4. Monetary Policy
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Fiat Money
Fiat money is currency that has no intrinsic value and is accepted as money because a government declares it legal tender.
Roles of Banks
Monopoly supplier of the currency;
Banker to the government and the bankers’ bank;
Lender of last resort;
Regulator and supervisor of the payments system;
Conductor of monetary policy; and
Supervisor of the banking system (not sole).
The Objectives of Monetary Policy
The mane objective of maintaining price stability (inflation).
Monetary Policy Tools
open market operations (via purchase and sale of government bonds);
the refinancing rate (through repurchase agreement – REPO);
reserve requirements.
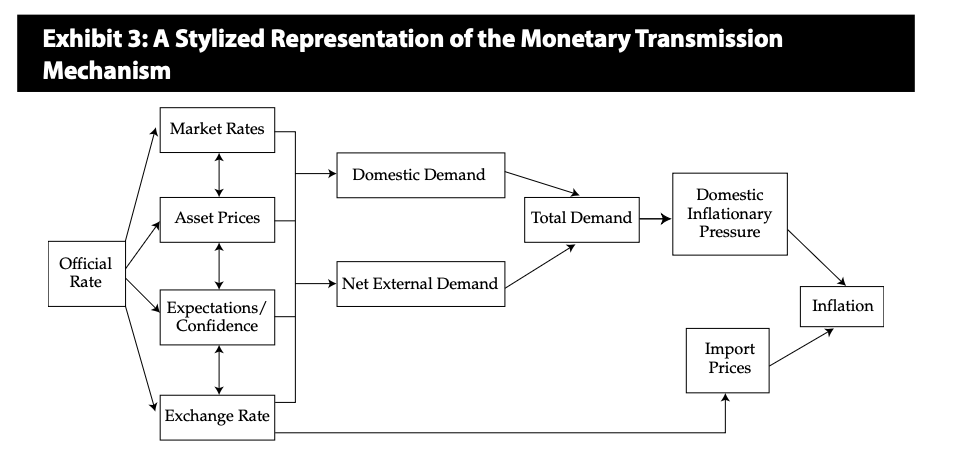
The Transmission Mechanism
To summarize, the central bank’s policy rate works through the economy via one
or more of the following interconnected channels:
Short-term interest rates;
Changes in the values of key asset prices;
The exchange rate; and
The expectations of economic agents.
Exchange Rate Targeting
1. Инфляция ↑ (в Стране А выше, чем в США):
Инфляция ↑
Центральный банк продаёт доллары → скупает свою валюту
Количество денег в экономике ↓
Процентные ставки ↑
Кредиты дороже → экономика охлаждается → инфляция ↓
2. Инфляция ↓ (в Стране А ниже, чем в США):
Инфляция ↓
Центральный банк покупает доллары → выпускает свою валюту
Количество денег в экономике ↑
Процентные ставки ↓
Кредиты дешевле → экономика разгоняется → инфляция ↑
Neutral Rate
Neutral rate = Trend growth + Inflation target
Expansionary < Neutral rate < Contractionary
Demand & Supply Shocks
1. Шок спроса (рост потребления и инвестиций)
→ спрос ↑
→ инфляция ↑
→ ЦБ повышает ставки
→ кредиты дороже → спрос ↓
→ инфляция ↓
2. Шок предложения (рост цен на нефть и издержки)
→ издержки ↑ (например, цена на топливо)
→ цены ↑ → инфляция ↑
→ прибыль компаний ↓, потребление ↓
→ безработица ↑, экономика тормозит
→ если ЦБ ещё поднимет ставки → спад усиливается → позже инфляция резко ↓
Liquidity trap
Liquidity trap – a situation when interest rates are near zero and people hoard money instead of spending or investing, making monetary policy ineffective.
Quantitative Easing
Quantitative easing (QE) – an unconventional monetary policy where a central bank buys large amounts of financial assets to inject money into the economy and stimulate growth when interest rates are near zero.
Fundamental limitation of monetary policy
Central bankers do not control the decisions of individuals and banks that can influence the money creation process.