1ry Hemostasis
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
hemostasis vs thrombosis
hemostasis is physiological
thrombosis is pathological
primary hemostasis (1ry HS) consists of ___ & ___.
vascular & plt plug
secondary & tertiary hemostasis (2ry & 3ry HS) consist of ___
fibrin clot formation
inhibition & lysis
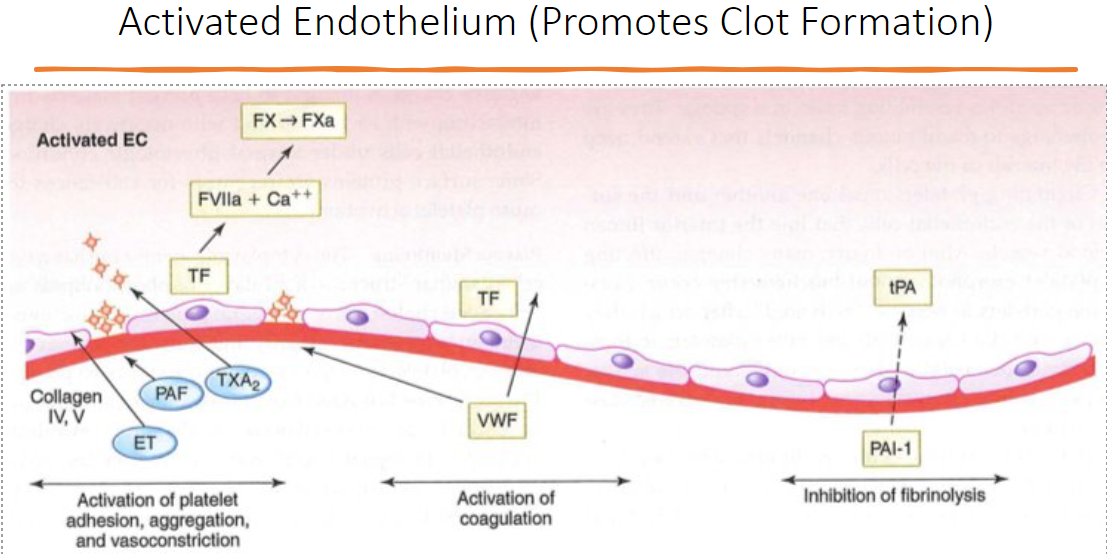
endothelial cells function
innermost layer of blood vessels
barrier b/t blood & interstitial spaces
regulates HS by inhibit/promoting clots
stores vWF
blood vessel (BV) injury → what are the steps to prevent bleeding?
vasoconstriction (slow blood flow)
diversion of blood flow
activation of plt (adhesion → aggregation)
activation of coag system
feedback amplification (more of) plt & coag activation
resting endothelium (coag not activated)
plt activation is inhibited by
PGI2, NO, ADPase
coag is inhibited by
AG
protein C & S
activated endothelium (promotes clot formation)
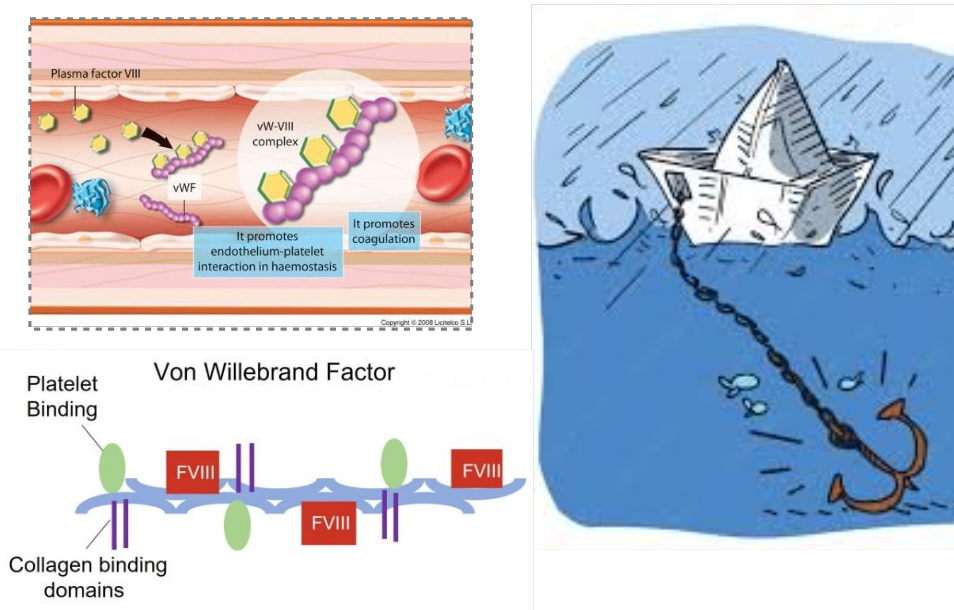
Von Willebrand Factor (vWF) function
what does it bind to?
where is it stored?
“anchor in HS”: binds to damaged collagen upon injury
unfolds from spherical → linear shape → recruits plts
binds to collagen, plts, factor VIII (vWF=carrier)
stored in megakaryocytes, plts, endothelium
plt receptor: GP1b binds to vWF that’s anchored to the collagen → plt activation → plt aggregation via TAX2, ADP → recruit fibrinogen (mesh) = plt plug
Von Willebrand Disease (vWD)
what is it?
what type of bleeding?
m/c inherited bleeding DO
defect in 1ry HS: dec adherence to vascular injury → inadequate plug
type: mucocutaneous/superficial
easy bruising, epistaxis (nosebleeds), subcut ecchymosis (under skin bleeding), GI bleeds, bleeding oral procedures
what are the subtypes of vWD?
usually autosomal dominant
mild dz
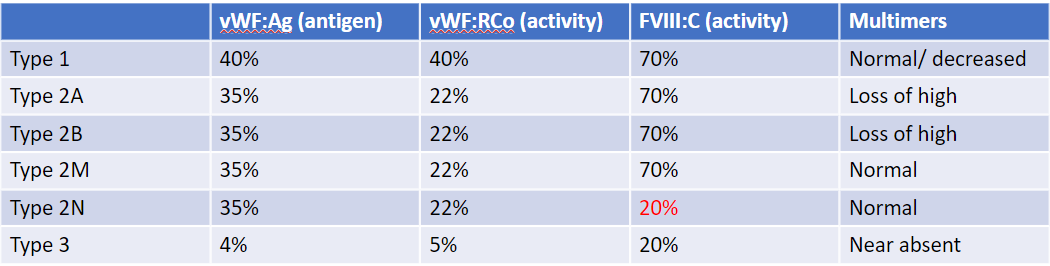
type 1 = dec qty of vWF
moderate dz (dec qty & quality)
type 2A
type 2B/plt type = gain of fxn plt binding
type 2M = dec collagen GP1b binding
type 2N = dec binding to fVIII → mimics hemophilia A
severe dz (near absence of vWF)
type 3: lethal bleeds, → fVIII will also decrease
acquired vWD
malignancies, prosthetic heart valves
resemble Type 1 or 2A
vWD testing: von Willebrand antigen
detects if protein is there, but not how it’s working
vWD testing: vWF activity (Ristocetin, GP1b, etc)
tells you how well vWF binds plts
vWD testing: factor VIII C assay
vWF binds to fVIII !
relationship b/t vWF and fVIII?
vWF is the carrier in the bloodstream for fVIII; and vWF protects fVIII from degradation
if vWD type 2N: dec binding to fVIII → mimics Hemophilia A (defic of fVIII)
other vWD testing:
vWF multimer
PFA 100 - replaces bleeding time
plt aggregation - Ristocetin induced plt aggregation (RIPA)
PT/PTT
how does the vWF Ristocetin cofactor activity test (RIPA) work?
Ristocetin exposes GP-1 binding site for vWF → plts agglutinate via GP1b forming bridges
tests how well vWF can bind to plt
→ aggregometer measures change in light transmission compared to a standard curve
vWD indicated if dec optical density
discontinued bc labor intensive → vWF latex agglutination
the RIPA was replaced by what test?
vWF latex agglutination
test is automated using ACL top
rgt = vWF Ab-coated latex-GP1b → pt’s vWF will bind → optical density recorded
ex of vWD types lab results
vWD treatment
cryo (rare)
Amicar or TXA (fibrinolytics)
Desmopressin (contraindicated in type 2B vWD)
vWD concentrates
??
vWD vs Bernard Soulier syndrome?
BSS have large plts and thrombocytopenia, vWD should not
type 2 vWD may mimic hemophilia A, so always run ___.
PT and PTT screening assay w vWD panel
vWF multimer analysis function
indicates vWF multimers that are formed via disulfide bonds
can detect if dec in functioning vWF → vWD type
** can also detect ultra-large vWF multimer = spontaneous plt aggregation → thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
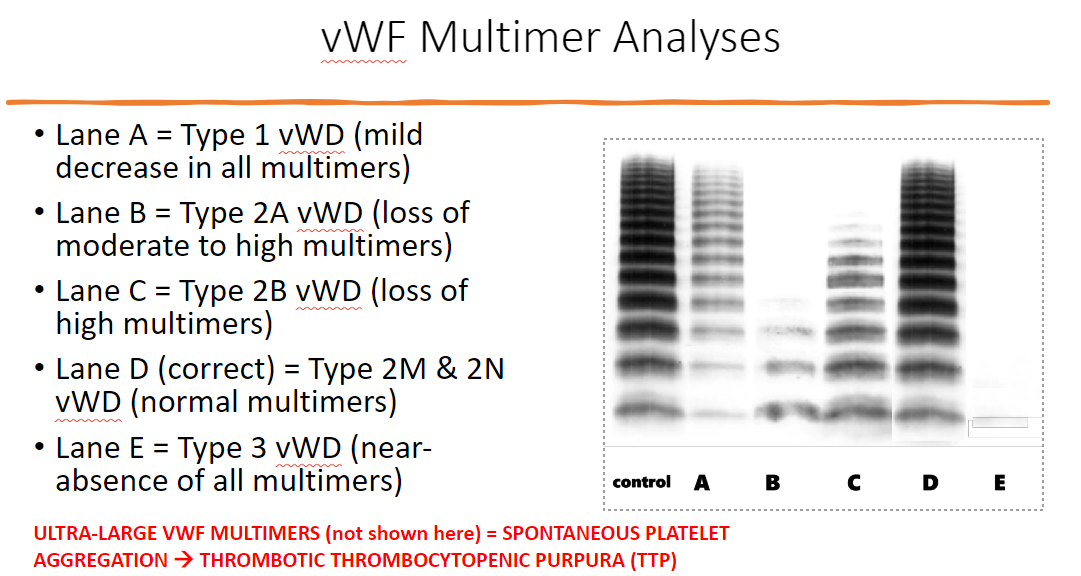
can you exclude presence of mild vWD based on vWF tests alone?
no, in inflammatory states (pregnancy), vWF Ag, vWF activity, and fVIII (acute phase reactants) are abnormally high
so in mild vWD → vWD may present w normal vWF levels
acute phase reactants are _
plasma proteins that inc/dec in response to inflammation
ex) vWF, fibrinogen, fVIII
plts facts
resting unactivated plt are disc shaped anucleated cell fragments that come from megakaryocytes
life span = 7-10 days
2-4um in size
N: 150k-400k plt/mL
plt periphery
glycocalyx: creates neg surface charge & adsorbs plasma proteins (vV, vWF, fibrinogen)
plasma membrane: phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol, proteins
plt membrane receptors & binding sites
GPIb/Ix: or vWF
GPIIb/IIIa: fibrinogen
GPIa/IIa: collagen
plt organelles
mitochondria
dense granules
alpha granules
lysosomes
peroxisomes
plts: dense granules store mediators of plt function and HS which are ___
ADP: aggregation
serotonin: vasoconstruction
Ca2+
plts: alpha granules store variety of bioactive substances ie _.
vWF
fibrinogen
plt factor 3 & 4: thrombin generation, heparin neutralizing
factor V
fibrinolytic factors (plasminogen)
steps of activated plt stages
adhesion
shape change
activation
secretion
aggregation
→ 1ry hemostatic plug
thrombocytopenia is caused by
decreased production:
inc consumption:
induced by:
m/c plt DO
plt count <150k
caused by dec production: aplastic anemia, radiation
inc consumption: splenic hepatic sequestration, ITP/TTP, HUS, bleed, DIC, NAIT (maternal fetal)
drug induced (heparin induced)
qualitative plt disorders
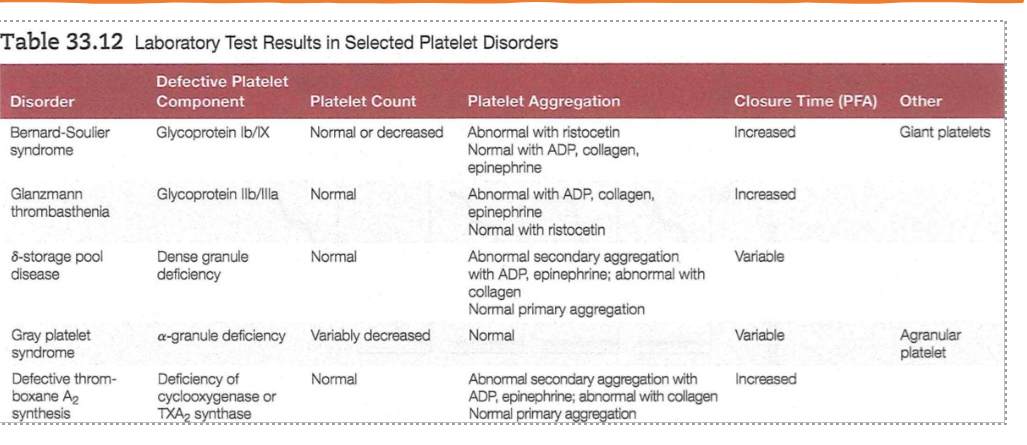
Bernard-Soulier syndrome: defective GPIb/IX, giant plt
Glanzmann thrombasthenia: defective GPIIb/IIIa (after plt activation, for plt aggregation)
delta-storage pool disease: dense granules defic
gray plt syndrome: alpha granule defic; agranular plt
defective thromboxane A2 synthesis: defic of cyclooxygenase or TXA2 synthase
→ all inc PFA (closure time)
Bernard-Soulier syndrome
defective GPIb/IX → abnormal RIPA
giant plt
**giant St. Bernard dog
Glanzmann thrombasthenia
defective GPIIb/IIIa → abnormal w ADP, collagen, epinephrine
delta-storage pool dz
dense granule defic → no ADP, serotonin → same w Glanzmann
GrAY plt syndrome
alpha-granule defic → agranular plt
normal plt aggregation
defective thromboxane A2 (TXA2) synthesis:
what is the reaction of TXA2 synthesis?
what OTC medicine inhibited TXA2 production?
defic of cyclooxygenase (COX1) or TXA2 synthase → abnormal 2ry plt aggregation
TXA2 = plt activator and BV vasoconstrictor (injury → plt produce TXA2)
in plt: arachidonic acid --(COX1)→ TXA2
inhibited by Aspirin!!
adhesion disorders
first 3 already mentioned, what is dz of collagen defect?
von Willebrand dz
Bernard-Soulier syndrome: defic of GPIb
Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia: absence or defic of GPIIb/IIIa , fibrinogen binding site
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (Indian Rubber man): collagen defect, prevents binding or vWF/plt to collagen fiber → vWF can’t anchor :((
release reaction defects
Aspirin therapy: inhibits production of TXA2 which prevent plts aggregation
m/c plt defect
storage pool disease: plts lack dense granules → no ADP
hypofibrinogenemia
congenital DO w low levels of fibrinogen = lack glue for aggregation
or
congenital afibrinogenemia: absence of fibrinogen
May-Hegglin anomaly
giant plts (cookies), Dohle bodies (croissant), thrombocytopenia
**May is a baker, uses EGG
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
dec ADP in dense granules
** my hermana LAKs a(D)p
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
dec dense granules (no ADP, serotonin) & thrombocytopenia
** Whisky → xs alcohol → ruins SD (can’t get dense…)
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
storage pool defect
LYST gene mutation → abnormal giant lysosomes
defective phagocytes → recurring infns
defective melanin production → albinism
TAR baby syndrome
storage pool defect
Alport’s disorder
DO of basement membranes
thrombotic DO or plts
plts are “hyperaggregable” → interact w relatively normal BV wall → sclerotic vessel dz, thrombosis ie stroke, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary emobolism, retinal vein occulsion
testing for plt quality & quantity
plt count
bleeding time (discontinued)
plt aggregation
plt function analysis (PFA)
thromboelastography: TEG or ROTEM
plt function analysis (PFA) is
in vitro bleeding time
doesn’t assess for vascular/collagen bleeding
screening test!
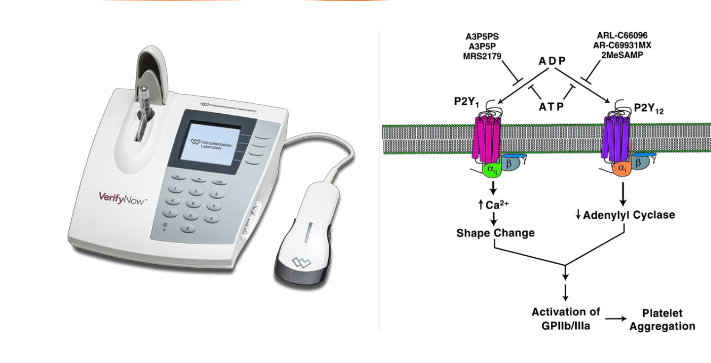
plt inhibition test
assess __ receptor inhibition? by what type of therapy?
what does the above receptor bind to? → plt aggregation
optical detection system to assess P2Y12 receptor inhibition, reported in P2Y12 reaction units (PRUs)
P2Y12 receptor: key in plt aggregation in response to ADP
measures extent of ADP-induced plt clumping of fibrinogen-coated beads (plt aggregation)
can monitor anti-plt therapy (ie Plavix)
thromboelastography (TEG)
evaluate formation, strength, lysis of clot
uses:
monitor anticoag therapy (warfarin/heparin)
assess DIC
trauma/surgery bleeding guiding
rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM)
similar to TEG, but difference in way machine works (more commonly used in Europe)
similar uses as TEG
common agonists (enhancers) used for plt aggregation
ADP concentrated
ADP diluted
epinephrine
collagen low vs high
Ristocetin high
Ristocetin dilute
arachidonic acid
thrombin
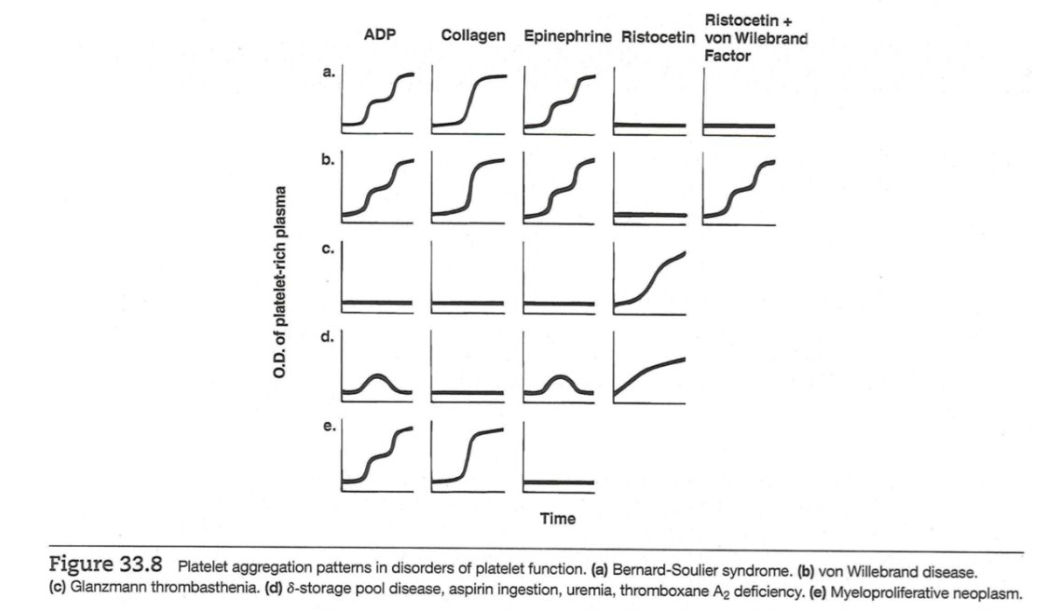
important plt DO table and plt aggregation patterns
plt aggregation curves
y-axis: OD dec, meaning inc plt aggregation
x-axis: time (min)