TEAs Reading (Nurse Cheung)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Topic Sentences - Where can you locate them in a text?
The topic sentence is usually the first sentence of the first paragraph.
Main Ideas - Where can you locate them in a text?
The main idea sentences is usually the last sentence of the first paragraph.
Supporting Details - Where can you locate them in a text?
Supporting Details are found in the same paragraph as the topic sentence.
Summary Sentences - Where can you locate them in a text?
The summary is usually comrpised of the first sentence of the last paragraph.
Making Inferences & Logical Conclusions
Def: A conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning, prior knowledge, and text evidence.
*Both terms are considered the same on the TEAs.
How To Identify:
1) Find Clues in the Text
2) Add Prior Knowledge
3) Combine Both & Make an Inference
Explicit Evidence
Def: Information that is stated clearly and in detail, leaving now room for doubt.
*Think: “E” = Explicit & Expressed
Implicit Bias
Def: Information that is not directly stated, but is implied or suggested.
*Think: “I” = Implicit & Implied
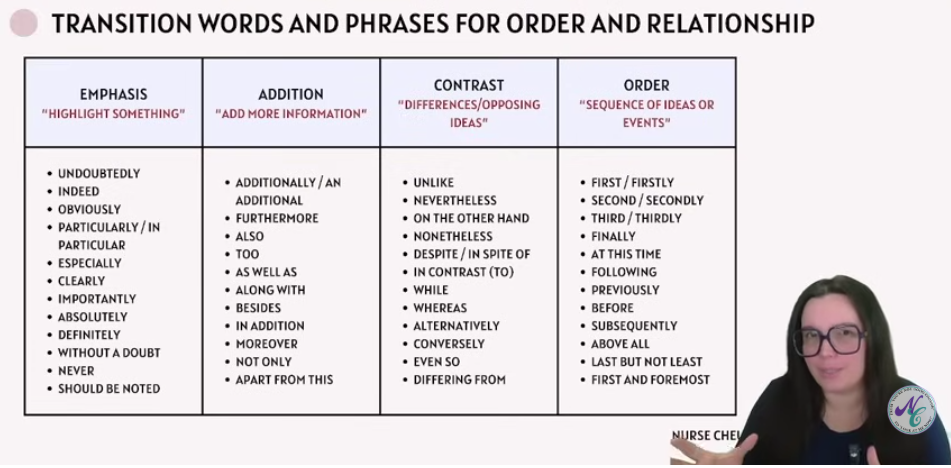
Transition Words & Phrases For Order & Relationship
Refer to attached image.
Headings —- Define the term and state its purpose.
Def: A title at the head of a page or document.
Purpose: Introduces the main topic or theme of a passage.
Subeadings —- Define the term and state its purpose.
Def: Headings underneath the main heading that provides additional details.
Purpose: Breaks down the main topic into more specific areas or aspects.
Transition Words & Sequence of Events
Refer to attached image.
Authors Point of View
Def: Biases that an author may have towards a subject; stem from personal experiences, cultural background, poltical beliefs.
Author’s Point of View
First Person
I
Me/My/Mine
We
Us
Our/Ours
Second Person
You
Your
Yours
Third Person
He/She
It
Him/Her
His/Hers
They/Them
Their/Theirs
Author’s Tone
Def: The author’s attitude or emotional stance towards a subject.
*Tone can be negative, neutral, or positive.
Bias versus Steryotype
Bias—-
Def: A personal opinion in favor or against a person, group, or thing.
Stereotype—
Def: A generalized belief some people have towards a group or class of people.
Figurative Language—-Similie
Def: A direct comparison between two ideas; uses “like” or “as.”
Ex:
“Life is like a box of chocolates!”
“I came in like a wrecking ball.”
Figurative Language—-Metaphor
Def: A comparison that makes an implied or hidden connection between two ideas; does NOT use “like” or “as.”
Ex:
“Love is an open door!”
“Life is a highway!”
Figurative Language—-Personification
Def: Giving a non-human object human characteristics.
Ex:
“The sea was angry that day.”
“I walk a lonely road.”
Figurative Language—-Hyperbole
Def: An exaggerated claim that emphasizes a point.
Ex:
“I would walk 500 miles!”
Types of Writing—-Informative
Facts and information from news articles and encyclopedias.
Types of Writing—-Descriptive
Creating a vivid picture in the readers mind.
Types of Writing—-Persuasive
Convince or Persuade the Reader
Types of Writing—-Expository
Explaining or clarifying ideas like steps in a process or explaining a concept.
Types of Writing—-Entertainment
Storytelling & Engagement
Theme
Def: A significant concept that is woven throughout a story; the theme answers questions and offers insights or morals that can be used in real-life,
*Differs from main ideas.
Primary Sources
Credible, Direct-Evidence Sources about:
Person
Events
Pheomena
*Interviews, Transcripts, Survey Results, Social Media Posts
Secondary Sources
Created using primary sources to:
Analyze
Interpret
Restate
*Newspaper Articles, Textbooks
Tertiary Sources
Use both primary and secondary sources but does NOT present any new information.
*Textbooks, Abstracts, References, Dictionaries, Encyclopedias
Rhetorocal Devices—-Ethos
Purpose: Earn the audiences trust in the speaker or writer.
*Credibility & Reliability
Rhetorical Devices—-Pathos
Purpose: Tap into the audience’s emotions.
*Emotional Connection & Empathy
Rhetorocal Devices—-Logos
Purpose: Engage in the audience’s reasoning and logic.
*Well-Reasoned Arguments & Logical Consistency