APES MIDTERM
1/403
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
404 Terms
Carbon Cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
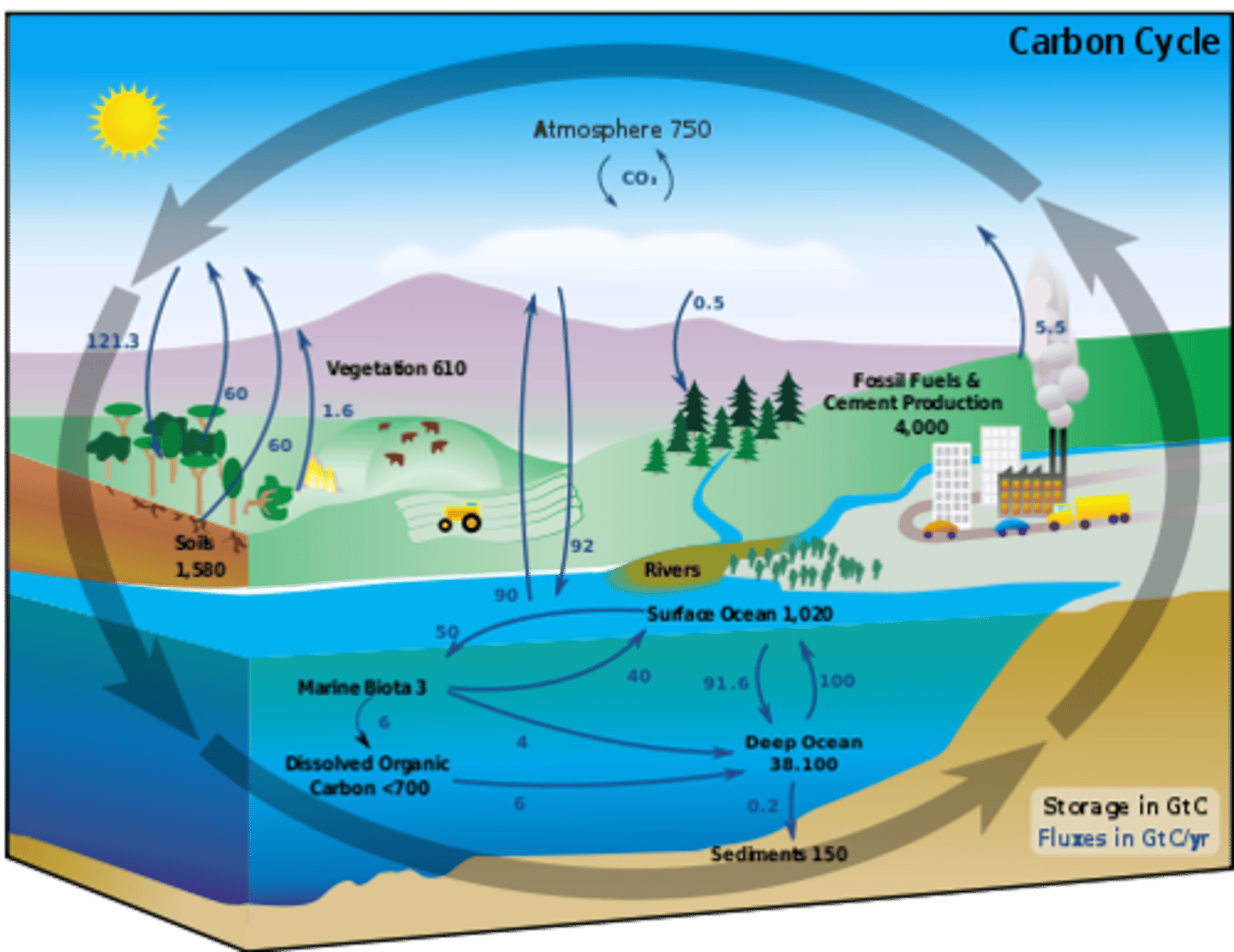
sink
a reservoir that stores more than it releases
source
a process that adds more than it reserves
photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars
key process in the carbon cycle
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
key process in the carbon cycle
direct exchange
CO2 moves directly between atmosphere and the ocean by dissolving into and out of ocean water at the surface
sedimentation
the action or process of forming or depositing sediment
process in the carbon cycle where marine organism bodies sink to the ocean floor and broken down into carbon sediments
burial
step in the carbon cycle where the long time pressure of water compresses carbon into sedimentary stone
Nitrogen cycle
The transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere
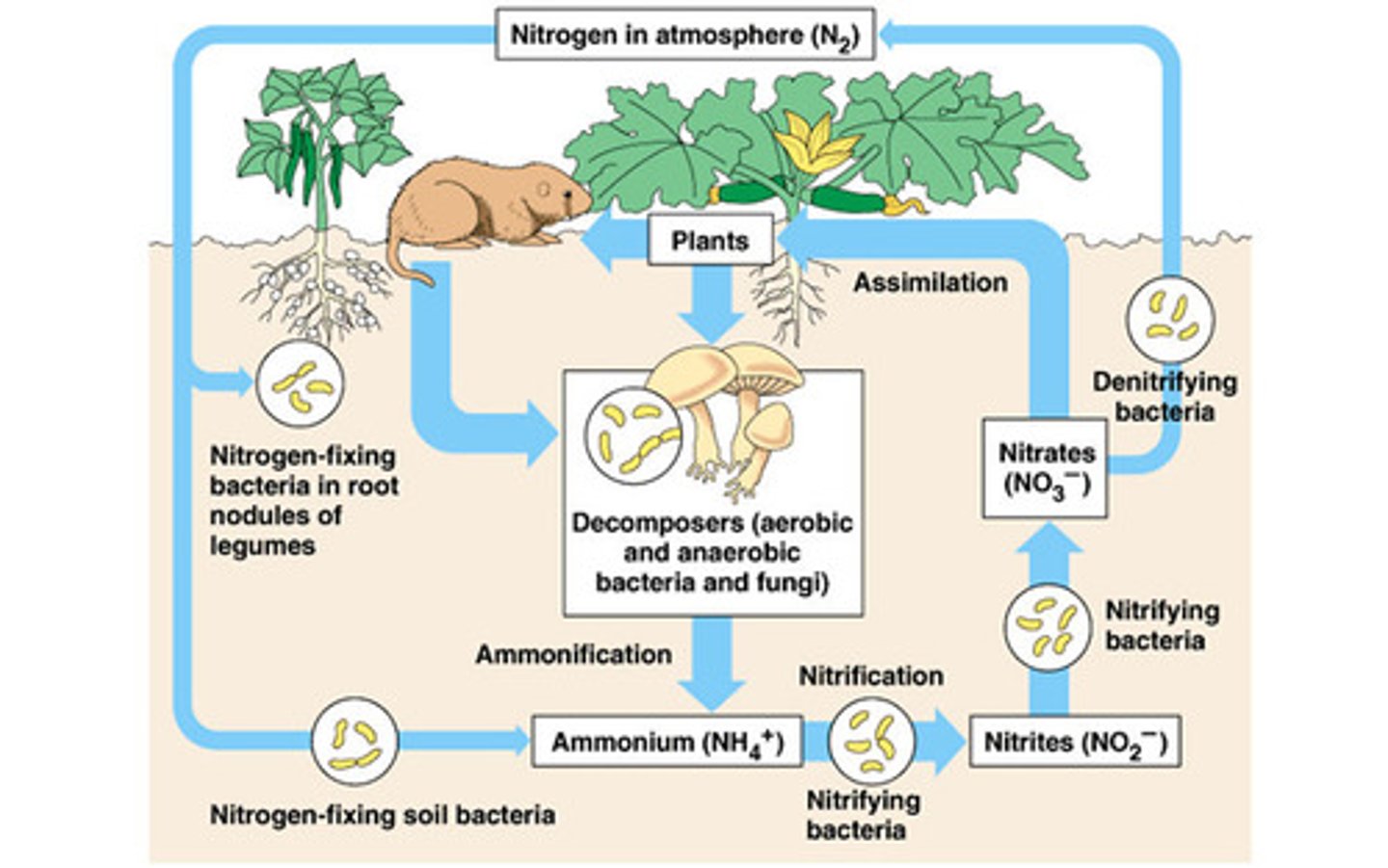
reservoir
the atmosphere is the biggest nitrogen ______________
nitrogen fixation
Process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia (usable form of nitrogen)
bacterial nitrogen fixation
Process by which certain bacteria living in soil convert nitrogen gas (N2) to ammonia (NH3).
synthetic nitrogen fixation
humans combust fossil fuels to convert N2 gas into nitrate (NO3)
Nitrogen cycle steps
nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, denitrification
assimilation
part of the biogeochemical cycles (especially of nitrogen and phosphorous) where plants and animals take in nutrients and other chemicals
ammonification
soil bacteria, microbes, decomposers convert waste and biomass back into NH3 and return it to the soil
nitrification
ammonia is converted to nitrate ions by soil bacteria
denitrification
Conversion of nitrates into nitrogen gas which returns to the atmosphere
ammonia volatilization
excess fertilizer use can lead to NH3 gas entering the atmosphere
causes acid rain and respiratory irritants
eutrophication
A process by which nutrients, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, become highly concentrated in a body of water, leading to increased growth of organisms such as algae or cyanobacteria.
phosphorous cycle
the cyclic movement of phosphorus in different chemical forms from the environment to organisms and then back to the environment
SLOW CYCLE
NO GAS PHASE (no phosphorous cycle in the atm)
phosphorous used in all organisms in DNA, ATP, bone and tooth enamel, etc
natural phosphorous sources
weathering of phosphorous containing rock that is broken down by the wind, where phosphorous is released and dissolved, rain carries phosphorous in soil
synthetic phosphorous sources
humans mine phosphorous rocks and adds phosphorous to fertilizers/detergents/cleaners --> often leads to phosphorous being carried out as waste
steps of the phosphorous cycle
Phosphate released by erosion of rock
Plants take up the phosphate (assimilation)) Phosphorus moves from producer to consumer
excretion
phosphorus seeps into groundwater from soil, forming rocks (sedimentation)
Rocks erode (geo uplift), cycle goes on
excretion
part of biogeochemical cycles where chemicals are excreted through waste and biomass is broken down to return/continue the cycle
geological uplift
exposing underground rocks to the surface
(part of the phosphorous cycle)
the deadzone
a location within a body of water that does not have enough dissolved oxygen to sustain life.
(often occurs from eutrophication)
Hydrologic cycle
the movement of water through the biosphere
DRIVEN BY THE SUN --> phase changes
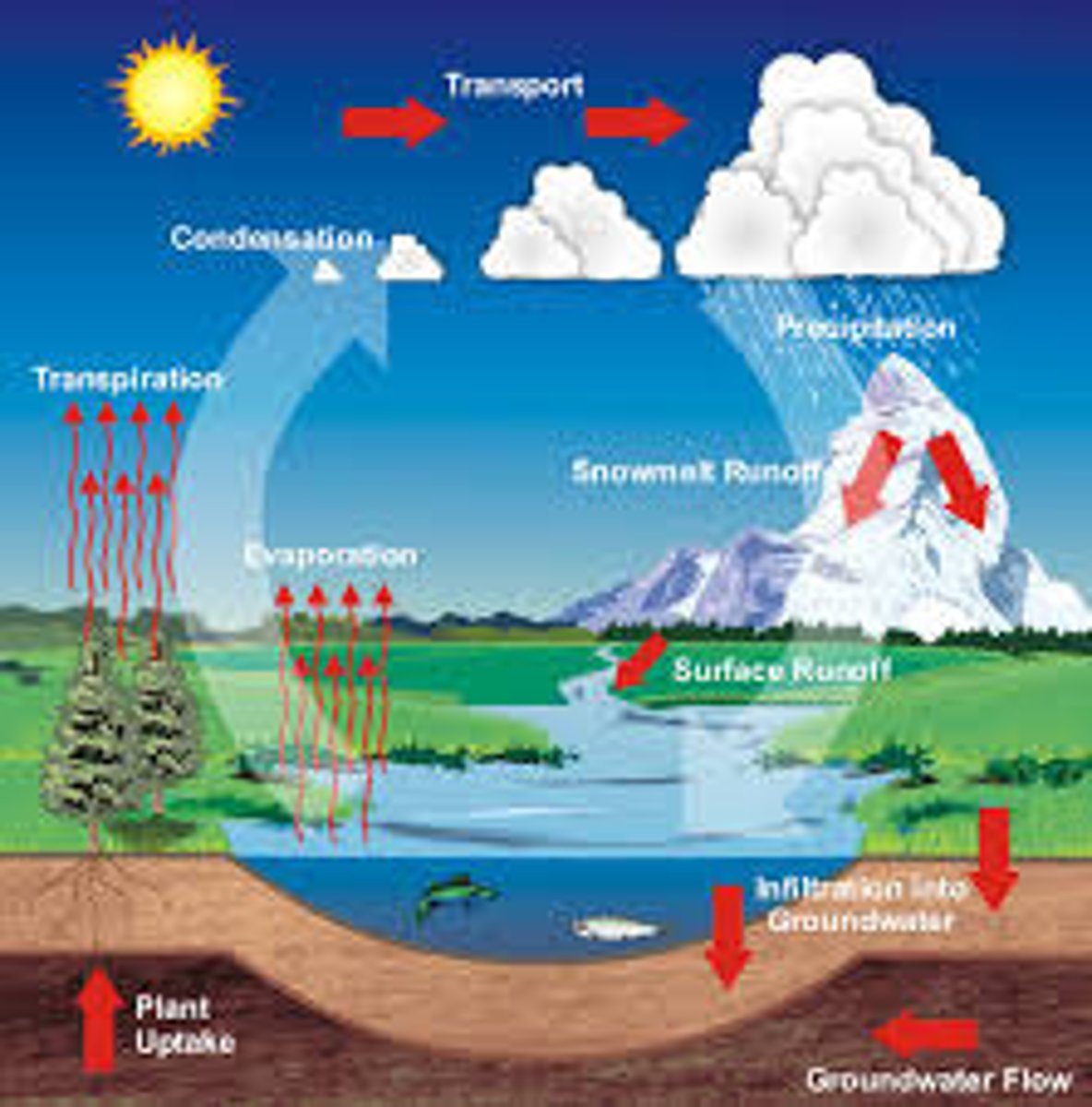
water reservoirs
the ocean is the largest water ______________
smaller __________________ include icecaps and groundwater
evaporation
The change of a substance from a liquid to a gas
transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
evapotranspiration
the amount of water that enters the atm. from transpiration and evaporation
runoff
water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground
infiltration
the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil
groundwater aquifers
water held within the spaces in porous, permeable rocks
components of soil
sand, silt, clay, humus, nutrients, water, air, living org
purpose of soil
anchors plants to the ground, filters rainwater, recycles nutrient, provides habitat
weathering
The physical (wind and rain), biological (tree roots), and chemical (acid) breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.
erosion
Processes by which rock, sand, and soil that have been broken down/weathered are carried away
deposition
Process in which sediment is laid down in new locations and deposited
soil formation
________ formation
the weathering of parent material to produce sand, silt, clay
the breakdown of organic matter to develop humus
soil horizons
distinct layers of soil
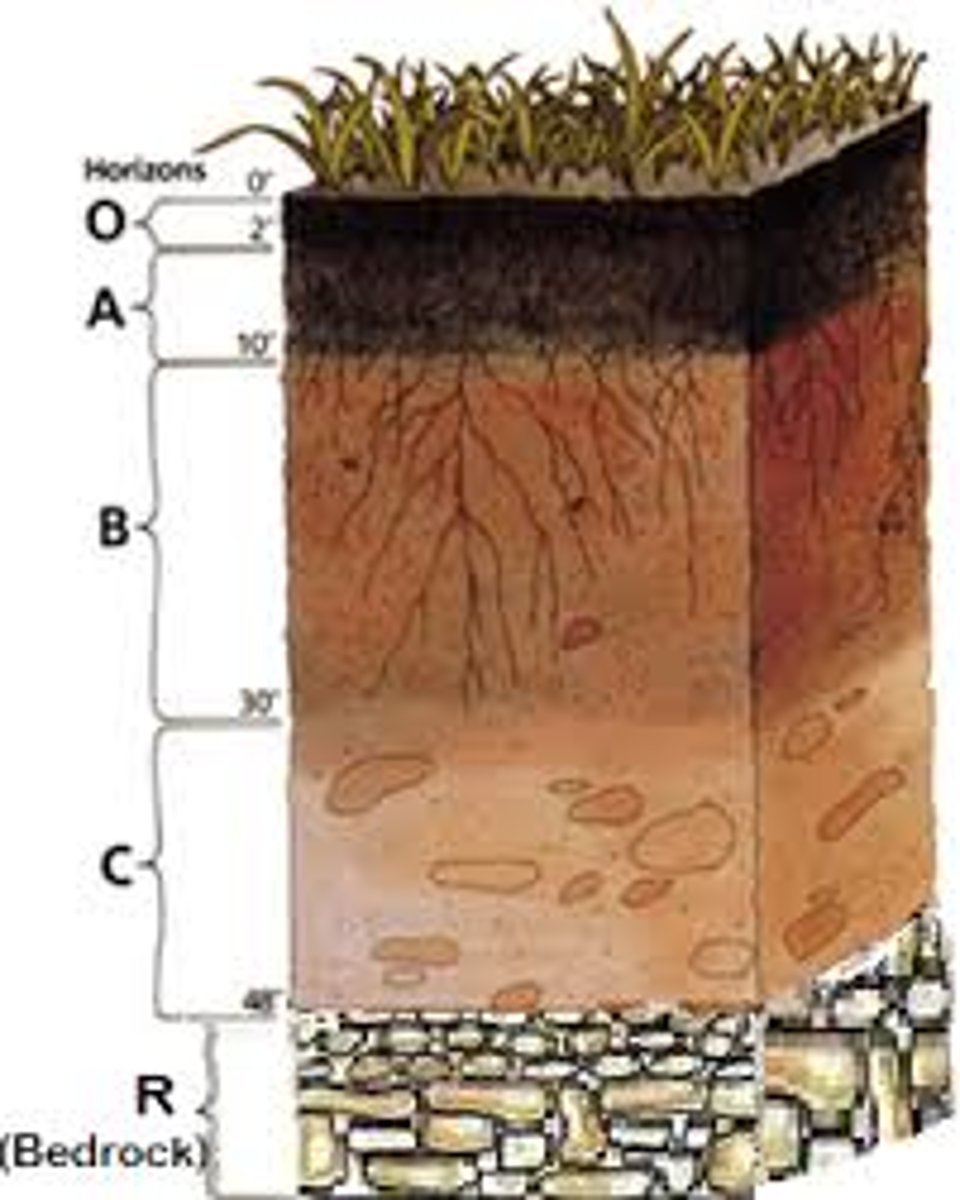
O horizon
The organic horizon at the surface/top of many soils, composed of organic material that traps moisture and provides nutrients
A Horizon
the topsoil that has layers of humus and minerals that has the MOST BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY. This is the layer of soil where nutrients are released
B Horizon
A soil horizon (subsoil) composed primarily of mineral material with very little organic matter
C Horizon
The least-weathered soil horizon, which is similar to the parent material.
soil degradation
The loss of some or all of a soil's ability to support plant growth
can occur from loss of topsoil, compaction, or nutrient depletion
tilling
The turning-over of soil before planting; contributes negatively to soil quality by disrupting soil structure, accelerating erosion and runoff
soil texture
the percent ratio of sand to silt to clay in the soil
soil porosity
pores or spaces in the soil. The greater pores or spaces, the greater the water holding ability. Sand has the most ___________ and clay has the least. Based on particle size
soil texture chart
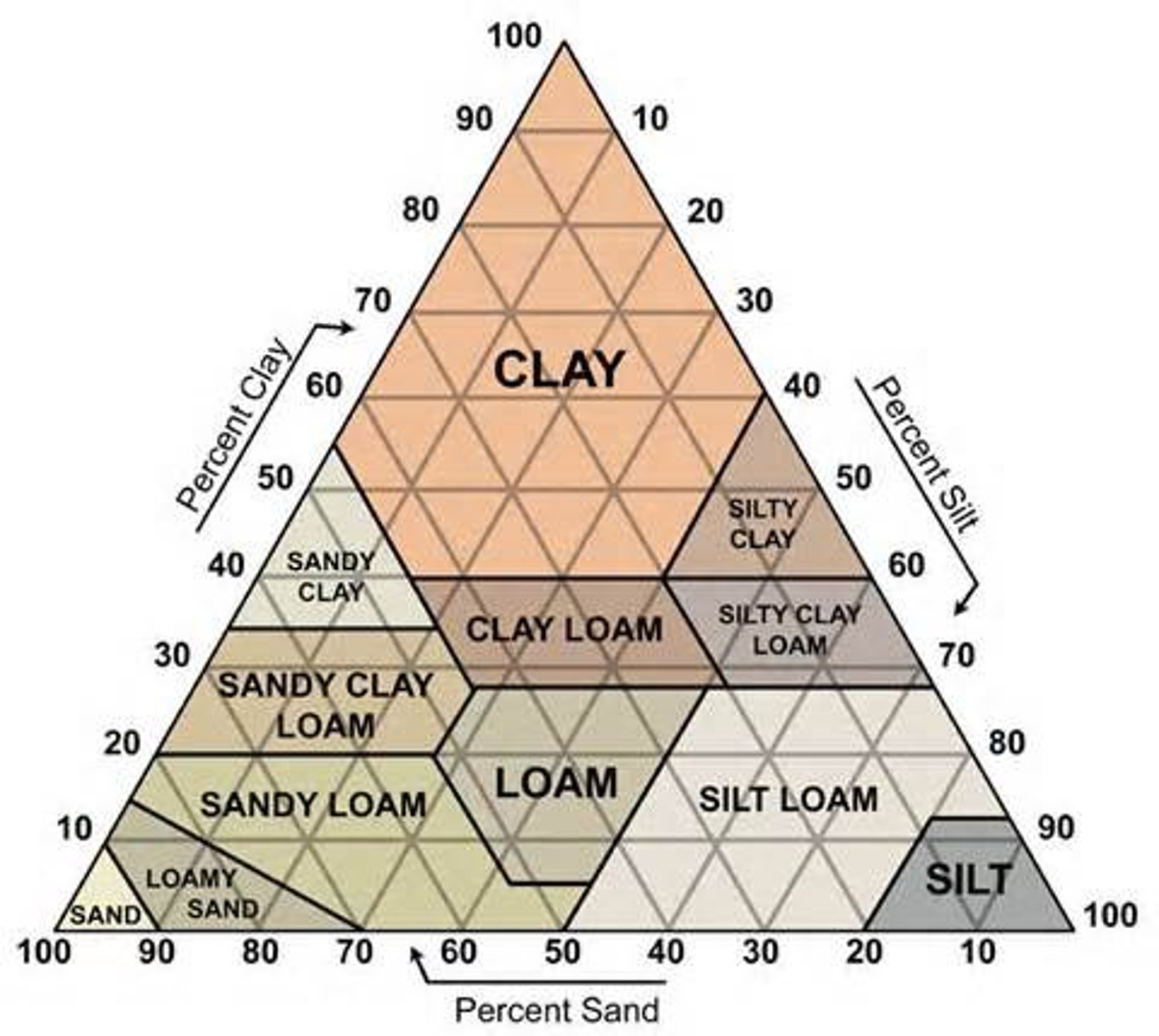
Water holding capacity
how well soil can retain water (sand is low, clay is high). Based on porosity , permeability, etc.
soil fertility
A measure of how well soil supports plant growth.
loam
Rich, fertile soil that is made up of about equal parts of clay, sand, and silt.
nutrients in soil
N, P, K+, Mg2+, Ca+, Na+
green revolution
Agricultural revolution that increased production through improved seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation; helped to support rising Asian populations.
mechanization
In agriculture, the replacement of human labor with technology or machines.
High Yield Variety
the development of crops, such as rice, corn, and wheat, specifically bred to replace lower yielding native crops.
synthetic fertilizers
Fertilizer produced commercially, normally with the use of fossil fuels
irrigation
A way of supplying water to an area of land
pesticides
Chemicals used on plants that do not harm the plants, but kill pests and have negative repercussions on other species who ingest the chemicals.
rodenticides, insecticides, herbicides, fungicides
DDT
an insecticide that is also toxic to animals and humans. Led to the thinning of bird shells. Silent Spring book
phthalates
plasticizers used in skin care formulas to moisturize and soften skin, and to dissolve or blend ingredients that are endocrine disruptors
atrazine
Herbicide. Endocrine disruptor that causes the feminization of males, low sperm count.
Monocropping
An agricultural method that utilizes large plantings of a single species or variety. Reduces biodiversity
Slash and burn
A farming method involving the cutting of trees, then burning them to provide ash-enriched soil for the planting of crops
GMO
Genetically modified organism made when DNA is removed from one organism and placed within the DNA of what can be a very different organism.
impact: reduces genetic diversity
Bt crops
crops that have been given a bacterial gene that gives chemical protection against pests
Roundup Ready
Crops that have been modified to withstand treatment with roundup herbicide (glyphosate).
IPM
Pest management using a variety of techniques, agricultural, biological and use of minimal amount of pesticides when necessary. Unfortunately more expensive than pesticides
Biocontrol
Use of one kind of organism that is a predator or parasite of a pest species in order to reduce or eliminate populations of the pest. For example, bringing natural predators, competitors, or parasites to control pests
Crop rotation
The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil and allowing pests to lay their eggs and breed there
Intercropping "Push - Pull" system
a agricultural system where pests are pushed out and pulled somewhere else nearby the crops
endocrine disruptors
chemicals that interfere with the normal functioning of hormones in an animal's body
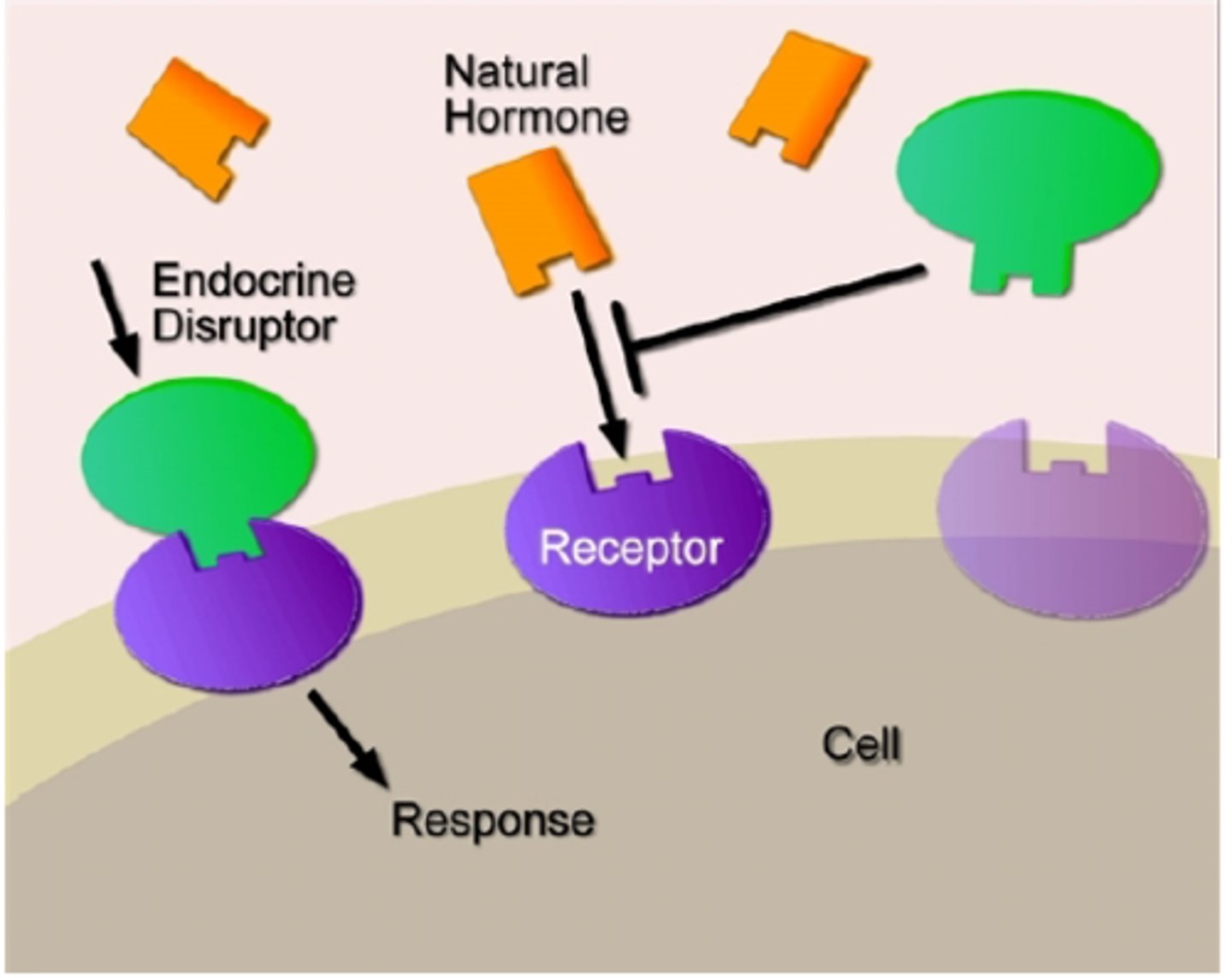
mercury
an endocrine disruptor made in coal burning, medical waste burning, limestone production for cement, and attaches to PM and is deposited. Inhibits estrogen and insulin
teratogen
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
Arsenic
an endocrine disruptor that is from rocks underground that dissolves easily in water. Used in pesticides, wood treatments, coal combustion, ash. It is a carcinogen
Lead
endocrine disruptor found in paint, old water pipes, soils, contaminated by PM from old vehicle exhaust. It is a neurotoxicant
coal ash
waste from coal mining that contains mercury, arsenic and lead
persistant organic pollutants (POPs)
compound with carbon in it that resists photochemical, biological and chemical degradation
long-lasting carbon based pollutants that do not easily break down (are stored in animal fat)
they travel with the wind and impact far away ecosystems
in wastewater, leachate, fertilizers, biomass, etc. and are often eaten by animals or enter soil and water
Tragedy of the Commons
situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community
overusing public/shared resources since they don't experience the negative consequences of doing so (acting in self interest)
Clean Water Act
(CWA, 1972) set maximum permissible amounts of water pollutants that can be discharged into waterways; aims to make surface waters swimmable and fishable
Clean Air act
(CAA, 1970) set emission standards for cars and limits for release of air pollutants
6 Air pollutants
- SO2
- NOx
- CO
- Pb
- PM
- O3
air pollutants
specific chemicals, compounds, or particles harmful to air
air pollution
the introduction of harmful pollutants into atmosphere
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide)
a pollutant from coal combustion
a respiratory irritant
causes acid rain
Reducing SOx and NOx
Reducing ______ and _____ (air pollutants)
- crushed limestone
- fluidized bed combustion
Crushed limestone
used to reduce SO2 from coal power plants
calcium carbonate + SO2 = calcium sulfate (rather than SO2)
Fluidized bed combustion
a clean-coal technology in which crushed coal is mixed with limestone to neutralize the acidic sulfur compounds produced during combustion
fluidized jets of air are pumped into the combustion "bed"
efficient combustion
brings SO2 into more contact with limestone
less NOx
NOx (Nitrogen Oxides)
pollutant occurs from fossil fuel combustion (gas)
causes smog and acid rain by creating O3
health impact:
- causes ozone formation
- respiratory irritant
- can form nitric acid and acid rain when combined with water and O2
CO (Carbon monoxide)
pollutant from incomplete combustion of fuel source (either from a lack of O2 or lack of temperature)
displaces O2 in the blood -- lethal
impacts:
causes suffocation
binds with hemoglobin in red blood cells
lethal in high concentration
oderless, colorless, and hard to detect
Pb (Lead)
a pollutant from metal plants and waste incineration
in 1978 the EPA prohibited its use in paint
impacts:
nuerotoxicant
damages nervous system
O3 (ozone)
a pollutant that causes photochemical oxidation and photochemical smog
respiratory irritant
causes plant damage
PM (particulate matter)
a pollutant from suspended particles -- common indoors
occurs from combustion, fire, construction, smoke
impacts:
respiratory irritant
causes smog
Electrostatic Precipitator
A device used for removing particulates from smokestack emissions. The charged particles are attracted to an oppositely charged metal plate, where they are precipitated out of the air.
Reduces PM
baghouse filter
Dirty air enters, combustion exhaust stream moes through and dust particles are trapped in a series of filter bags, cleaner and filtered air moves out of unit, shaker mechanism activated periodically to dislodge trapped particles which can then be collected from below unit.
reduces PM
VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds)
chemical pollutants used in home
products that easily vaporize
ex. adhesives, formaldehydes
carcinogens
ex. plastics and fabrics
impacts:
irritate the eyes and lungs
asbestos
A long, thin, fibrous silicate mineral with insulating properties (no longer used but may be present in older architecture), which can cause cancer when inhaled.
can enter the air and the respiratory track
mesothelioma
lung cancer
Radon Gas
Radioactive gas from uranium decay
can leak into houses through cracks in the ground
impacts:
2nd leading cause of cancer