Quantum thoery
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
quantization
When an e is confined (attractive force between the electron and proton) to a finite region of space by the forces exerted on it, its total energy is restricted to certain special values
Light
electromagnetic radiation that transmits energy through space of some other medium
Electromagnetic radiation
produced when electrical charges undergo some sort of acceleration
what is the motion that allows atoms to produce electric and magnetic fields in light bulb
back and forth oscillation
wavelength
is the distance between adjacent maxima / unit m
period (T)
the time it takes for the electric field to return to its maximum strength / unit s
Frequency (v)
number of times per second the electric field reaches its maximum value / in Hz or s^-1
what is the relationship between wavelength and frequency
where c=3×108
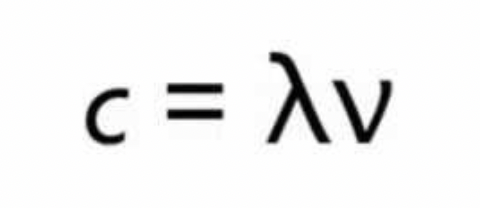
What is the name and order (from longest wavelength to shortest wavelength) of the various regions of the electromagnetic spectrum —> state which way is inc frequency and which is inc wavelength
(short wavelength) gamma ray / x-ray / ultraviolet / visible / infrared / microwaves / radio waves (long wavelength)
—→ inc wavelength
←— inc frequency
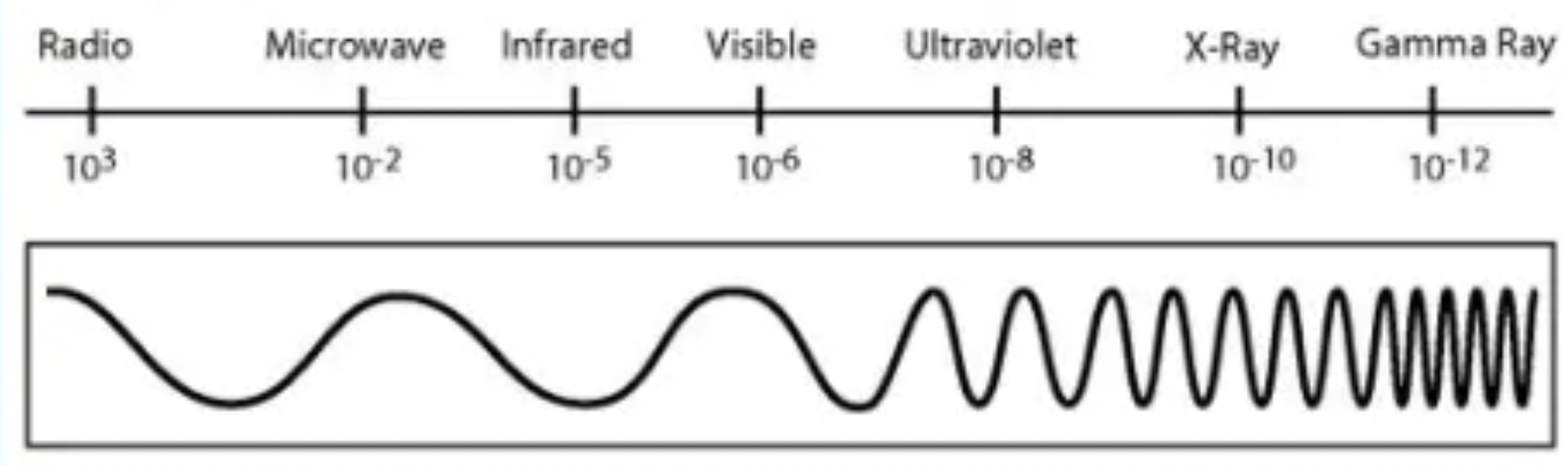
what are the colour of the EM spectrum?
(high energy) purple / blue / green / yellow / orange / red (low energy)
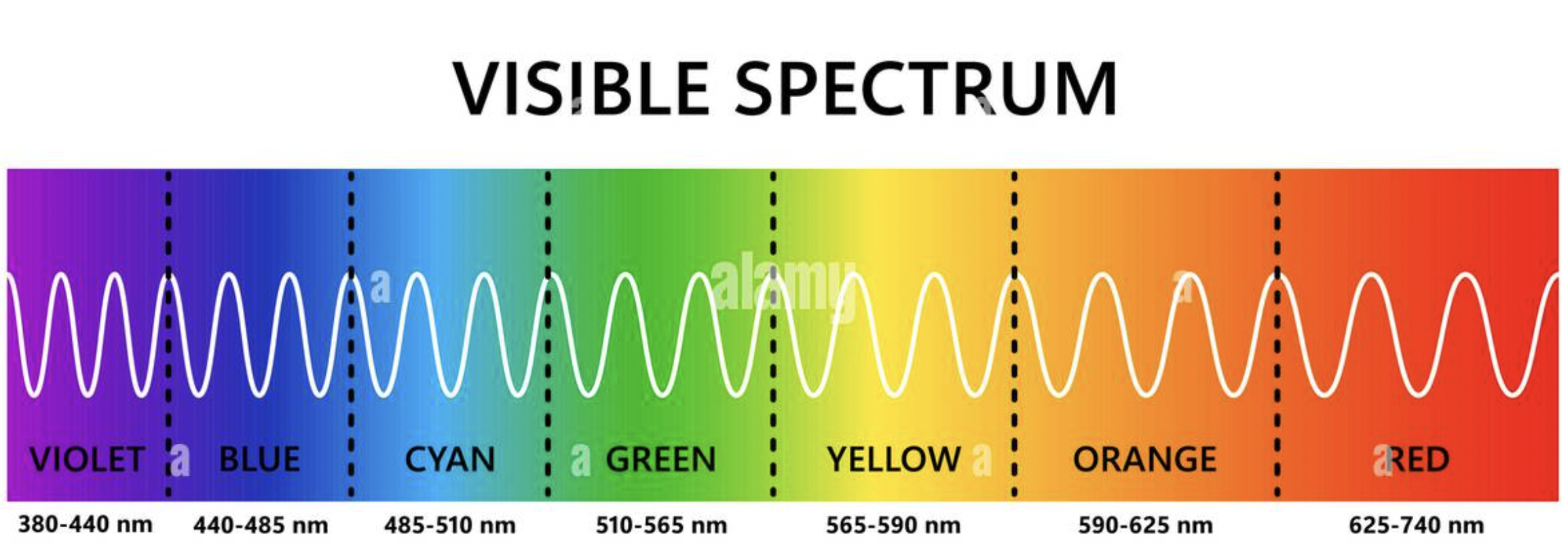
what is the value for visible light?
400nm to 750nm
Blackbody radiation - key ideas
energy is quantized: atoms ocillate with specific energies only (planks’s constant) - 1st evidence that energy is quantized
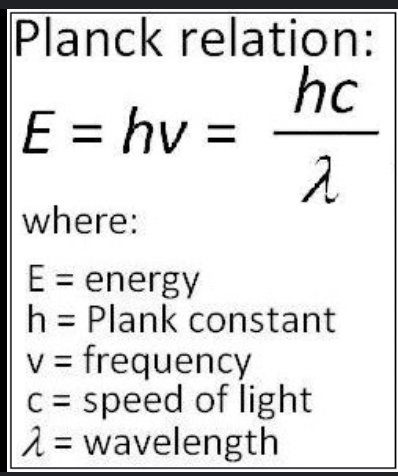
Photoelectric effect
light exists as photons with energy (confirmation of energy is quantized)
Line spectra of atoms
electrons energies in atoms not continuous but restricted to special values
problem with bohr model
does not explain why angular momentum and enrgy of e is quantized (model is wrong)
the model could not extended to other atoms
why doesnt H atom emit radiation continuously?