BCS 111 Unit 6.3
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Short term memory encoding strategies
Chunking
Story making
Rehearsal
A more comprehensive framework than STM: working memory
“Includes short-term memory AND other processing mechanisms that help to make use of short-term memory”
Not just about storage, but also processing
Incorporates the role of attention in memory encoding
Assumes different processing and storing mechanisms based on the nature of input
Working memory: Processing input + temporary storage
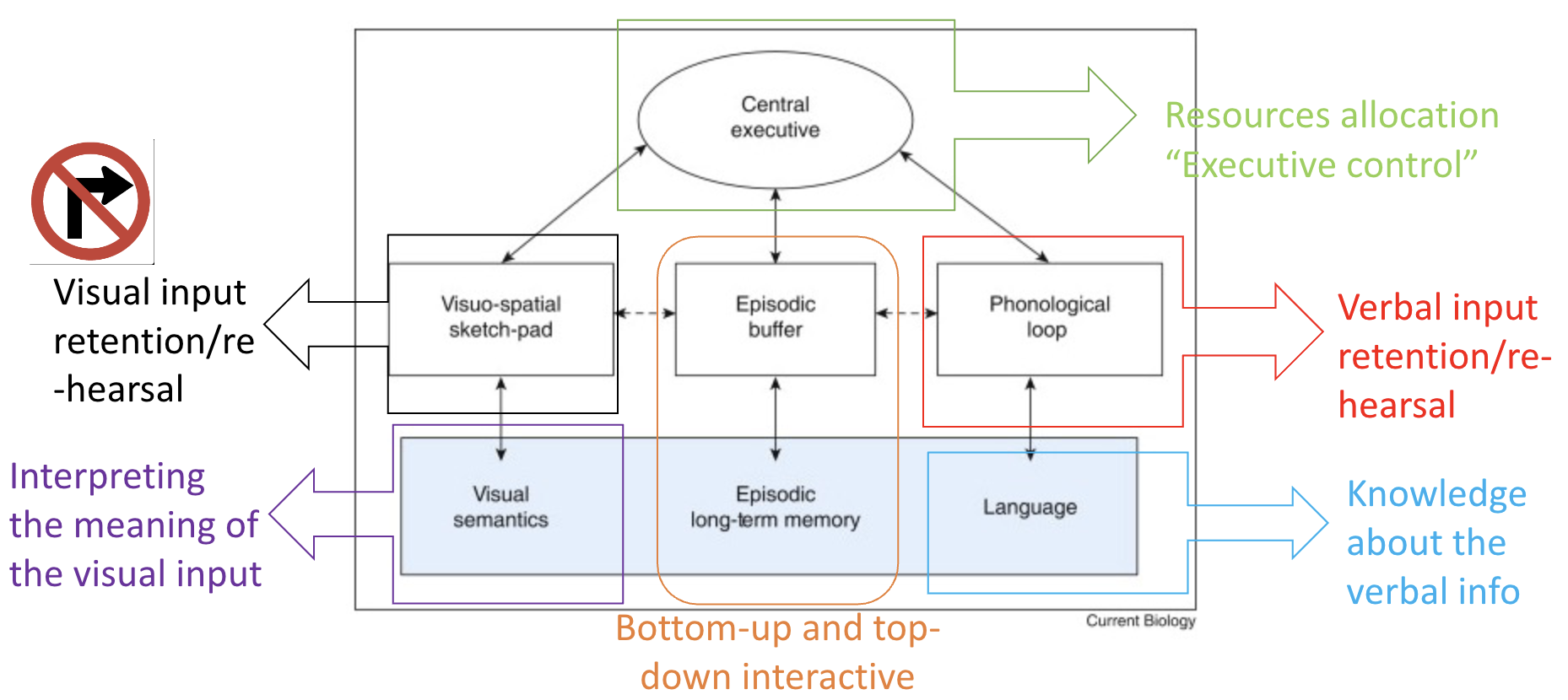
Working memory - Phonological loop
Why so important
Rehearsal in memory recall tasks
Free recall of words: Fast presentation → less time to rehearse → poorer recall of initial items (reduces primacy effect)
(cont)
Free recall of words:
Slow presentation → more time to rehearse → better recall of initial items
How to prevent rehearsal
Add another distraction task to interfere
The role of phonological loop in the probe digital task
Predictions:
Slow presentation → more information decay
Fast presentation → less time to rehearse but also less information decay
Is rehearsal useful in all tasks? Not necessarily
Probe-digit task
Better recall in fast (when lots of interfering items) → rehearsal not quite useful in probe-digit task
Working memory - central executive
When do we use this?
Anything that needs attention!
Correlation between working memory capacity and attention control
Larger working memory capacity → better control over attention
Kane et al (2001): letter identification in prosaccade vs antisaccade condition
Procedure cue → target (letter) → identify
Prosaccade: cue and target on the same side of the display
Antisaccade: cue and target on the opposite side
Participants divided into two groups based on working memory capacity
Kane et al. (2001): Results
Higher WM span leads to better attention control (faster resp. in antisaccade condition)
”Attention” is NOT just about attention! WM is also an integral part of it.
Common working memory measures
Digit Span
Forward
Backward
Nonword span
Forward
Backward
Complex span
N-back
Working memory – Complex span
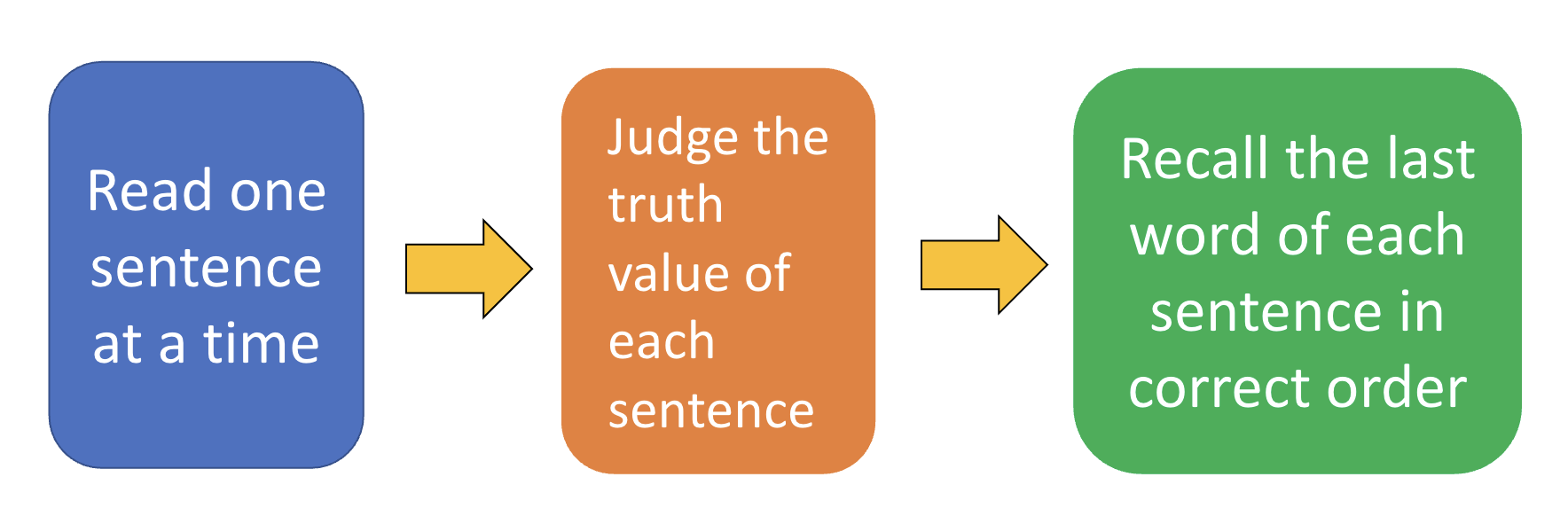
Complex span task
Instruction: read out aloud each sentence
and decide whether the sentence is true.
After a few trials, you will be asked to
recall the last word of each sentence in the
correct order.
Two components of complex span
Word span
One sentence at a time
After a few sentences, Ss recall the last word of each sentence in correct order
Comprehension
True/False judgment on each sentence
Complex span task (cont)
Measures not only storage capacity but also storage quality (thru comprehension of materials)
Reading sentences: central executive, phonological loop and visuo-spatial sketchpad
If sentences are presented auditorily only: central executive and phonological loop
Think about what factors experimenters should consider when designing a complex span task
Complex span task (cont 2)
Some factors to consider
Sentence length
Frequency of the last word
Sentence structure
Sentence meaning
Length of the last word in each sentence
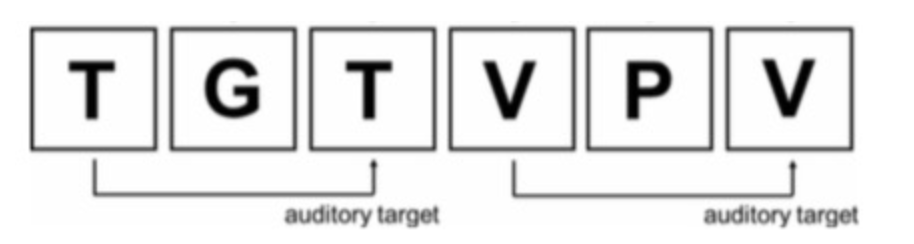
Another measure of WM: n-back
Can be either auditory or visual
Letter, number, or spatial location
Example: Auditory 2-back (press a button on the target)
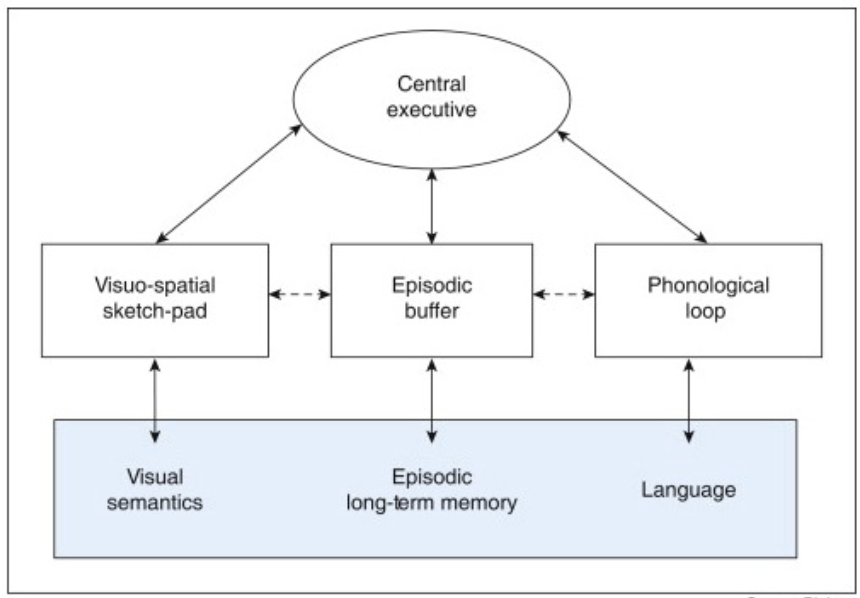
Summary: Working memory: Processing input + temporary storage
Not just about storage but also processing of input
Interconnected components
Visual WM indirectly connects with phonological loop via central executive
Interaction with long-term memory
Attention and working memory interacts with each other
WM also crucial in dichotic listening task and dual task
WM capacity correlated with attention control
Working memory measures
How do the complex span task and n-back task work?
What do they measure?