POLYMERS OF LIFE OCR B A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY.
1.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:31 PM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
1
New cards
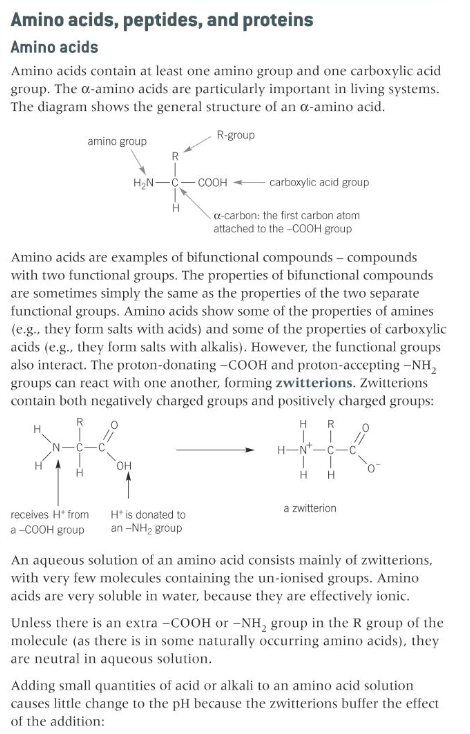
describe the general structure of amino acids
2
New cards
describe proteins as condensation polymers formed from amino acid monomers (including the hydrolysis of peptides)
Hydrolysis of peptides: the peptide link in proteins can be hydrolysed to release individual amino acids, peptides are secondary amides and hydrolysis can be carried out by heating with moderately concentrated acid or alkali. The breakdown of proteins is routinely carried out by boiling with moderately concentrated hydrochloric acid to hydrolyse the amide C-N bonds; this is usually catalysed by enzymes in living organisms than by acid or alkali. Paper chromatography can be used to identify the individual amino acids present in a peptide. The petite is hydrolysed under reflux and the product is compared to known samples of pure amino acids using chromatography.

3
New cards
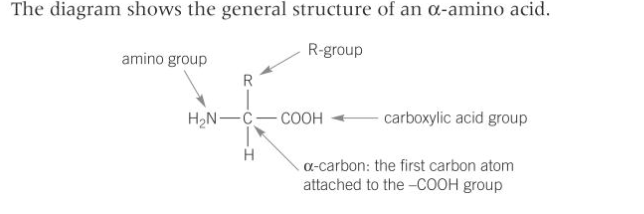
describe paper chromatography
4
New cards
describe the primary structure of proteins
the order of amino acid residues
5
New cards
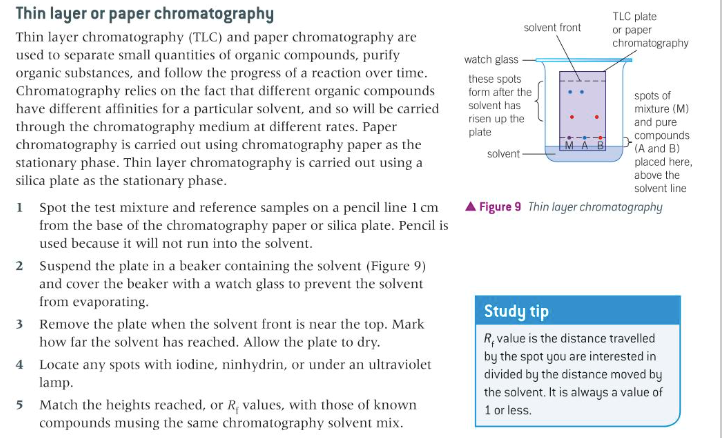
describe the secondary stricture of proteins
the coiling of parts of the chain into a helix or the formation of a region of a sheet.
6
New cards
describe the tertiary structure of proteins
the folding of a secondary structure.
7
New cards
explain the role of intermolecular bonds in determining the secondary and tertiary structures and hence the properties of proteins
8
New cards
explain the phosphate units join by condensation with deoxyribose or ribose to form the phosphate–sugar backbone in DNA and RNA

9
New cards
what are the four bases present in DNA and RNA join by condensation with the deoxyribose or ribose in the phosphate–sugar backbone
These bases are Adenine, Thiamine, Cytosine, and Guanine.
10
New cards
explain how two strands of DNA form a double-helix structure through base pairing
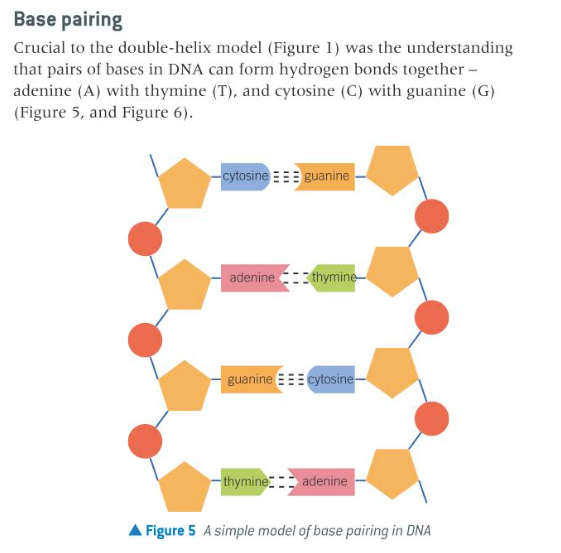
11
New cards
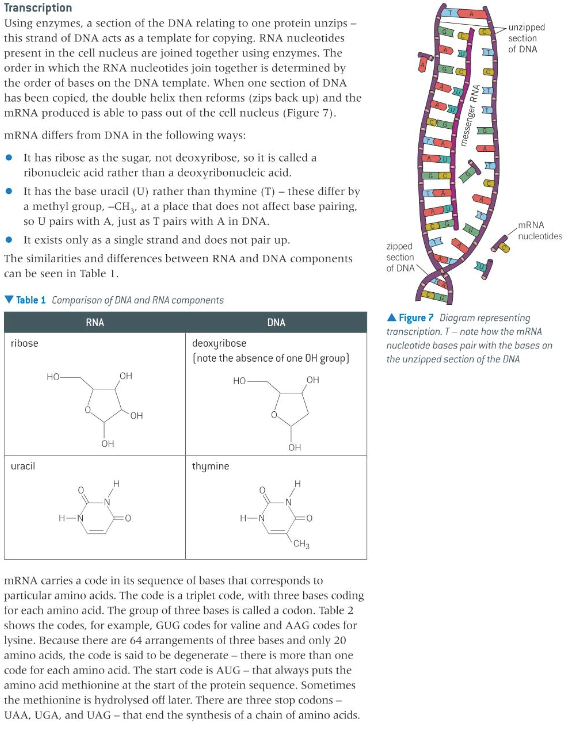
the significance of hydrogen bonding in the pairing of bases in DNA and relation to the replication of genetic information; how DNA encodes for RNA which codes for an amino acid sequence in a protein
12
New cards
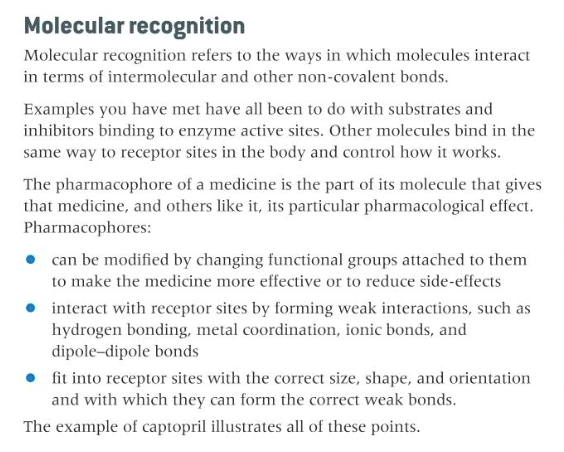
describe the pharmacophore and groups that modify it, its interaction with receptor sites, the ways that species interact in three dimensions (size, shape, bond formation, orientation)
13
New cards
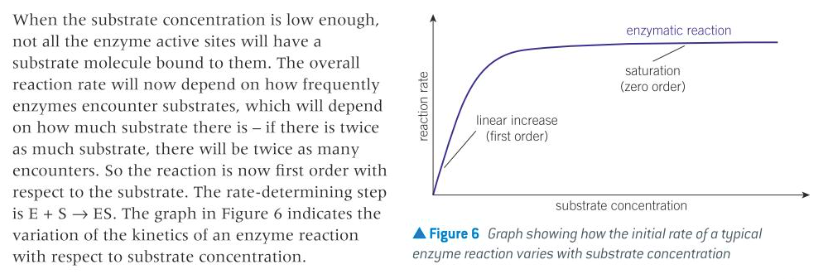
describe the shape of the rate versus substrate concentration curve for an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
14
New cards
describe specificity in terms of enzyme catalysis
15
New cards
describe temperature in terms of enzyme catalysis
continued..... Some of the tertiary structure bonds are weak dipole-dipole bonds and hydrogen bonds. These can be broken easily by raising the temperature, which causes them to vibrate more vigorously and weaken or break.
At higher temperatures, the enzyme is denatured and the activity falls.
At higher temperatures, the enzyme is denatured and the activity falls.
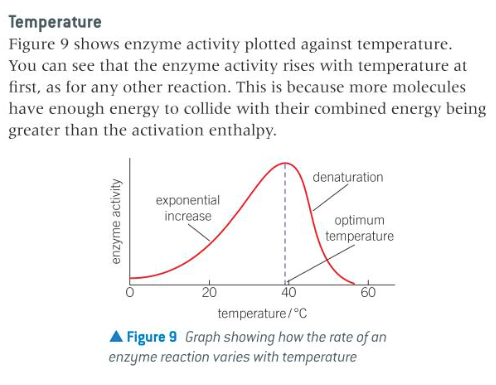
16
New cards
describe pH in terms of enzyme catalysis
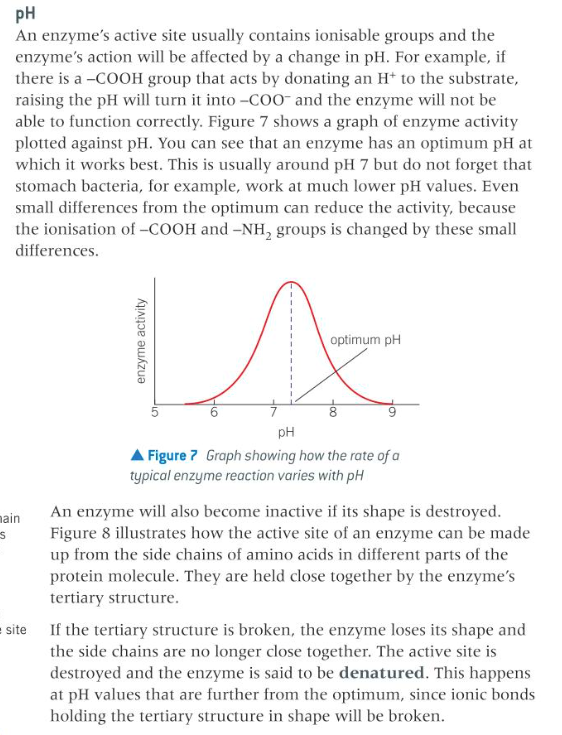
17
New cards
describe inhibition in terms of enzyme catalysis

18
New cards
explanation of these characteristics of enzyme catalysis in terms of a three-dimensional active site (part of the tertiary structure)

19
New cards
the acidic nature of carboxylic acids, and their
reaction with metals, alkalis and carbonates
reaction with metals, alkalis and carbonates
The salt formed is calcium ethanoate.

20
New cards
the acidic nature of carboxylic acids, and their
reaction with metals, alkalis and carbonates (continued).
reaction with metals, alkalis and carbonates (continued).

21
New cards
describe the acid-base properties of amino acids and their existence as zwitterions