3.3 - CompTIA A+ Core 1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Memory
Electrical components that store data and instructions for a computer, allowing the CPU to access and process information quickly.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Volatile, high-speed temporary storage for loading data/application instructions.
Data and programs in RAM
Can only be used when moved to RAM.
Memory slots
Designed to quickly transfer data from applications to the CPU, impacting system speed.
Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM)
Dynamic RAM that is synchronous with a computer’s system clock, queuing up one process while waiting for another.
Small Outline Dual in-line Memory Module (SO-DIMM)
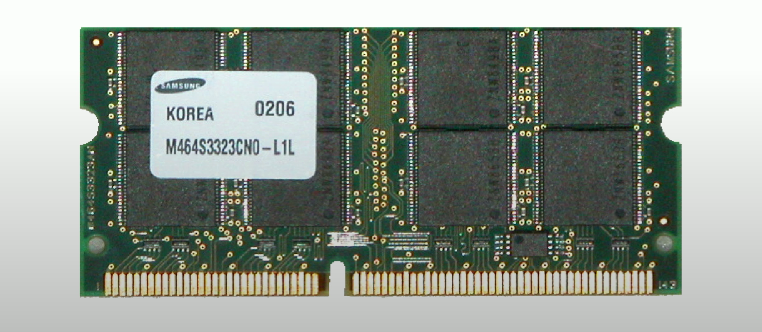
A type of RAM module that is half the width of a DIMM, used in laptops and mobile devices.
DIMM Memory characteristics
Dynamic/volatile (needs constant refreshing) and random access (any storage location accessible directly).
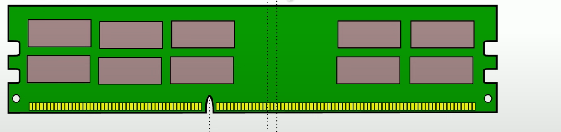
Dual In-line Memory Module (DIMM)
A memory module with different electrical contacts on each side, typically with a 64-bit data width.
Double Data Rate (DDR)
Type of memory that transfers two bits to/from memory per system clock cycle, with different notches for form factors.
Double Data Rate 3 (DDR3)
Twice the data rate of DDR2, with a maximum RAM of 16 GB per DIMM.
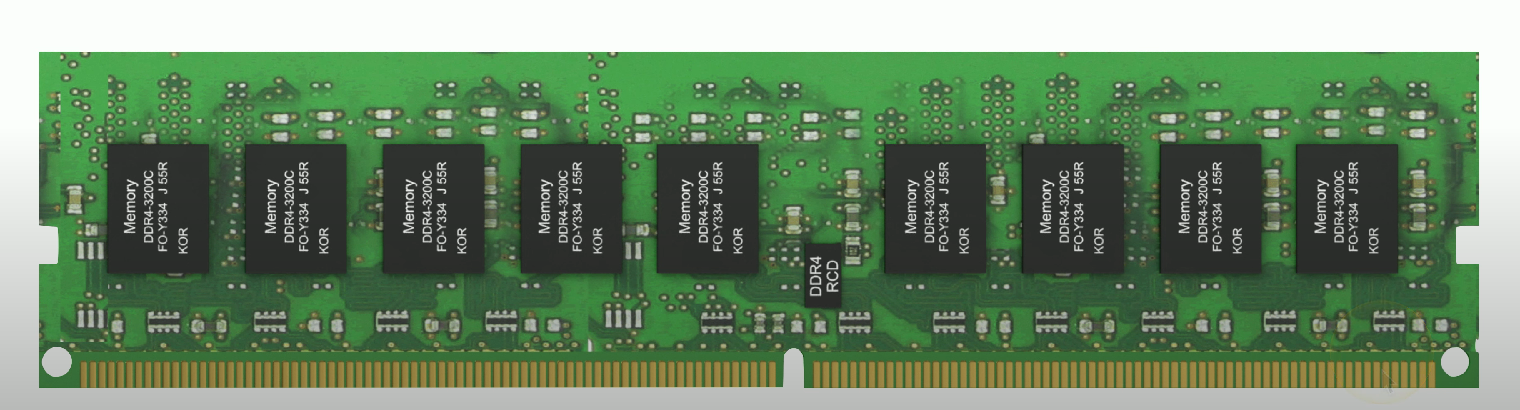
Double Data Rate 4 (DDR4)
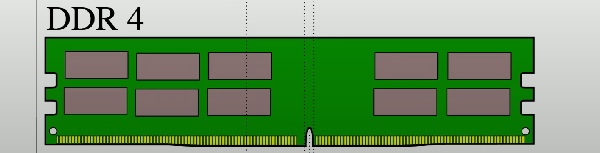
Faster frequencies than DDR3, with maximum 64GB data transfer per DIMM.
Double Data Rate 5 (DDR5)
Provides faster data transfers between memory module and motherboard compared to DDR4, with a maximum of 64GB per DIMM.
Error-Correcting Code (ECC) RAM
A type of RAM used in critical systems that checks and fixes errors as they occur.
Parity Memory
A type of memory that adds an additional parity bit to stored data to check for errors, but is less effective than ECC.
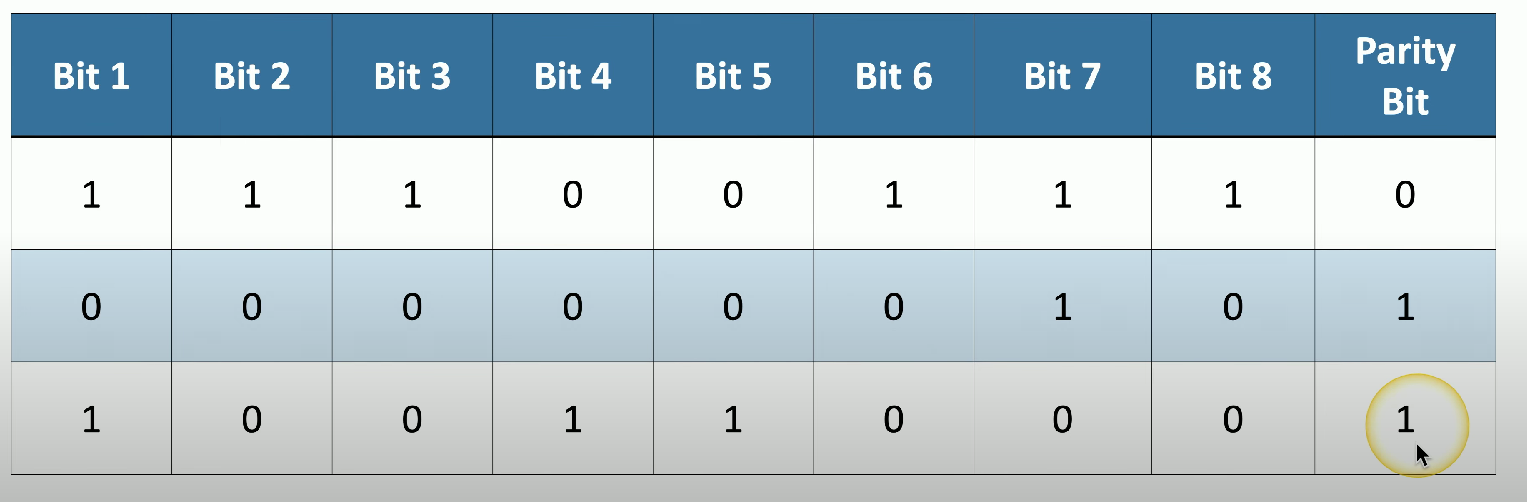
Function of parity bit
To check an 8-bit stream for an even number of 1’s and add an extra 1 if there's an odd number.
Single-channel Configuration
A memory setup that operates using a single memory module, leading to standard performance.
Dual-channel Configuration
A memory setup that uses two memory modules to enhance throughput by spreading the load.
Triple-channel Configuration
A memory configuration that utilizes three memory modules to improve performance further.
Quad-channel Configuration
A memory setup that involves four memory modules, maximizing performance through distributing the workload.
Multi-channel
A system of memory configurations (dual, triple, quad) that enhances performance by distributing data across multiple memory modules.
Indication of Multi-channel setups
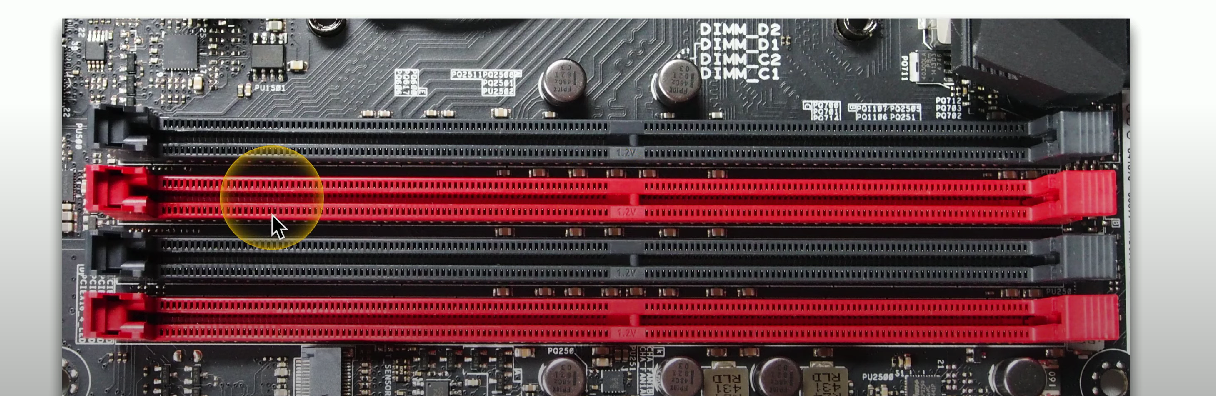
Typically indicated by matching colors on the module slots.