162 lab_Lesson 3: Medication Use Process (Answer with Term)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
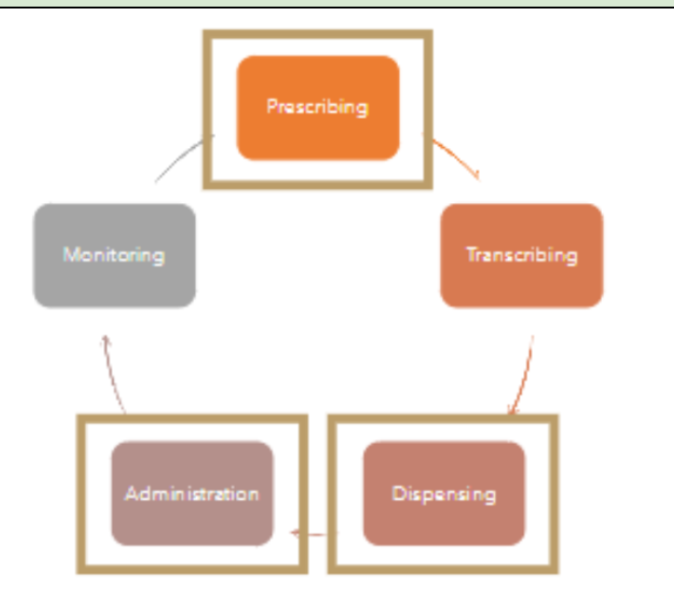
Prescribing
Transcribing
Dispensing
Administration
Monitoring
Look at it as a cycle
Medication Use Process
To Prescribe
To advise and authorize the use of a medicine or treatment for someone, especially in writing (Oxford University Press, 2014)
Deciding on the medication
Preparing the prescription for dispensing and/or administration
Prescribing Error
Failure to review a prescribed regimen for appropriateness and detection of problems
Failure to use appropriate clinical or laboratory data for adequate assessment of patient response to prescribed therapy
Prescribing Factors
Patient Factors
Medication Factors
Patient Preferences
Organizational Factors
Influences on a prescribing decision [5]
Previous experience
Clinical knowledge and skills
Values and beliefs
Influences on a prescribing decision - Prescribing Factors [3]
Medical history
Physiological parameters
Comorbidities
Concurrent medications
Influences on a prescribing decision - Patient Factors [4]
Research evidence
National guidelines
Side-effect profile
Cost
Monitoring requirements
Influences on a prescribing decision - Medication Factors [5]
Acceptability (Side effects, regime, formulation)
Previous experience
Values and beliefs
Influences on a prescribing decision - Patient Preferences [3]
Local guidelines and protocols
Formularies
Prescribing norms
Cost
Influences on a prescribing decision - Organizational Factors [4]
Decision-making errors (clinical errors)
Prescription writing errors (clerical or technical errors)
Two main types of Prescribing Errors
Decision-making errors (clinical errors)
[Type of Prescribing Error]
E.g., errors in choice, dose or frequency of medication to be prescribed
Dosing errors are the most common and more serious type of this error
Prescription writing errors (clerical or technical errors)
[Type of Prescribing Error]
E.g., omission of the route of medication, illegibility of the prescription
Cardiovascular drugs
Analgesics
Hypoglycemic agents
Three categories of medication responsible for over four-fifths of preventable ADEs in ambulatory care (Thomsen, et. al., 2007):
Superscription: age (72.44%), gender (32.66%), date (18%)
Inscription: dose (22%), dosage form (23%)
Signa: directions for use (46%)
Types of omission errors in handwritten outpatient prescriptions (Shahaibi, et. al., 2012):
Individual Factors
Team Factors
Latent conditions
Patient Factors
Work Environment Factors
Causes of Prescribing Errors [5]
Dispensing Error
Deviations from a written prescription occurring during the dispensing process of selecting and assembling medication, generating and affixing of dispensing labels, and issue of the dispensed products to patients
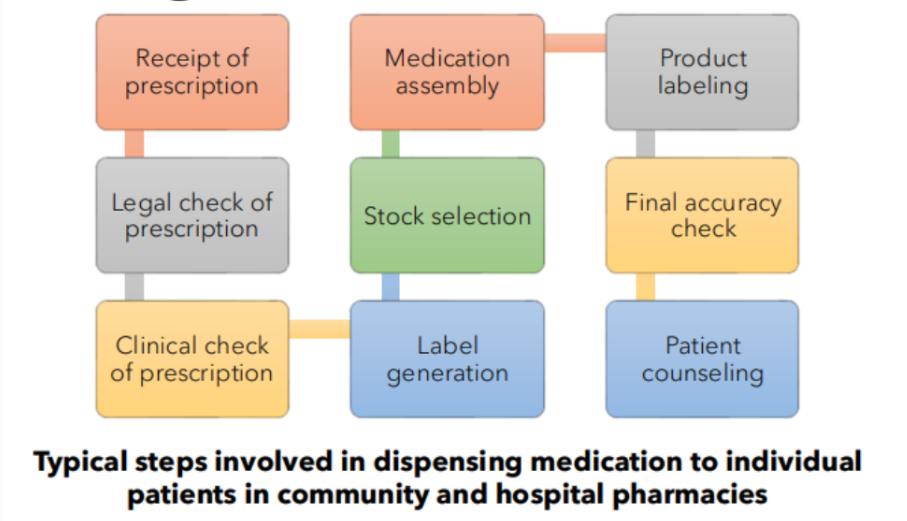
Receipt of prescription
Legal check of prescription
Clinical check of prescription
Label generation
Stock selection
Medication assembly
Product labeling
Final accuracy check
Patient counseling
Typical steps involved in dispensing medication to individual patients in community and hospital pharmacies [9]
Technical errors
Clinical judgement errors
Types of Dispensing Errors
Technical error
These are the errors usually experienced in a pharmacy
Dispensing error that may occur during the process of checking prescriptions for legal validity, product assembly or preparation, labeling, and completion of appropriate documentation or registers
Clinical judgement error
Dispensing error that may occur during screening of prescriptions for clinical appropriateness or during patient counseling
External errors
Internal errors
Two kinds of technical error
External Errors
Detected and reported after medication left the pharmacy
Harm can happen
After dispensing error, we could have communicated with the patient or not
Internal Errors
Detected during dispensing before the medication has been issued
E.g. Near miss
Umabot kay patient yung error pero no harm

Drug Content Errors

Labeling Errors

Issue Errors

Documentation Errors
Workload
Look Alike, Sound Alike Drugs (SALAD’s)
Work Environment
Causes of Dispensing Error
Administration
Composed of:
Preparation
Actual drug administration
Medication administration error (MAE):
the administration of a dose of medication that deviates from the prescription, as written on the patient medication chart, or from standard hospital policy and procedures
Right patient
Right drug
Right time
Right dose
Right route
During administration, we usually check 5 rights of medication administration:
Omission
Wrong dose/improper dose
Wrong dosage form
Deteriorated drug
extra/ dose/unordered dose
Wrong drug
Unordered/non-prescribed drug
Wrong route
Wrong dose preparation/preparation technique
Wrong patient
Wrong rate of administration
Drug incompatibility
Wrong time
Wrong administration technique
Fast IV bolus
Wrong diluent
Examples of Administration Error
Patient
Staff
Working Environment
Medication
Causes of Administration Error