Specialist Technical Principles
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQA GCSE Design & Technology Specialist Technical Principles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Wood Pulp
Wood fibers processed & reduced down with chemicals or mechanically broken down into smaller parts to make paper.
Cellulose
A carbohydrate, forming cell walls in plant cells.
Total cost (formula)
= individual price x quantity needed
A designer requires 300 sheets of embossed A4 paper, costing 15p per sheet. What is the total cost?
= 300 × 0.15 = £45.00
Tensile strength
Ability to resist pulling forces without snapping.
Lamination
Using at least 2 layers of materials to be bonded together.
Recycle
Break down & process a discarded product, so a new material is produced
Deforestation
Cutting down of trees & forests to allow a different land use
Hardwood trees
Grow slowly and are deciduous (drop their leaves)
Forest Stewardship Council (FSC)
International organization dedicated to promoting responsible management of forests. They provide a certification for products.
Reduce
Making decisions that decrease the amount of waste produced.
Reuse
Use a product again rather than replacing it with a new one.
Rethink
Change the design of a product to be more environmentally friendly.
Refuse
Avoid using a product to save on waste.
Repair
To fix a broken product.
How is paper made?
Paper is made from fibers or recycled materials. Wood pulp is obtained and the bark & chip[pings are removed to extract the cellulose fibers. The pulp is filtered squeezed & bleached. Excess water is drained out through calenders.
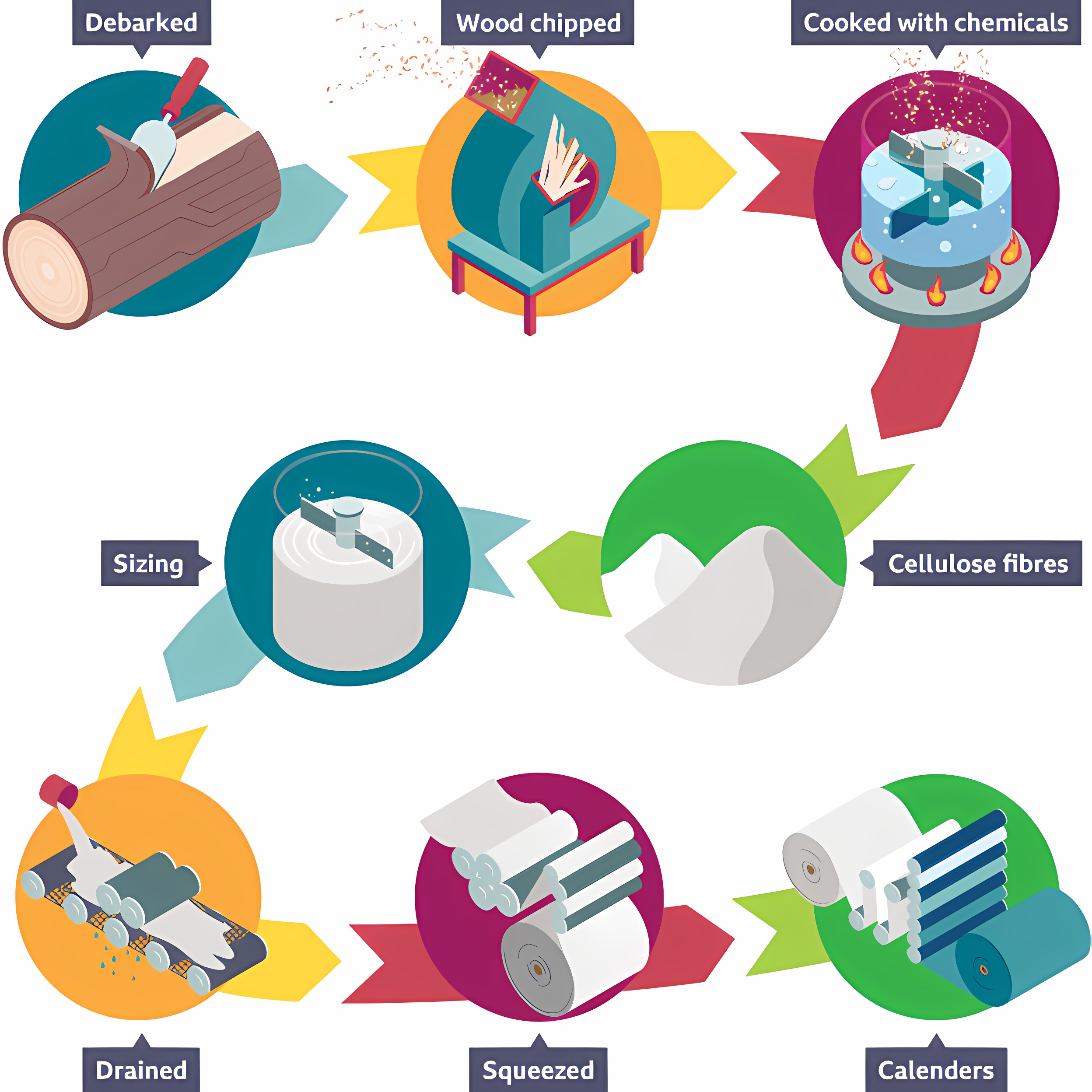
Debarking
Removing chippings and ground down.
Cooking with chemicals
Wood pulp is cooked with chemicals to extract the cellulose fibers.
Sizing
The addition of chemicals that are applied to paper to make the paper resistant to liquid.
Draining
The excess water and chemicals are removed from the pulp, as it is pushed through calendars (a set of rollers)
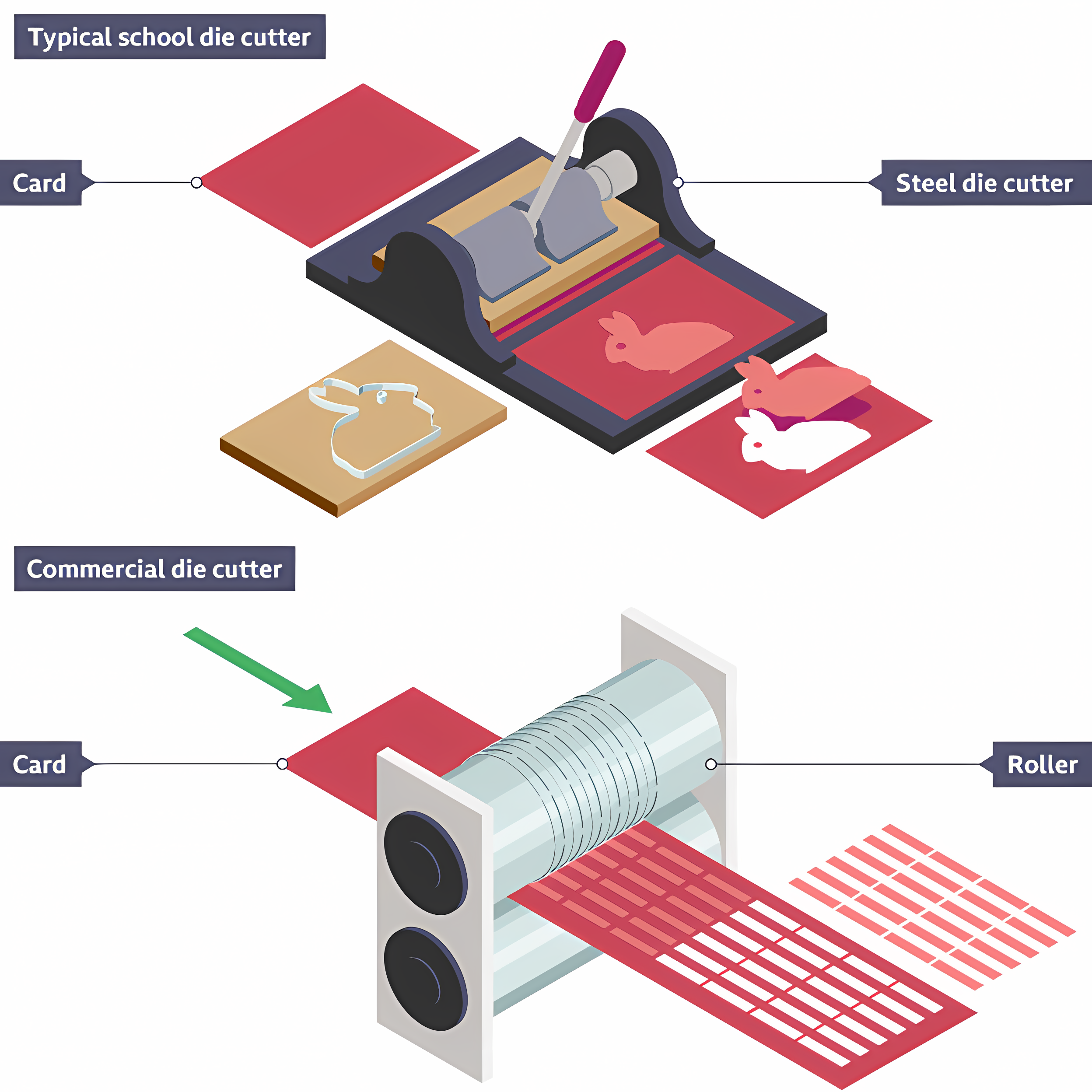
Die cutting
Method of cutting paper or card by pushing a blade through the material.
Scoring
Indented scratch allowing paper or card to fold with ease.
Offset Lithography
Commercial printing method using 4 colors:
Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black (CMYK)
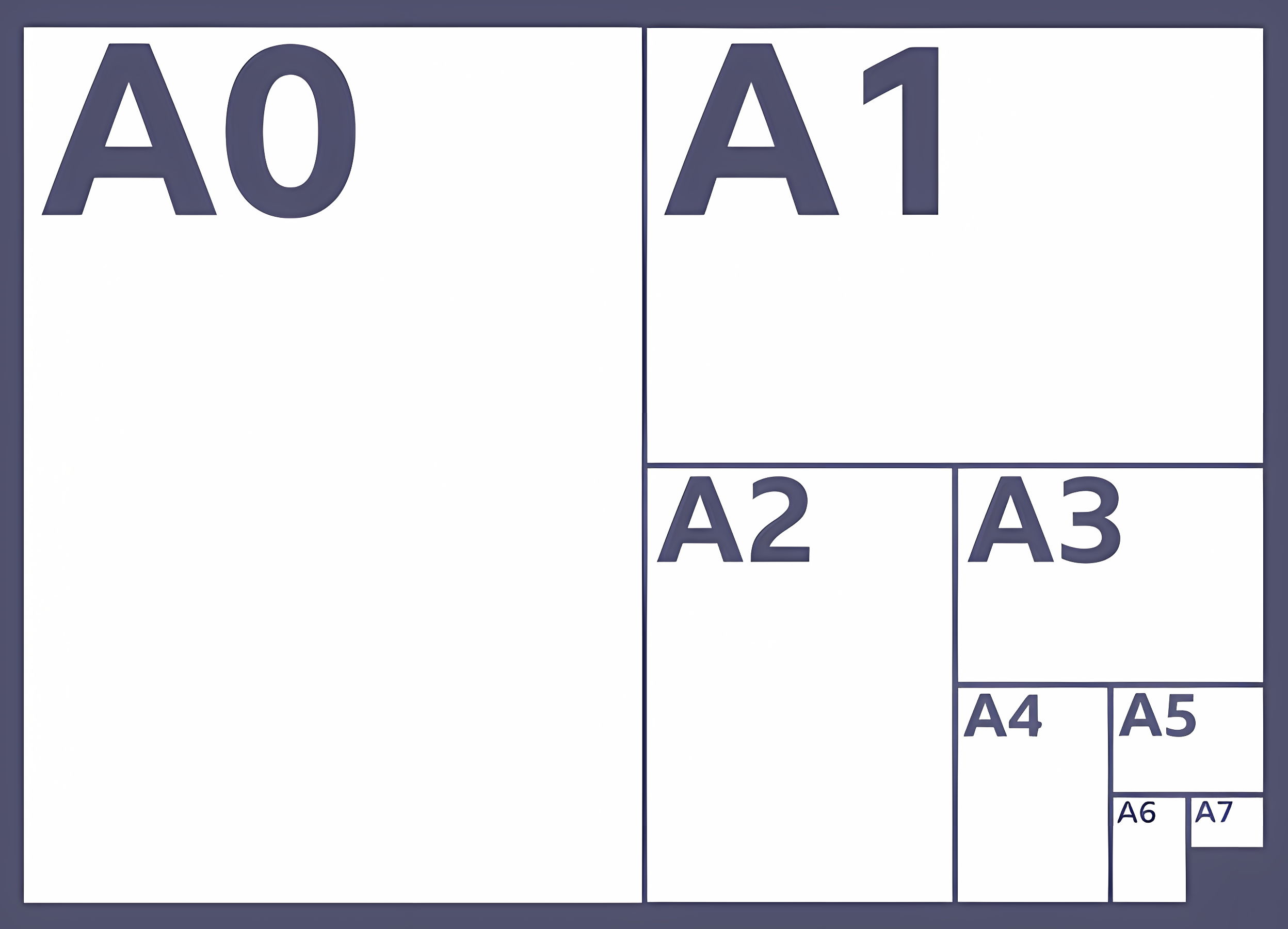
Types of paper
A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7
Layout paper
Properties: Lightweight, thin, cheap, smooth surface
Uses: Graphic drawings, animations
Bleed proof (marker) paper
Properties Contains more chalk, smooth, hard, doesn’t absorb ink, doesn’t bleed
Uses: Creating special effects for designers or artists
Tracing paper
Properties: Good transparency, expensive
Uses: For seeing an image underneath
Grid paper
Properties: Covered with continuous square grid
Uses: Used in many mathematical contexts
Cartridge paper
Properties: Heavier weight, good quality, opaque
Uses: Writing and sketching
Types of board
Board is selected by its thickness, measured in microns.
One micron is 1/1,000th of 1 mm
Corrugated cardboard
Properties: Strong, lightweight
Uses: Packaging protection in transportation of products and used to package some hot food such as a pizza due to its insulating properties.
Duplex board
Properties: Cheaper than white board, available with different finishes (metallic, holographic etc.)
Uses: Food packaging, eg biscuit boxes or containers
Solid white board
Properties: Top quality, range of thicknesses, excellent to print on
Uses: Hardback books
Foil-lined board
Properties: Expensive, good quality, aluminium foil lining, excellent barrier against moisture
Uses: Pre-packed food packages, cosmetic cartons
Inkjet board
Properties: Expensive, printable, photo quality
Uses: Posters, photography, art reproductions
Foam-core board (foam board)
Properties: Strong, lightweight, paper face, foam core
Uses: Model making, mounting photographs
Prototype
First working model of a design used for testing, development, and evaluation.
Batch production
A group of identical products are made at the same time.
Mass production
Same product is manufactured multiple times.
Continuous production
Leads to many similar products being made, continuously.
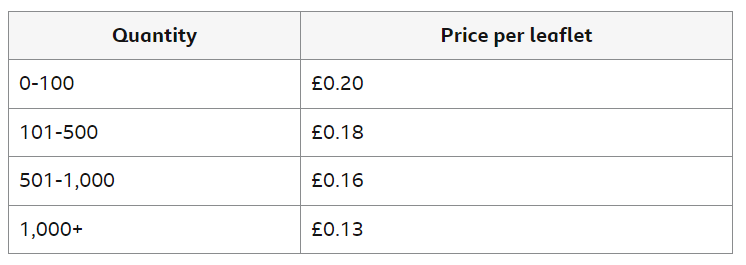
Using the information shown above, calculate the total cost if 1,500 leaflets were needed.
= 0.13 × 1,500 = £195.00
Designing template
Form used to ensure other parts are made to match.
Pattern
Repeated design or recurring sequence.
Ruler
Used to measure a distance & draw a straight line.
Protractor
Used to measure angles.
Set square
Used to draw lines at specific angles.
French curve
Used to draw curves of different sizes.
Guillotine
Used to cut a large number of paper sheets at once with a straight edge.
Craft knife
Used to cut and score paper & cardboard, particularly useful when cutting internal shapes.
Compass cutter
Used to cut a circle or an arc from thin paper or cardboard.
Rotary cutter
Used to cut a circle or an arc from thicker paper or cardboard.
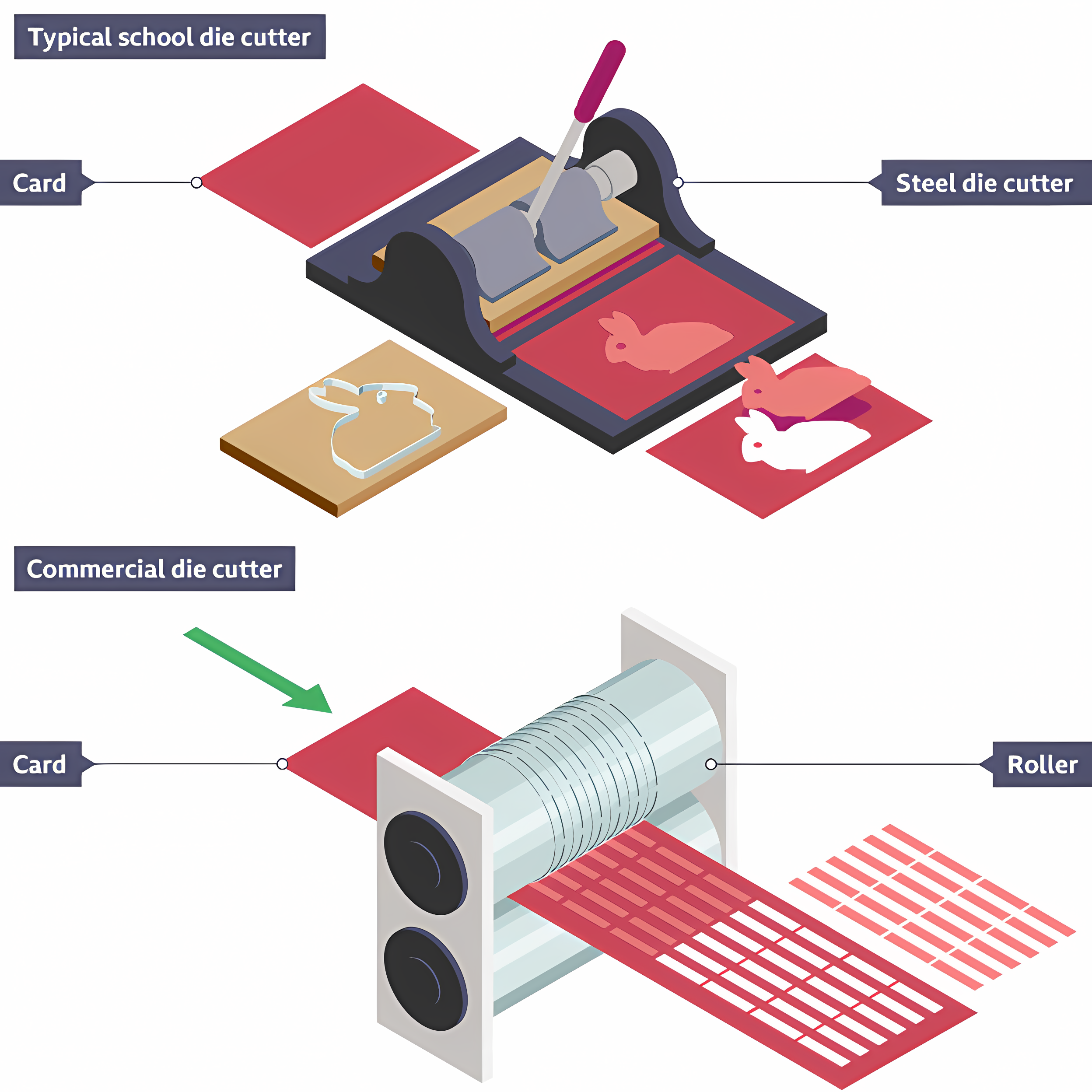
Die cutter
Used to cut, crease, and perforate paper and card at high speeds and accuracy/
Laser cutter
Performs perfect intricate cuts to paper and card, if the speed and power are set correctly.
What are the 4 colors used for in offset lithography?
The 4 colors in offset lithography are used for:
Checking the alignment of the printer using a registration mark.
Registration mark
Circular pattern that is printed using CMYK. When all 4 overlap (when they’re aligned), they create a black circle.

Tolerance
The amount of error a measurement can vary without affecting the product.
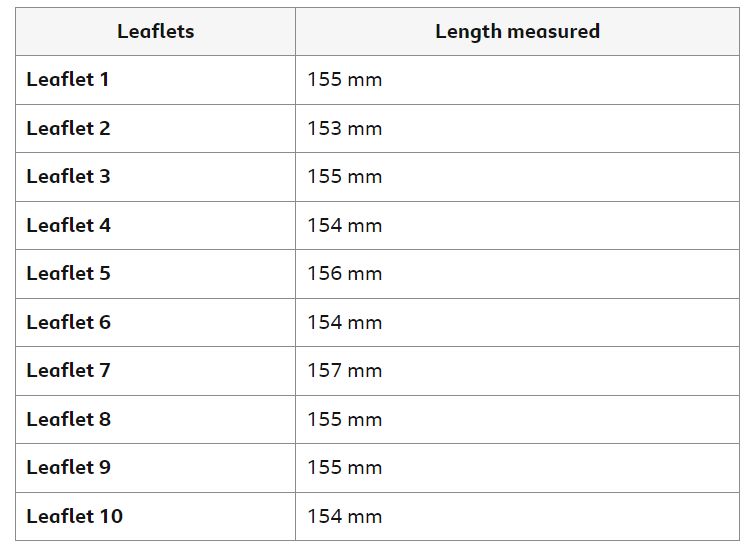
A quality control check is made on a random sample of leaflets. Each leaflet should be 155 mm in length +/- 1mm.
Table of the lengths recorded of a sample of ten leaflets:
How many leaflets were out of tolerance and should not be used, and which leaflets are they?
Two leaflets were produced out of tolerance. These were leaflet 2 and leaflet 7.
Crop marks
Small lines in each corner of paper or board, indicating where it needs to be cut.
Color bars
Reference chart on a sheet of paper to check whether the color is printed to the correct intensity.