Colored Stones Essentials
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Organic
Once living, or produced by a living organism.
Mineral
A natural, inorganic substance with a characteristic chemical composition and usually characteristic structure.
Inorganic
Composed of, or arising from, non-living matter.
Chemical Composition
Kinds and relative quantities of atoms that make up a material.
Durability
A gemstone’s ability to withstand wear, heat, and chemicals.
What are the three traits of all gems?
Beauty, rarity, and durability
Chemical Formula
Written description of a material’s chemical make-up.
Trace Elements
Atoms in a gem that aren’t part of its essential chemical composition.
Crystal Structure
Regular, repeating internal arrangement of atoms in a material.
Amorphus
Lacking a regular crystal structure.
Luster
The appearance of a material’s surface in reflected light.
Transparency
Degree to which material allows light to pass through it.
Transparent
Light passes through a material with little or no distortion.
Translucent
Light diffuses as it passes through the material.
Hardness
How well a gemstone resists scratches and abrasion.
Toughness
How well a gemstone resists breaking, chipping, and cracking.
Stability
How well a gemstone resists the effects of light, heath, and chemicals.
Gem Species
A broad gem category based on chemical composition and crystal structure.
Gem Variety
A subcategory of species, based on color, transparency, or phenomenon.
Phenomenon
An unusual optical effect displayed by a gem.
When did the US Congress create the Federal trade Commission (FTC)?
1914
When did the FTC publish Trade Practice Rules for the Jewelry Industry?
1957
What is the most important factor in a colored stone’s beauty?
Color
What three things are required for color to exist?
Interaction of light, an object, and an observer
Selective Absorption
Process by which a material absorbs some components of visible light and returns others.
Hue
The first impression of an object’s basic color.
Tone
Degree of darkness or lightness of a color.
Saturation
A color’s strength or intensity.
Bodycolor
A gemstone’s basic color, determined by its selective absorption of light.
Color Center
A small defect in the atomic structure of a material that can absorb light and give rise to a color.
Color Zoning
Areas of different color in a gem, caused by variations in growth conditions.
What kind of light looks best for green, blue, and violet gems?
Fluorescent lighting
What kind of lighting looks best for red, orange, and yellow gems?
incandescent light or the sun’s rays at sunset
Pleochroism
When a gem shows different bodycolors from different directions.
Color Range
The selection of colors in which a gemstone occurs.
Fine Color
The color or colors in a gemstone’s color range considered by the trade to be the most desireable.
Window
An area of weak saturation in a transparent gemstone’s bodycolor that usually results from the way the gem was cut.
Extinction
Dark areas in a faceted transparent colored stone.

What type of effect is shown here?
color zoning

What type of effect is shown here?
pleochroism

What cutting effect is shown here?
window

What cutting effect is shown here?
Extinction
Dispersion
The separation of white light into spectral colors.
Fluroescence
Emission of visible light by a material when it’s stimulated by ultraviolet radiation.
Trade Terms
Terms used to describe gemstone colors or link gems with specific locations.
Play-of-Color
The flashing rainbow colors in opal.
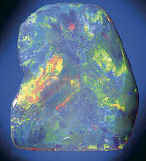
What type of phenomena is this?
Play-of-color
Adularescence
The cloudy bluish white light in a moonstone, caused by scattering of light.

What type of phenomena is this?
adularescence
Color Change
A distinct change in gem color under different types of lighting.

What type of phenomena is this?
color change
Chatoyancy
Bands of light in certain gems, caused by reflection of light from many parallel, needle-like inclusions or hollow tubes.

What type of phenomena is this?
chatoyancy

What type of phenomena is this?
milk and honey
Milk and Honey
A two-toned effect seen when a chatoyant gem is positioned at right angles to a light source.
Asterism
Crossing of chatoyant bands, creating a star in the dome of a cabochon.

What type of phenomena is this?
asterism
Labradorescence
A broad flash of color in labradorite feldspar that disappears when the gem is moved.

What type of phenomena is this?
labradorescence
Iridescence
A rainbow effect created when light is broken up into spectral hues by thin layers.

What type of phenomena is this?
iridescence
Orient
Iridescence seen in some natural and cultured pearls and mother-of-pearl.
Aventurescence
A glittery effect caused by light reflecting from small, flat inclusions within a gemstone.

What type of phenomena is this?
aventurescence