(ESS) Topic 2: Ecosystems and Ecology
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- Species and populations - Communities and ecosystems - Flows of energy and matter - Biomes, zonation and succession - Investigation ecosystems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
species
a group of organisms that share common characteristics and that interbreed to produce fertile offspring
biosphere
the part of the planet where organisms live, including the ground and the air
ecology
study of living organisms in relationship to their environment
habitat
the environment in which a species normally lives
niche
the particular set of abiotic and biotic conditions and resources to which an organism or population responds
fundamental niche
the full range of conditions and resources in which a species could survive and reproduce
realized niche
the actual conditions and resources in which a species exists due to biotic interactions
abiotic factors
the non-living, physical factors that influence the organisms and ecosystems
(temperature, sunlight, pH, salinity, and precipitation)
biotic factors
living components of an ecosystem
the interactions between organisms
predation, herbivory, parasitism, mutualism, disease, and competition
population
a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time, and which are capable of interbreeding
S and J curves
a generalized response of populations to a particular set of conditions (abiotic and biotic factors)
S curve
(ex.: mammals)
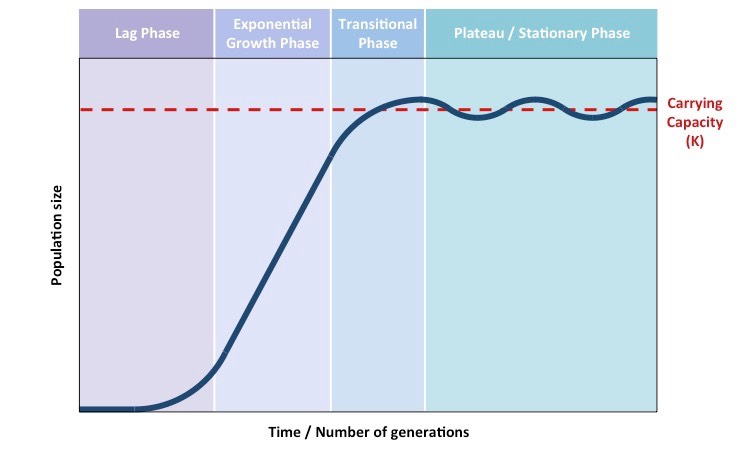
J curve
exponential growth (ex.: colonizing populations - roaches)
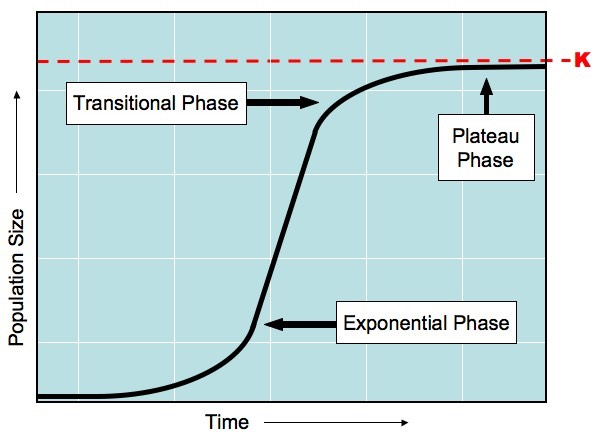
carrying capacity (K)
the maximum number of specific organisms a habitat can sustain
limiting factors
slow population growth as it approaches the carrying capacity of the system
(water availability)
community
a group of populations living and interacting with each other in a common habitat
ecosystem
a community and the physical environment with which it interacts
food web
a complex series of interactions showing the feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem
respiration
the conversion of organic matter into carbon dioxide and water in all living organisms, releasing energy
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
aerobic respiration word equation
photosynthesis
produces the raw material for producing biomass
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
photosynthesis word equation
primary producers
produce their own food using photosynthesis
form the first trophic level in a food chain
(autotrophs)
→ typically plants or algae
trophic level
the position that an organism occupies in a food chain, or the position of a group of organisms in a community that occupy the same position in food chains
feeding relationships
producers
consumers
decomposers
modelled using:
food chains
food webs
ecological pyramids
ecological pyramids
quantitative models (usually measured for a given area and time)
pyramids of numbers
pyramids of biomass
pyramids of productivity
bioaccumulation
the build-up of persistent or non-biodegradable pollutants within an organism or trophic level because they cannot be broken down
biomagnification
the increase in concentration of persistent or nonbiodegradable pollutants along a food chain
toxins
accumulate along food chains due to the decrease of biomass and energy
→ DDT, mercury
pyramid of numbers
(can sometimes display different patterns when individuals at lower trophic levels are large)

pyramid of biomass
represents the standing stock or storage of each trophic level (g m–2 or J m-2)
(can show greater quantities at higher trophic levels because it’s measured at a fixed point in time)
pyramid of productivity
the flow of energy through a trophic level, indicating the rate at which biomass is being generated

productivity
the conversion of energy into biomass for a given period of time
solar energy unavailable for ecosystems
solar radiation (insolation) that is absorbed by inorganic matter or reflected back into the atmosphere
pathways of energy through an ecosystem
conversion of light energy to chemical energy
transfer of chemical energy from one trophic level to another with varying efficiencies
overall conversion of ultraviolet and visible light to heat energy by an ecosystem
re-radiation of heat energy to the atmosphere
net primary productivity (NPP)
total amount of energy stored as biomass in producers (energy available for consumers)
NPP
= GPP – R
= gross primary productivity - respiratory losses
gross secondary productivity (GSP)
total energy assimilated by consumers
GSP
= food eaten – fecal loss
net secondary productivity (NSP)
total amount of energy stored as biomass in consumers (energy available for next trophic level)
NSP
= GSP – R
= gross secondary productivity - respiratory losses
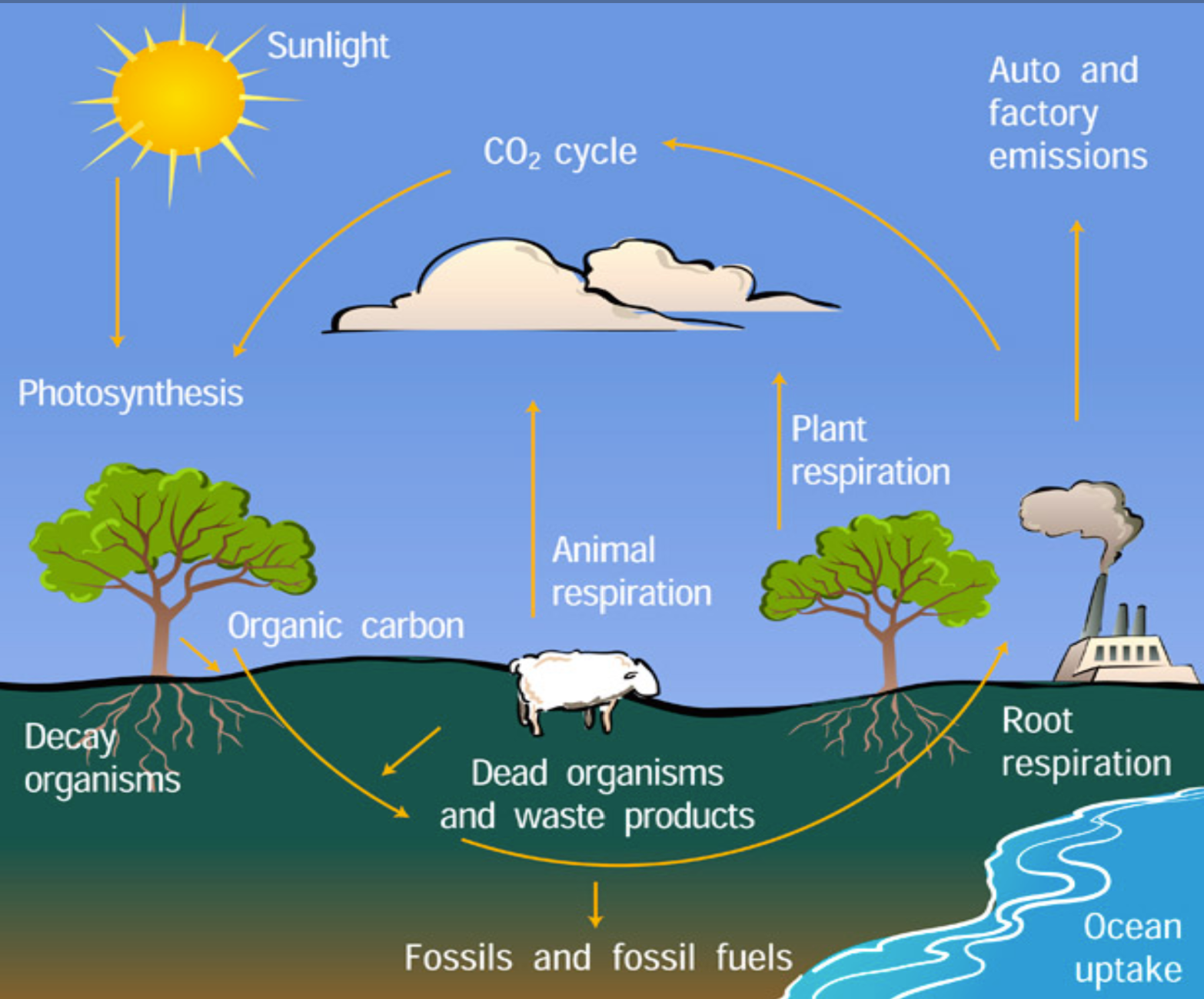
carbon cycle
storages:
organic - organisms and forests
inorganic - the atmosphere, soil, fossil fuels and oceans
flows:
consumption (feeding)
death and decomposition
photosynthesis
respiration
dissolving
fossilization
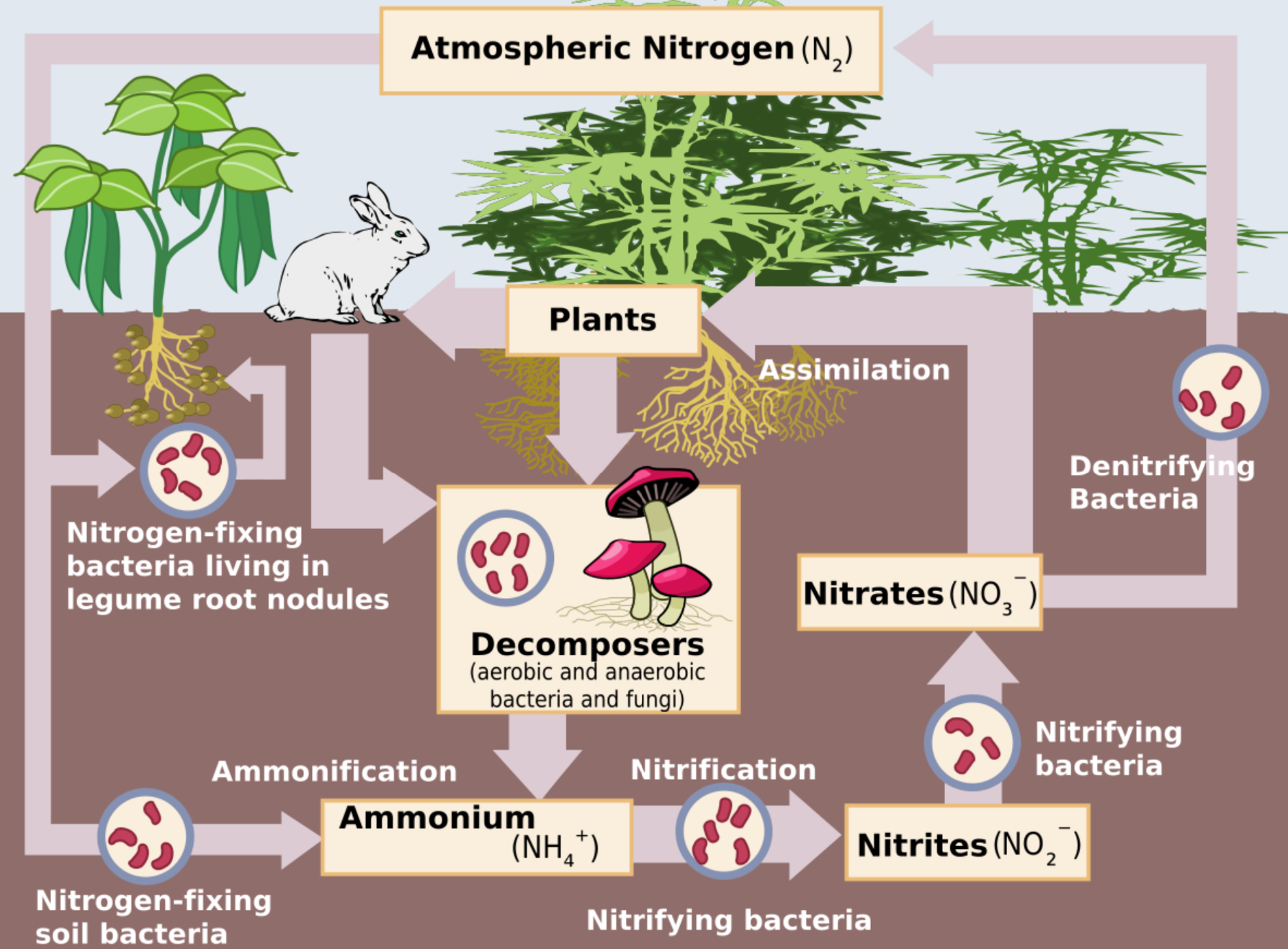
nitrogen cycle
stores:
organic - organisms
inorganic - soil, fossil fuels, atmosphere and water bodies
flows:
nitrogen fixation by bacteria and lightning
absorption
assimilation
consumption (feeding)
excretion
death and decomposition
denitrification by bacteria
biomes
collections of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions
aquatic
forest
grassland
desert
tundra
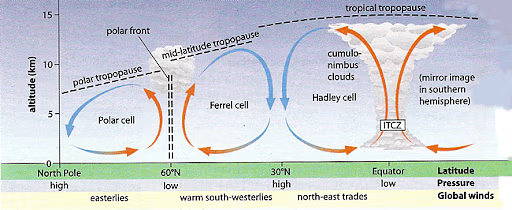
insolation, precipitation and temperature
3 main factors governing the distribution of biomes
tricellular model of atmospheric circulation
explains the distribution of precipitation and temperature and how they influence structure and relative productivity of different terrestrial biomes
zonation
changes in community along an environmental gradient
→ due to changes in altitude, latitude, tidal level or distance from shore (coverage by water)
succession
the process of change over time in an ecosystem involving pioneer, intermediate and climax communities
(patterns of energy flow, gross and net productivity, diversity, and mineral cycling change over time)
early stages of succession
low biomass
low gross productivity
low proportion of energy lost through respiration
high net productivity
later stages of succession (climax community)
high biomass
high gross productivity - balanced by respiration
~0 net productivity
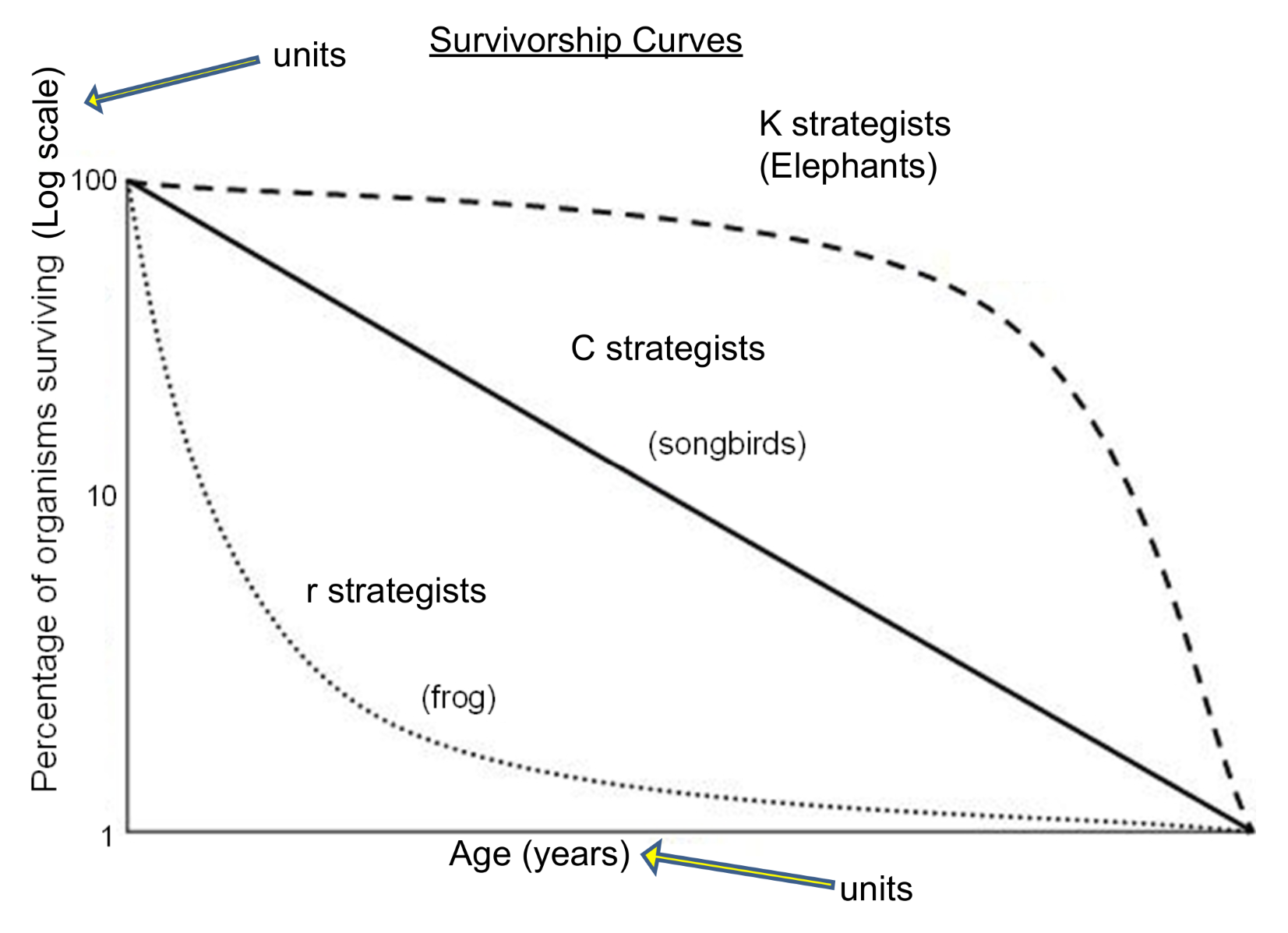
r-strategists
grow fast
mature early
produce many small offspring
give little care to young
→ cockroaches, frogs
favored by natural selection - pioneer communities
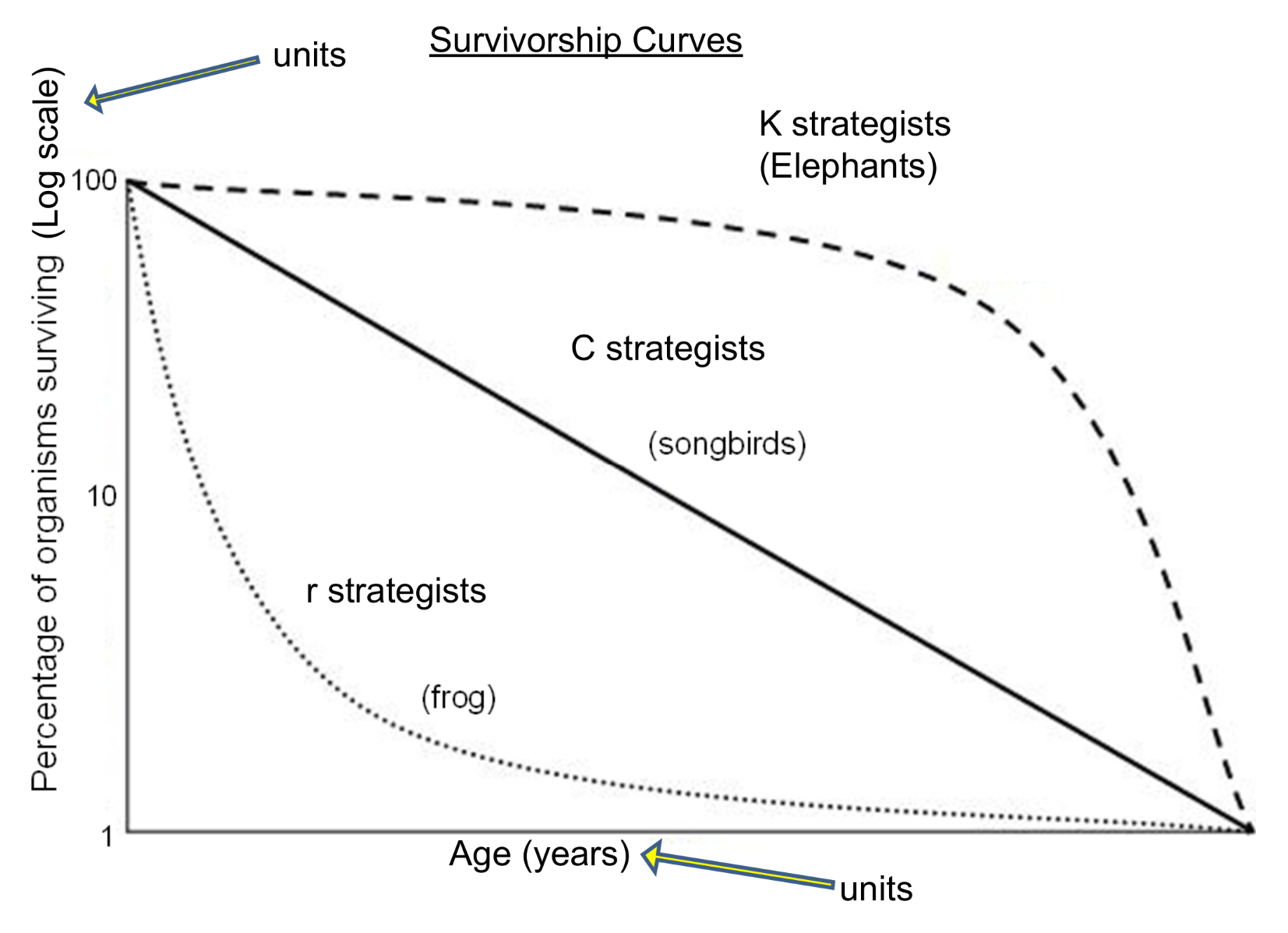
K-stategists
slow growing
usually large
have few large offspring
mature slowly
→ hippopotamus, dolphin, elephant
favored by predictable environments - climax communities
tools for identifying organisms in an ecosystem
keys
comparison to herbarium or specimen collections
technologies
scientific expertise
Secchi disk
for measuring turbidity
observing effect and classing using Beufort scale or digital anemometer
for measuring wind
dynamometer
for measuring wave action
methods for estimating the biomass in a community
measurement of dry mass
controlled combustion
extrapolation from samples
methods for estimating the abundance of non-motile organisms
counting using a quadrat
measuring population density
measuring percentage cover
measuring percentage frequency
indirect methods for estimating the abundance of motile organisms
capture–mark–recapture with the application of the Lincoln index
N = (n1 x n2) ÷ m
n1 - # caught in first sample
n2 - # caught in second sample
nm - # recaptured
species richness
the number of species in a community
→ a useful comparative measure
species diversity
function of the number of species and their relative abundance
Simpson diversity index
D = (N(N-1)) ÷ (Σn(n-1))
N - total # organisms of all species
n - # individuals of a particular species
→ only useful when comparing two similar habitats, or the same habitat over time
→ the higher the result (D), the greater the species diversity
consumer
an organism that obtains its energy from other organisms
detritivore
an organism that feeds on decaying matter (detritus)
food chain
a sequence of steps that describes how an organism derives energy from the ones before it
interspecific
interactions occuring between members of the same species
intraspecific
interactions between different species
mutualism
interactions between species in which both participants benefit
parasitism
expolitation by an organism of its host
(the host is detrimentally effected by the relationship, but is not usually killed)
ecto-
endo-
klepto parasitism
when one animal deliberately takes food from another to feed itself
(manor warbirds attacking tropic birds)
sapotroph
an organism that obtains its energy from dead material by extracellular digestion
keystone species
a species which has a very large influence on the equilibrium stability
transect line (systematic sampling)
sampling used where there is an environmental gradient
rye grass → green common grasshopper → eggs of house sparrow → brown rats → red fox
food chain example
carbon sink
living organisms or non-living materials that store carbon
(ex.: forest, grasslands, kelp, oil, gas, coal, diamonds)
carbon fixing
when gasous carbon is transformed into solid form → photosynthesis
stages of succession
lichens and moss are blown to an area with very little water and nutrients, but establish anyway → pioneer community
they die and decompose - create soil
grasses (dandelion)
herbaceous plants (stinging nettle)
shrubs (pines)
climax community (deciduous trees)
plagioclimax
interrupted succetion - when the climax community isn’t reached
dichotomous key
used to identify an organism by asking yes or no questions
0 - tropical rainforest
low pressure (rising air)
high precipitation
high temperature
high productivity
30 - hot desert
high pressure (descending air)
low precipitation
large temperature range
low productivity
Hadley
Ferrel
Polar
cells in tricellular model of global atmospheric circulation (down from equator)