a “low orbiting satellite”?
180 - 2000 km
What are some pros and cons about low orbiting satellites?
Pros: Cheaper to launch, require less powerful transmitters since they are closer
Cons: Need multiple satellites for full coverage of earth.
If required to calculate the total energy a satellite has, and the gravitational potential energy is negative, do you use the modulus of that or still add the negative?
Add the negative
Etotat = Ek + (-Ep)
What is the definition of a satellite?
A small object that orbits a larger object
What is the orbit speed the inverse of?
1/®^1/2 (r being orbital radius)
What must you not forget about the escape velocity equation?
It is (2GM/r)^1/2 (ALL SQUARE ROOTED EVEN DENOMINATOR)
What equation can you use to work out the angular speed of a satellite in geostationary orbit around the earth?
w = 2 pi / T
NOT 2 pi r since the equation is w = theta / t
When using Keplers law, what is the time period given in?
Seconds!
If you are given the acceleration of an object on a planet, what can it equal to?
g (gravitational field strength
Why can equate F =ma = GMm/r² ?
a may be the gravitational acceleration (if released from rest and no resistance to motion). meaning:
g = Gm/r²
What is another way of phrasing gravitational attraction?
Gravitational force (F)
What is a propellant?
A substance that propels something (not a physical object)
How do thrusters produce thrust in space?
Chemical combustion of propellant occurs.
Gas is expelled and expands through nozzle