AS Biology - Unit 5 - The mitotic cell cycle
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
-"___" means to fill in the blank. the number of underscores do not equal the number of characters required. -number of points needed to be given for the answer is in '[ ]'
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
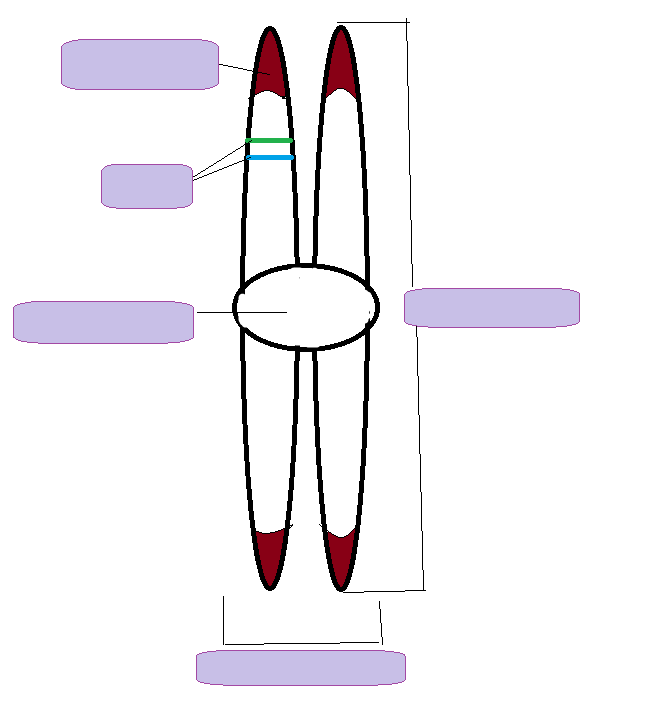
label the parts of a chromosome
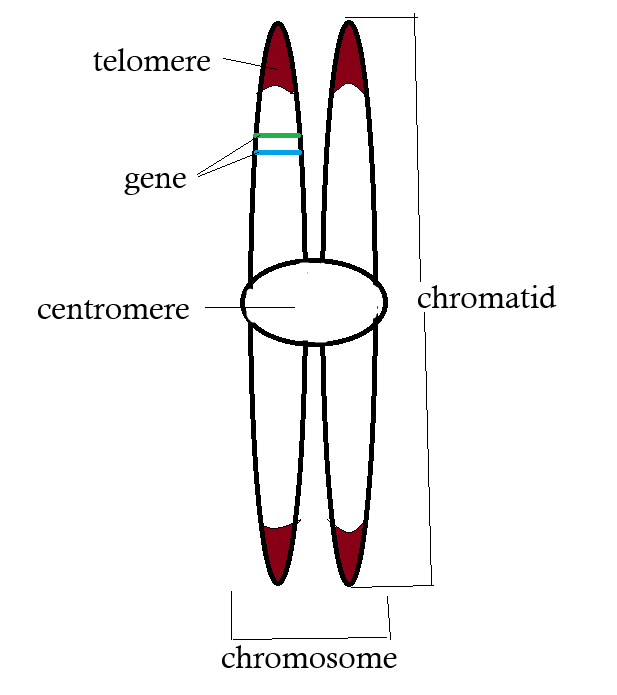
two chromatids joined together are called ____
sister chromatids
mutation
the changing of the structure of a gene, resulting in a variant form that may be transmitted to subsequent generations, caused by the alteration of single base units in DNA
types of mutation**
-deletion
-addition
-substitution
histones
protein DNA wraps around
nucleosome
8 histone proteins with DNA wrapped around it
each chromatid contains ___ DNA molecule
1(one)
PMAT stands for ___
P - prophase
M - metaphase
A - anaphase
T - telophase
reasons for mitosis [4]
-asexual reproduction
-growth
-repair
-immune response
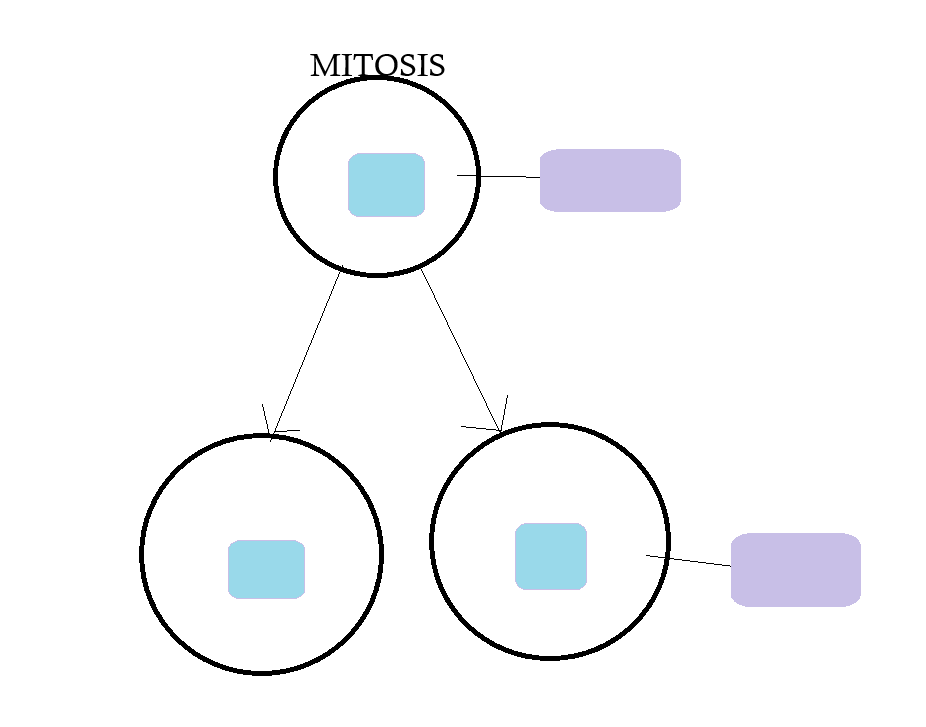
complete the diagram for mitosis
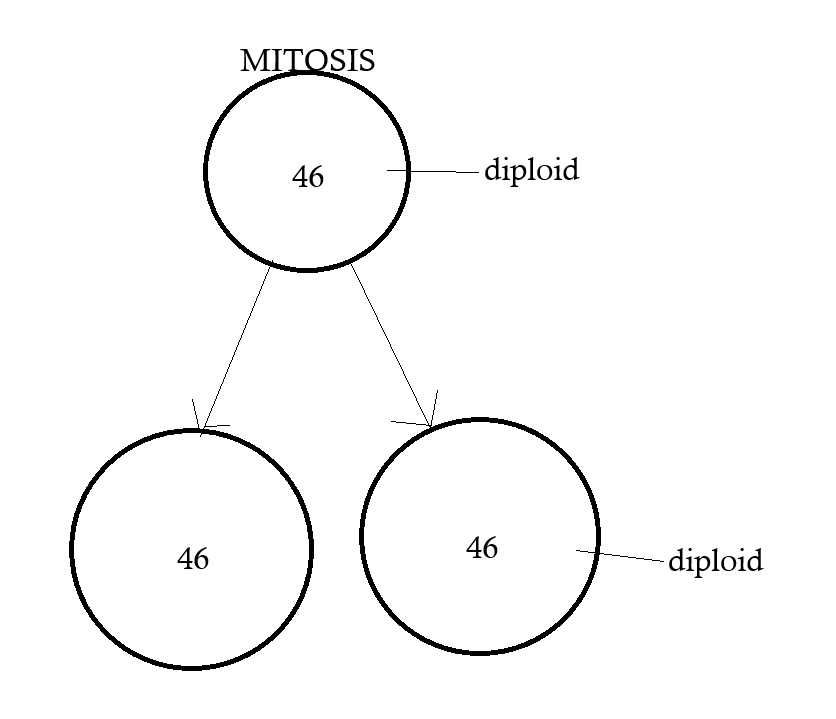
complete the cell cycle.
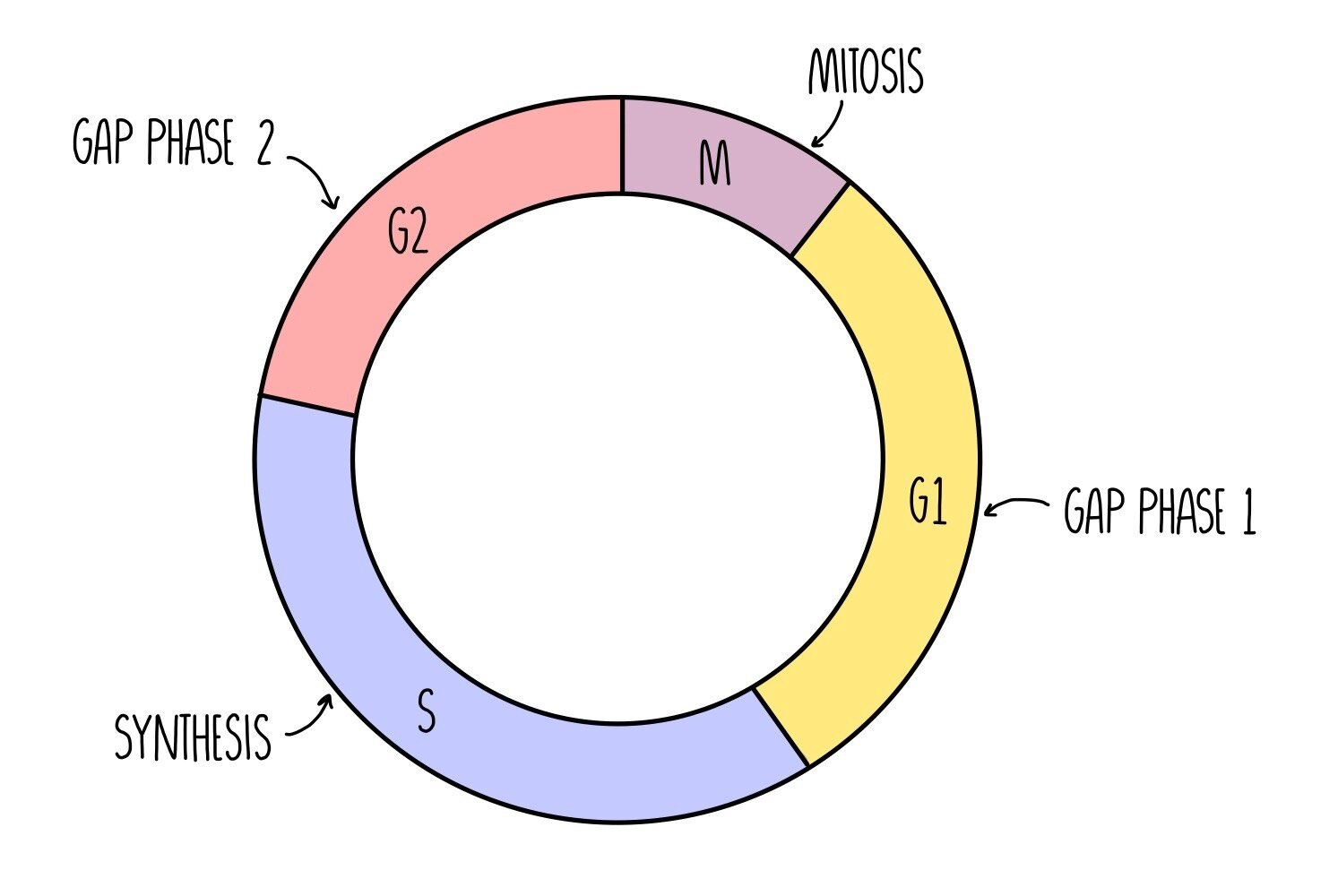
what colours and stages represent interphase.
yellow,blue pink. (G1,S,G2)
what occurs directly after mitosis
cytokinesis
where is ‘S’ in the mitotic cell cycle
between G1 and G2 (during interphase)
heterochromatin
-more tightly coiled(looks darker)
-mostly inactive genes
euchromatin
-more loosely coiled(looks lighter)
-more active genes
telomeres form ___ at the ends of each chromatid
telomeres form caps at the ends of each chromatid
telomeres are made of ____ ____ sequences, high in ___ and ___ nucleotides
telomeres are made of repeating nucleotide sequences, high in G and C nucleotides.
telomeres do:
-ensure all DNA is copied
function of telomerase
to rebuild telomeres
potency
extent to which cells can produce different cell types
totipotent
can produce any cell up to 16 cell stage of zygote division
pluripotent
can produce most cell types except for the ones making up the blastocyst which surrounds the placenta
multipotent
cells that have the capacity to self-renew by dividing and to develop into multiple specialized cell types present in a specific tissue or organ
cancer results from …
… uncontrolled mitosis forming tumours
oncogenes
mutated genes which trigger cancer to start
carcinogen
any agent that causes cancer(ex. UV light, tar, asbestos)
malignant
tumors which can spread through the body through blood and lymph
metastasis
the spread of cancers in the body du to cells breaking off and being carried in vessels(blood/lymphatic)
how does cytokinesis occur in an animal cell
at the centre of the cell, a ring of microfilaments contracts to form a clevage furrow that pinches the cell in to form two daughter cells
how does cytokinesis occur in a plant cell
carbohydrate-rich vesicles form in a row at the centre of the cell. thy fuse to form a cell plate in the middle of the cell. the cell plate extends outwards and fuses with the cell wall, dividing the cell into to two daughter cells