Functional Groups
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Alkyl Halide
A compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms of an alkane have been replaced by halogen atoms.
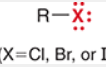
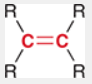
Alkene
A hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
Alkyne
A hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon-carbon triple bond.

Alcohol
Characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom.

Ether
An organic compound that contains an alkoxy group (-O-) connected to two carbon atoms.

Thiol
A compound containing a sulfhydryl (-SH) group attached to a carbon atom.

Sulfide
An organic compound containing a sulfur atom bonded to two carbon atoms, often found in various biochemical processes.

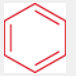
Aromatic (or arene)
A compound that contains one or more benzene rings, characterized by its stability and unique chemical properties.
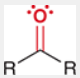
Ketone
characterized by a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms, typically found in sugars and other biological molecules.
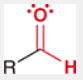
Aldehyde
containing a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to at least one hydrogen atom, commonly found in sugars and fragrances.
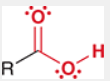
Carboxylic Acid
contains a carboxyl group (–COOH), known for its acidic properties and common occurrence in various biological molecules.
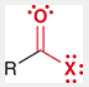
Acyl Halide
An organic compound derived from carboxylic acids by substituting the hydroxyl group with a halide
Anhydride
formed from two carboxylic acid molecules by the removal of a water molecule, typically used in the formation of esters and amides.
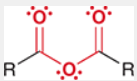
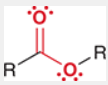
Ester
formed from the reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, characterized by the presence of a carbonyl (C=O) and an ether (–O–) functional group.
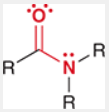
Amide
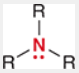
Amine