Academic Decathlon Economics
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Scarcity
an inescapable fact of human existence that results from the fact that the available resources are always less than our limitless desires
Opportunity Cost
the cost of any choice is what must be given up by making that choice
Rationality
when individual choices are made by comparing the benefits and costs of different actions and then selecting the action that produces the greatest benefit
Positive Economics
the use of the tools of economic analysis to describe and explain economic phenomena and to make predictions about what will happen under particular circumstances
Consumption
spending by households on goods and services, with the exception of the purchase of new housing
Normative Economics
economic analysis used to guide decisions about what should be as opposed to what is the case
Pareto Efficiency
describes an allocation in which the only way to make any individual or group of individuals better off would require making at least one other person worse off
Microeconomics
the interaction of supply and demand in markets
Market
comprised of all buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
Demand
the quantity of goods that buyers will take at a particular price
Law of Demand
the negative relationship between a good's price and the quantity demanded
Demand Curve
a graphical representation of the quantity of a good or service demanded as a function of the price
Normal Good
a good or service for which demand is positively relative to the buyer's income
Inferior Good
a good for which the quantity demanded falls as buyers' income increases
Substitutes
two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the demand for the other
Complements
two goods for which a rise in the price of one leads to a decline in the demand for the other
Supply
the quantity of a commodity that is in the market and available for purchase or that is available for purchase at a particular price
Law of Supply
the quantity supplied is positively related to the price; the higher the price is, the number of suppliers that want to produce increases
Supply Curve
a graphical representation of the quantity of a good or service supplied as a function of the price
Equilibrium
a situation in which the forces in a system are in balance so that the situation is stable and changing

Competitive Market
a market with many buyers and sellers trading a homogeneous good or service in which each buyer and seller is a price taker
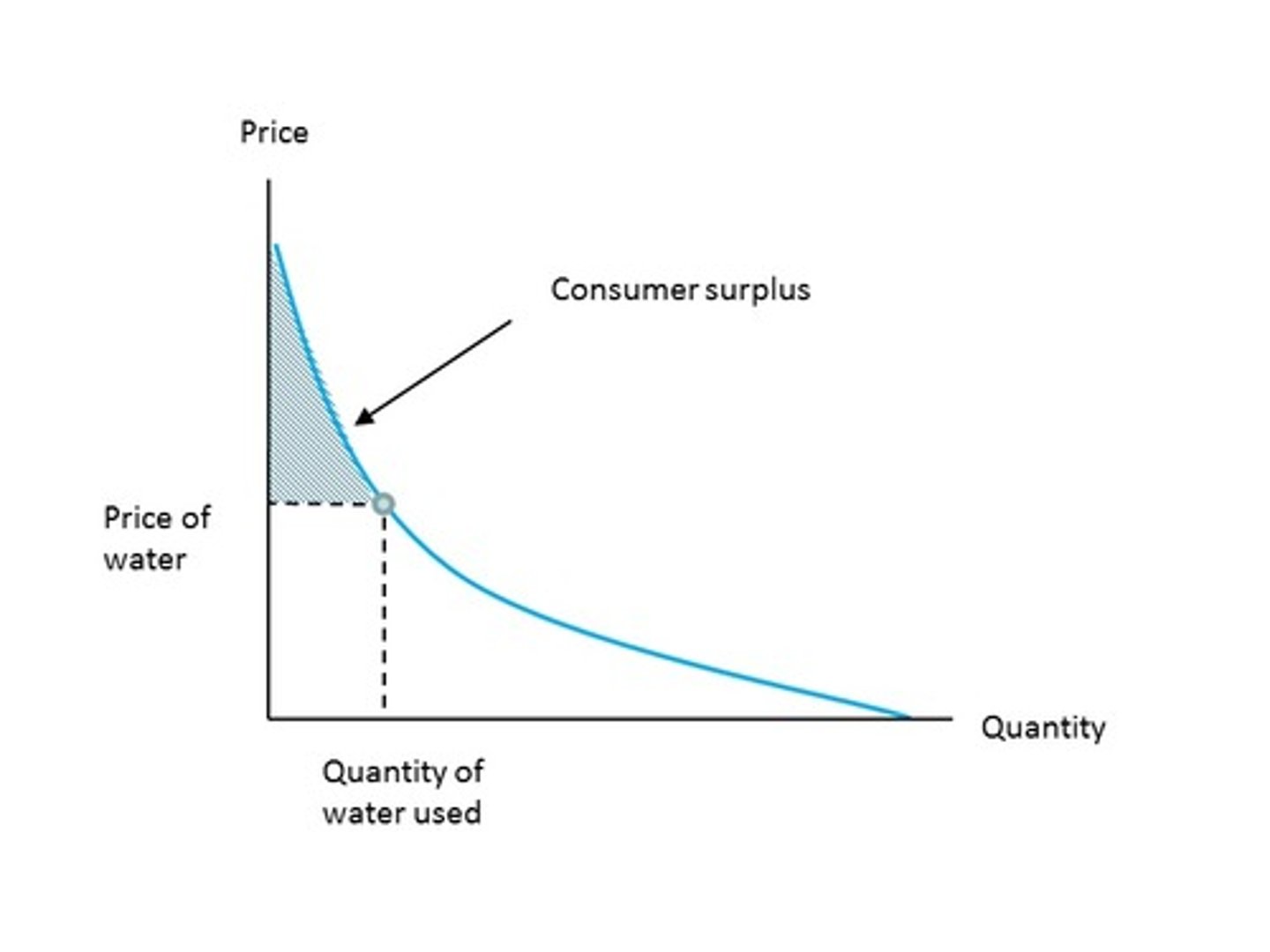
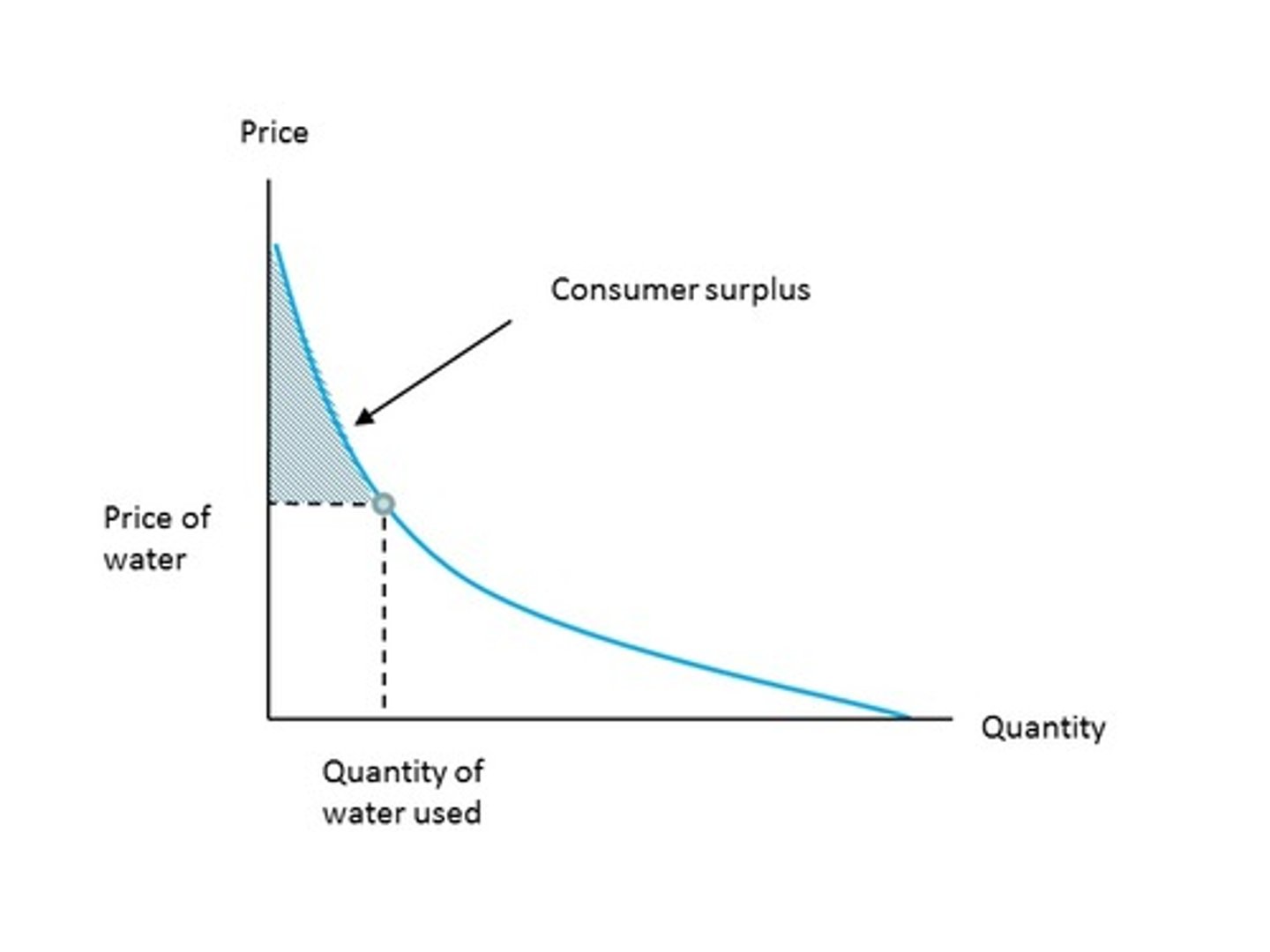
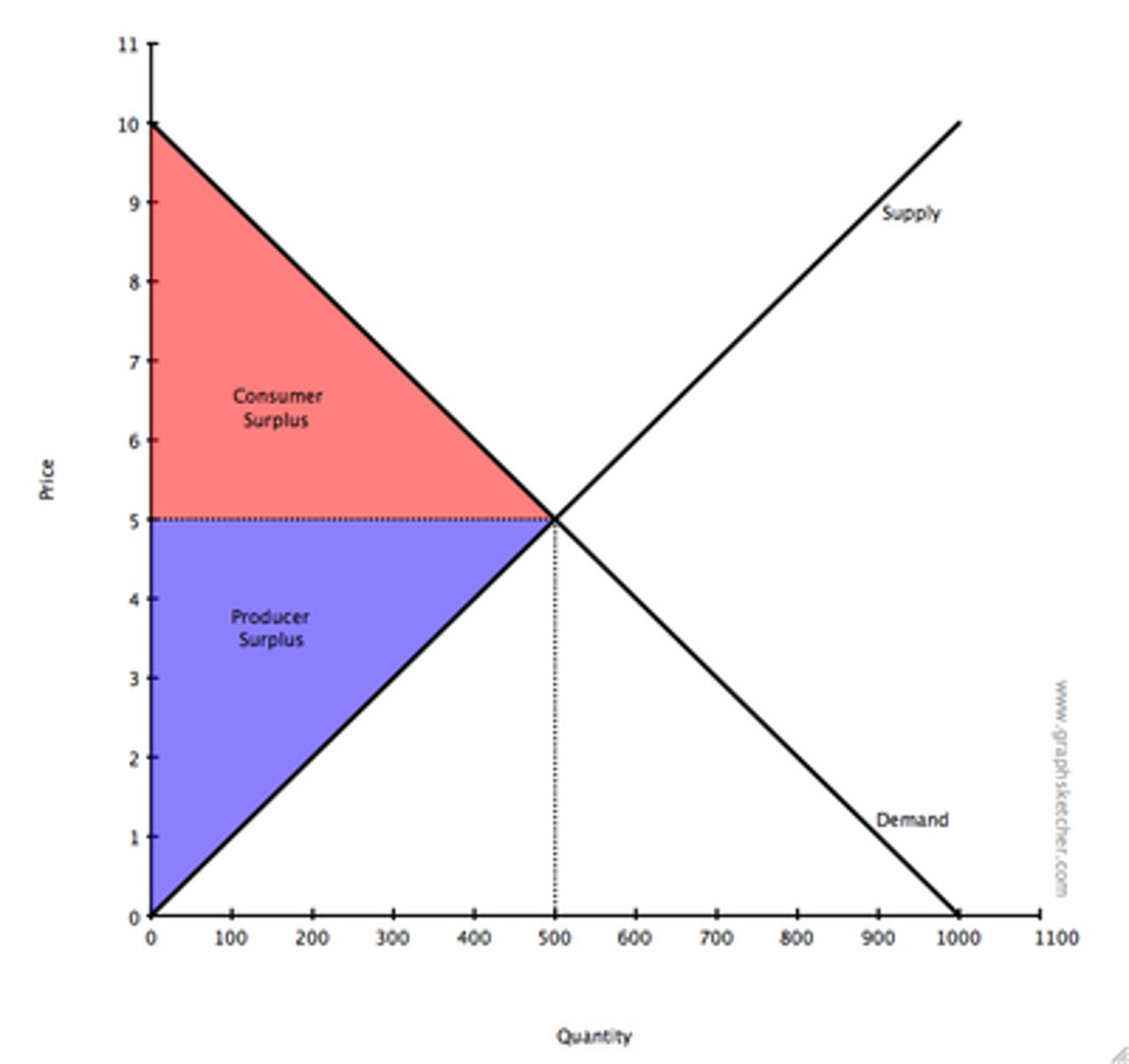
Consumer Surplus
the difference between the amount that a buyer would be willing to pay for a good or service and the price actually paid
Producer Surplus
the difference between the price that producers receive for supplying a good and their marginal cost of producing it
Elasticity
the percentage change in quantity demanded or supplied as a result of a 1% change in price
Total Revenue
the total revenue received by a supplier
Deadweight Loss
the reduction in total surplus that results from a market distortion such as a tax
Gains from Trade
the benefits that both individuals or nations realize from mutuality beneficial exchange
Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)
a graphical depiction of the combinations of output that can be produced by an economy
Comparative Advantage
the ability to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than other producers
Economic Profit
the difference between the revenue realized by a producer and the opportunity cost of production
Fixed Cost
a cost of production that is independent of the quantity produced
Variable Cost
a cost of production that depends on the quantity produced
Marginal Cost
the additional cost of production associated with a small increase in the quantity produced
Diminishing Returns to Scale
the property whereby each additional increase in inputs results in a smaller increase in the quantity produced
Marginal Revenue
the additional revenue resulting from a small increase in the quantity produced
Market Power
the situation in which a producer knows that changes in the quantity produced will alter the price at which the good or service can be sold
Monopoly
a market in which there's a single producer
Barriers to Entry
conditions that prevent firms from freely entering or exiting a market
Price Discrimination
when a business sells the same product to different buyers at different prices
Oligopoly
a market in which there are just a few producers
Cartel
an agreement between suppliers to restrict production and raise prices
Imperfect Competiton
the case of a market with a small number of sellers, so that sellers have market power
Monopolistic Competition
a market in which there is free entry or exit, but every producer supplies a differentiated product and faces a downward sloping demand curve
Entrepreneur
an individual who takes on the risk of attempting to create new products or services, establish new markets, or develop new methods of production
Market Failures
conditions in which a competitive market fails to produce a socially efficient outcome
Externality
when the action of one person affects the well-being of someone else, but where neither party pays nor is paid for these effects
Public Good
A good or service for which it is not possible to establish individual property rights
Coase Theorem
the proposition that if private parties can bargain without cost over the allocation of resources, then they can solve the problem of externalities on their own
Tragedy of the Commons
the depletion of a common resource due to overuse
Rival Goods
goods or services characterized by the fact that one's person's enjoyment of the good or service reduces the quantity available for others' enjoyment
Excludability
the ability to prevent buyers from enjoying the benefits of consuming a good or service without paying for it
Private Goods
characterized by a high degree in rivalry in consumption and a high degree of excludability
ex. pizza, gasoline, & haircuts

Common Resources
characterized by a high degree in rivalry in consumption, but a low degree of excludability
ex. fish in the ocean, city streets, & the environment

Collective Goods
low degree of rivalry but a high degree of excludability
ex. Websites, satellite radio, & pay-per-view TV

Public Goods
combines non-rivalry in consumption with non-excludability
ex. radio broadcasts, tornado sirens, & national defense

Institutions
formal and informal rules that structure human interactions
Logrolling
the practice of elected officials trading votes
Rent Seeking
using political influence to increase one's economic profits at the expense of others
Macroeconomics
deals with the broad and general aspects of an economy, such as the relationship between the income and investments of a country as a whole; concerned with performance of national economies
Unemployment Rate
the number of unemployed workers as a fraction of the total labor force
Inflation
a general increase in prices
Unemployment
the state of actively seeking paid work but being unable to find it
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
the market value of final goods and services produced in an economy during a specified period of time
Per Capita
literally per head, used to denote an average value for a population
Average Labor Productivity
total output divided by the quantity of labor employed in its production
Expansions
periods of rapid growth of output
ex. World War 2
Recessions
periods of slow growth or decline in output
ex. Great Depression
Great Depression
Most severe episode of economic decline observed to date; the economic crisis and period of low business activity in the U.S. and other countries, roughly beginning with the stock-market crash in October, 1929, and continuing through most of the 1930s.
Depression
a severe recession
Business Cycle
fluctuations in aggregate economic activity; alternation of periods of expansion & recession
Trade Surplus
when exports exceed imports
Trade Deficit
when exports are less than imports
Aggregation
combination of many different things into a single economic varable
Final Goods
goods or services that are purchased by their ultimate user
Intermediate Goods
goods or services that are used in the process of producing the final good
Capital Goods
long-lived goods that are themselves produced and are used to produce other goods and services, but aren't used up in the production process
Labor Force
sum of employed and unemployed individuals
Investment
spending on capital equipment, inventories, and structures, including household purchases of new housing
3 Categories of Investment
1) Business fixed investment
2) Residential fixed investment
3) Inventories
Business fixed investment
business purchases of factories, offices, machinery, and equipment
Residential fixed investment
purchase of new homes and apartment buildings
Inventories
consists of additions of unsold goods to company inventories
Government Purchases
spending on goods and services by federal, state, and local governments
Net Exports
difference between value of domestically produced goods sold to foreigners (exports) and value of foreign-produced goods purchased by domestic buyers
Real GDP
production of goods and services valued at constant prices
Nominal GDP
production of goods and services valued at current prices
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
an index constructed by comparing the cost of purchasing a fixed basket of goods at different time; measures the cost of purchasing a market basket of goods and services intended to be representative of the consumption of a typical consumer
Employed
if the person worked for pay either full or part time during the previous week/is on vacation/sick leave from a regular job
Unemployed
if the person didn't work for the previous week but made some effort to find paid employment during the past 4 weeks
Out of Labor Force
if the person didn't work for the past week and didn't actively seek work during the previous four weeks
Labor Force Participation Rate
the ratio of the working-age population to those in the labor force
Frictional Unemployment
unemployment that results because it takes time for workers to search for jobs that are best suited to their tastes and skills
Structural Unemployment
unemployment that results from the mismatch in skills, locations, or other characteristics between job seekers and the available jobs
Cyclical Unemployment
unemployment caused by deviations of output from its potential level
Physical Capital
modern manufacturing methods rely on the use of large quantities of capital per worker to achieve high levels of production
Human Capital
skills and experience that are acquired through education, training, and on the job experience that increase a worker's productivity
Natural Resources
contribute to the wealth of their citizens
Wealth
the total value of assets used as a store of value
Financial Markets
the institutions through which individuals with savings can supply these funds to persons of firms that wish to borrow money to purchase consumption goods or invest in physical capital
Bond
a certificate of indebtedness that specifies the obligations of the borrower to the holder of the bond; like an IOU