ANP 220 fundamentals of evolutionary theory II
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
natural selection
by which the individuals best adapted to the environment contribute more offspring to succeeding generations than others do
favors traits that enhance ability to survive and reproduce
acts on ALL individuals EQUALLY
adaptation
a trait that better suits an organism to its environment
improves chances of survival and reproduction
usual result of natural selection
fitness
reproductive success (surviving offspring)
combines survival, mate find reproduction (offspring production and survival
surviving to old age is not everything
example of adaptation guppies
spots on guppes
size genetically controlled to help blend in
experiment
with predators
blend in with background
how many individuals with small and large spots
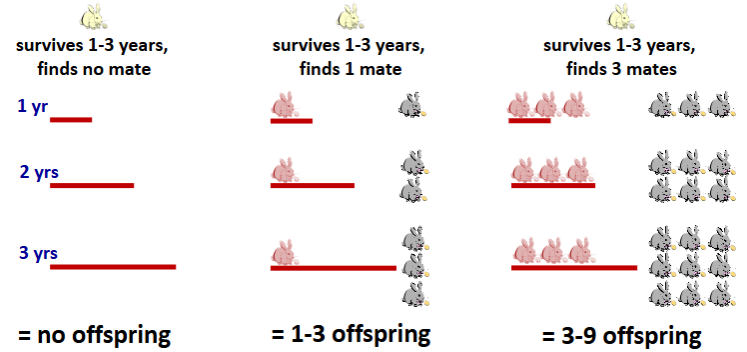
why the number of mates matters a lot for fitness
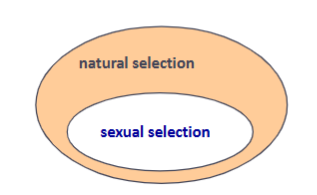
sexual selection
category of natural selection
favors traits that increase success in access to mates
acts on individuals in ONE SEX only
forms of sexual selection
intrasexual selection (male) competition (winner)
female mate choice (best)
mechanisms of evolutionary change
non-adaptive - mutation - gene flow - genetic drift
adaptive - natural selection - sexual selection
inter means between
intra means within
major questions
In what way do characters change
stasis (uncaged) slow, fast direction
In what way do species evolve
single lineage evolving, lineage, splitting
biological evaluation
definition
descent with inherited modication
change through time
genetic inheritance
small scale
population level
microevolution
large scale
population level
macroevolution
→ explains biodiversity
small scale
population level
microevolution
change within species from one generation to the next over few generations
large scale
population level
macroevolution
change over many generations, species divergence new species
mechanisms
short term similar
both micro and marco
macroevolution
concerned with species and higher taxonomic levels
What is a species - species concept - biological species concept (BSC)
a group of actually or potentially interbreeding natural populations that are reproductively isolated from other such populations
species concepts - more than two dozen concepts
reproducing fertile offspring
producing fertile offspring
mate recognition species concept
recognizing one another as protentional mates
ecological species concept
exploiting or adapted to a single niche
phylogenic species concept (PSC)
smallest uniquely identifiable cluster wit parental pattern of ancestry and descent example: orangutans on Sumatra and Borneo and elephants

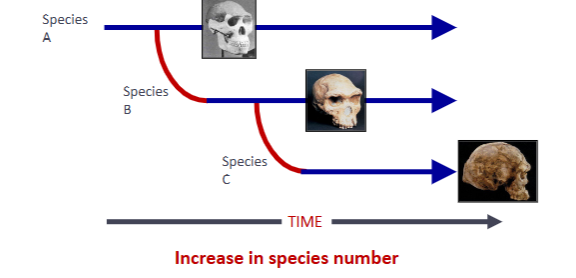
mode of species origin I
cladogenesis - branching evolution involving the splitting of a species
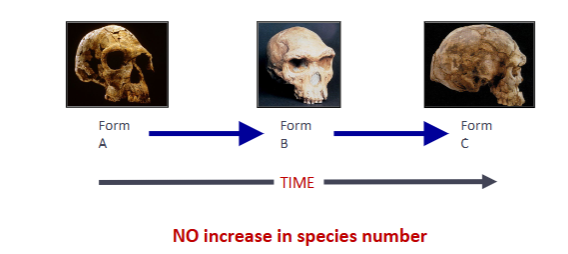
mode of species origin II
anagenesis - single species undergoes gradual cane and transforms over time
causes of speciation
geographic isolation - reduction of gene flow
necessary for speciation - reproductive isolation - difference in mating - lack of fit sexual organs - offspring non-viable / sterile
allopatric speciation
interbreeding populations (gene flow)
barrier prevents interbreeding (no gene flow)
isolated populations may develop differently (natural selection, mutation, genetic drift, founder effect
two new species (do not interbreed even if they meet)
pace of evolution
phyletic gradualism - change is consistent and slow
punctuated equilibrium - periods of little and rapid change
learning objectives or what i should know
