Prehistoric Art & Early civilizations
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Early civilizations: Mesopotamia and the Persian Empire
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Characterictics - Paleolithic Era
Nomadic lifestyle, hunter-gatherers.
Art was spiritual, often found in caves.
Focused on animals and fertility.
Techniques - Paleolithic Era
Natural pigments like ochre and charcoal.
Used brushes made from hair or sticks, and hands.
Engraving, carving, and painting.
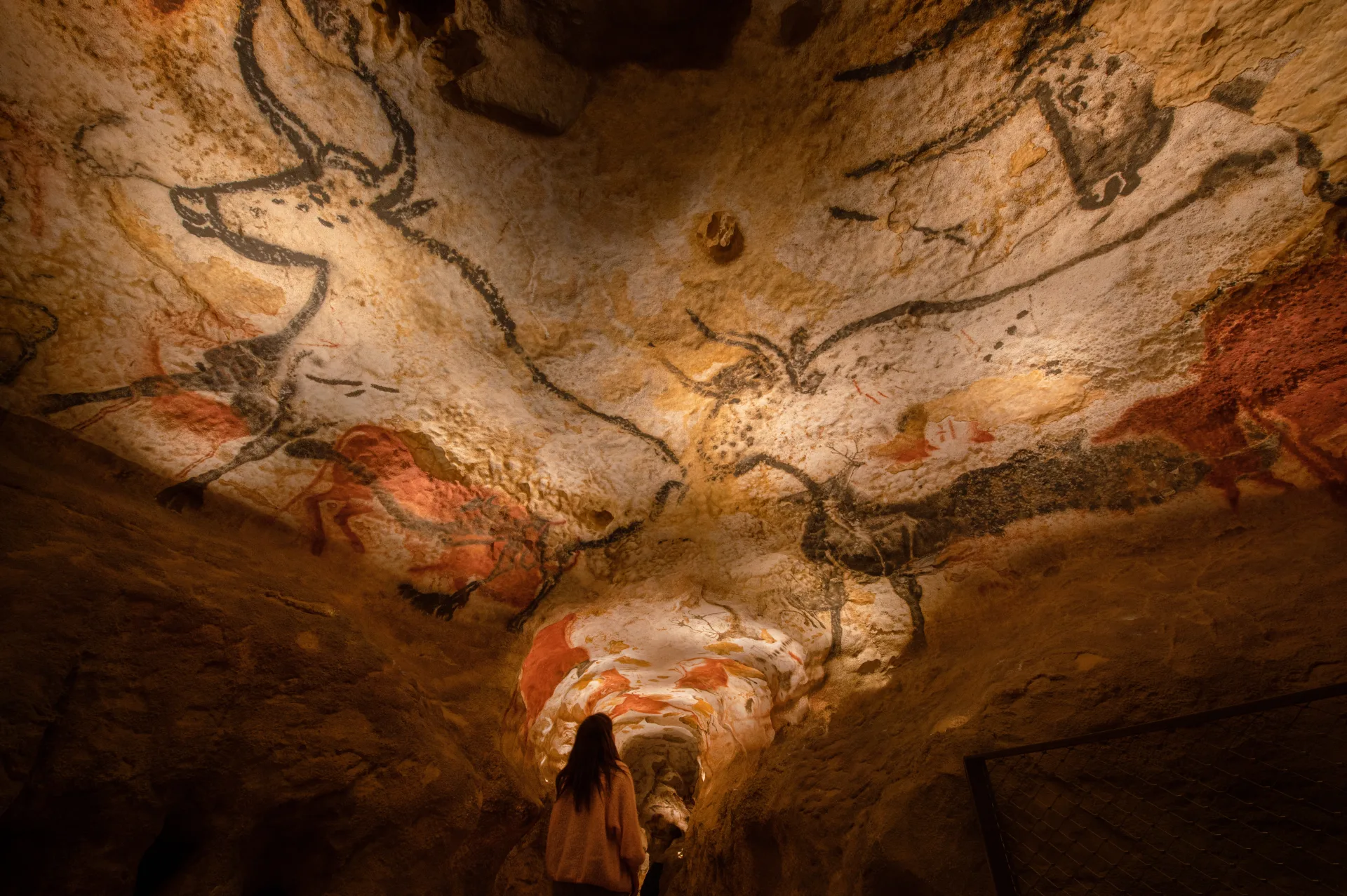

Lascaux
Famous cave paintings (~17,000 BCE).
Depicts animals like bulls, horses, and deer.
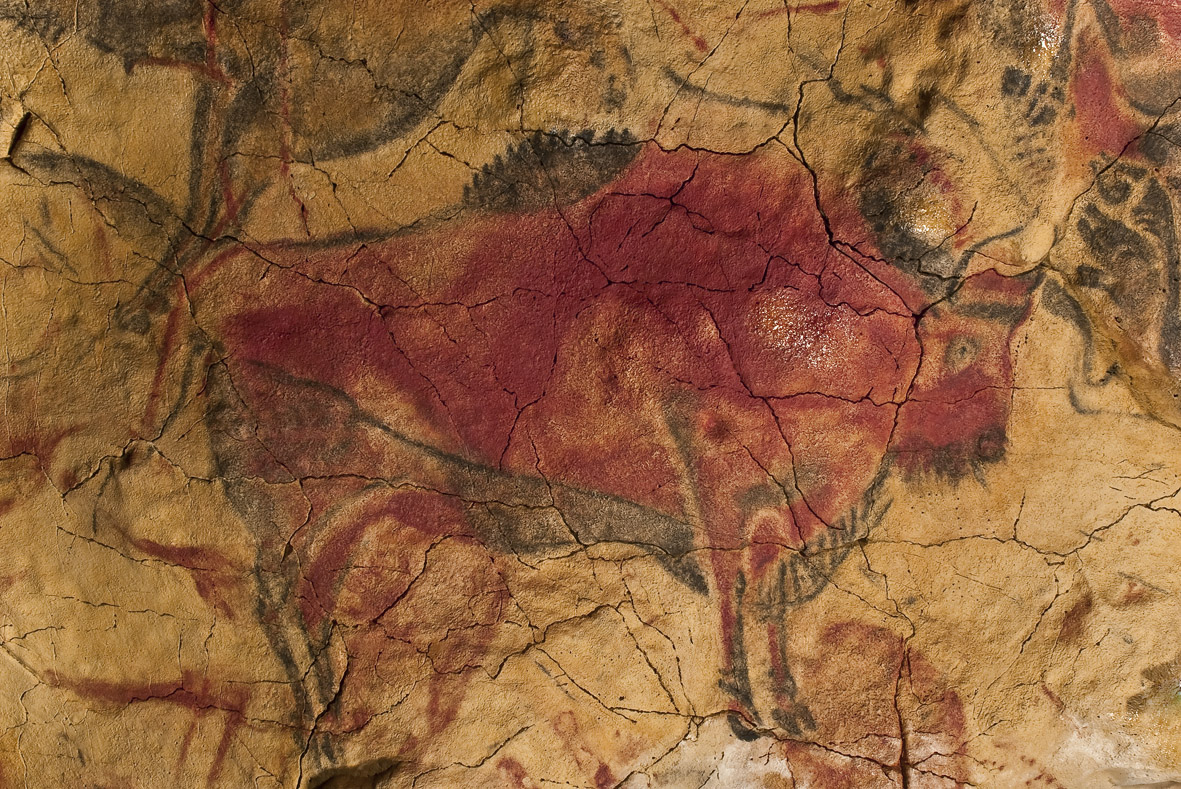

Altamira
Polychrome cave paintings
Noted for bison imagery and use of natural contours.

Chauvet
One of the oldest caves (~30,000 BCE).
Realistic depictions of animals, overlapping images for movement.
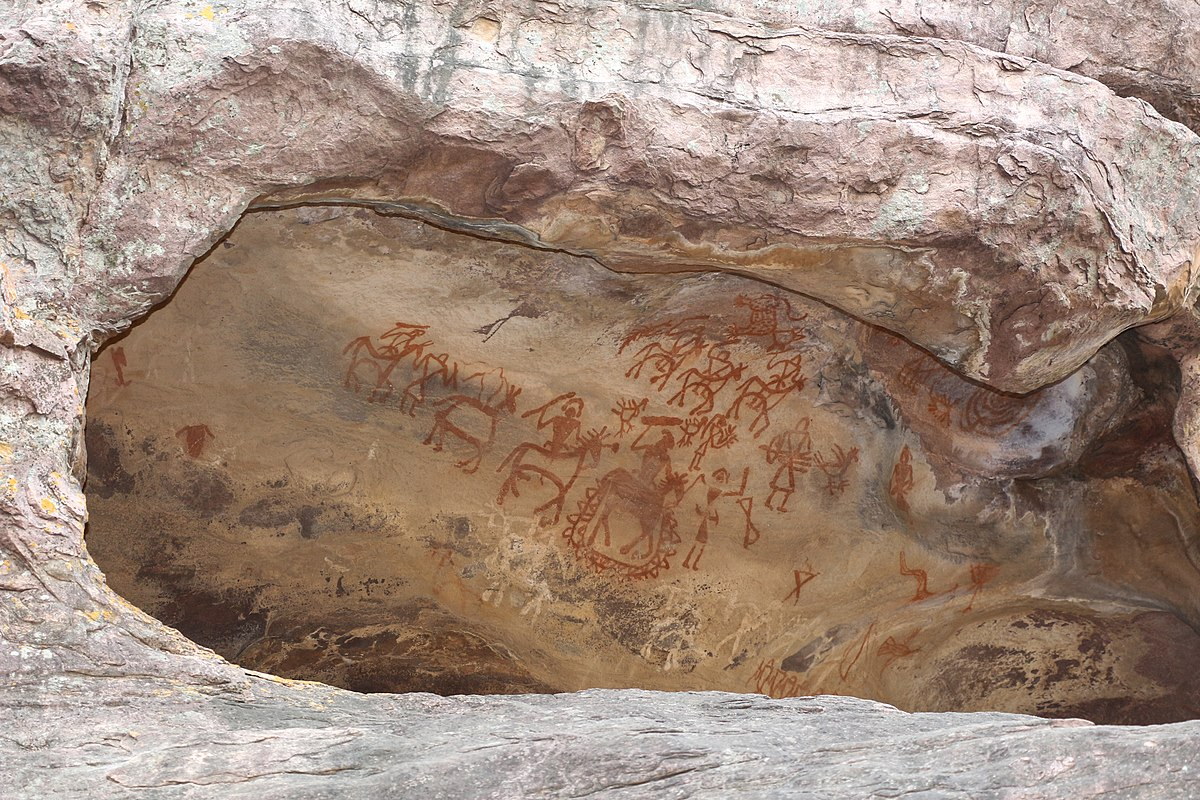

Bhimbetka
Rock shelters with prehistoric paintings.
Shows early human life and hunting scenes.

Willendorf woman
Small fertility figurine (~28,000 BCE).
Exaggerated female features, symbol of fertility.
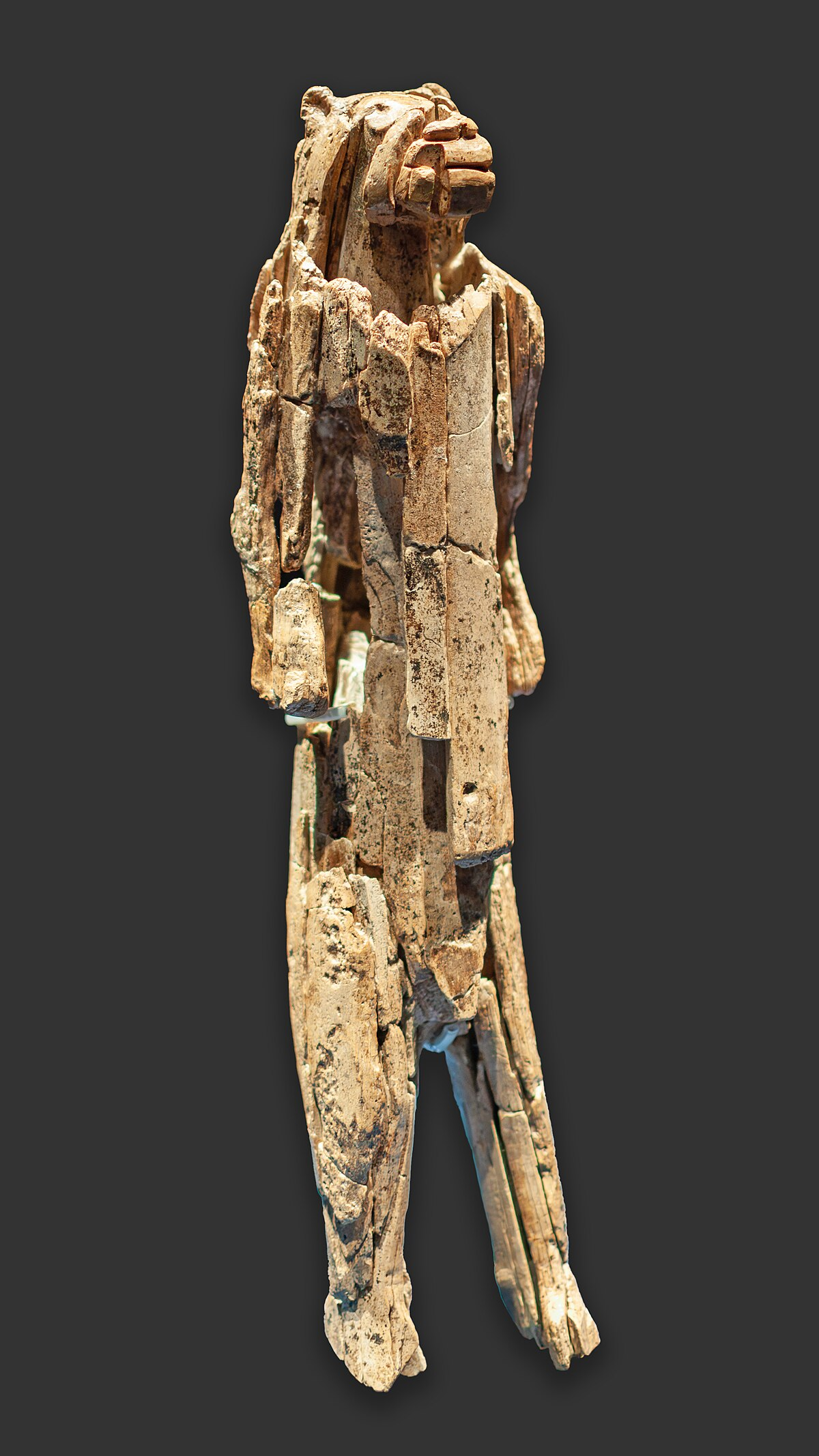

Lion Man
Ivory sculpture of a human-lion hybrid.
Possibly religious or mythological.
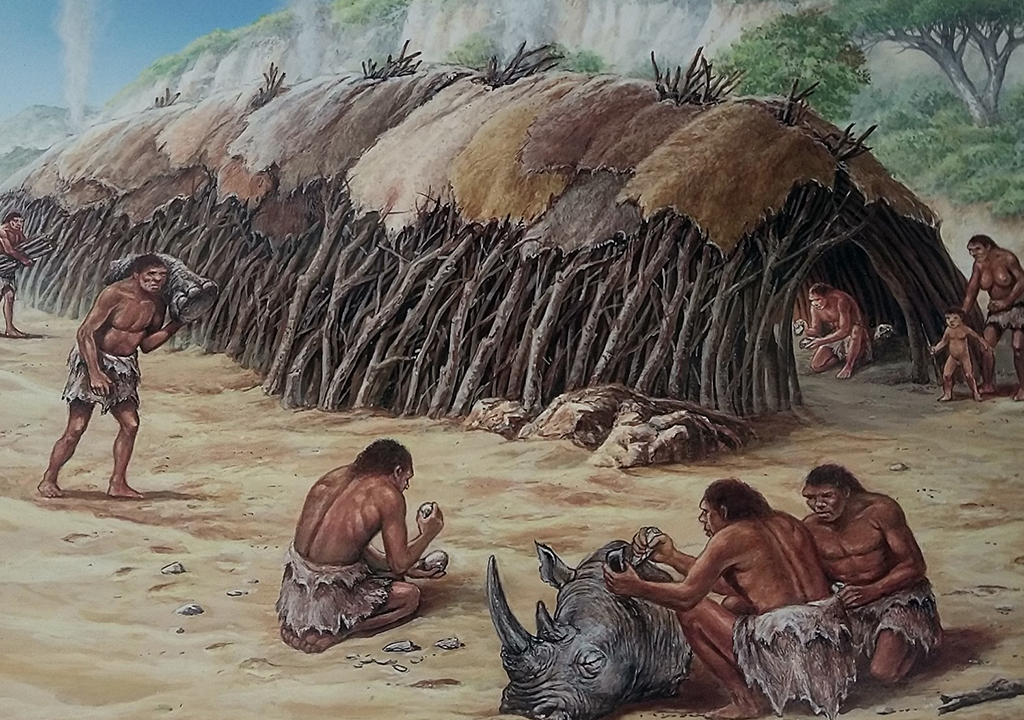

Terra Amata - The Beginnings of Architecture
Early evidence of human dwellings (~400,000 BCE).
Circular huts showing the beginning of architecture.
Characteristics - Neolithic Era
Settled farming communities.
Art includes pottery, architecture, and figurines.
Focus on daily life and ritual.
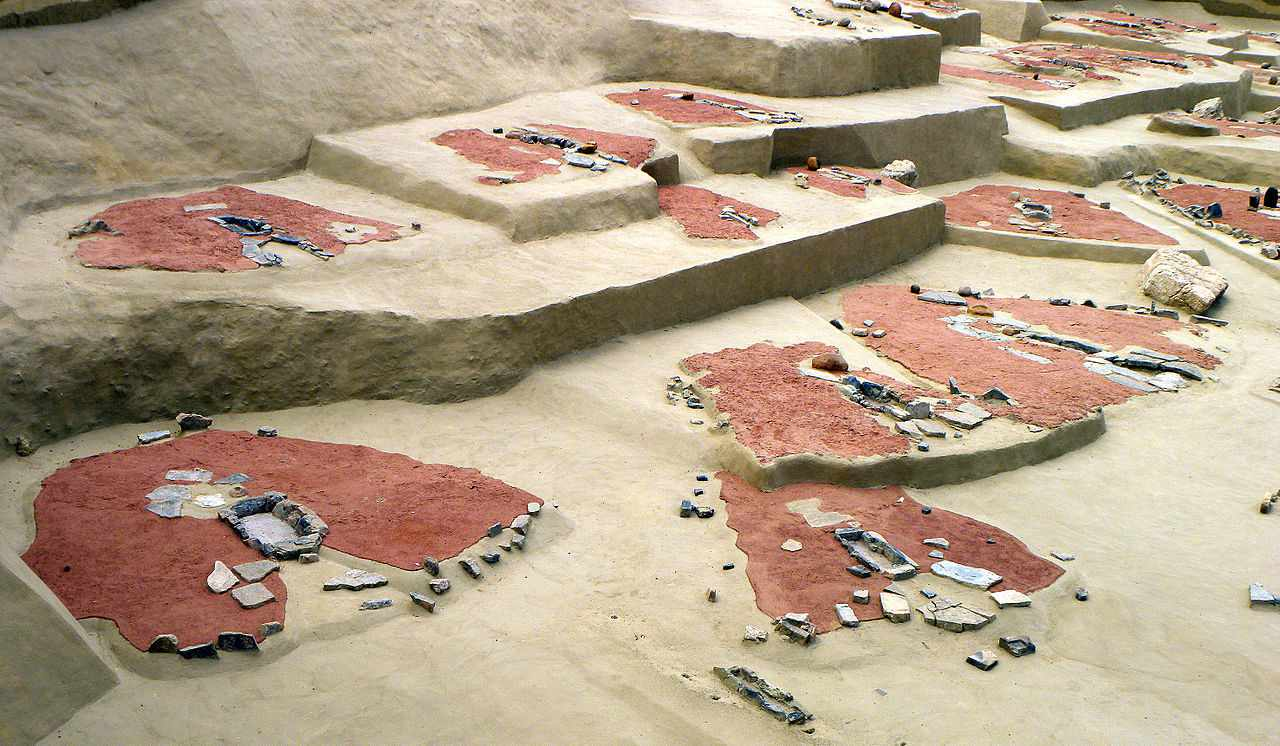

Lepenski Vir
Settlement with trapezoidal houses (~7000 BCE).
Includes fish-like sculptures and planned architecture.
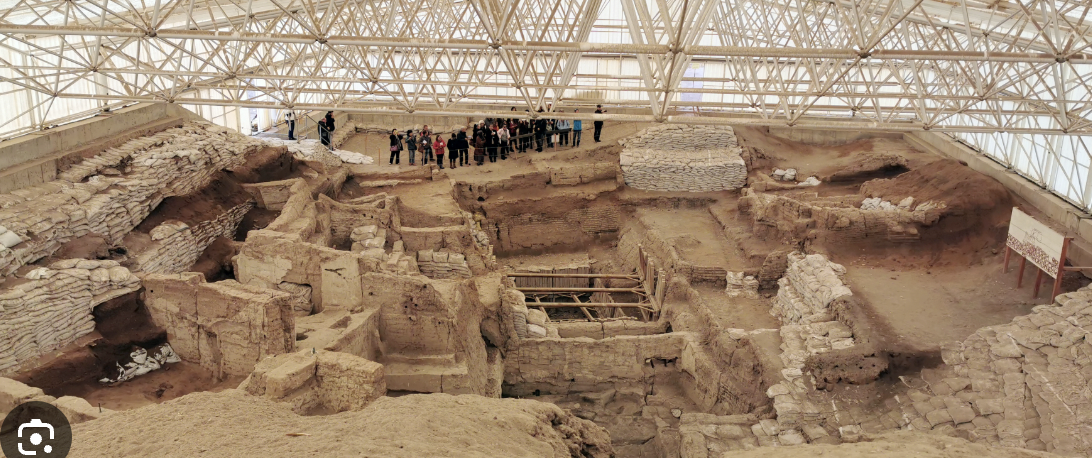

Çatal Hüyük
Large Neolithic city (~7500 BCE).
Murals, shrines, and early urban planning.
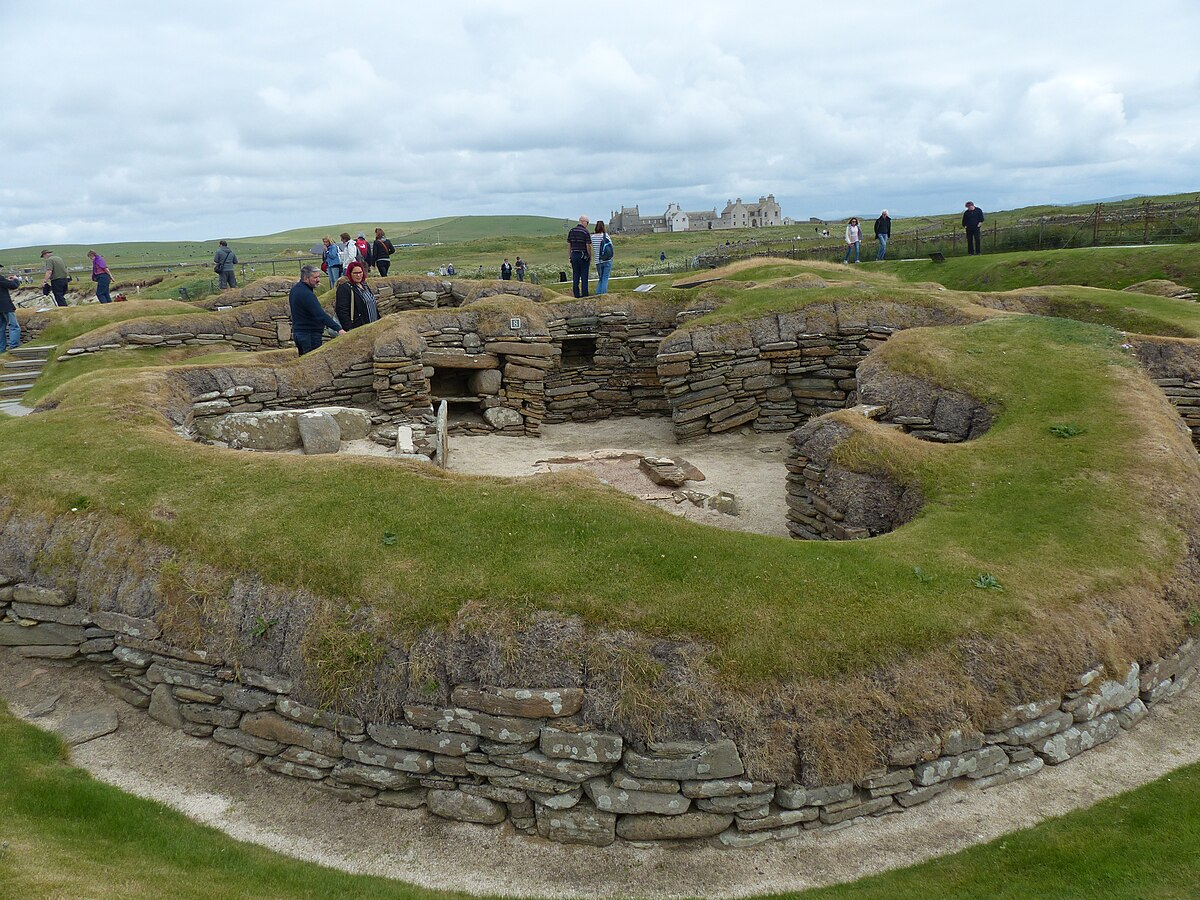

Skara Brae
Stone-built houses (~3000 BCE).
Preserved furniture and domestic spaces.
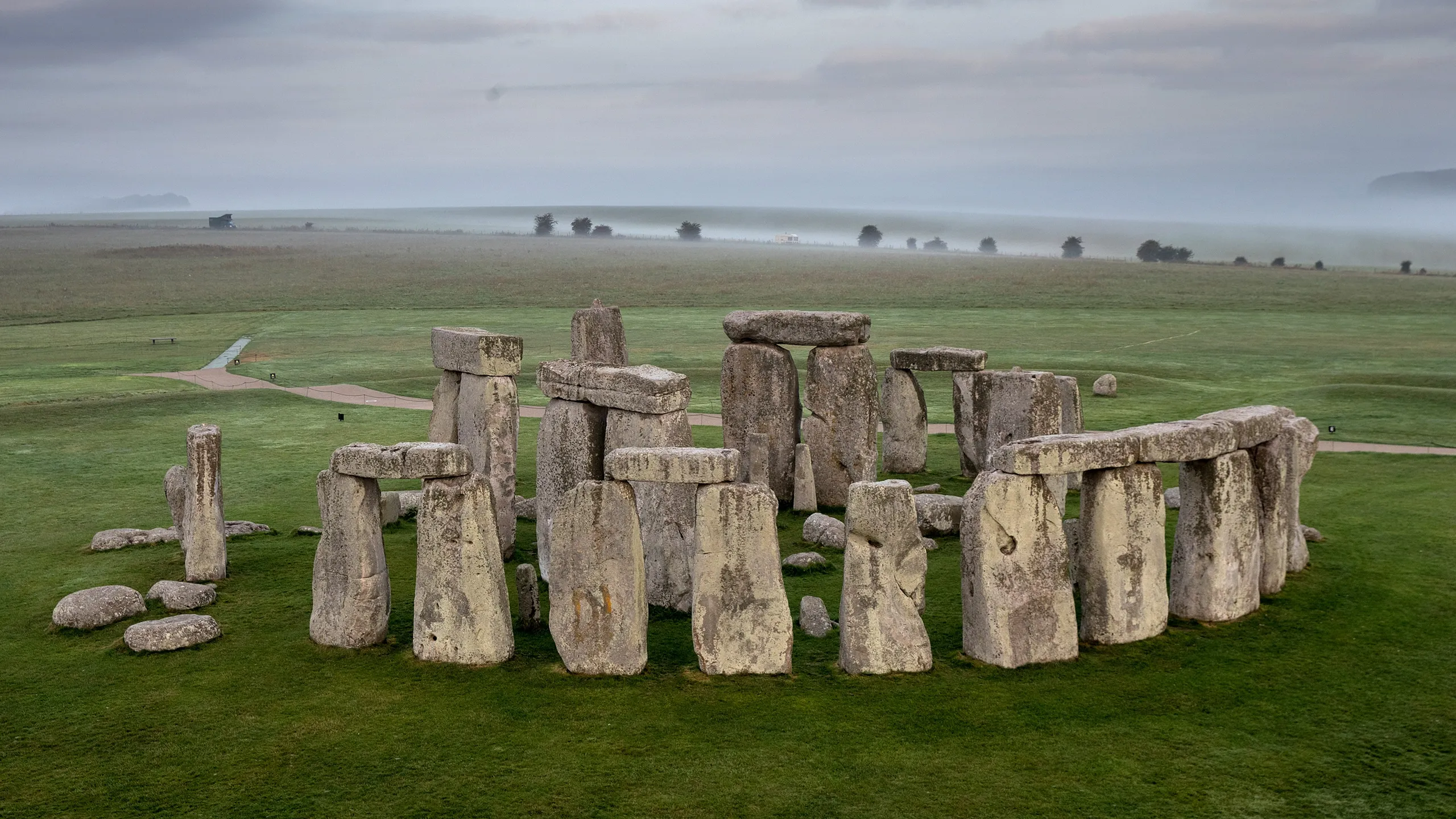

Stonehenge
Megalithic stone circle (~2500 BCE).
Likely used for rituals or astronomical observation.
Cromlech, Dolmens, Lintel, Menhir
Attributes of a civilization
Urban settlements
Full-time specialists not involved in agricultural activities
Class structure
Monumental public building
Writing (Cuneiform: a logo-syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages)
Early civilizations: Mesopotamia
considered the cradle of civilization, where urban societies, writing, and monumental architecture first developed
Use of registers in narrative reliefs (e.g., Warka Vase).
Rich materials like lapis lazuli, gold, shell in luxury objects (Ram in a Thicket).

City of Uruk
One of the first major cities
Site of the White Temple, Stone Cold Temple and Uruk Vase
associated with early writing and religious architecture (Ziggurats: A type of temple, consisted of a pyramidal structure built in successive stages with outside staircases and a shrine at the top.
Beginnings of Mosaics and Registers

Royal Cemetery of Ur
Burial site with rich grave goods; famous for the Standard of Ur, Queen Puabi's headdress, and Ram in a Thicket.
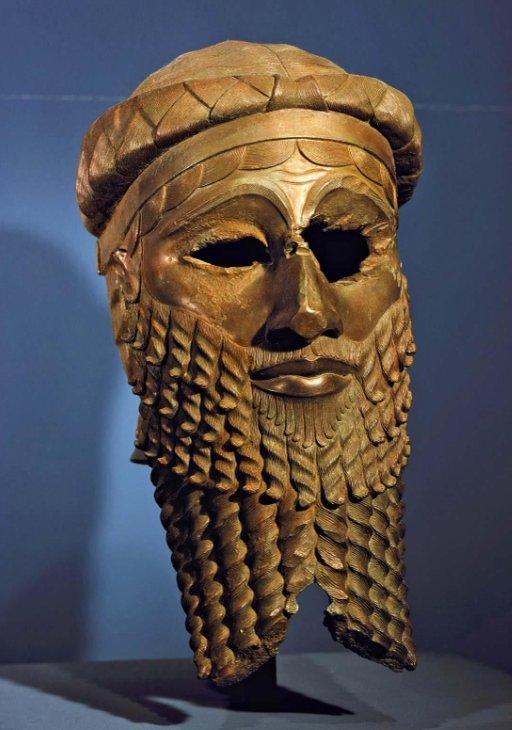

Akkadian Empire - Head of Ruler
Centralized power and realistic portraiture began to emerge.
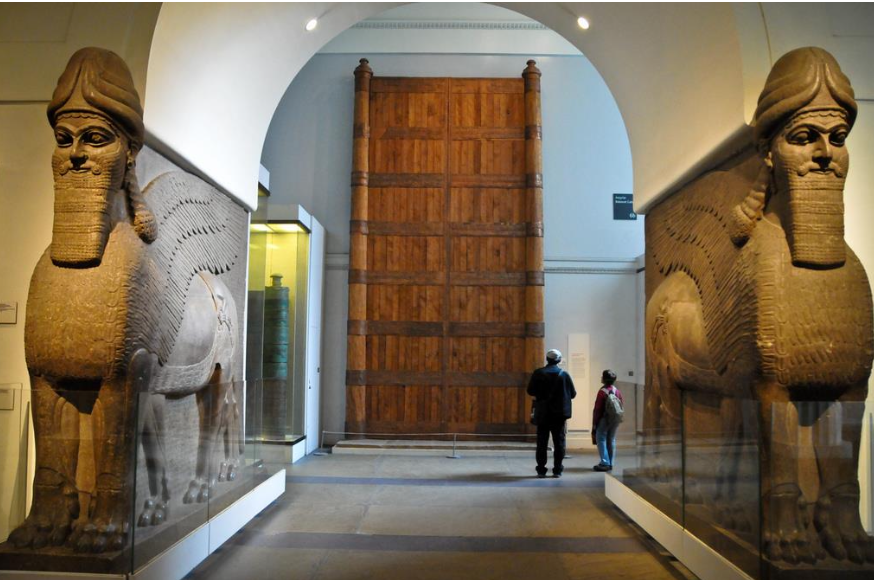

Assyrian civilization - Sarjon Palace
Military empire
Known for statues and reliefs in palaces
Architecture showed strength and intimidation.

Babilonian civilization
Famous for the Ishtar Gate, and Queen of the Night
Combined religion, architecture, and vibrant glazed brick.
Early civilizations: Persian Empire
known for its vast territory, administrative efficiency, and sophisticated art and architecture.
Use of glazed ceramic bricks, Reliefs, architectural developments, gold armlets and luxury objects (e.g., from the Oxus Treasure) show wealth and craftsmanship.

Persepolis: Palace of Darius
Ceremonial capital
included a hypostyle hall and stone reliefs of tribute bearers
symbolized imperial control and grandeur.
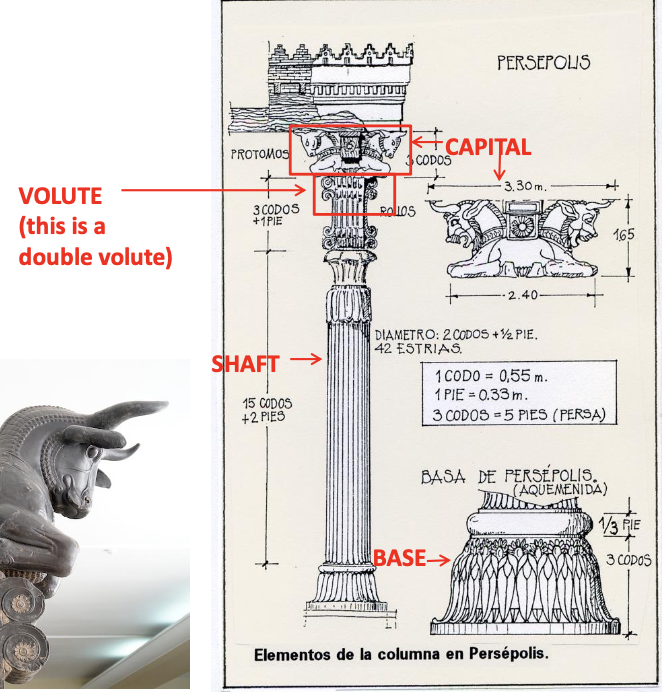
Elements of a Column
Volute: A spiral or scroll-like ornament, decorative, not structural.
Shaft: The long, vertical part of the column between the base and the capital; usually cylindrical.
Base: The bottom support of the column that rests on the ground or platform; not present in Doric columns.
Capital: The topmost part of a column; transitions from the shaft to the structure it supports; decorated differently in Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian styles.
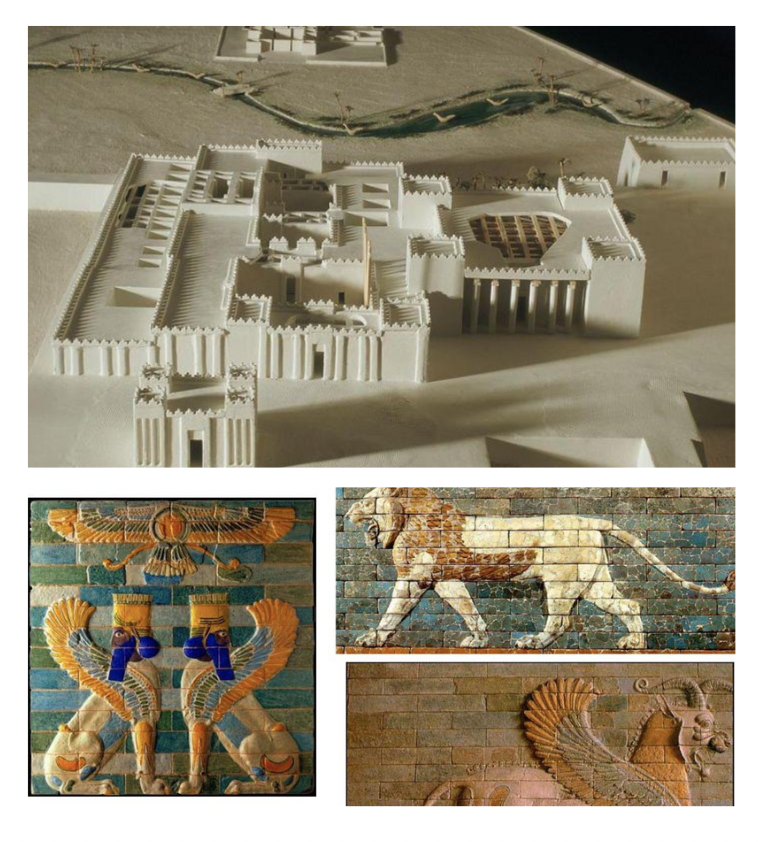

Susa: Palace of Darius
Known for colorful reliefs
important for its glazed brickwork
use of symbolism in Persian propaganda.